-
Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
-
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e21. Published online May 5, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e21
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF Supplementary Material Supplementary Material PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
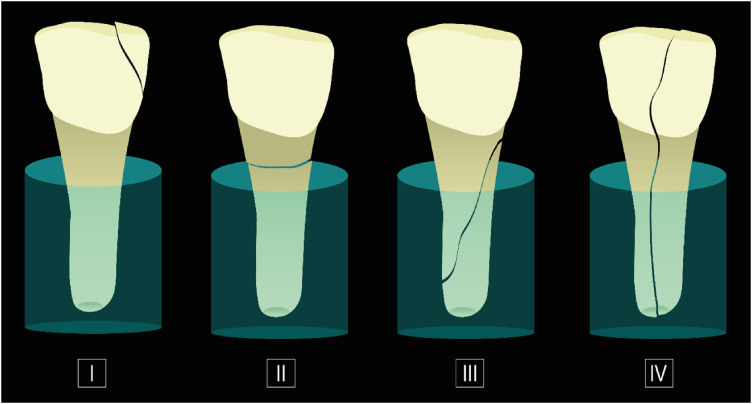
This study evaluated the effects of Biodentine (BD), Bio-C Repair (BCR), and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) plug on the fracture resistance of simulated immature teeth with replacement root resorption (RRR) and in vitro-induced osteoclastogenesis. Materials and MethodsSixty bovine incisors simulating immature teeth and RRR were divided into 5 groups: BD and BCR groups, with samples completely filled with the respective materials; MTA group, which utilized a 3-mm apical MTA plug; RRR group, which received no root canal filling; and normal periodontal ligament (PL) group, which had no RRR and no root canal filling. All the teeth underwent cycling loading, and compression strength testing was performed using a universal testing machine. RAW 264.7 macrophages were treated with 1:16 extracts of BD, BCR, and MTA containing receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B ligand (RANKL) for 5 days. RANKL-induced osteoclast differentiation was assessed by staining with tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase. The fracture load and osteoclast number were analyzed using 1-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test (α = 0.05). ResultsNo significant difference in fracture resistance was observed among the groups (p > 0.05). All materials similarly inhibited osteoclastogenesis (p > 0.05), except for BCR, which led to a lower percentage of osteoclasts than did MTA (p < 0.0001). ConclusionsThe treatment options for non-vital immature teeth with RRR did not strengthen the teeth and promoted a similar resistance to fractures in all cases. BD, MTA, and BCR showed inhibitory effects on osteoclast differentiation, with BCR yielding improved results compared to the other materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - In vitro comparison of fracture strength of maxillary incisors with the simulated external root resorption cavities repaired with BioMTA or Biodentine
Tufan Ozasir, Birgul Ozasir, Nagihan Aribal, Derin Bugu Yuzer, Baris Kandemir, Kamran Gulsahi
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(3): 1532. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Gene Expression in Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Exposed to Biodentine and Bio-C Repair: Implications for Cementogenesis—An In Vitro Study
Mahmoud M. Bakr, Mahmoud Al Ankily, Mohammed Meer, Mohamed Shamel
Oral.2025; 5(1): 19. CrossRef - Efficacy of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Versus Biodentine as a Direct Pulp Capping Material in Carious Human Mature Permanent Teeth: A Systematic Review
Rashmi Misra, Nikita Toprani, Sumita Bhagwat, Aashaka Vaishnav, Aastha Dureja, Omkar Bhosale
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Restoration Strategy and Cavity Location on the Fracture Resistance of Teeth with External Cervical Resorption
Saadet Elpe, Öznur Sarıyılmaz
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Techniques and Materials for Filling in 3-dimensional Printed Teeth Replicas with Perforating Internal Resorption by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography
Angelo J.S. Torres-Carrillo, Helena C. Assis, Rodrigo E. Salazar-Gamarra, Leonardo Moreira Teodosio, Alice C. Silva-Sousa, Jardel F. Mazzi-Chaves, Priscila B. Ferreira-Soares, Manoel D. Sousa-Neto, Fabiane C. Lopes-Olhê
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 205. CrossRef
-
2,782
View
-
68
Download
-
3
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
|