Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Determination of optimal horizontal beam angulations for canal separation in mandibular molars using cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective image-based analysis
- Benedikt Schneider, Tamina Tepe, Daniel Rapp, Wilhelm Frank, Maria Lessani, Constantin von See, Sebastian Fitzek, Jörg Philipp Tchorz
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e9. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
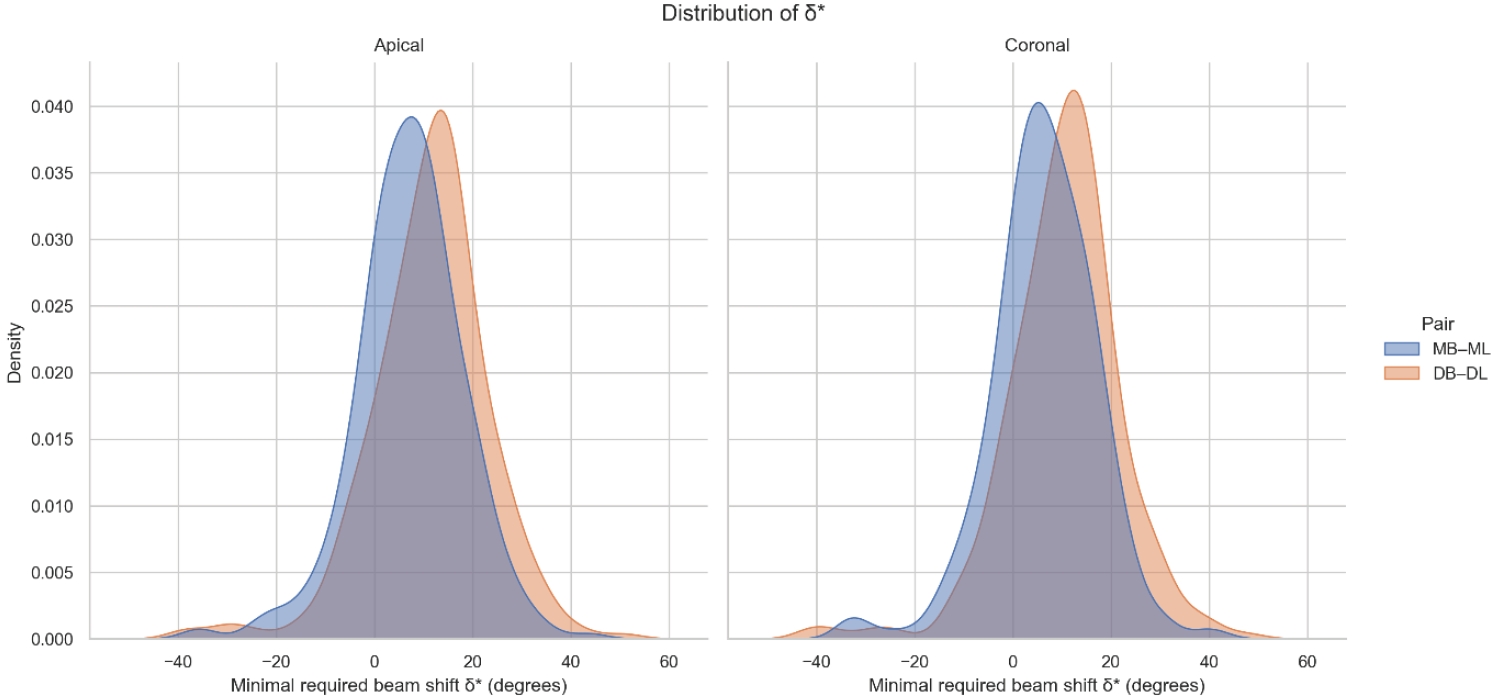
Two-dimensional intraoral radiographs often obscure canals due to superimposition, especially in mandibular molars with complex anatomy. This cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) study identified the horizontal beam angles at which first and second molar canals overlap and derived clinically applicable angulations for enhanced canal separation.
Methods
Eighty-five CBCT datasets from 100 patients met the inclusion criteria, yielding 318 mandibular molars (160 first, 158 second). Using ImageJ, absolute horizontal overlap angles (α) were measured to determine the corresponding theoretical separation angles defined as δ* = 90° – α. Separability was modeled across horizontal beam angulation increments from −45° to +45° in five steps, and Wilson’s 95% confidence intervals were computed. Group comparisons used the Mann-Whitney U and independent t-tests (p ≤ 0.05)
Results
Minimal mesial beam angulations for effective canal separability (δ* = 90° − α) ranged from approximately 7° to 15° for mesial roots and approximately 10° to 13° for distal roots. No significant mesial differences were observed between first and second molars (p > 0.30). Distal roots of second molars exhibited significantly higher angulations (p = 0.003 coronal, p < 0.001 apical). Mesial canals achieved ≥95% separability at approximately 25° and ≥99% at approximately 35°; distal canals required approximately 30° and approximately 40°.
Conclusions
A mesial beam angulation of 30° to 35° provides probable canal differentiation in mandibular molars, separating mesial canals in ≥99% and distal canals in ≥95% of cases. This range refines previous recommendations and supports the as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) principle.
- 443 View
- 16 Download

- Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule occlusion by desensitizing agents after tooth bleaching: an in vitro study
- Dimitrios Dionysopoulos, Petros Mourouzis, Spyros Papageorgiou, Kosmas Tolidis
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e8. Published online February 10, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e8
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
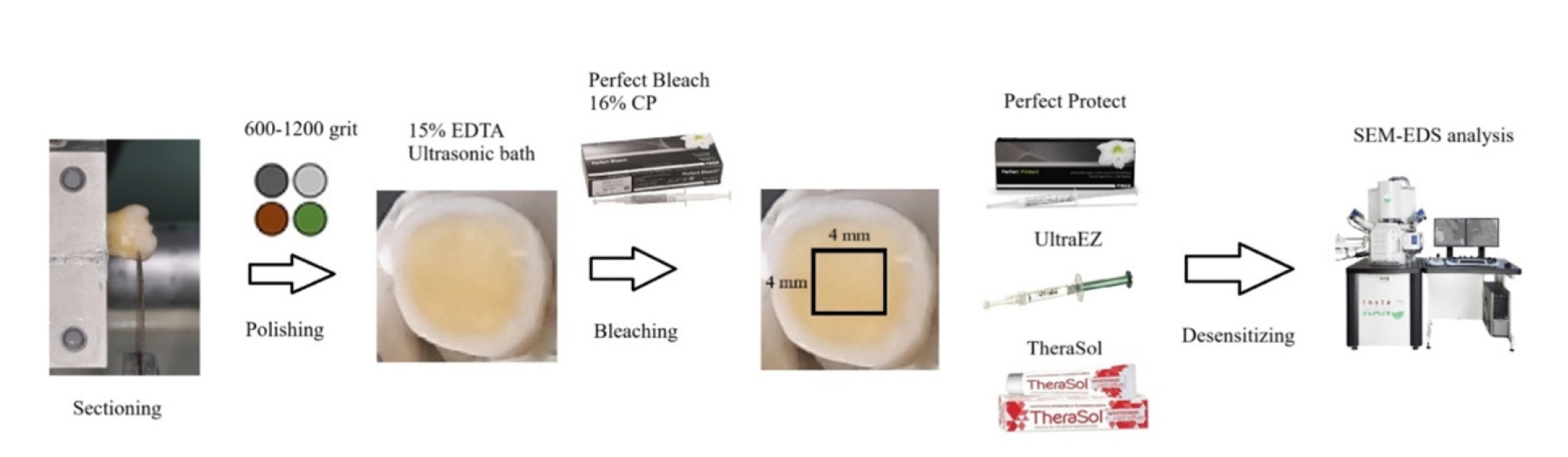
This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy of three commercially available desensitizing agents in occluding dentinal tubules, which may help reduce tooth sensitivity following a bleaching treatment.
Methods
Twenty healthy human third molars were utilized in this investigation. The samples were prepared by transversely sectioning 2.5 mm of the crowns to expose the dentin. They were initially treated with 15% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid gel for 4 minutes, followed by application of Perfect Bleach (VOCO GmbH) bleaching agent (16% carbamide peroxide) for 2 hours. The samples were randomly allocated into four groups (n = 5), each receiving one of the following treatments: group 1: No treatment (control), group 2: treated with UltraEZ (Ultradent Products Inc.,), containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride, group 3: treated with Perfect Protect (VOCO GmbH), also containing potassium nitrate and sodium fluoride and group 4: treated with TheraSol Whitening & Sensitive (ABC Kinitron IKE), containing strontium acetate and sodium monofluorophosphate. Subsequently, the specimens were examined using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy to evaluate dentin tubule occlusion.
Results
SEM observations showed no occlusion of dentin tubules in the control group, whereas groups 2 to 4 exhibited significant occlusion. The most effective treatment was Perfect Protect (p < 0.05), while UltraEZ and TheraSol Whitening & Sensitive demonstrated similar effectiveness, with no statistically significant difference between them (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
The tested desensitizing agents effectively occluded dentin tubules to a considerable extent. Differences in their effectiveness were attributed to variations in their formulations.
- 486 View
- 47 Download

- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
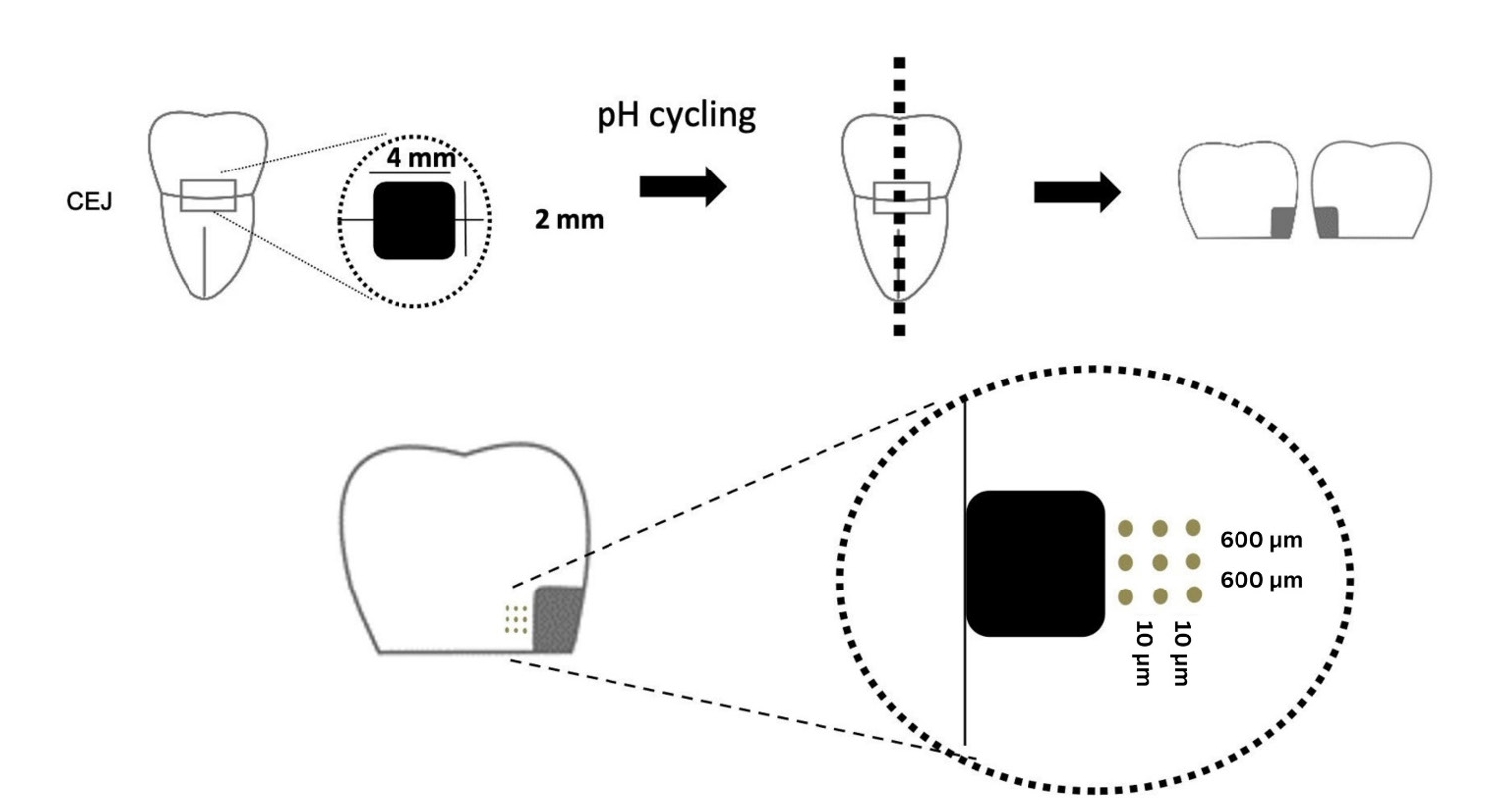
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,861 View
- 215 Download

- Effectiveness of endodontic retreatment using WaveOne Primary files in reciprocating and rotary motions
- Patricia Marton Costa, Renata Maíra de Souza Leal, Guilherme Hiroshi Yamanari, Bruno Cavalini Cavenago, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e15. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the efficiency of WaveOne Primary files (Dentsply Sirona) for removing root canal fillings with 2 types of movement: reciprocating (RCP) and continuous counterclockwise rotation (CCR).
Materials and Methods Twenty mandibular incisors were prepared with a RCP instrument (25.08) and filled using the Tagger hybrid obturation technique. The teeth were retreated with a WaveOne Primary file and randomly allocated to 2 experimental retreatment groups (
n = 10) according to movement type: RCP and CCR. The root canals were emptied of filling material in the first 3 steps of insertion, until reaching the working length. The timing of retreatment and procedure errors were recorded for all samples. The specimens were scanned before and after the retreatment procedure with micro-computed tomography to calculate the percentage and volume (mm3) of the residual filling material. The results were statistically evaluated using paired and independentt -tests, with a significance level set at 5%.Results No significant difference was found in the timing of filling removal between the groups, with a mean of 322 seconds (RCP) and 327 seconds (CCR) (
p < 0.05). There were 6 instrument fractures: 1 in a RCP motion file and 5 in continuous rotation files. The volumes of residual filling material were similar (9.94% for RCP and 15.94% for CCR;p > 0.05).Conclusions The WaveOne Primary files used in retreatment performed similarly in both RCP and CCR movements. Neither movement type completely removed the obturation material, but the RCP movement provided greater safety.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
Gülsen Kiraz, Bulem Üreyen Kaya, Mert Ocak, Muhammet Bora Uzuner, Hakan Hamdi Çelik
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Micro-CT evaluation of the removal of root fillings using rotary and reciprocating systems supplemented by XP-Endo Finisher, the Self-Adjusting File, or Er,Cr:YSGG laser
- 2,594 View
- 57 Download
- 1 Crossref

- How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
- Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e2. Published online December 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
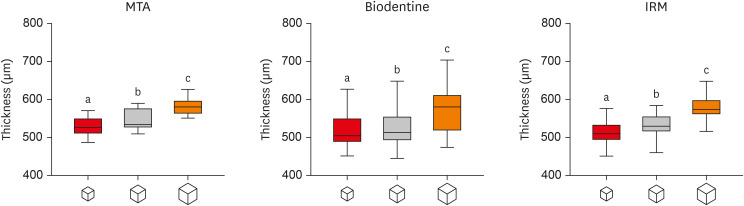
ePub Objectives This study investigated the impact of micro-computed tomography (micro-CT)-based voxel size on the analysis of material/dentin interface voids and thickness of different endodontic cements.
Materials and Methods Following root-end resection and apical preparation, maxillary premolars were filled with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), Biodentine, and intermediate restorative material (IRM) (
n = 24). The samples were scanned using micro-CT (SkyScan 1272; Bruker) and the cement/dentin interface and thickness of materials were evaluated at voxel sizes of 5, 10, and 20 µm. Analysis of variance and the Tukey test were conducted, and the degree of agreement between different voxel sizes was evaluated using the Bland and Altman method (p < 0.05).Results All materials showed an increase in thickness from 5 to 10 and 20 µm (
p < 0.05). When evaluating the interface voids, materials were similar at 5 µm (p > 0.05), while at 10 and 20 µm Biodentine showed the lowest percentage of voids (p < 0.05). A decrease in the interface voids was observed for MTA and IRM at 20 µm, while Biodentine showed differences among all voxel sizes (p < 0.05). The Bland-Altman plots for comparisons among voxel sizes showed the largest deviations when comparing images between 5 and 20 µm.Conclusions Voxel size had an impact on the micro-CT evaluation of thickness and interface voids of endodontic materials. All cements exhibited an increase in thickness and a decrease in the void percentage as the voxel size increased, especially when evaluating images at 20 µm.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
Shuting Feng, Weiqing Zhou, Xiaojun Chu, Shuaimei Xu, Xiongqun Zeng
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1380. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Supplementary methods for filling material removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of micro-CT imaging studies
Bruna Venzke Fischer, Taynara Santos Goulart, Filipe Colombo Vitali, Diego Leonardo de Souza, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 151: 105445. CrossRef
- Effect of ultrasonic activation of endodontic sealers on root canal filling quality during the single-cone obturation procedure: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory-based studies
- 2,149 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Porosity and pore size distribution in high-viscosity and conventional glass ionomer cements: a micro-computed tomography study
- Aline Borburema Neves, Laísa Inara Gracindo Lopes, Tamiris Gomes Bergstrom, Aline Saddock Sá da Silva, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Aline de Almeida Neves
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e57. Published online October 29, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e57
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
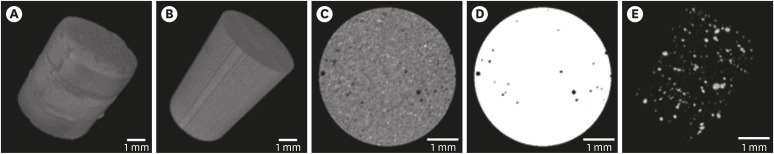
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare and evaluate the porosity and pore size distribution of high-viscosity glass ionomer cements (HVGICs) and conventional glass ionomer cements (GICs) using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT).
Materials and Methods Forty cylindrical specimens (
n = 10) were produced in standardized molds using HVGICs and conventional GICs (Ketac Molar Easymix, Vitro Molar, MaxxionR, and Riva Self-Cure). The specimens were prepared according to ISO 9917-1 standards, scanned in a high-energy micro-CT device, and reconstructed using specific parameters. After reconstruction, segmentation procedures, and image analysis, total porosity and pore size distribution were obtained for specimens in each group. After checking the normality of the data distribution, the Kruskal-Wallis test followed by the Student-Newman-Keuls test was used to detect differences in porosity among the experimental groups with a 5% significance level.Results Ketac Molar Easymix showed statistically significantly lower total porosity (0.15%) than MaxxionR (0.62%), Riva (0.42%), and Vitro Molar (0.57%). The pore size in all experimental cements was within the small-size range (< 0.01 mm3), but Vitro Molar showed statistically significantly more pores/defects with a larger size (> 0.01 mm3).
Conclusions Major differences in porosity and pore size were identified among the evaluated GICs. Among these, the Ketac Molar Easymix HVGIC showed the lowest porosity and void size.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of contouring instruments on immediate quality and porosity of direct restorations
Carlos Soler-Tornero, Pekka Toivonen, Jaakko Suorsa, Sakari S. Karhula, Simo Saarakkala, Vuokko Anttonen, Jukka Leinonen
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Human Blood Contamination on Microhardness of Glass-Ionomer Cements and Glass-Hybrid Material
Katarina Franić, Ana Brundić, Jurica Matijević, Ana Ivanišević, Ivana Miletić, Anja Baraba
Materials.2025; 18(17): 4075. CrossRef - Effect of crown seating methods on the remnant cement in the subgingival region of a cement-retained implant crown
Fanghui Ji, Ji Suk Shim, Jeongyol Lee, Hwiseong Oh, Jae Jun Ryu
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing Wear Resistance in Glass Ionomer Cement through Green-mediated Chitosan-, Titanium-, Zirconium-, and Hydroxyapatite-based Nanocomposites: An Analysis before and after Chewing Simulator Endurance
Jessy Paulraj, Rajeshkumar Shanmugam, Subhabrata Maiti, Srinavasa Surya Sitaram
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(11): 1229. CrossRef - The effect of mesoporous silica doped with silver nanoparticles on glass ionomer cements; physiochemical, mechanical and ion release analysis
Syed Saad Bin Qasim, Ali Bmuajdad
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyperbaric Pressure Effect on Dental Luting Cements
Secil OZKAN ATA, Nazım ATA, Rıfat UGURLUTAN
Journal of Basic and Clinical Health Sciences.2023; 7(1): 464. CrossRef - In Vitro Comparison of Differences in Setting Time of Premixed Calcium Silicate-Based Mineral Trioxide Aggregate According to Moisture Content of Gypsum
Hyun-Jin Kim, Jun-Seok Lee, Dong-Hoon Gwak, Yong-Seok Ko, Chun-Il Lim, Seung-Youl Lee
Materials.2023; 17(1): 35. CrossRef - Adhesion and Surface Roughness of Apatite-Containing Carbomer and Improved Ionically Bioactive Resin Compared to Glass Ionomers
Handan Yıldırım Işık, Aylin Çilingir
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(7): 367. CrossRef - An influence of finishing procedures and protective coating on the ultrastructure of conventional and hybrid glass ionomer cement restorations
Antonije Stankovic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Nikolic, Aleksandar Mitic, Nenad Stosic, Radomir Barac, Aleksandra Milovanovic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2023; 70(3): 138. CrossRef - Effect of aging on mechanical and antibacterial properties of fluorinated graphene reinforced glass ionomer: In vitro study
Suzan Khaled Arafa, Dalia Ibrahim Sherief, Mohamed Salah Nassif
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2023; 142: 105803. CrossRef
- The effect of contouring instruments on immediate quality and porosity of direct restorations
- 2,642 View
- 17 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref

- Combination of a new ultrasonic tip with rotary systems for the preparation of flattened root canals
- Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e56. Published online October 27, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e56
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
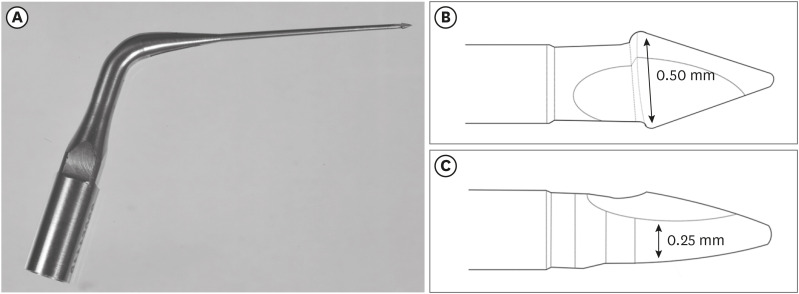
ePub Objectives This study evaluated 2 nickel-titanium rotary systems and a complementary protocol with an ultrasonic tip and a small-diameter instrument in flattened root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty-two human maxillary second premolars with flattened canals (buccolingual diameter ≥4 times larger than the mesiodistal diameter) at 9 mm from the radiographic apex were selected. The root canals were prepared by ProDesign Logic (PDL) 30/0.01 and 30/0.05 or Hyflex EDM (HEDM) 10/0.05 and 25/0.08 (
n = 16), followed by application of the Flatsonic ultrasonic tip in the cervical and middle thirds and a PDL 25/0.03 file in the apical third (FPDL). The teeth were scanned using micro-computed tomography before and after the procedures. The percentage of volume increase, debris, and uninstrumented surface area were analyzed using the Kruskal-Wallis, Dunn, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance/Tukey, and paired and unpairedt -tests (α = 0.05).Results No significant difference was found in the volume increase and uninstrumented surface area between PDL and HEDM (
p > 0.05). PDL had a higher percentage of debris than HEDM in the middle and apical thirds (p < 0.05). The FPDL protocol resulted in less debris and uninstrumented surface area for PDL and HEDM (p < 0.05). This protocol, with HEDM, reduced debris in the middle and apical thirds and uninstrumented surface area in the apical third (p < 0.05).Conclusions High percentages of debris and uninstrumented surface area were observed after preparation of flattened root canals. The HEDM, Flatsonic tip, and 25/0.03 instrument protocol enhanced cleaning in flattened root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
Ayşenur Kızıltaş Gül, Turan Mert Hisar, Seniha Miçooğulları
Selcuk Dental Journal.2025; 12(1): 157. CrossRef - Flatsonic Ultrasonic Tip Optimizes the Removal of Remaining Filling Material in Flattened Root Canals: A Micro–computed Tomographic Analysis
Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 612. CrossRef - The Effect of Combined Ultrasonic Tip and Mechanized Instrumentation on the Reduction of the Percentage of Non-Instrumented Surfaces in Oval/Flat Root Canals: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Marcella Dewes Cassal, Pedro Cardoso Soares, Marcelo dos Santos
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Heat-treated NiTi instruments and final irrigation protocols for biomechanical preparation of flattened canals
Kleber Kildare Teodoro CARVALHO, Igor Bassi Ferreira PETEAN, Alice Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Rafael Verardino CAMARGO, Jardel Francisco MAZZI-CHAVES, Yara Terezinha Corrêa SILVA-SOUSA, Manoel Damião SOUSA-NETO
Brazilian Oral Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Kök Kanal Tedavisi Yenilemelerinde Ultrasonik Uç Kullanımı
- 1,849 View
- 26 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of single-cone obturation with three sealers
- Sahar Zare, Ivy Shen, Qiang Zhu, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e25. Published online April 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
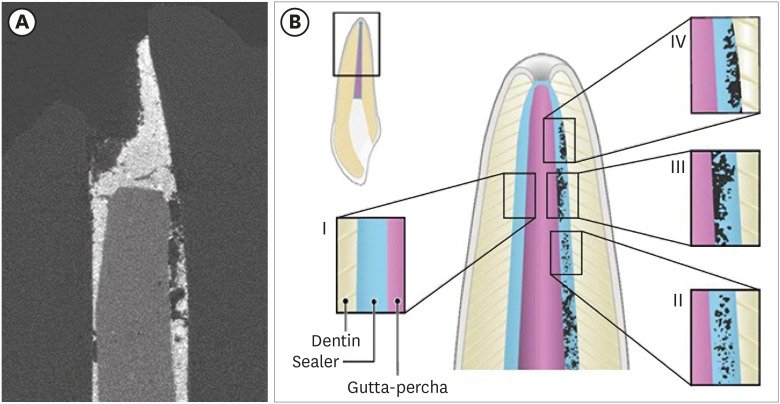
ePub Objectives This study used micro-computed tomography (µCT) to compare voids and interfaces in single-cone obturation among AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype surface pre-reacted glass ionomer (S-PRG) sealers and to determine the percentage of sealer contact at the dentin and gutta-percha (GP) interfaces.
Materials and Methods Fifteen single-rooted human teeth were shaped using ProTaper NEXT size X5 rotary files using 2.5% NaOCl irrigation. Roots were obturated with a single-cone ProTaper NEXT GP point X5 with AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, or prototype S-PRG sealer (
n = 5/group).Results The volumes of GP, sealer, and voids were measured in the region of 0–2, 2–4, 4–6, and 6–8 mm from the apex, using image analysis of sagittal µCT scans. GP volume percentages were: AH Plus (75.5%), EndoSequence BC (87.3%), and prototype S-PRG (94.4%). Sealer volume percentages were less: AH Plus (14.3%), EndoSequence BC (6.8%), and prototype S-PRG (4.6%). Void percentages were AH Plus (10.1%), EndoSequence BC (5.9%), and prototype S-PRG (1.0%). Dentin-sealer contact ratios of AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype S-PRG groups were 82.4% ± 6.8%, 71.6% ± 25.3%, and 70.2% ± 9.4%, respectively. GP-sealer contact ratios of AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype S-PRG groups were 65.6% ± 29.1%, 80.7% ± 25.8%, and 87.0% ± 8.6%, respectively.
Conclusions Prototype S-PRG sealer created a low-void obturation, similar to EndoSequence BC sealer with similar dentin-sealer contact (> 70%) and GP-sealer contact (> 80%). Prototype S-PRG sealer presented comparable filling quality to EndoSequence BC sealer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of gap areas of root filling techniques in teeth with 3D-printed different configurations of C-shaped root canals: a micro-computed tomography study
Tuba Gok, Adem Gok, Haydar Onur Aciksoz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of the quality of root canal filling using three different sealers: Micro-computed tomography and scanning electron microscope study
Loai Alsofi, Mohammed Yagmoor, Tariq AbuHaimed, Hassan Abed, Ehab Alshouibi, Rafif Mandura, Turki Bakhsh, Hanaa Ashkar, Mey Al-Habib
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 152. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of bioactive calcium silicate coating on functionalized gutta-percha and its effect on bioceramic sealer wettability – An in vitro study
Bollineni Swetha, B. Devi Priya, K. Hanisha Reddy, G. Prasanthi, T. Murali Mohan, Dumpa Tejaswi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(7): 613. CrossRef - Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
Yang Yu, Chong-Yang Yuan, Xing-Zhe Yin, Xiao-Yan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 169. CrossRef - Micro-CT determination of the porosity of two tricalcium silicate sealers applied using three obturation techniques
Jinah Kim, Kali Vo, Gurmukh S. Dhaliwal, Aya Takase, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(3): 163. CrossRef - Ex-vivo evaluation of clinically-set hydraulic sealers used with different canal dryness protocols and obturation techniques: a randomized clinical trial
Nawar Naguib Nawar, Mohamed Mohamed Elashiry, Ahmed El Banna, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Edgar Schäfer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydraulic (Single Cone) Versus Thermogenic (Warm Vertical Compaction) Obturation Techniques: A Systematic Review
Haytham S Jaha
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sealing ability of various endodontic sealers with or without ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) treatment on bovine root canal
Yusuke AIGAMI, Tomofumi SAWADA, Shunsuke SHIMIZU, Akiko ASANO, Mamoru NODA, Shinji TAKEMOTO
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(3): 420. CrossRef - A Literature Review of the Effect of Heat on the Physical-Chemical Properties of Calcium Silicate–Based Sealers
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, James Ghilotti, María Melo
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(8): 1044. CrossRef - Assessment of the Prevalence of Head Lice Infestation and Parents’ Attitudes Towards Its Management: A School-based Epidemiological Study in İstanbul, Türkiye
Özben Özden, İnci Timur, Hale Ezgi Açma, Duygu Şimşekli, Barış Gülerman, Özgür Kurt
Turkish Journal of Parasitology.2023; 47(2): 112. CrossRef - Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro‐CT assessment of gap‐containing areas along the gutta‐percha‐sealer interface in oval‐shaped canals
Gustavo De‐Deus, Gustavo O. Santos, Iara Zamboni Monteiro, Daniele M. Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Felipe G. Belladonna, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Erick M. Souza, Raphael Licha, Carla Zogheib, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 795. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Use of micro-CT to examine effects of heat on coronal obturation
Ivy Shen, Joan Daniel, Kali Vo, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(3): 224. CrossRef - Obturation of Root Canals By Vertical Condensation of Gutta-Percha – Benefits and Pitfalls
Calkovsky Bruno, Slobodnikova Ladislava, Bacinsky Martin, Janickova Maria
Acta Medica Martiniana.2021; 21(3): 103. CrossRef
- Assessment of gap areas of root filling techniques in teeth with 3D-printed different configurations of C-shaped root canals: a micro-computed tomography study
- 2,283 View
- 32 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Shaping ability and apical debris extrusion after root canal preparation with rotary or reciprocating instruments: a micro-CT study
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Sara Gomes de Moura, Carolina Oliveira de Lima, Ana Flávia Almeida Barbosa, Waleska Florentino Misael, Mariane Floriano Lopes Santos Lacerda, Luciana Moura Sassone
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e16. Published online February 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e16

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
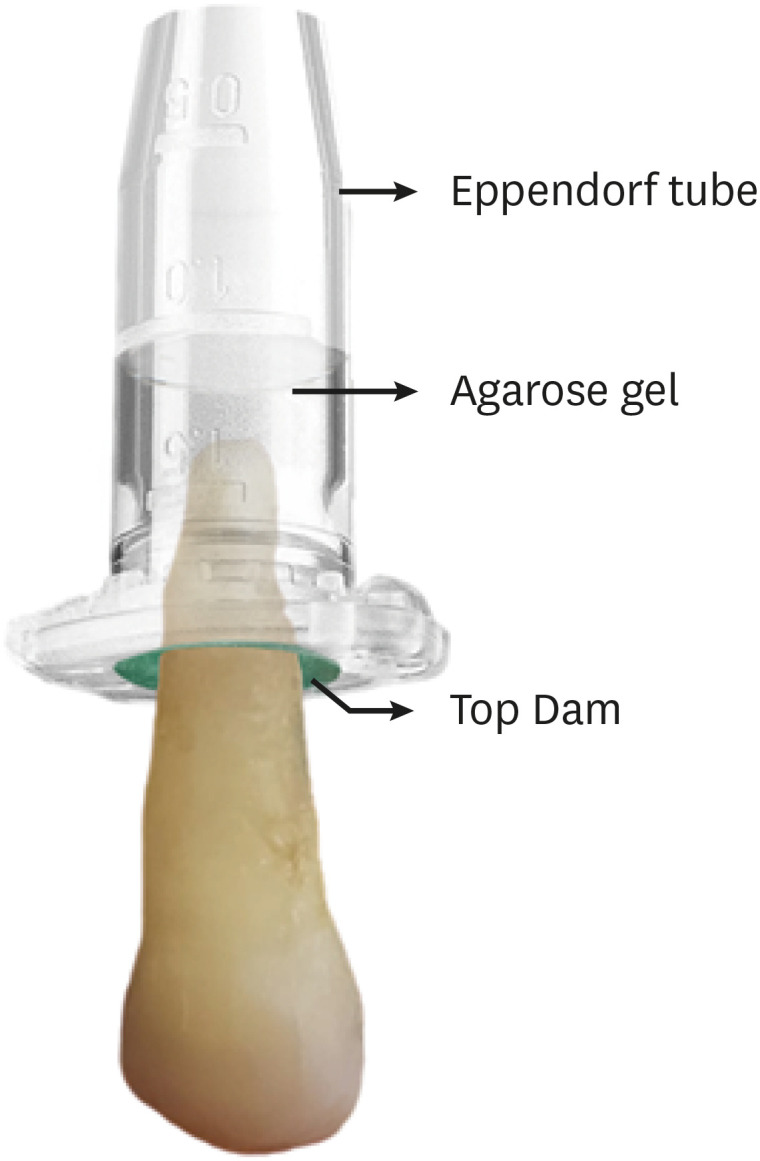
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the shaping ability of the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems and the apical extrusion of debris after root canal instrumentation. The ProTaper Universal system was used as a reference for comparison.
Materials and Methods Thirty-three mandibular premolars with a single canal were scanned using micro-computed tomography and were matched into 3 groups (
n = 11) according to the instrumentation system: TruShape, Reciproc Blue and ProTaper Universal. The teeth were accessed and mounted in an apparatus with agarose gel, which simulated apical resistance provided by the periapical tissue and enabled the collection of apically extruded debris. During root canal preparation, 2.5% sodium hypochlorite was used as an irrigant. The samples were scanned again after instrumentation. The percentage of unprepared area, removed dentin, and volume of apically extruded debris were analyzed. The data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test for multiple comparisons at a 5% significance level.Results No significant differences in the percentage of unprepared area were observed among the systems (
p > 0.05). ProTaper Universal presented a higher percentage of dentin removal than the TruShape and Reciproc Blue systems (p < 0.05). The systems produced similar volumes of apically extruded debris (p > 0.05).Conclusions All systems caused apically extruded debris, without any significant differences among them. TruShape, Reciproc Blue, and ProTaper Universal presented similar percentages of unprepared area after root canal instrumentation; however, ProTaper Universal was associated with higher dentin removal than the other systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endomotor integration, file kinematics impact on apical debris extrusion in severely curved canals
Anshika Saxena, Vineeta Nikhil
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 87. CrossRef - Comparison of post-operative pain prevalence after single visit endodontic treatment with two NiTi rotary files - a randomized clinical trial
M. E. Khallaf, Yousra Aly, Amira Ibrahim Mohamed
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Silver-Ion-Coated Rotary Nickel Titanium Files - An In Vitro Study
Jhanvi H. Sadaria, Kondas V. Venkatesh, Dhanasekaran Sihivahanan
Indian Journal of Dental Research.2025; 36(3): 344. CrossRef - A quantitative comparison of apically extruded debris during root canal preparation using NiTi full-sequence rotary and single-file rotary systems: An in vitro study
Pallavi Goel, R. Vikram, R. Anithakumari, M. S. Adarsha, M. E. Sudhanva
Endodontology.2024; 36(3): 235. CrossRef - Extrusion of Sodium Hypochlorite in Oval-Shaped Canals: A Comparative Study of the Potential of Four Final Agitation Approaches Employing Agarose-Embedded Mandibular First Premolars
Aalisha Parkar, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Alexander Maniangat Luke
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(10): 2748. CrossRef - Shaping Efficiency of Rotary and Reciprocating Kinematics of Engine-driven Nickel-Titanium Instruments in Moderate and Severely curved Root Canals Using Microcomputed Tomography: A Systematic Review of Ex Vivo Studies
Claudiu Călin, Ana-Maria Focșăneanu, Friedrich Paulsen, Andreea C. Didilescu, Tiberiu Niță
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 907. CrossRef - Intracanal removal and apical extrusion of filling material after retreatment using rotary or reciprocating instruments: A new approach using human cadavers
Thamyres M. Monteiro, Victor O. Cortes‐Cid, Marilia F. V. Marceliano‐Alves, Andrea F. Campello, Luan F. Bastos, Ricardo T. Lopes, José F. Siqueira, Flávio R. F. Alves
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(1): 100. CrossRef - Assessment of debris extrusion on using automated irrigation device with conventional needle irrigation – An ex vivo study
Sahil Choudhari, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Raja Kumar, Sindhu Ramesh
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(3): 263. CrossRef - Postoperative pain perception and associated risk factors in children after continuous rotation versus reciprocating kinematics: A randomised prospective clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Dania Ibrahem Sermani, Mahmoud Ahmed Abdelmotelb
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 345. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study apical extrusion of debris and irrigants
Jale Tanalp
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 153. CrossRef - Quantitative evaluation of apically extruded debris using TRUShape, TruNatomy, and WaveOne Gold in curved canals
Nehal Nabil Roshdy, Reham Hassan
BDJ Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Shaping ability of new reciprocating or rotary instruments with two cross‐sectional designs: An ex vivo study
Isabela G. Guedes, Renata C. V. Rodrigues, Marília F. Marceliano‐Alves, Flávio R. F. Alves, Isabela N. Rôças, José F. Siqueira
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(12): 1385. CrossRef
- Endomotor integration, file kinematics impact on apical debris extrusion in severely curved canals
- 2,770 View
- 52 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref

- A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
- Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(1):e2. Published online December 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e2
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
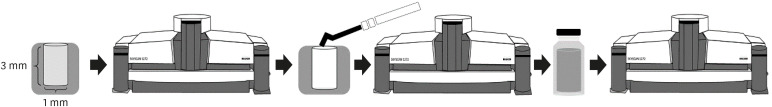
ePub Objectives New premixed bioceramic root repair materials require moisture for setting. Using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT), this study evaluated the filling ability and volumetric changes of calcium silicate-based repair materials (mineral trioxide aggregate repair high-plasticity [MTA HP] and Bio-C Repair, Angelus), in comparison with a zinc oxide and eugenol-based material (intermediate restorative material [IRM]; Dentsply DeTrey).
Materials and Methods Gypsum models with cavities 3 mm deep and 1 mm in diameter were manufactured and scanned using micro-CT (SkyScan 1272. Bruker). The cavities were filled with the cements and scanned again to evaluate their filling capacity. Another scan was performed after immersing the samples in distilled water for 7 days to assess the volumetric changes of the cements. The statistical significance of differences in the data was evaluated using analysis of variance and the Tukey test with a 5% significance level.
Results Bio-C Repair had a greater filling ability than MTA HP (
p < 0.05). IRM was similar to Bio-C and MTA HP (p > 0.05). MTA HP presented the largest volumetric change (p < 0.05), showing more volume loss than Bio-C and IRM, which were similar (p > 0.05).Conclusions Bio-C Repair is a new endodontic material with excellent filling capacity and low volumetric change. The gypsum model proposed for evaluating filling ability and volumetric changes by micro-CT had appropriate and reproducible results. This model may enhance the physicochemical evaluation of premixed bioceramic materials, which need moisture for setting.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of sealing potential of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine, and bio-C repair in furcation perforations: A glucose penetration study
Ashwija Shetty, Hajira Anjum Sultana, A. Srirekha, C. Champa, Suditi Pal, V. Sahithi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(2): 144. CrossRef - Evaluation of volumetric and surface stability of calcium silicate-based repair cements at different pHs
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Débora Leticia Bittencourt Leite Alves, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Nilvan Alves da Silva, Matheus Barros-Costa, Luciano Augusto Cano Martins, Francisco Haiter Neto, Marina Angélica Marciano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations—A Review
Peramune Arachchilage Amila Saman Prasad Kumara, Paul Roy Cooper, Peter Cathro, Maree Gould, George Dias, Jithendra Ratnayake
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 157. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties and periodontal ligament stem cell response to NeoMTA 2
Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Ariadne Letra, Renato Menezes Silva, Letícia Chaves de Souza, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Ultrasonic Condensation Time on Void Formation and Microhardness of Well-RootTM PT Apical Plugs in 3D-Printed Immature Teeth
Krasimir Hristov, Ralitsa Bogovska-Gigova
Materials.2025; 18(21): 4835. CrossRef - Effect of pH on the solubility and volumetric change of ready-to-use Bio-C Repair bioceramic material
Luana Raphael da SILVA, Jader Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Brazilian Oral Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of blood and artificial saliva contamination on marginal adaptation and sealing ability of different retrograde filling materials: A comparative analysis
Yantrapragada Lakshmi Sunanda, Krishna Prasad Parvathaneni, T. B. V. G. Raju, Abitha Seshadri, Gowtam Dev Dondapati
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(7): 743. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Volumetric change of calcium silicate-based repair materials in a simulated inflammatory environment: A micro-computed tomography study
Giovanna da Cunha Mendonça, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(8): 817. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, bioactivity, porosity, and sealer/dentin interface of bioceramic ready-to-use sealers using a dentin-tube model
Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Camila Soares Lopes, Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Juliane Maria Guerreiro–Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Healing the Open Apex: A Case Report on Innovative Apexogenesis of a Maxillary Molar Using Bio-C Repair
Ashwija Shetty, Hajira A Sultana, Keerthan B V, Nithin S Reddy
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation the Marginal Adaptation for the Bio C Repair and Other Root end Filling Material by Using Scanning Electron Microscope (A Comparative In Vitro Study)
Fatimah HAMADHİ, Zainab M.
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(3): 261. CrossRef - Biocompatibility, bioactive potential, porosity, and interface analysis calcium silicate repair cements in a dentin tube model
Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Camila Soares Lopes, Evelin Carine Alves Silva, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Paulo Sérgio Cerri, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(7): 3839. CrossRef - A new proposal for evaluating of the solubility of bioceramic materials in dentin tubes after immersion in PBS: a laboratory investigation
Giovanna da Cunha MENDONÇA, Karina Ines Medina Carita TAVARES, Airton Oliveira SANTOS-JUNIOR, Jáder Camilo PINTO, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mário TANOMARU-FILHO
Revista de Odontologia da UNESP.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of sealing potential of mineral trioxide aggregate, biodentine, and bio-C repair in furcation perforations: A glucose penetration study
- 2,483 View
- 32 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of a new system for root canal filling using calcium silicate-based root canal sealers
- Mario Tanomaru-Filho, Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e34. Published online June 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
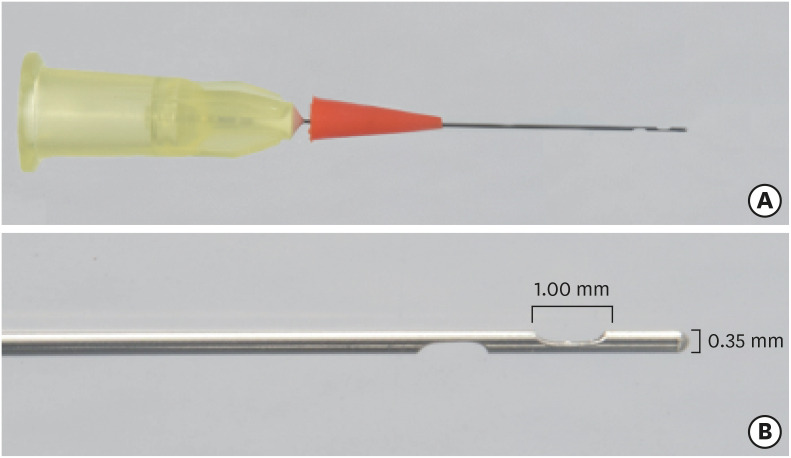
ePub Objectives This study evaluated by using micro-computed tomography (micro-CT) the filling ability and sealer apical extrusion promoted by a new Sealer Injection System (SIS; Angelus) with side openings needle, in comparison with the conventional injection system, associated with a new ready-to-use calcium silicate-based sealer (Bio-C Sealer).
Materials and Methods Acrylic resin models containing a main curved artificial canal and 3 simulated lateral canals in apical, middle and cervical thirds were used. The main root canals were prepared using a rotary system up to size 35.05. The canals were filled with Bio-C sealer by using a single cone technique and the conventional delivery system or SIS. Samples were scanned in micro-CT. The percentage of voids throughout the entire extension of the main root canal and in each third of the lateral canals, besides the apical extrusion of the sealer was calculated. Data were submitted to
t -test (p < 0.05).Results There was no difference between both systems in the main root canals filling. Although the volume percentage of voids was similar in the apical and middle thirds of lateral canals, SIS had the greatest filling ability of the cervical third lateral canal. Moreover, the conventional system showed the highest apical extrusion of the sealer.
Conclusions The conventional and SIS obturation systems had an appropriate filling ability of the main root canal. SIS had the best filling of the cervical third of the lateral canals, besides lower sealer apical extrusion, suggesting its clinical indication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
Amira Galal Ismail, Manar M. Galal, Tamer M. Hamdy
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2026; 16(2): 101400. CrossRef - Remineralizing capacity of zinc oxide eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vivo animal study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2025; 67(1): 100567. CrossRef - Advanced analytical tests and acellular bioactivity of zinc oxide eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vitro study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 149. CrossRef - Tissues response and bone-forming capacity of zinc oxide–eugenol sealer following the addition of nanohydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid: An in vivo animal study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(3): 322. CrossRef - Filling ability of ready-to-use or powder-liquid calcium silicate-based sealers after ultrasonic agitation
Mário Tanomaru-Filho, Maíra Bonassi Lucchesi, Airton Oliveira Santos-Junior, Karina Ines Medina Carita Tavares, Jáder Camilo Pinto, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment the bioactivity of zinc oxid eugenol sealer after the addition of different concentrations of nano hydroxyapatite-tyrosine amino acid
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa, Raghad A. Al-Askary
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2024; 23: e243733. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of dentinal tubule penetration and push-out bond strength of new injectable hydraulic calcium disilicate based root canal sealer: A single blinded in vitro study
Aman Verma, Anshul Arora, Sonali Taneja
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2024; 14(2): 143. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef - Contribution of XP‐Endo files to the root canal filling removal: A systematic review and meta‐analysis ofin vitrostudies
Emel Uzunoglu‐Özyürek, Selen Küçükkaya Eren, Sevilay Karahan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 703. CrossRef - Micro‐CT evaluation of filling of flattened root canals using a new premixed ready‐to‐use calcium silicate sealer by single‐cone technique
Karina I. M. C. Tavares, Jáder C. Pinto, Airton O. Santos‐Junior, Fernanda F. E. Torres, Juliane M. Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho
Microscopy Research and Technique.2021; 84(5): 976. CrossRef - Development of A Nano-Apatite Based Composite Sealer for Endodontic Root Canal Filling
Angelica Bertacci, Daniele Moro, Gianfranco Ulian, Giovanni Valdrè
Journal of Composites Science.2021; 5(1): 30. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis between resin-based root canal sealer and recent bioceramic-based root canal sealers using MicroCT, film thickness, and solubility
- 1,962 View
- 16 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic assessment of the shaping ability of the One Curve, One Shape, and ProTaper Next nickel-titanium rotary systems
- Pelin Tufenkci, Kaan Orhan, Berkan Celikten, Burak Bilecenoglu, Gurkan Gur, Semra Sevimay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e30. Published online May 22, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This micro-computed tomographic (CT) study aimed to compare the shaping abilities of ProTaper Next (PTN), One Shape (OS), and One Curve (OC) files in 3-dimensionally (3D)-printed mandibular molars.
Materials and Methods In order to ensure standardization, 3D-printed mandibular molars with a consistent mesiobuccal canal curvature (45°) were used in the present study (
n = 18). Specimens were instrumented with the OC, OS, or PTN files. The teeth were scanned pre- and post-instrumentation using micro-CT to detect changes of the canal volume and surface area, as well as to quantify transportation of the canals after instrumentation. Two-way analysis of variance was used for statistical comparisons.Results No statistically significant differences were found between the OC and OS groups in the changes of the canal volume and surface area before and after instrumentation (
p > 0.05). The OC files showed significantly less transportation than the OS or PTN systems for the apical section (p < 0.05). In a comparison of the systems, similar values were found at the coronal and middle levels, without any significant differences (p > 0.05).Conclusions These 3 instrumentation systems showed similar shaping abilities, although the OC file achieved a lesser extent of transportation in the apical zone than the OS and PTN files. All 3 file systems were confirmed to be safe for use in mandibular mesial canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of different kinematics and perforation diameter on integrated electronic apex locator accuracy in detecting root canal perforations
Ecenur Tuzcu, Safa Kurnaz
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro‐CT Evaluation of the Shaping Outcomes of Different Instruments in Oval‐Shaped Maxillary Premolar Canals
Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Seda Falakaloğlu, Ali Keleş, Özkan Adıgüzel, Sadullah Kaya
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bidirectional evaluation of canal transportation, centering ability and curvature changes of three NiTi rotary systems using cone beam computed tomography (invitro study)
Ahmed A. Soliman, Raef A. Sherif, Amr M. Abdallah, Ahmed M. Mobarak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Efficiencies of Different Rotary File Systems in Terms of Remaining Dentin Thickness Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography: An In Vitro Study
Vivek P Vadera , Sandhya K Punia, Saleem D Makandar, Rahul Bhargava, Pradeep Bapna
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Different Rotary Nickel–titanium Systems to Evaluate Coronal Leakage of Root Canals: An in Vitro Study
Rasha M. Al-Shamaa
Dental Hypotheses.2023; 14(3): 81. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of canal transportation and canal centering ability in oval canals with newer nickel–titanium rotary single file systems – A cone-beam computed tomography study
SimarKaur Manocha, SuparnaGanguly Saha, RollyS Agarwal, Neelam Vijaywargiya, MainakKanti Saha, Anjali Surana
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 326. CrossRef - Accumulated Hard Tissue Debris and Root Canal Shaping Profiles Following Instrumentation with Gentlefile, One Curve, and Reciproc Blue
Chi Wai Chan, Virginia Rosy Romeo, Angeline Lee, Chengfei Zhang, Prasanna Neelakantan, Eugenio Pedullà
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(10): 1344. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of canal transportation and centering ability of rotary and reciprocating file systems using cone-beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Tanisha Singh, Manju Kumari, Rohit Kochhar
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(3): 332. CrossRef - Retreatability of Bioceramic Sealer Using One Curve Rotary File Assessed by Microcomputed Tomography
Dina G Mufti, Saad A Al-Nazhan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(10): 1175. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef
- Effect of different kinematics and perforation diameter on integrated electronic apex locator accuracy in detecting root canal perforations
- 1,900 View
- 15 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
- Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e11. Published online January 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
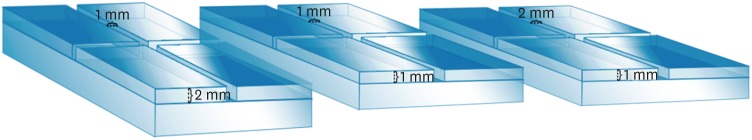
ePub Objectives This study compared the flow and filling of several retrograde filling materials using new different test models.
Materials and Methods Glass plates were manufactured with a central cavity and 4 grooves in the horizontal and vertical directions. Grooves with the dimensions used in the previous study (1 × 1 × 2 mm; length, width, and height respectively) were compared with grooves measuring 1 × 1 × 1 and 1 × 2 × 1 mm. Biodentine, intermediate restorative material (IRM), and mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) were evaluated. Each material was placed in the central cavity, and then another glass plate and a metal weight were placed over the cement. The glass plate/material set was scanned using micro-computed tomography. Flow was calculated by linear measurements in the grooves. Central filling was calculated in the central cavity (mm3) and lateral filling was measured up to 2 mm from the central cavity.
Results Biodentine presented the least flow and better filling than IRM when evaluated in the 1 × 1 × 2 model. In a comparison of the test models, MTA had the most flow in the 1 × 1 × 2 model. All materials had lower lateral filling when the 1 × 1 × 2 model was used.
Conclusions Flow and filling were affected by the size of the test models. Higher grooves and materials with greater flow resulted in lower filling capacity. The test model measuring 1 × 1 × 2 mm showed a better ability to differentiate among the materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physical, chemical and biological properties of MTA Angelus and novel AGM MTA: an in vitro analysis
Sara Nashibi, Parisa Amdjadi, SeyedehSana Ahmadi, Sara Hekmatian, Maryam Torshabi
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Limitations and Future Innovations—A Review
Peramune Arachchilage Amila Saman Prasad Kumara, Paul Roy Cooper, Peter Cathro, Maree Gould, George Dias, Jithendra Ratnayake
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(4): 157. CrossRef - Marginal Adaptation and Porosity of a Novel MTA Brand Applied as Root-End Filling Material: A Micro-CT Study
Yaneta Kouzmanova, Ivanka Dimitrova
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(7): 2758. CrossRef - Evaluation of the physical properties of bromelain-modified biodentine for direct pulp capping
Paridhi Agrawal, Manoj Chandak, Aditya Patel, Jay Bhopatkar
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - How do imaging protocols affect the assessment of root-end fillings?
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Reinhilde Jacobs, Mostafa EzEldeen, Karla de Faria-Vasconcelos, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Mário Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-computed tomography in preventive and restorative dental research: A review
Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Reza Tayefeh Davalloo, Gelareh Tajziehchi, Paria Shams
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2021; 51(4): 341. CrossRef
- Physical, chemical and biological properties of MTA Angelus and novel AGM MTA: an in vitro analysis
- 1,738 View
- 15 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of canal retreatments performed by undergraduate students using different techniques
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marianna Fernandes Carapiá, Brenda Leite Muniz, Mariana Santoro Rocha, Edson Jorge Lima Moreira
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e5. Published online January 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
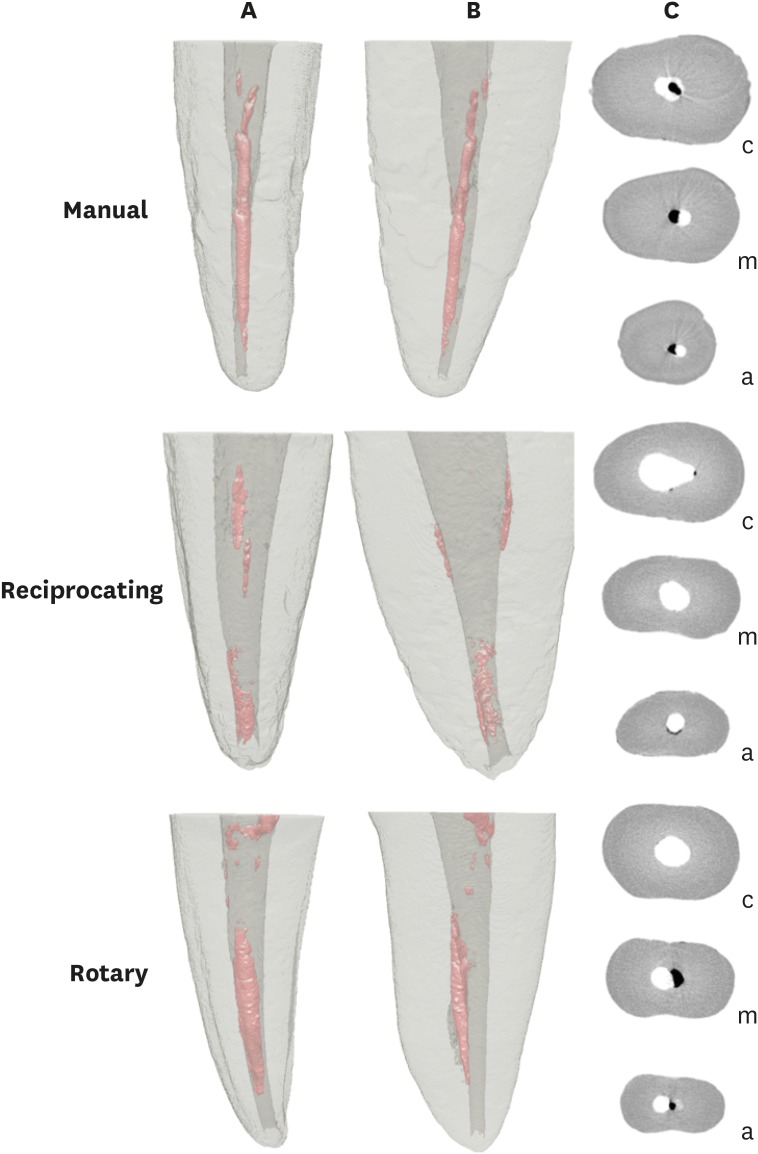
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the amount of remaining root canal filling materials after retreatment procedures performed by undergraduate students using manual, rotary, and reciprocating techniques through micro-computed tomographic analysis. The incidence of instrument fracture and the instrumentation time were also evaluated.
Materials and Methods Thirty maxillary single rooted teeth were prepared with Reciproc R25 files and filled with gutta-percha and AH Plus sealer by the continuous wave of condensation technique. Then, the specimens were assigned to 3 groups (
n = 10), according to the retreatment technique used: manual, rotary, and reciprocating groups, which used K-file, Mtwo retreatment file, and Reciproc file, respectively. Retreatments were performed by undergraduate students. The sample was scanned after root canal filling and retreatment procedures, and the images of the canals were examined to quantify the amount of remaining filling material. The incidence of instrument fracture and the instrumentation time were recorded.Results Remaining filling material was observed in all specimens regardless of the technique used. The mean volume of remaining material was significantly lower in the Reciproc group than in the manual K-file and Mtwo retreatment groups (
p < 0.05). The time required to achieve a satisfactory removal of canal filling material and refinement was significantly lower in the Mtwo retreatment and Reciproc groups (p < 0.05) when compared to the manual K-file group. No instrument fracture was observed in any of the groups.Conclusions Reciproc was the most effective instrument in the removal of canal fillings after retreatments performed by undergraduate students.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
Yang Yu, Chong-Yang Yuan, Xing-Zhe Yin, Xiao-Yan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 169. CrossRef - Optical microscopy evaluation of root canal filling removal by beginner operators in posterior teeth
Bogdan Dimitriu, Ioana Suciu, Oana Elena Amza, Mihai Ciocârdel, Dana Bodnar, Ana Maria Cristina Țâncu, Mihaela Tanase, Maria Sabina Branescu, Mihaela Chirilă
Journal of Medicine and Life.2024; 17(6): 555. CrossRef - Micro-CT Study on the Supplementary Effect of XP-Endo Finisher R after Endodontic Retreatment with Mtwo-R
I Tsenova-Ilieva, V Dogandzhiyska, M Raykovska, E Karova
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 26(12): 1844. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Efficiency of Supplementary Contemporary Single-file Systems in Removing Filling Remnants from Oval-shaped Canals: An In Vitro Study
Neveen A Shaheen, Dalia A Sherif, Nahla G Elhelbawy
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1055. CrossRef - Efficacy of an arrow‐shaped ultrasonic tip for the removal of residual root canal filling materials
Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva, Carolina O. de Lima, Ana F.A. Barbosa, Cláudio M. Ferreira, Bruno M. Crozeta, Ricardo T. Lopes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 467. CrossRef - XP‐endo Finisher R instrument optimizes the removal of root filling remnants in oval‐shaped canals
G. De‐Deus, F. G. Belladonna, A. S. Zuolo, D. M. Cavalcante, J. C. A. Carvalhal, M. Simões‐Carvalho, E. M. Souza, R. T. Lopes, E. J. N. L. Silva
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(6): 899. CrossRef
- Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
- 1,446 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Root canal volume change and transportation by Vortex Blue, ProTaper Next, and ProTaper Universal in curved root canals
- Hyun-Jin Park, Min-Seock Seo, Young-Mi Moon
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(1):e3. Published online December 24, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to compare root canal volume change and canal transportation by Vortex Blue (VB; Dentsply Tulsa Dental Specialties), ProTaper Next (PTN; Dentsply Maillefer), and ProTaper Universal (PTU; Dentsply Maillefer) nickel-titanium rotary files in curved root canals.
Materials and Methods Thirty canals with 20°–45° of curvature from extracted human molars were used. Root canal instrumentation was performed with VB, PTN, and PTU files up to #30.06, X3, and F3, respectively. Changes in root canal volume before and after the instrumentation, and the amount and direction of canal transportation at 1, 3, and 5 mm from the root apex were measured by using micro-computed tomography. Data of canal volume change were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance and Tukey test, while data of amount and direction of transportation were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney
U test.Results There were no significant differences among 3 groups in terms of canal volume change (
p > 0.05). For the amount of transportation, PTN showed significantly less transportation than PTU at 3 mm level (p = 0.005). VB files showed no significant difference in canal transportation at all 3 levels with either PTN or PTU files. Also, VB files showed unique inward transportation tendency in the apical area.Conclusions Other than PTN produced less amount of transportation than PTU at 3 mm level, all 3 file systems showed similar level of canal volume change and transportation, and VB file system could prepare the curved canals without significant shaping errors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
Yaprak Cesur, Sevinc Askerbeyli Örs, Ahmet Serper, Mert Ocak
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro-Computed Tomographic Evaluation of the Shaping Ability of Vortex Blue and TruNatomyTM Ni-Ti Rotary Systems
Batool Alghamdi, Mey Al-Habib, Mona Alsulaiman, Lina Bahanan, Ali Alrahlah, Leonel S. J. Bautista, Sarah Bukhari, Mohammed Howait, Loai Alsofi
Crystals.2024; 14(11): 980. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Centering Ability and Canal Transportation of Rotary File Systems in Different Kinematics Using CBCT
Nupur R Vasava, Shreya H Modi, Chintan Joshi, Mona C Somani, Sweety J Thumar, Aashray A Patel, Anisha D Parmar, Kruti M Jadawala
World Journal of Dentistry.2024; 14(11): 983. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of nickel titanium rotary instruments on canal transportation and centering ability in curved canals by using cone beam computed tomography: An in vitro study
Krishnaveni Krishnaveni, Nikitha Kalla, Nagalakshmi Reddy, Sharvanan Udayar
Journal of Dental Specialities.2023; 11(2): 105. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Root Canal Centering Ability of Two Heat-treated Single-shaping NiTi Rotary Instruments in Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Preethi Varadan, Chakravarthy Arumugam, Athira Shaji, R R Mathan
World Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(6): 535. CrossRef - A Comparison of Canal Width Changes in Simulated Curved Canals prepared with Profile and Protaper Rotary Systems
Aisha Faisal, Huma Farid, Robia Ghafoor
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2022; : 55. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Respect of the Root Canal Trajectory by Rotary Niti Instruments (Protaper®Universal): Retrospective Radiographic Study
Salma El Abbassi, Sanaa Chala, Majid Sakout, Faïza Abdallaoui
Integrative Journal of Medical Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The effect of nickel-titanium rotary systems on the biomechanical behaviour of mandibular first molars with curved and straight mesial roots: a finite element analysis study
- 1,821 View
- 12 Download
- 7 Crossref

- The reduction methods of operator's radiation dose for portable dental X-ray machines
- Jeong-Yeon Cho, Won-Jeong Han
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):160-164. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.160
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was aimed to investigate the methods to reduce operator's radiation dose when taking intraoral radiographs with portable dental X-ray machines.
Materials and Methods Two kinds of portable dental X-ray machines (DX3000, Dexcowin and Rextar, Posdion) were used. Operator's radiation dose was measured with an 1,800 cc ionization chamber (RadCal Corp.) at the hand level of X-ray tubehead and at the operator's chest and waist levels with and without the backscatter shield. The operator's radiation dose at the hand level was measured with and without lead gloves and with long and short cones.
Results The backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the hand level of X-ray tubehead to 23 - 32%, the lead gloves to 26 - 31%, and long cone to 48 - 52%. And the backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the operator's chest and waist levels to 0.1 - 37%.
Conclusions When portable dental X-ray systems are used, it is recommended to select X-ray machine attached with a backscatter shield and a long cone and to wear the lead gloves.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the Occupational Radiation Dose from a Handheld Portable X-ray Unit During Full-mouth Intraoral Dental Radiographs in the Dog and the Cat – A Pilot Study
Lenin A. Villamizar-Martinez, Jeannie Losey
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2024; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - Seguridad y protección radiológica con el uso de rayos X portátiles. Revisión de literatura
Francisco Javier Marichi-Rodríguez, Janeth Serrano-Bello, Marine Ortiz-Magdaleno, Febe Carolina Vázquez-Vázquez
Revista Odontológica Mexicana Órgano Oficial de la Facultad de Odontología UNAM.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Operator and Patient Doses after Irradiation with Handheld X-ray Devices
Ali Altındağ, Hakan Eren, Kaan Orhan, Sebahat Görgün
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(18): 10414. CrossRef - Hand-held dental X-ray device: Attention to correct use
Guilherme Ceschia Martins, Thaíza Gonçalves Rocha, Thaís de Lima Azeredo, Andréa de Castro Domingos, Maria Augusta Visconti, Eduardo Murad Villoria
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2023; 53(3): 265. CrossRef - Effect of cranium structure on dose distribution during intraoral radiography
Takeru Ishii, Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Atsuharu Nitanda, Akihiro Ochiai, Shinji Kito, Hirofumi Aboshi, Hideki Saka
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2022; 64(1): 131. CrossRef - Application of the Monte Carlo Method for the Evaluation of Scattered Radiation Dose Due to the Use of Handheld X-Ray in Dentistry
A Cc Gonzales, M R Soares, W O G Batista, A R Cardeña, J P Marquez, J R Vega
Radiation Protection Dosimetry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ASSESSMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL RADIATION DOSE FROM CAMERA MODEL INTRAORAL HANDHELD X-RAY DEVICE WITHOUT STRAY RADIATION PROTECTION SHIELD
Mahkameh Moshfeghi, Yaser Safi, Alireza Afzalan, Mitra Ghazizadeh Ahsaie
Radiation Protection Dosimetry.2022; 198(1-2): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of radiation exposure to operators of portable hand-held dental X-ray units
Justin Leadbeatter, Jennifer Diffey
Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine.2021; 44(2): 377. CrossRef - Comparison of air dose and operator exposure from portable X-ray units
Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Ruri Asami, Takeru Ishii, Shinji Kito, Yuichi Tamatsu, Hirofumi Aboshi, Hideki Saka
Legal Medicine.2020; 47: 101787. CrossRef - Dental research using intraoral techniques with portable digital radiography adapted for fieldwork in Qubbet el-Hawa (Egypt)
Sandra López-Lázaro, Violeta C. Yendreka, Alejandro Jiménez-Serrano, José Alba-Gómez, Gabriel M. Fonseca
Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of stray radiation to the operator for five hand-held dental X-ray devices
Richard Smith, Richard Tremblay, Graeme M Wardlaw
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2019; 48(5): 20180301. CrossRef - Assessment of image quality and exposure parameters of an intraoral portable X-rays device
Elton G Zenóbio, Madelon AF Zenóbio, Carolina DB Azevedo, Maria do Socorro Nogueira, Cláudio D Almeida, Flávio R Manzi
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2019; 48(3): 20180329. CrossRef - The study of protection of operators and surrounding workers at the time of using portable intraoral X-ray unit
Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Ruri Asami, Tomonori Ozawa, Maki Izawa, Hideki Saka
Legal Medicine.2018; 33: 66. CrossRef - The effects of device position on the operator's radiation dose when using a handheld portable X-ray device
Jimmy Makdissi, Ravikiran R Pawar, Ben Johnson, Bun S Chong
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2016; 45(3): 20150245. CrossRef - Patient and staff dosimetry during radiographic procedures in an intensive care unit
Rosario Fernández, Miguel Moreno-Torres, Antonia M Contreras, María I Núñez, Damián Guirado, Luis Peñas
Journal of Radiological Protection.2015; 35(3): 727. CrossRef - The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
Wook-Jin Seong, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Soocheol Jeong, Youngcheul Heo, Woo-Bin Song, Mansur Ahmad
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 146. CrossRef
- Assessment of the Occupational Radiation Dose from a Handheld Portable X-ray Unit During Full-mouth Intraoral Dental Radiographs in the Dog and the Cat – A Pilot Study
- 5,678 View
- 33 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Theory of X-ray microcomputed tomography in dental research: application for the caries research
- Young-Seok Park, Kwang-Hak Bae, Juhea Chang, Won-Jun Shon
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):98-107. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.98
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Caries remains prevalent throughout modern society and is the main disease in the field of dentistry. Although studies of this disease have used diverse methodology, recently, X-ray microtomography has gained popularity as a non-destructive, 3-dimensional (3D) analytical technique, and has several advantages over the conventional methods. According to X-ray source, it is classified as monochromatic or polychromatic with the latter being more widely used due to the high cost of the monochromatic source despite some advantages. The determination of mineral density profiles based on changes in X-ray attenuation is the principle of this method and calibration and image processing procedures are needed for the better image and reproducible measurements. Using this tool, 3D reconstruction is also possible and it enables to visualize the internal structures of dental caries. With the advances in the computer technology, more diverse applications are being studied, such automated caries assessment algorithms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Synchrotron X-ray Studies of the Structural and Functional Hierarchies in Mineralised Human Dental Enamel: A State-of-the-Art Review
Cyril Besnard, Ali Marie, Sisini Sasidharan, Robert A. Harper, Richard M. Shelton, Gabriel Landini, Alexander M. Korsunsky
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(4): 98. CrossRef - Revelation of microcracks as tooth structural element by X-ray tomography and machine learning
Irma Dumbryte, Donatas Narbutis, Arturas Vailionis, Saulius Juodkazis, Mangirdas Malinauskas
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-dimensional non-destructive visualization of teeth enamel microcracks using X-ray micro-computed tomography
Irma Dumbryte, Arturas Vailionis, Edvinas Skliutas, Saulius Juodkazis, Mangirdas Malinauskas
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiological Appraisal of Biodentine and Pulpotec Individually or in Combination with Photo-activated Disinfection as Pulp-capping Cements in Mature Teeth
Pratik Agrawal, Gaurav Patri, Surabhi Soumya, Prasanti K Pradhan, Vijeta Patri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(9): 1014. CrossRef - Ex vivoevaluation of new 2D and 3D dental radiographic technology for detecting caries
Laurence Gaalaas, Donald Tyndall, André Mol, Eric T Everett, Ananta Bangdiwala
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2016; 45(3): 20150281. CrossRef - Stationary intraoral digital tomosynthesis using a carbon nanotube X-ray source array
J Shan, A W Tucker, L R Gaalaas, G Wu, E Platin, A Mol, J Lu, O Zhou
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2015; 44(9): 20150098. CrossRef - Comparative efficacy of photo-activated disinfection and calcium hydroxide for disinfection of remaining carious dentin in deep cavities: a clinical study
Sidhartha Sharma, Ajay Logani, Naseem Shah
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 195. CrossRef - Current status of dental caries diagnosis using cone beam computed tomography
Young-Seok Park, Jin-Soo Ahn, Ho-Beom Kwon, Seung-Pyo Lee
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2011; 41(2): 43. CrossRef
- Synchrotron X-ray Studies of the Structural and Functional Hierarchies in Mineralised Human Dental Enamel: A State-of-the-Art Review
- 2,653 View
- 13 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Ingredients and cytotoxicity of MTA and 3 kinds of Portland cements
- Seok-Woo Chang, Hyun-Mi Yoo, Dong Sung Park, Tae-Seok Oh, Kwang-Shik Bae
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):369-376. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.369
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to compare the compositions and cytotoxicity of white ProRoot MTA (white mineral trioxide aggregate) and 3 kinds of Portland cements. The elements, simple oxides and phase compositions of white MTA (WMTA), gray Portland cement (GPC), white Portland cement (WPC) and fast setting cement (FSC) were measured by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) and X-ray diffractometry (XRD). Agar diffusion test was carried out to evaluate the cytotoxicity of WMTA and 3 kinds of Portland cements.
The results showed that WMTA and WPC contained far less magnesium (Mg), iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and zinc (Zn) than GPC and FSC. FSC contained far more aluminum oxide (Al2O3) than WMTA, GPC, and WPC. WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC were composed of main phases, such as tricalcicium silicate (3CaO·SiO2), dicalcium silicate (2CaO·SiO2), tricalcium aluminate (3CaO·Al2O3), and tetracalcium aluminoferrite (4CaO·Al2O3·Fe2O3). The significance of the differences in cellular response between WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC was statistically analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis Exact test with Bonferroni's correction. The result showed no statistically significant difference (p > 0.05).
WMTA, GPC, WPC and FSC showed similar compositions. However there were notable differences in the content of minor elements, such as aluminum (Al), magnesium, iron, manganese, and zinc. These differences might influence the physical properties of cements.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Multi-functional Composite Cement with Strength Improvement Using Disposable Waste Masks
Jong-Won Chung, Hyun-Kyoung Yang
Journal of Power System Engineering.2022; 26(3): 31. CrossRef - The effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on osteo/odontogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive and systematic literature review
Danial Babaki, Sanam Yaghoubi, Maryam M. Matin
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2020; 7(1): 175. CrossRef - Remineralization of demineralized dentin using a dual analog system
Neha Saxena, Stefan Habelitz, Grayson W. Marshall, Laurie B. Gower
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2019; 22(S1): 76. CrossRef - Chemical analysis and biological properties of two different formulations of white portland cements
Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Norhayati Luddin, Thirumulu Ponnuraj Kannan, Khairani Idah Mokhtar, Azlina Ahmad
Scanning.2016; 38(4): 303. CrossRef - In vitrocytotoxicity of four calcium silicate-based endodontic cements on human monocytes, a colorimetric MTT assay
Sedigheh Khedmat, Somayyeh Dehghan, Jamshid Hadjati, Farimah Masoumi, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 149. CrossRef - Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 258. CrossRef - Chemical characteristics of mineral trioxide aggregate and its hydration reaction
Seok-Woo Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(4): 188. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 344. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 473. CrossRef - Physical properties of novel composite using Portland cement for retro-filling material
Sang-Jin Lee, Ok-In Cho, Jiwan Yum, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(6): 445. CrossRef - A bioactivity study of Portland cement mixed with β-glycerophosphosphate on human pulp cell
Young-Hwan Oh, Young-Joo Jang, Yong-Bum Cho
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 415. CrossRef - Comparison of biocompatibility of four root perforation repair materials
Min-Kyung Kang, In-Ho Bae, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 192. CrossRef - Effects of condensation techniques and canal sizes on the microleakage of orthograde MTA apical plug in simulated canals
Deuk-Lim Nam, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(3): 208. CrossRef
- Development of Multi-functional Composite Cement with Strength Improvement Using Disposable Waste Masks
- 1,441 View
- 3 Download
- 13 Crossref

- A comparison of canal centering abilities of four root canal instrument systems using X-ray micro-computed tomography
- Hye-Suk Ko, Heyon-Mee You, Dong-Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2007;32(1):61-68. Published online January 31, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2007.32.1.061
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the centering abilities of four root canal instrument systems and the amounts of dentin removed after root canal shaping using them.
The mesial canals of twenty extracted mandibular first molars having 10 - 20° curvature were scanned using X-ray micro-computed tomography (XMCT)-scanner before root canals were instrumented. They were divided into four groups (n = 10 per group). In Group 1, root canals were instrumented by the step-back technique with stainless steel K-Flexofile after coronal flaring. The remainders were instrumented by the crown-down technique with Profile (Group 2), ProTaper (Group 3) or K3 system (Group 4). All canals were prepared up to size 25 at the end-point of preparation and scanned again. Scanned images were processed to reconstruct three-dimensional images using three-dimensional image software and the changes of total canal volume were measured. Pre- and post-operative cross-sectional images of 1, 3, 5, and 7 mm from the apical foramen were compared. For each level, centering ratio were calculated using Adobe Photoshop 6.0 and image software program.
ProTaper and K3 systems have a tendency to remove more dentin than the other file systems. In all groups, the lowest value of centering ratio at 3 mm level was observed. And except at 3 mm level, ProTaper system made canals less centered than the other systems (p < 0.05).
- 1,376 View
- 5 Download

- Three dimensional reconstruction of teeth using x-ray microtomography
- Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):485-490. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Complete understanding of the exterior and interior structure of the tooth would be prerequisite to the successful clinical results, especially in the restorative and endodontic treatment.
Although three-dimensional reconstruction method using x-ray microtomography could not be used in clinical cases, it may be the best way to reconstruct the morphologic characteristics of the tooth structure in detail without destructing the tooth itself. This study was done to three dimensionally reconstruct every teeth in the arch in order to increase the understanding about the endodontic treatment and to promote the effective restorative treatment by upgrading the knowledge of the tooth morphology.
After placing tooth between the microfocus x-ray tube and the image intensifier to obtain two-dimensional images of each level, scanning was done under the condition of 80 keV, 100 µA, 16.8 magnification with the spot size of 8 µm. Cross-section pixel size of 16.28 µm and 48.83 cross-section to cross-section distance were also used.
From the results of this study, precise three dimensional reconstructed images of every teeth could be obtained. Furthermore, it was possible to see image that showed interested area only, for example, enamel portion only, pulp and dentin area without enamel structure, pulp only, combination image of enamel and pulp, etc.
It was also possible to see transparent image without some part of tooth structure. This image might be used as a guide when restoring and preparing the full and partial crown by showing the positional and morphological relationship between the pulp and the outer tooth structure.
Another profit may be related with the fact that it would promote the understanding of the interior structure by making observation of the auto-rotating image of .AVI file from the various direction possible.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fracture Flow of Radionuclides in Unsaturated Conditions at LILW Disposal Facility
Won-Seok Kim, Jungjin Kim, Jinmo Ahn, Seongsik Nam, Wooyong Um
Journal of Korean Society of Environmental Engineers.2015; 37(8): 465. CrossRef
- Fracture Flow of Radionuclides in Unsaturated Conditions at LILW Disposal Facility
- 1,076 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


