Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Restor Dent Endod > Volume 33(3); 2008 > Article
- Original Article Fracture resistance of the three types of undermined cavity filled with composite resin
- Hoon-Soo Choi, Dong-Hoon Shin
-
2008;33(3):-183.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.3.177
Published online: May 31, 2008
Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Korea.
- Corresponding Author: Dong-Hoon Shin. Department of Conservative Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, San 7-1, Shinbu-dong, Cheonan 330-716, Korea. Tel: 82-41-550-1965, Fax: 82-41-550-1963, donyshin@dankook.ac.kr
• Received: February 28, 2008 • Revised: April 14, 2008 • Accepted: April 15, 2008
Copyright © 2008 The Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry
- 1,529 Views
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref
Abstract
-
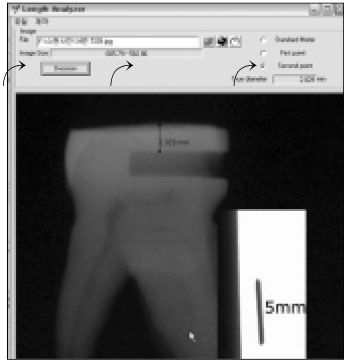
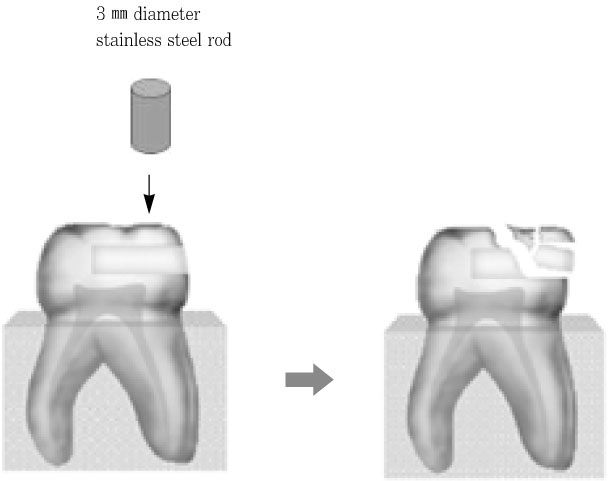
It was reported that esthetic composite resin restoration reinforces the strength of remaining tooth structure with preserving the natural tooth structure. However, it is unknown how much the strength would be recovered. The purpose of this study was to compare the fracture resistance of three types of undermined cavity filled with composite resin with that of non-cavitated natural tooth.Forty sound upper molars were allocated randomly into four groups of 10 teeth. After flattening occlusal enamel, undermined cavities were prepared in thirty teeth to make three types of specimens with various thickness of occlusal structure (Group 1 ~ 3). All the cavity have the 5 mm width mesiodistally and 7 mm depth bucco-lingually. Another natural 10 teeth (Group 4) were used as a control group. Teeth in group 1 have remaining occlusal structure about 1 mm thickness, which was composed of mainly enamel and small amount of dentin. In Group 2, remained thickness was about 1.5 mm, including 0.5 mm thickness dentin. In Group 3, thickness was about 2.0 mm, including 1 mm thickness dentin. Every effort was made to keep the remaining dentin thickness about 0.5 mm from the pulp space in cavitated groups. All the thickness was evaluated with radiographic Length Analyzer program.After acid etching with 37% phosphoric acid, one-bottle adhesive (Single Bond™, 3M/ESPE, USA) was applied following the manufacturer's recommendation and cavities were incrementally filled with hybrid composite resin (Filtek Z-250™, 3M/ESPE, USA). Teeth were stored in distilled water for one day at room temperature, after then, they were finished and polished with Sof-Lex system.All specimens were embedded in acrylic resin and static load was applied to the specimens with a 3 mm diameter stainless steel rod in an Universal testing machine and cross-head speed was 1 mm/min. Maximum load in case of fracture was recorded for each specimen.The data were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and a Tukey test at the 95% confidence level.The results were as follows:Within the limits of this study, it can be concluded the fracture resistance of the undermined cavity filled with composite resin was lower than that of natural teeth, however remaining tooth structure may be supported and saved by the reinforcement with adhesive restoration, even if that portion consists of mainly enamel and a little dentin structure.
- 1. Mount GJ, Hume WR. Preservation and restoration of tooth structure. 1998;Philadelphia: Mosby; 126-153.
- 2. Lacy AM. The class III posterior composite restoration. Dent Today. 2002;80-82. 84-85.
- 3. Setien V, Armstrong SR, Vargas MA. Conservative restoration of proximal-cervical lesions. Oper Dent. 2003;28(3):321-323.PubMed
- 4. Abu-Hanna AA, Mjör IA. Resin composite reinforcement of undermined enamel. Oper Dent. 2004;29(2):234-237.PubMed
- 5. Wilson AD, McLean JW. Glass-ionomer cement. Quintessence Int. 1988;30(3):197-200.
- 6. Mount GJ. An Atlas of Glass-ionomer cements. 1994;second ed. London: Martin Dunitz; 118-122.
- 7. Denehy GE, Torney DL. Internal enamel reinforcement through micromechanical bonding. J Prosthet Dent. 1976;36(2):171-175.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Eakle WS, Staninec M. Effect of bonded gold inlays on fracture resistance of teeth. Quintessence Int. 1992;23: 421-425.PubMed
- 9. Jagadish S, Yogesh BG. Fracture resistance of teeth with class II silver amalgam, posterior composite and glass cermet restorations. Oper Dent. 1990;15(2):42-47.PubMed
- 10. Borges AFS, Correr GM, Sinhoreti MAC, Consani S, Sobrinho LC, Rontani RMP. Compressive strength recovered by composite onlays in primary teeth Substrate treatment and luting agent effects. J Dent. 2006;34: 478-484.PubMed
- 11. Roggenkamp CL, Cochran MA, Lund MR. The facial slot preparation: a non-occlusal option for Class 2 carious lesions. Oper Dent. 1982;7(3):102-106.PubMed
- 12. Croll TP. Lateral-access class II restoration using resin-modified glass-ionomer or silver-cermet cement. Quintessence Int. 1995;26: 121-126.PubMed
- 13. Gorucu J, Ozgunaltay G. Fracture resistance of teeth with class II bonded amalgam and new tooth-colored restorations. Oper Dent. 2003;28(5):501-507.PubMed
- 14. Johnston WM, Leung RL, Fan PL. A mathematical model for post-irradiation hardening of photoactivated composite resins. Dent Mater. 1985;1(5):191-194.PubMed
- 15. Eick JD, Welch FH. Dentin adhesives-do they protect the dentin from acid etching? Quintessence Int. 1986;17(9):533-544.PubMed
- 16. Wieczkowski G, Joynt RB, Klockowski R, Davis EL. Effects of incremental versus bulk fill technique on resistance to cuspal fracture of teeth restored with posterior composites. J Prosthet Dent. 1988;60(3):283-287.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Martins LRM, Secco AS. Influence of the glass ionomer cement and composite resin on enamel supported and its effect in the cuspal stiffness and flexure. J Dent Res. 1997;76: Abstract No. 3232.
- 18. Eidelman E. Composite resin support of undermined enamel in amalgam restorations. Pediatr Dent. 1999;21: 118-120.PubMed
- 19. Yaman SD, Yetmez M, Turkoz E, Akkas N. Fracture resistance of class II approximal slot restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2000;84: 297-302.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Gracis SE, Nicholls JI, Chalupnik JD, Yuodelis RA. Shock-absorbing behavior of five restorative materials used on implants. Int J Prosthodont. 1991;4: 282-291.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Strand GV, Tveit AB, Gjerdet NR. Marginal ridge strength of tunnel-prepared teeth restored with various adhesive filling materials. Cement Concr Res. 1999;29: 645-650.Article
- 22. St-Georges AJ, Sturdevant JR, Swift EJ Jr, Thompson JY. Fracture resistance of prepared teeth restored with bonded inlay restorations. J Prosthet Dent. 2003;89: 551-557.PubMed
- 23. Latino C, Troendle K, Summitt JB. Support of undermined occlusal enamel provided by restorative materials. Quintessence Int. 2001;32: 287-291.PubMed
REFERENCES
Tables & Figures
REFERENCES
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Fracture resistance of crown-root fractured teeth repaired with dual-cured composite resin and horizontal posts
Seok-Woo Chang, Yong-Keun Lee, Seung-Hyun Kyung, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Tae-Seok Oh, Dong-Sung Park
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 383. CrossRef
Fracture resistance of the three types of undermined cavity filled with composite resin
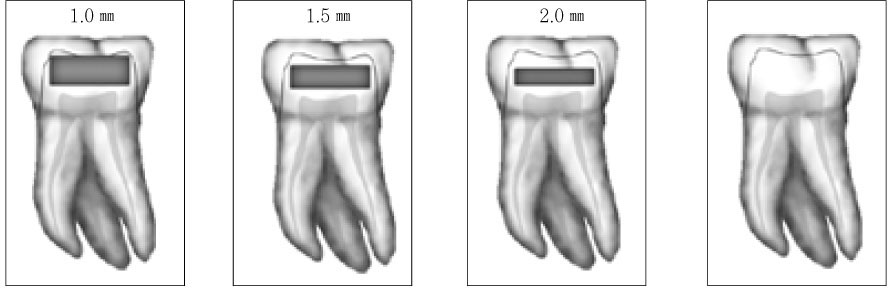
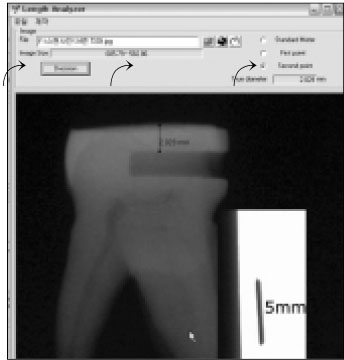
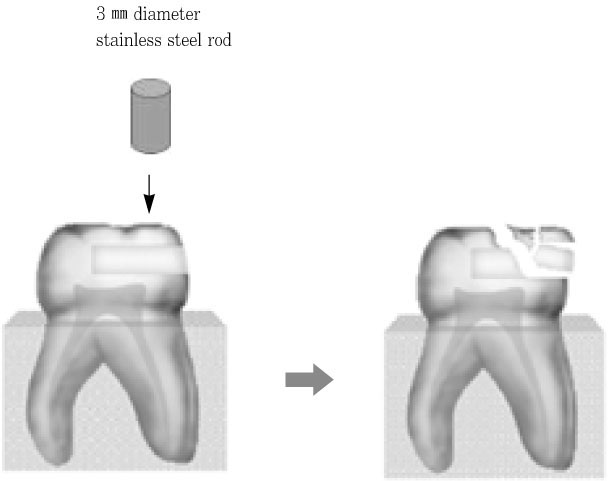
Figure 1
Schematic drawing of cavity form.
Figure 2
Length Analyzer Program.
Figure 3
Measurement of fracture strength.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3
Fracture resistance of the three types of undermined cavity filled with composite resin
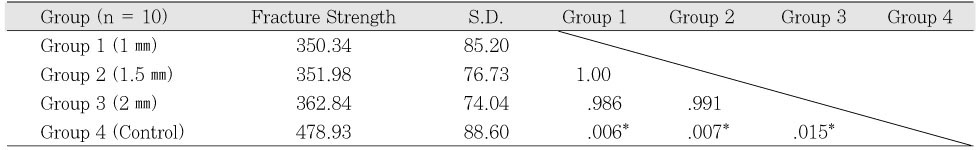
Fracture Strength (MPa) and ANOVA result
*: Significant difference at p < 0.05
Table 1
Fracture Strength (MPa) and ANOVA result
*: Significant difference at p < 0.05

 KACD
KACD
 ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite

