-
Comparative analysis of bond strength to root dentin and compression of bioceramic cements used in regenerative endodontic procedures
-
Maykely Naara Morais Rodrigues, Kely Firmino Bruno, Ana Helena Gonçalves de Alencar, Julyana Dumas Santos Silva, Patrícia Correia de Siqueira, Daniel de Almeida Decurcio, Carlos Estrela
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e59. Published online November 9, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e59
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
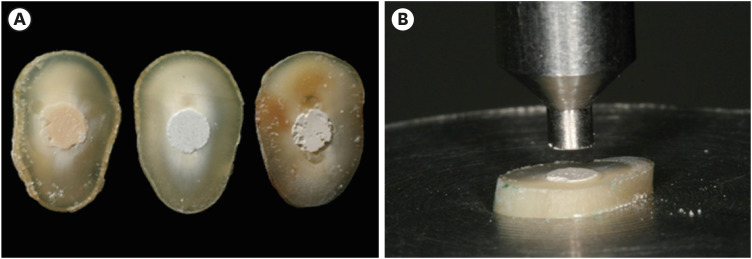
This study compared the Biodentine, MTA Repair HP, and Bio-C Repair bioceramics in terms of bond strength to dentin, failure mode, and compression. Materials and MethodsFifty-four slices obtained from the cervical third of 18 single-rooted human mandibular premolars were randomly distributed (n = 18). After insertion of the bioceramic materials, the push-out test was performed. The failure mode was analyzed using stereomicroscopy. Another set of cylindrically-shaped bioceramic samples (n = 10) was prepared for compressive strength testing. The normality of data distribution was analyzed using the Shapiro-Wilk test. The Kruskal-Wallis and Friedman tests were used for the push-out test data, while compressive strength was analyzed with analysis of variance and the Tukey test, considering a significance level of 0.05. ResultsBiodentine presented a higher median bond strength value (14.79 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (8.84 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (3.48 MPa), with a significant difference only between Biodentine and Bio-C Repair. In the Biodentine group, the most frequent failure mode was mixed (61%), while in the MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair groups, it was adhesive (94% and 72%, respectively). Biodentine showed greater resistance to compression (29.59 ± 8.47 MPa) than MTA Repair HP (18.68 ± 7.40 MPa) and Bio-C Repair (19.96 ± 3.96 MPa) (p < 0.05). ConclusionsBiodentine showed greater compressive strength than MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair, and greater bond strength than Bio-C Repair. The most frequent failure mode of Biodentine was mixed, while that of MTA Repair HP and Bio-C Repair was adhesive.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of marginal adaptation and bond strength of apical root canal plugs using different bioceramic cements
Michel Sena Fernandes Faria Lima, Alberto Nogueira da Gama Antunes, Kênia Maria Pereira Soares de Toubes, Fábio Fernandes Borém Bruzinga, Camila de Sousa Caneschi, Luís Fernando dos Santos Alves Morgan, Frank Ferreira Silveira
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Release of Calcium Ions from Apical Plugs of Different Bioceramic Sealers in Regenerative Endodontics for Immature Permanent Teeth
Alok Dubey, Nischitha Naik, Bhavana Sujanamulk, Mushir Mulla, Munaz Mulla, Alkananda Sahoo, Mohamed T Salama, Murali Patla S Bhat
World Journal of Dentistry.2026; 17(1): 69. CrossRef - Obturation quality analysis of furcation perforations repaired with different magnifications and biomaterials
Mustafa Mert Tulgar, Yağmur Kılıç, Merve Işık Aydın, Ali Keleş
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparación de la resistencia compresiva entre el Agregado Trióxido Mineral y BiodentineTM en perforaciones de furca de molares inferiores permanentes
Jheymy Gerardo Huatuco-Granda, John Paul Torres-Navarro, Rosa Josefina Roncal-Espinoza
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of different calcium-silicate based materials on fracture resistance of immature permanent teeth with replacement root resorption and osteoclastogenesis
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Maria Tereza Hordones Ribeiro, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Carlos José Soares, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation the Marginal Adaptation for the Bio C Repair and Other Root end Filling Material by Using Scanning Electron Microscope (A Comparative In Vitro Study)
Fatimah HAMADHİ, Zainab M.
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(3): 261. CrossRef - Dentin Bond Strength of Calcium Silicate-Based Materials: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Natalia Radulica, José Luis Sanz, Adrián Lozano
Applied Sciences.2023; 14(1): 104. CrossRef - Evaluation Of The Push-out Bond Strength Of The Bio-C Repair And Compare It With The Mineral Trioxide Aggregate And Amalgam When Used As Root-end Filling Material
Fatimah R. Hammadi, Zainab M Abdul-Ameer
Dental Hypotheses.2023; 14(2): 62. CrossRef - Effect of different root canal irrigants on push-out bond strength of two novel root-end filling materials
Nada Omar, Rasha M. Abdelraouf, Tamer M. Hamdy
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of irrigation systems on the bond strength of calcium-silicate-based cement used as pulp barrier in regenerative endodontic treatment
Cihan Hascizmeci, Burak Buldur
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(23): 3393. CrossRef
-
3,357
View
-
77
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
10
Crossref
|