Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Comparison of YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram as digital sources for obtaining information about pulp therapy in primary and permanent teeth
- Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, Emine Kaya, Dila Nur Okumuş, Merve Gül Erence
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e26. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e26
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to compare the content, educational quality, and dependability of videos on Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube about pulp therapy (PT) in pediatric dentistry and endodontics.
Methods
Three popular video sites, Instagram (Meta Platforms, Inc.,), TikTok (ByteDance Ltd.), and YouTube (Google LLC), were searched for PT content to analyze for compliance with the American Association of Endodontists and American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry guidelines for clinical endodontists and pediatric dentists. The searched hashtags were #pulpaltherapy, #pulpaltreatment, #pulptherapy, and #pulptreatment. The classification of 158 English-language videos was based on several variables: communication quality, duration, likes and dislikes, views, source, treatment, and genre. The videos were evaluated using a usefulness score and the Global Quality Scale (GQS), Video Information and Quality Index (VIQI), Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) score, and modified DISCERN score to rate their quality and reliability. The majority of the videos were published by healthcare professionals, dental clinics, and universities.
Results
Significant relationships existed between video length, source of upload, usefulness score, tooth type, pulp status, and VIQI, JAMA, GQS, and DISCERN scores for all three platforms (p<0 .05). A statistically significant relationship existed of YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram with the number of views, number of months since upload, view rates, comments and likes (p< 0.05).
Conclusions
TikTok and Instagram reel videos provided high- to moderate-quality information about PT, especially in children, but YouTube may provide more reliable information than other social media tools. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- New Technologies and Materials in Oral Health and Dental Care of Pediatric Dentistry
Giuseppe Minervini
Children.2025; 12(10): 1310. CrossRef
- New Technologies and Materials in Oral Health and Dental Care of Pediatric Dentistry
- 2,224 View
- 64 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- YouTube as a source of information about rubber dam: quality and content analysis
- Gülsen Kiraz, Arzu Kaya Mumcu, Safa Kurnaz
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(1):e10. Published online February 5, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the content, quality and demographics of YouTube videos about rubber dam as an information source for clinicians and dental students.
Materials and Methods “Rubber dam,” “rubber dam application,” “dental isolation,” “rubber dam isolation,” and “dental dam” were determined as keywords for the detection of YouTube videos related to rubber dam. Seventy 3 videos were evaluated and a total of 34 videos met the inclusion criteria. All selected videos were evaluated according to 8 parameters. The videos were scored 1 if the videos contained information about the selected parameter, but if the videos did not contain enough information, they were scored 0. The data were statistically analyzed with the analysis of variance and
post hoc Tukey test (p < 0.05).Results We found that 41% of the videos have poor, 47% have moderate, and 12% have good information. There is a statistically significant difference in time between poor and good information content (
p < 0.05). There is a statistically significant difference between the poor and good information in the video information and quality index 1.Conclusions Rubber dam-related videos available on YouTube are generally moderately informed and insufficient. YouTube is currently not sufficient as a source of information for patients and clinicians at the moment. The YouTube platform should be developed and enriched with quality information on current and dental issues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing the Quality of YouTube® Videos on Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Inhalation: A Multi-Dimensional Approach for Pediatric Dentists
Sanaa N. Al-Haj Ali, Nehal AlHarbi, Hessah H. Almutairi
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the reliability and educational value of YouTube videos on computer-controlled local anesthesia in dentistry
Hulya Cerci Akcay, Erdal Cem Kargu, Nefise Seker, Tanay Chaubal
PLOS One.2025; 20(8): e0329291. CrossRef - Evaluation of Endodontic Retreatment Videos on The Youtube Platform: Quality and Content Analysis
Birgül Özaşır, Tufan Özaşır, Derin Buğu Yüzer, Deniz İmamoğlu, Kamran Gülşahı
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2025; 52(2): 103. CrossRef - Assessing the usefulness of educational videos on endodontic irrigation for dental students: a pilot study
Jin Wey Kock, Shahmin Kar Sze Yeap, Naveen Chhabra, Philip Yuan-Ho Chien, Shekhar Bhatia
BMC Medical Education.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Assessing the Quality of YouTube® Videos on Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Inhalation: A Multi-Dimensional Approach for Pediatric Dentists
- 2,974 View
- 55 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- YouTube as a source of information about pulpotomy and pulp capping: a cross sectional reliability analysis
- Konstantinos Kodonas, Anastasia Fardi
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e40. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to critically evaluate the quality, reliability and educational content of the information of vital pulp treatment videos available on YouTube.
Materials and Methods The keywords “pulpotomy” and “pulp capping” were searched on YouTube on 5th July 2020, until 60 English language videos of each search term with a duration shorter than 15 minutes were acquired. Video characteristics were recorded and Video Power Index (VPI) was calculated. Reliability and educational quality of videos were evaluated using the Modified DISCERN score, the
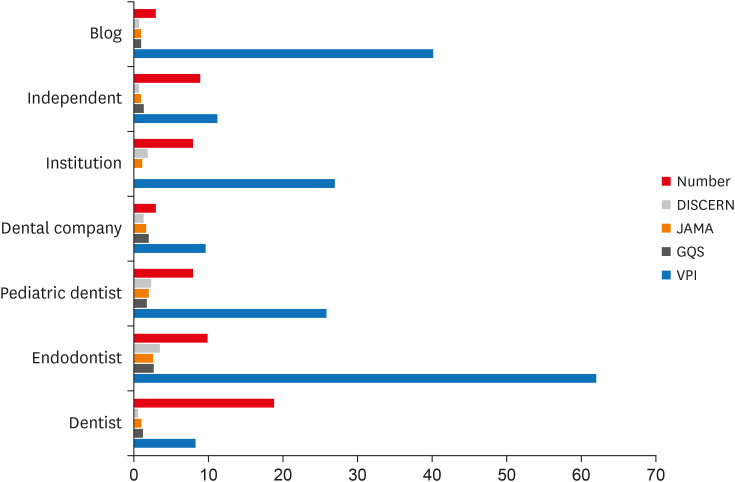
Journal of American Medical Association (JAMA) benchmark criteria and Global Quality Scores (GQS). Videos were categorized by uploading source.Results Regarding pulpotomy, 31.7% of the videos were uploaded by specialists and 68.3% were directed by non-specialists. In the case of pulp capping, the corresponding percentages were 45% and 55%, respectively. Videos uploaded by specialists had significantly higher modified DISCERN, JAMA and GQS scores compared to those uploaded by non-specialists. Endodontists tended to have the highest reliability and VPI scores.
Conclusions YouTube videos on vital pulp treatment contain low educational quality or incomplete information. Low popularity of dental pulp capping and pulpotomy videos may be attributed to the specialized nature of these procedures. As YouTube represents an important source for patient information about different health topics, reliable informative videos should be uploaded by specialized dental professionals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of YouTubeTM Videos Regarding ICON as an Information Resource: A Cross-Sectional Study
Sevim Atılan Yavuz, Zeyneb Merve Ozdemır, Derya Gursel Surmelioglu
Mersin Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Lokman Hekim Tıp Tarihi ve Folklorik Tıp Dergisi.2026; 16(1): 282. CrossRef - Assessing the Quality of YouTube® Videos on Nitrous Oxide/Oxygen Inhalation: A Multi-Dimensional Approach for Pediatric Dentists
Sanaa N. Al-Haj Ali, Nehal AlHarbi, Hessah H. Almutairi
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Is YouTube™ a useful resource of information about bichectomy? A cross-sectional study
H.ɪ. Durmuş, B. Ege, S. Bayazıt, M. Koparal
Annales de Chirurgie Plastique Esthétique.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the reliability and educational value of YouTube videos on computer-controlled local anesthesia in dentistry
Hulya Cerci Akcay, Erdal Cem Kargu, Nefise Seker, Tanay Chaubal
PLOS One.2025; 20(8): e0329291. CrossRef - A content analysis of YouTube videos on interproximal enamel reduction
Weng Yan Tam, Jack Shen Tham, Smita Nimbalkar, Shilpa Gunjal, Kirti Saxena
APOS Trends in Orthodontics.2025; 0: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of YouTube, TikTok, and Instagram as digital sources for obtaining information about pulp therapy in primary and permanent teeth
Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, Emine Kaya, Dila Nur Okumuş, Merve Gül Erence
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(3): e26. CrossRef - Evaluation of Endodontic Retreatment Videos on The Youtube Platform: Quality and Content Analysis
Birgül Özaşır, Tufan Özaşır, Derin Buğu Yüzer, Deniz İmamoğlu, Kamran Gülşahı
European Annals of Dental Sciences.2025; 52(2): 103. CrossRef - Is YouTube a reliable source for learning pre-endodontic build-up? A cross-sectional study
Merve Gökyar, İdil Özden, Hesna Sazak Öveçoğlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(3): e27. CrossRef - Quality of Patient-Centered eHealth Information on Erosive Tooth Wear: Systematic Search and Evaluation of Websites and YouTube Videos
Lena Holland, Amelie Friederike Kanzow, Annette Wiegand, Philipp Kanzow
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2024; 26: e49514. CrossRef - Is it safe to learn about vital pulp capping from YouTube™ videos? A content and quality analysis
Celalettin Topbaş, Tuğçe Paksoy, Ayşe Gülnihal İslamoğlu, Kemal Çağlar, Abdurrahman Kerim Kul
International Journal of Medical Informatics.2024; 185: 105409. CrossRef - Assessment of the quality of oral biopsy procedure videos shared on YouTube
A. Díaz‐Rodríguez, J. Limeres‐Posse, R. Albuquerque, V. Brailo, R. Cook, J. C. Fricain, G. Lodi, L. Monteiro, L. Silva, B. Carey, M. Diniz‐Freitas
Oral Diseases.2024; 30(5): 3081. CrossRef - İmplant üstü protezler hakkında bilgi veren internet sitelerinin okunabilirliklerinin değerlendirilmesi
Tugba TEMİZCİ
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(4): 156. CrossRef - Online Audio-Visual Information on the Treatment of OSA with Mandibular Advancement Devices: Analysis of Quality, Reliability and Contents
Serena Incerti-Parenti, Maria Lavinia Bartolucci, Elena Biondi, Andrea Fiordelli, Corrado Paganelli, Giulio Alessandri-Bonetti
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(9): 5727. CrossRef - Evaluating YouTube as a Patient Information Source for the Risks of Root Canal Treatment
Stewart McLean, Neil Cook, Alexander Rovira-Wilde, Shanon Patel, Shalini Kanagasingam
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(2): 155. CrossRef - Assessment of reliability and information quality of YouTube videos about root canal treatment after 2016
Myoung-jun Jung, Min-Seock Seo
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Is the YouTube™ a useful resource of information about orthognathic surgery?: A cross-sectional study
Seyma Bayazıt, Bilal Ege, Mahmut Koparal
Journal of Stomatology, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2022; 123(6): e981. CrossRef - YoutubeTM Content Analysis as a Means of Information in Oral Medicine: A Systematic Review of the Literature
Antonio Romano, Fausto Fiori, Massimo Petruzzi, Fedora Della Vella, Rosario Serpico
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(9): 5451. CrossRef
- Evaluation of YouTubeTM Videos Regarding ICON as an Information Resource: A Cross-Sectional Study
- 1,966 View
- 21 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


