Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 28(5); 2003 > Article
- Original Article Effect of a desensitizer on microtensile bond strength of different adhesives
- Sung-Yeon Hwang, Kyung-Ha Lee, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee
-
2003;28(5):-384.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.5.378
Published online: September 30, 2003
Department of Conservative Dentistry & Institute for Oral Bioscience College of Dentistry, Chonbuk National University, Korea.
- Corresponding author (lkw@moak.chonbuk.ac.kr)
Copyright © 2003 Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 916 Views
- 2 Download
Abstract
-
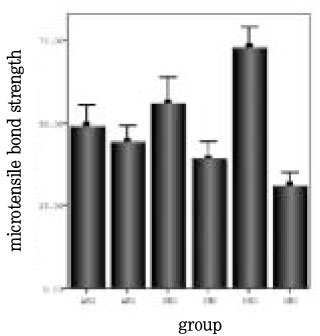
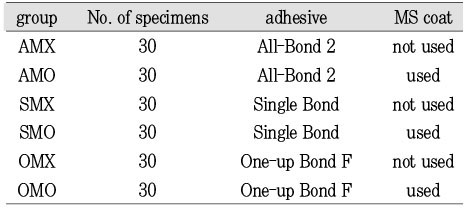
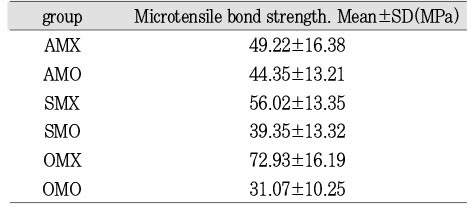
This study evaluated the influence of a desensitizer(MS coat) on microtensile bond strength of different adhesives: a three-step adhesive(All-Bond 2), a two-step adhesive(Single Bond), a one-step adhesive(One-up Bond F).Non-caries extracted human molars were used. Dentin surface was obtained by horizontal section on midportion of crown using a water-cooled low speed diamond saw. Teeth were randomly divided into 6 group. AMO(MS coat + All Bond)-, SMO(MS coat + Single Bond)- and OMO(MS coat + One-up Bond F)-dentin surface were treated with 17% EDTA before bonded adhesive. AMX-, SMX- and OMX-dentin surface were bonded with All-Bond 2, Single Bond and One-up Bond F, respectively, with no previous treatment with MS coat and 17% EDTA. About 1cm high resin composite(Z-250™) were incrementally build-up on the treated surface. The specimens for the microtensile test were serially sectioned perpendicular to the adhesive layer to obtain 0.7×0.7 mm sticks. 30 sticks were prepared from each group.After that, tensile bond strength for each stick was measured with Microtensile Tester at a 1mm/min crosshead speed. Fractured dentin surfaces were observed under the SEM. The results were statistically analysed by using a One-way ANOVA and Tukey's test(p<0.05).Value in MPa were: AMO-44.35±13.21; SMO-39.35±13.32; OMO-31.07±10.25; AMX-49.22±16.38; SMX-56.02±13.35; OMX-72.93±16.19. Application of MS coat reduced microtensile bond strengths of both Single Bond and One-up Bond F, whereas microtensile bond strengths of All-Bond 2 were not affected significantly.
- 1. Braem M, Lambrecchts P, Vanherle G. Stress-induced cervical lesion. J Prosthet Dent. 1992;67: 718-722.PubMed
- 2. Levitch LC, Barder JD, Shugars DA, Heymann HO. Non-carious cervical lesion(review). J Dent. 1994;22: 195-207.PubMed
- 3. Yoshiyama M, Noire Y, Azoic K, et al. Transmission electron microscopic characterization of hypersensitive hyman radicular dentin. J Dent Res. 1990;69: 1293-1297.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Pashley DH. Dentin permeability, dentin sensitivity, and treatment through tubule occlusion. J Endod. 1986;12: 465-474.PubMed
- 5. Kerns DG, Scheidt MJ, Pashley DH. Dentinal tubule occlusion and root hypersensitivity. J Periodontol. 1991;62(7):421-428.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Camps J, Pizant S, Dejou J, Franquin JC. Effect of desensitizing agents on human dentin permeability. Am J Dent. 1998;11(6):286-290.PubMed
- 7. Jain P, Vargas MA, Denehy GE, Boyer DB. Dentin desensitizing agents: SEM and X-ray microanalysis assessment. Am J Dent. 1997;10(1):21-26.PubMed
- 8. Mausner IK, Goldstein GR, Georgescu M. Effect of two dentinal desensitizing agents on retention of complete cast coping using four cements. J Prosthet Dent. 1996;75(2):129-134.PubMed
- 9. Zhang Y, Agee K, Pashley DH, Pashley EL. The effects of pain-free® desensitizer on dentine permeability and tobule occlusion over time, in vitro. J Clin Periodontol. 1998;25: 884-891.PubMed
- 10. Gillam DG, Mordan NJ, Sinodiou AD, Tang JY, Knowles JC, Gibsson R. the effect of oxalate-containing products on the exposed dentine surface: an SEM investigation. J Oral Rehabil. 2001;28: 1037-1044.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Snuggs AK, Cox LK, et al. In: Shimona M, Maeda T, Suda H, et al, editors. Colloidal MSE for differential diagnosis and treatment of dentin permeability. Dentin/pulp complex. 1996;Quintessence; 245-247.
- 12. Seara SF, Erthral BS, Ribeiro M, Kroll L, Pereira GDS. The influence of a dentin desensitizer on the microtensile bond strength of two bonding systems. Oper Dent. 2002;27: 154-160.PubMed
- 13. Pashley EL, Tao L, Pashely D. Effects of oxalate on dentin bonding. Am J Dent. 1993;6(3):116-118.PubMed
- 14. Swift EJ Jr, Lloyd AH, Felton DA. The effect of resin desensitizing agents on crown retention. J Am Dent Assoc. 1997;128: 195-200.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Yim NH, Rueggeberg FA, Caughman WF, Gardner FM, Pashley DH. Effect of dentin desensitizers and cementing agents on retention of fuul crowns using stsndardized crown preparations. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;83: 459-465.PubMed
- 16. Soeno K, Taira Y, Matsumura H, Atsuta M. Effect of desensitizers on bond strength of adhesive luting agents to dentin. J Oral Rehabil. 2001;28: 1122-1128.PubMed
- 17. Tagami J, Tao L, Pashley DH. Correlation among dentin depth, permeability and bond strength of adhesive resins. Dent Mater. 1990;6(1):45-50.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Pashley DH, Carvalho RM, Sano H, Nakajima M, Yoshiyama M, Shono Y, Fernandes CA, Tay F. The microtensile bond test : a review. J Adhes Dent. 1999;1: 299-309.PubMed
- 19. Armstrong SR, Boyer DB, Keller JC. Microtensile bond strength testing and failure analysis of two dentin adhesives. Dent Mater. 1998;14: 44-50.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Trowbridge HO, Silver DR. A review of current approaches to in-office management of tooth hypersensitivity : a Review. Dent Clin North Am. 1990;34(3):561-581.PubMed
- 21. Hogan LC, Burrow MF. The microtensile strength of bonding resins. Aust Dent J. 2001;46(3):194-197.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

Effect of a desensitizer on microtensile bond strength of different adhesives
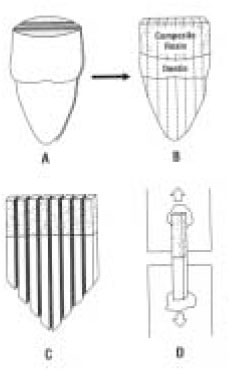
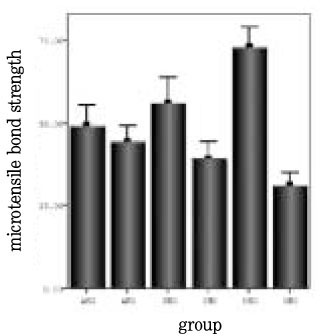
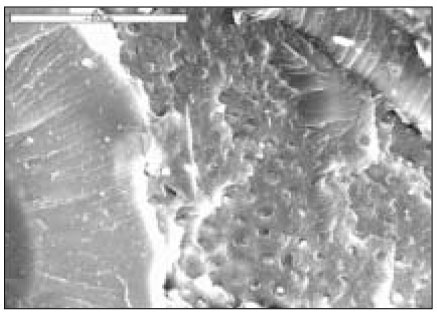
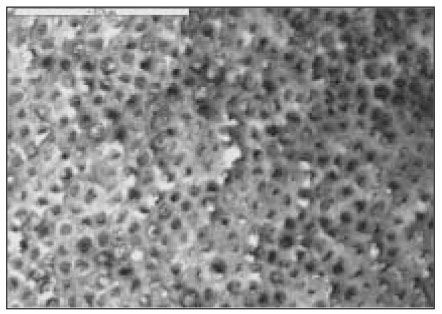
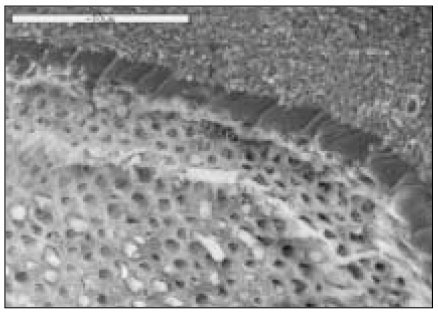
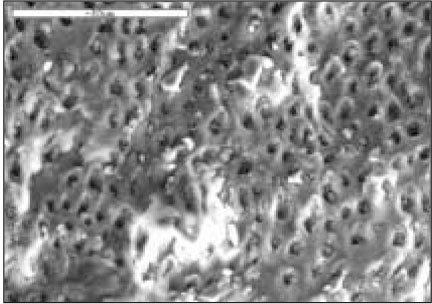
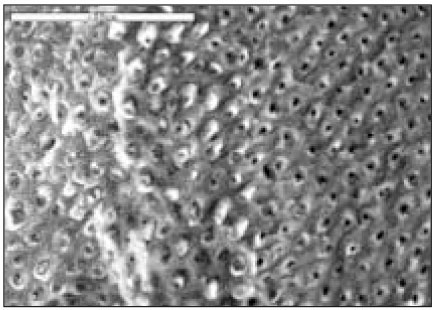
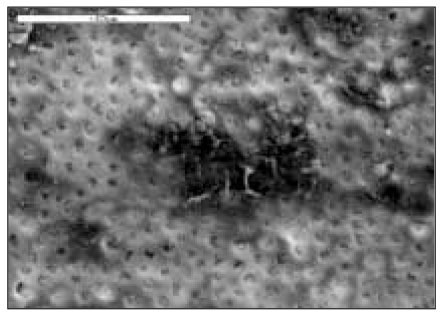
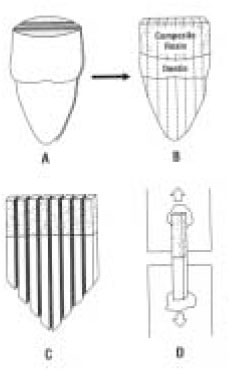
Fig. 1
Schematic illustration of microtensile test
Fig. 2
Bar graph for comparison of microtensile bond strength of experimental groups.
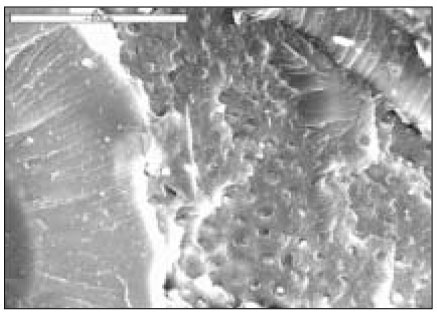
Fig. 3
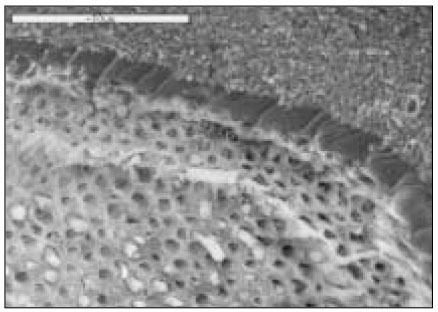
AMX group(×1000)
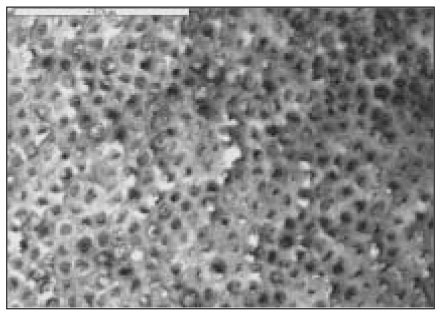
Fig. 4
AMO group(×1000)
Fig. 5
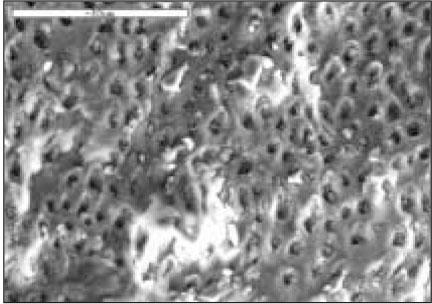
SMX group(×1000)
Fig. 6
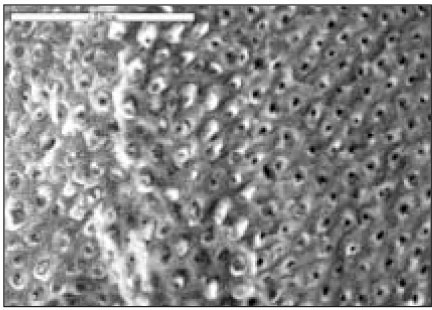
SMO group(×1000)
Fig. 7
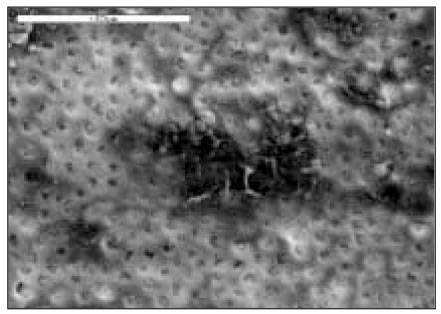
OMX group(×1000)
Fig. 8
OMO group(×1000)
Fig. 1
Fig. 2
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
Fig. 5
Fig. 6
Fig. 7
Fig. 8
Effect of a desensitizer on microtensile bond strength of different adhesives
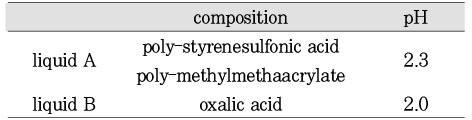
The composition of MS coat
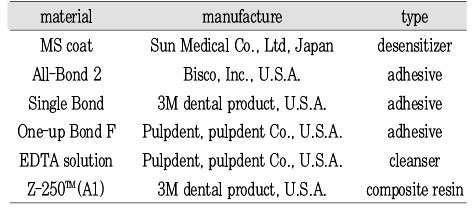
Materials used in this study
Each group is classified as following
Microtensile bond strength of experimental groups
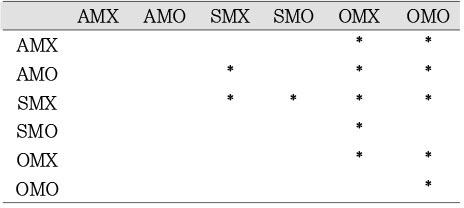
Comparison of microtensile bond strength among groups
Table 1
The composition of MS coat
Table 2
Materials used in this study
Table 3
Each group is classified as following
Table 4
Microtensile bond strength of experimental groups
Table 5
Comparison of microtensile bond strength among groups

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

