-
Physicochemical characterization of two bulk fill composites at different depths
-
Guillermo Grazioli, Carlos Enrique Cuevas-Suárez, Leina Nakanishi, Alejandro Francia, Rafael Ratto de Moraes
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e39. Published online July 5, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e39
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
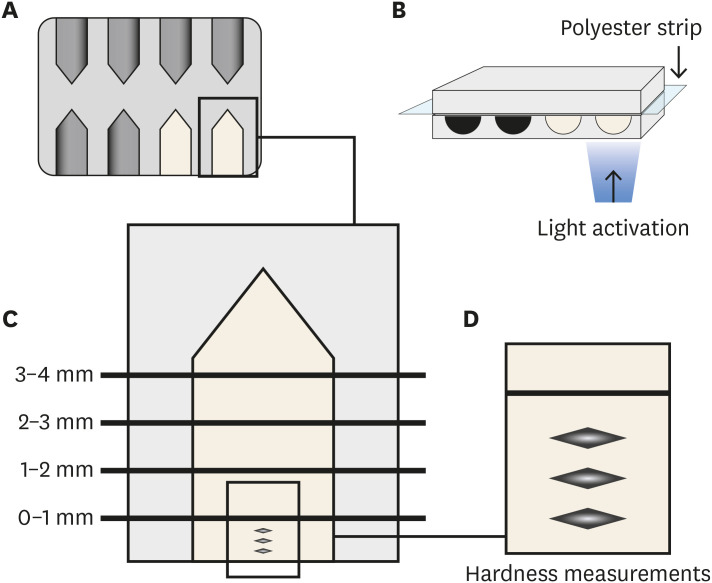
This study analyzed the physical-chemical behavior of 2 bulk fill resin composites (BFCs; Filtek Bulk Fill [FBF], and Tetric-N-Ceram Bulk Fill [TBF]) used in 2- and 4-mm increments and compared them with a conventional resin composite (Filtek Z250). Materials and MethodsFlexural strength and elastic modulus were evaluated by using a 3-point bending test. Knoop hardness was measured at depth areas 0–1, 1–2, 2–3, and 3–4 mm. The translucency parameter was measured using an optical spectrophotometer. Real-time polymerization kinetics was analyzed using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. ResultsFlexural strength was similar among the materials, while TBF showed lower elastic modulus (Z250: 6.6 ± 1.3, FBF: 6.4 ± 0.9, TBF: 4.3 ± 1.3). The hardness of Z250 was similar only between 0–1 mm and 1–2 mm. Both BFCs had similar hardness until 2–3 mm, and showed significant decreases at 3–4 mm (FBF: 33.45 ± 1.95 at 0–1 mm to 23.19 ± 4.32 at 3–4 mm, TBF: 23.17 ± 2.51 at 0–1 mm to 15.11 ± 1.94 at 3–4 mm). The BFCs showed higher translucency than Z250. The polymerization kinetics of all the materials were similar at 2-mm increments. At 4-mm, only TBF had a similar degree of conversion compared with 2 mm. ConclusionsThe BFCs tested had similar performance compared to the conventional composite when used in up to 2-mm increments. When the increment was thicker, the BFCs were properly polymerized only up to 3 mm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Microhardness According to Surface, Distance and Time of Photopolymerization of a Bulk-Fill Resin: In Vitro Study
María José Loayza-Gallegos, Gino Hernan Vidalón-Romo, Julissa Amparo Dulanto-Vargas
Odovtos - International Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 1(1): 384. CrossRef - Comparative In Vitro Analysis of Mechanical Properties in Three High-Viscosity Bulk-Fill Composite Resins
Carlos I. Santacruz, Jorge I. Fajardo, César A. Paltán, Ana del Carmen Armas-Vega, Eleonor Vélez León
Journal of Composites Science.2025; 9(11): 623. CrossRef - Translucency of bulk‐fill composite materials: A systematic review
Gaetano Paolone, Sofia Baldani, Niccolò De Masi, Mauro Mandurino, Giacomo Collivasone, Nicola Scotti, Enrico Gherlone, Giuseppe Cantatore
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(7): 995. CrossRef - Can composite packaging and selective enamel etching affect the clinical behavior of bulk-fill composite resin in posterior restorations? 24-month results of a randomized clinical trial
Marcos de Oliveira BARCELEIRO, Chane TARDEM, Elisa Gomes ALBUQUERQUE, Leticia de Souza LOPES, Stella Soares MARINS, Luiz Augusto POUBEL, Roberta BARCELOS, Romina ÑAUPARI-VILLASANTE, Alessandro Dourado LOGUERCIO, Fernanda Signorelli CALAZANS
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - No-Cap Flowable Bulk-Fill Composite: Physico-Mechanical Assessment
Abdullah Alshehri, Feras Alhalabi, Ali Robaian, Mohammed A. S. Abuelqomsan, Abdulrahman Alshabib, Eman Ismail, Faisal Alzamil, Nawaf Alotaibi, Hamad Algamaiah
Polymers.2023; 15(8): 1847. CrossRef - The Microhardness and Surface Roughness Assessment of Bulk-Fill Resin Composites Treated with and without the Application of an Oxygen-Inhibited Layer and a Polishing System: An In Vitro Study
Ann Carrillo-Marcos, Giuliany Salazar-Correa, Leonor Castro-Ramirez, Marysela Ladera-Castañeda, Carlos López-Gurreonero, Hernán Cachay-Criado, Ana Aliaga-Mariñas, Alberto Cornejo-Pinto, Luis Cervantes-Ganoza, César Félix Cayo-Rojas
Polymers.2022; 14(15): 3053. CrossRef
-
2,242
View
-
20
Download
-
6
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
|