Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of single-cone obturation with three sealers
- Sahar Zare, Ivy Shen, Qiang Zhu, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e25. Published online April 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e25
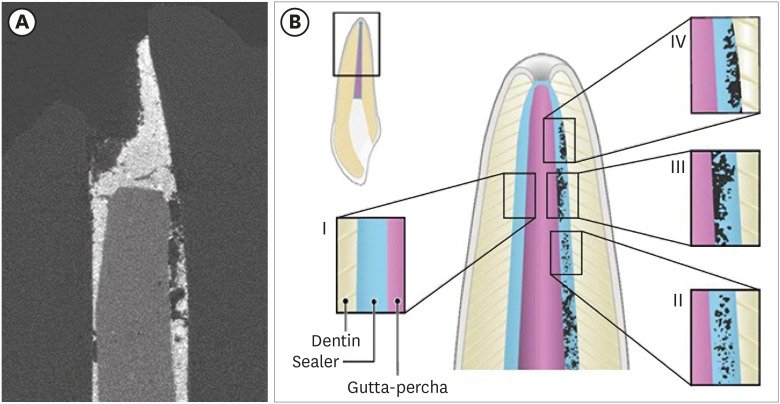
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study used micro-computed tomography (µCT) to compare voids and interfaces in single-cone obturation among AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype surface pre-reacted glass ionomer (S-PRG) sealers and to determine the percentage of sealer contact at the dentin and gutta-percha (GP) interfaces.
Materials and Methods Fifteen single-rooted human teeth were shaped using ProTaper NEXT size X5 rotary files using 2.5% NaOCl irrigation. Roots were obturated with a single-cone ProTaper NEXT GP point X5 with AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, or prototype S-PRG sealer (
n = 5/group).Results The volumes of GP, sealer, and voids were measured in the region of 0–2, 2–4, 4–6, and 6–8 mm from the apex, using image analysis of sagittal µCT scans. GP volume percentages were: AH Plus (75.5%), EndoSequence BC (87.3%), and prototype S-PRG (94.4%). Sealer volume percentages were less: AH Plus (14.3%), EndoSequence BC (6.8%), and prototype S-PRG (4.6%). Void percentages were AH Plus (10.1%), EndoSequence BC (5.9%), and prototype S-PRG (1.0%). Dentin-sealer contact ratios of AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype S-PRG groups were 82.4% ± 6.8%, 71.6% ± 25.3%, and 70.2% ± 9.4%, respectively. GP-sealer contact ratios of AH Plus, EndoSequence BC, and prototype S-PRG groups were 65.6% ± 29.1%, 80.7% ± 25.8%, and 87.0% ± 8.6%, respectively.
Conclusions Prototype S-PRG sealer created a low-void obturation, similar to EndoSequence BC sealer with similar dentin-sealer contact (> 70%) and GP-sealer contact (> 80%). Prototype S-PRG sealer presented comparable filling quality to EndoSequence BC sealer.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of gap areas of root filling techniques in teeth with 3D-printed different configurations of C-shaped root canals: a micro-computed tomography study
Tuba Gok, Adem Gok, Haydar Onur Aciksoz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of the quality of root canal filling using three different sealers: Micro-computed tomography and scanning electron microscope study
Loai Alsofi, Mohammed Yagmoor, Tariq AbuHaimed, Hassan Abed, Ehab Alshouibi, Rafif Mandura, Turki Bakhsh, Hanaa Ashkar, Mey Al-Habib
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 152. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of bioactive calcium silicate coating on functionalized gutta-percha and its effect on bioceramic sealer wettability – An in vitro study
Bollineni Swetha, B. Devi Priya, K. Hanisha Reddy, G. Prasanthi, T. Murali Mohan, Dumpa Tejaswi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(7): 613. CrossRef - Assessment of isthmus filling using two obturation techniques performed by students with different levels of clinical experience
Yang Yu, Chong-Yang Yuan, Xing-Zhe Yin, Xiao-Yan Wang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 169. CrossRef - Micro-CT determination of the porosity of two tricalcium silicate sealers applied using three obturation techniques
Jinah Kim, Kali Vo, Gurmukh S. Dhaliwal, Aya Takase, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(3): 163. CrossRef - Ex-vivo evaluation of clinically-set hydraulic sealers used with different canal dryness protocols and obturation techniques: a randomized clinical trial
Nawar Naguib Nawar, Mohamed Mohamed Elashiry, Ahmed El Banna, Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Edgar Schäfer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydraulic (Single Cone) Versus Thermogenic (Warm Vertical Compaction) Obturation Techniques: A Systematic Review
Haytham S Jaha
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sealing ability of various endodontic sealers with or without ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) treatment on bovine root canal
Yusuke AIGAMI, Tomofumi SAWADA, Shunsuke SHIMIZU, Akiko ASANO, Mamoru NODA, Shinji TAKEMOTO
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(3): 420. CrossRef - A Literature Review of the Effect of Heat on the Physical-Chemical Properties of Calcium Silicate–Based Sealers
Israa Ashkar, José Luis Sanz, Leopoldo Forner, James Ghilotti, María Melo
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(8): 1044. CrossRef - Assessment of the Prevalence of Head Lice Infestation and Parents’ Attitudes Towards Its Management: A School-based Epidemiological Study in İstanbul, Türkiye
Özben Özden, İnci Timur, Hale Ezgi Açma, Duygu Şimşekli, Barış Gülerman, Özgür Kurt
Turkish Journal of Parasitology.2023; 47(2): 112. CrossRef - Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Micro‐CT assessment of gap‐containing areas along the gutta‐percha‐sealer interface in oval‐shaped canals
Gustavo De‐Deus, Gustavo O. Santos, Iara Zamboni Monteiro, Daniele M. Cavalcante, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Felipe G. Belladonna, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Erick M. Souza, Raphael Licha, Carla Zogheib, Marco A. Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(7): 795. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - Use of micro-CT to examine effects of heat on coronal obturation
Ivy Shen, Joan Daniel, Kali Vo, Chul Ahn, Carolyn Primus, Takashi Komabayashi
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(3): 224. CrossRef - Obturation of Root Canals By Vertical Condensation of Gutta-Percha – Benefits and Pitfalls
Calkovsky Bruno, Slobodnikova Ladislava, Bacinsky Martin, Janickova Maria
Acta Medica Martiniana.2021; 21(3): 103. CrossRef
- Assessment of gap areas of root filling techniques in teeth with 3D-printed different configurations of C-shaped root canals: a micro-computed tomography study
- 2,253 View
- 32 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref

- Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
- Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):258-262. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.258
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restorative management of deep carious lesions and the preservation of pulp vitality of immature teeth present real challenges for dental practitioners. New tricalcium silicate cements are of interest in the treatment of such cases. This case describes the immediate management and the follow-up of an extensive carious lesion on an immature second right mandibular premolar. Following anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, the carious lesion was removed and a partial pulpotomy was performed. After obtaining hemostasis, the exposed pulp was covered with a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine, Septodont) and a glass ionomer cement (Fuji IX extra, GC Corp.) restoration was placed over the tricalcium silicate cement. A review appointment was arranged after seven days, where the tooth was asymptomatic with the patient reporting no pain during the intervening period. At both 3 and 6 mon follow up, it was noted that the tooth was vital, with normal responses to thermal tests. Radiographic examination of the tooth indicated dentin-bridge formation in the pulp chamber and the continuous root formation. This case report demonstrates a fast tissue response both at the pulpal and root dentin level. The use of tricalcium silicate cement should be considered as a conservative intervention in the treatment of symptomatic immature teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
A. Lavanya
The Traumaxilla.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of pulpotomy materials in permanent teeth: a systematic review of calcium hydroxide, MTA, biodentine, and iRoot BP plus
Anggi Putri Riandani, Arief Cahyanto, Rana Abdelbaset Lotfy Diab, Ratih Widyasari, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Hendra Dian Adhita Dharsono, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - How Does Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Irrigation Affect Biodentine? A Multimethod Ex Vivo Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2024; 17(6): 1230. CrossRef - Evaluation of Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement after Chlorhexidine Irrigation
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(19): 8702. CrossRef - Evaluation of the chemical, physical, and biological properties of a newly developed bioceramic cement derived from cockle shells: an in vitro study
Monthip Wannakajeepiboon, Chankhrit Sathorn, Chatvadee Kornsuthisopon, Busayarat Santiwong, Thanakorn Wasanapiarnpong, Pairoj Linsuwanont
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Protección pulpar directa y posterior apexogénesis. Informe de un caso clínico / Direct pulp capping followed by apexogenesis. A clinical case report
Osvaldo Zmener, Ana C. Boetto
Revista de la Asociación Odontológica Argentina.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Irrigation with Citric Acid on Biodentine Tricalcium Silicate-Based Cement: SEM-EDS In Vitro Study
Katarzyna Dąbrowska, Aleksandra Palatyńska-Ulatowska, Leszek Klimek
Materials.2022; 15(10): 3467. CrossRef - The Immunomodulatory and Regenerative Effect of Biodentine™ on Human THP‐1 Cells and Dental Pulp Stem Cells: In Vitro Study
Duaa Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Rand Zaza, Hanan Jafar, Suzan Zalloum, Renata Atoom, Walhan Alshaer, Mairvat Al-Mrahleh, Abdalla Awidi, Bruna Sinjari
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine: Material of choice for apexification
Himanshu Aeran, Mahema Sharma, Avantika Tuli
International Journal of Oral Health Dentistry.2021; 7(1): 54. CrossRef - Minimal Intervention in Dentistry: A Literature Review on Biodentine as a Bioactive Pulp Capping Material
Naji Ziad Arandi, Mohammad Thabet, Mona Abbassy
BioMed Research International.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Biodentine Pulpotomies on Permanent Traumatized Teeth with Complicated Crown Fractures
Léa Haikal, Beatriz Ferraz dos Santos, Duy-Dat Vu, Marina Braniste, Basma Dabbagh
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(9): 1204. CrossRef - Influence of sodium hypochlorite and ultrasounds on surface features and chemical composition of Biodentine tricalcium silicate-based material
Aleksandra PALATYŃSKA-ULATOWSKA, Katarzyna BUŁA, Leszek KLIMEK
Dental Materials Journal.2020; 39(4): 587. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting pulp-capping materials on cell viability and osteogenic differentiation in human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro study
Yan Sun, Jun Liu, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Ling Zou
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 100: 100. CrossRef - Healing Capacity of Autologous Bone Marrow–derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Partially Pulpotomized Dogs' Teeth
Mona H. El-Zekrid, Salah H. Mahmoud, Fawzy A. Ali, Mohamed E. Helal, Mohammed E. Grawish
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(3): 287. CrossRef - Large Periapical or Cystic Lesions in Association with Roots Having Open Apices Managed Nonsurgically Using 1-step Apexification Based on Platelet-rich Fibrin Matrix and Biodentine Apical Barrier: A Case Series
Sarang Sharma, Vivek Sharma, Deepak Passi, Dhirendra Srivastava, Shibani Grover, Shubha Ranjan Dutta
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(1): 179. CrossRef - Microleakage and Shear Bond Strength of Biodentine at Different Setting Time
Yong Ho Song, Nanyoung Lee, Sangho Lee, Myeongkwan Jih
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2018; 45(3): 344. CrossRef - Biodentine™ material characteristics and clinical applications: a 3 year literature review and update
S. Rajasekharan, L. C. Martens, R. G. E. C. Cauwels, R. P. Anthonappa
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2018; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Case Report: Immediate pain relief after partial pulpotomy of cariously exposed young permanent molar using mineral trioxide aggregate and root maturation, with two years follow-up
Passant Nagi, Nevine Waly, Adel Elbardissy, Mohammed Khalifa
F1000Research.2018; 7: 1616. CrossRef - Factors affecting the outcomes of direct pulp capping using Biodentine
Mariusz Lipski, Alicja Nowicka, Katarzyna Kot, Lidia Postek-Stefańska, Iwona Wysoczańska-Jankowicz, Lech Borkowski, Paweł Andersz, Anna Jarząbek, Katarzyna Grocholewicz, Ewa Sobolewska, Krzysztof Woźniak, Agnieszka Droździk
Clinical Oral Investigations.2018; 22(5): 2021. CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part I: vital pulp therapy
M. Parirokh, M. Torabinejad, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 177. CrossRef - Effect of iRoot Fast Set root repair material on the proliferation, migration and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells in vitro
Yan Sun, Tao Luo, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Ling Zou, Jun Liu, Gianpaolo Papaccio
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(10): e0186848. CrossRef - Dislodgement resistance of calcium silicate‐based materials from root canals with varying thickness of dentine
Ö. İ. Ulusoy, Y. N. Paltun, N. Güven, B. Çelik
International Endodontic Journal.2016; 49(12): 1188. CrossRef - Expression of Mineralization Markers during Pulp Response to Biodentine and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate
Mariana O. Daltoé, Francisco Wanderley G. Paula-Silva, Lúcia H. Faccioli, Patrícia M. Gatón-Hernández, Andiara De Rossi, Léa Assed Bezerra Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 596. CrossRef - Biodentine Reduces Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha–induced TRPA1 Expression in Odontoblastlike Cells
Ikhlas A. El Karim, Maelíosa T.C. McCrudden, Mary K. McGahon, Tim M. Curtis, Charlotte Jeanneau, Thomas Giraud, Chris R. Irwin, Gerard J. Linden, Fionnuala T. Lundy, Imad About
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(4): 589. CrossRef - Coronal Pulpotomy Technique Analysis as an Alternative to Pulpectomy for Preserving the Tooth Vitality, in the Context of Tissue Regeneration: A Correlated Clinical Study across 4 Adult Permanent Molars
Raji Viola Solomon, Umrana Faizuddin, Parupalli Karunakar, Grandhala Deepthi Sarvani, Sevvana Sree Soumya, Jiiang H. Jeng
Case Reports in Dentistry.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review on Biodentine, a Contemporary Dentine Replacement and Repair Material
Özlem Malkondu, Meriç Karapinar Kazandağ, Ender Kazazoğlu
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - The use of platelet rich plasma in the treatment of immature tooth with periapical lesion: a case report
Günseli Güven Polat, Ceren Yıldırım, Özlem Martı Akgün, Ceyhan Altun, Didem Dinçer, Cansel Köse Özkan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 230. CrossRef - Biodentine-a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification
Gurudutt Nayak, Mohammad Faiz Hasan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 120. CrossRef
- Bioceramic Pulpotomy and Direct Pulp
Capping on Complicated Fractures
Reattachment of Young Mature
Permanent Teeth: Case Series
- 2,102 View
- 5 Download
- 28 Crossref

- Chemical characteristics of mineral trioxide aggregate and its hydration reaction
- Seok-Woo Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):188-193. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.188
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) was developed in early 1990s and has been successfully used for root perforation repair, root end filling, and one-visit apexification. MTA is composed mainly of tricalcium silicate and dicalcium silicate. When MTA is hydrated, calcium silicate hydrate (CSH) and calcium hydroxide is formed. Formed calcium hydroxide interacts with the phosphate ion in body fluid and form amorphous calcium phosphate (ACP) which finally transforms into calcium deficient hydroxyapatite (CDHA). These mineral precipitate were reported to form the MTA-dentin interfacial layer which enhances the sealing ability of MTA. Clinically, the use of zinc oxide euginol (ZOE) based materials may retard the setting of MTA. Also, the use of acids or contact with excessive blood should be avoided before complete set of MTA, because these conditions could adversely affect the hydration reaction of MTA. Further studies on the chemical nature of MTA hydration reaction are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Discoloration, radiopacity, and push-out bond strength of bismuth-based radiopacifiers in endodontic sealers
Mohammad Ali Saghiri, Mina Shekarian, Amir Abdolmaleki, Michael Conte, Steven M. Morgano
Odontology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrieval of AH Plus Bioceramic and Ceraseal Versus AH Plus in Endodontic Retreatment
Eurok Shim, Jee Woo Son, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(6): 1826. CrossRef - Inducing Osteogenesis in Human Pulp Stem Cells Cultured on Nano-Hydroxyapatite and Naringin-Coated 3D-Printed Poly Lactic Acid Scaffolds
Reem Mones Dawood, Anas Falah Mahdee
Polymers.2025; 17(5): 596. CrossRef - Enhancing the Physical Properties of Calcium Silicate Cement Modified with Elastin-like Polypeptides and Bioactive Glass
Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(5): 188. CrossRef - Physicochemical properties and apatite precipitation behavior of experimental calcium silicate-based cements doped with phosphate compounds
Kenta Tsuchiya, Salvatore Sauro, Hidehiko Sano, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, Yu Toida, Rafiqul Islam, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Dental Materials.2025; 41(9): 1058. CrossRef - Microstructural Evaluation of the Mineralized Apical Barrier Induced by a Calcium Hydroxide Paste Containing Iodoform: A Case Report
Motoki Okamoto, Katsuaki Naito, Henry Fergus Duncan, Yoshifumi Kinomoto, Nanako Kuriki, Jiro Miura, Manabu Mizuhira, Maiko Suzuki, Mikako Hayashi
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 243. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Shear Bond Strength of Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement with ProRoot MTA and MTA Angelus
Siddharth Anand, Ravi Prakash, Nimish Tyagi, Chandrakar Chaman, Anjali Dhull, Himanshu Tomar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(1): 35. CrossRef - Analysis of the bond strength between conventional, putty or resin‐modified calcium silicate cement and bulk fill composites
İ Ipek, B Karaağaç Eskibağlar, Ş Yildiz, O Ataş, M Ünal
Australian Dental Journal.2023; 68(4): 265. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide and niobium pentoxide treatment effects before MTA placement
Kolli Sankeerthana, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 48. CrossRef - Effect of different chelating agents on the shear bond strength of calcium silicate‐based cements to coronal dentin
Mohamed Ahmed Elsayed, Md Sofiqul Islam, Karim Elbeltagy, Mohannad Nassar
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 426. CrossRef - Phosphoric acid treatment enhances adaptation of glass-ionomer cement to bioceramic sealer-conditioned dentin
Nandini Suresh, Sooriaprakas Chandrasekaran, M. C. V. Ashritha, Mohammed Abdul Raoufe, Aishwarya Vasudevan, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
Dental Research Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Surface Morphological Analysis and Evaluation of the Sealing Ability of a Nanoparticle-Incorporated Hydraulic Root-End Cement
Teena Sheethal Dsouza, Aditya Shetty
International Journal of Nanoscience.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Four Bioceramic Materials with Different Restorative Materials and Timings
Abeer S. Alqahtani, Ayman M. Sulimany, Abdullah S. Alayad, Abdulaziz S. Alqahtani, Omar A. Bawazir
Materials.2022; 15(13): 4668. CrossRef - Alkalizing Properties of Six Calcium-Silicate Endodontic Biomaterials
Katarzyna Kot, Łukasz Kucharski, Ewa Marek, Krzysztof Safranow, Mariusz Lipski
Materials.2022; 15(18): 6482. CrossRef - Physicochemical and biological properties of four calcium silicate-based endodontic cements
Seok Woo Chang, Alexis Gaudin, Mirek Tolar, Soram Oh, Su-Young Moon, Ove A. Peters
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1586. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of bioactive glass addition on the physical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate
Jei Kim, Hyun-Jung Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Biomaterials Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Different Pulp-Capping Materials against Enterococcus faecalis: An In vitro Study
Jenny Atom, Ningthoukhongjam Rati Devi, Ronel Lairenlakpam, Mohammed Hussain Dafer Al Wadei, Abdulrahim R. Hakami, Abdulkarim S. BinShaya
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S608. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Bioactivity of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Bioactive Endodontic Type Cements: A Systematic Review
Uma Dixit, Rucha Shivajirao Bhise Patil, Rupanshi Parekh
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(1): 30. CrossRef - A Silk Fibroin Based Hydration Accelerator for Root Canal Filling Materials
Ching-Shuan Huang, Sung-Chih Hsieh, Nai-Chia Teng, Wei-Fang Lee, Poonam Negi, Wendimi Fatimata Belem, Hsuan-Chen Wu, Jen-Chang Yang
Polymers.2020; 12(4): 994. CrossRef - Synthesis and characterization of novel calcium phosphate glass-derived cements for vital pulp therapy
Jerry Howard, Levi Gardner, Zahra Saifee, Aladdin Geleil, Isaac Nelson, John S. Colombo, Steven E. Naleway, Krista Carlson
Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of mineral trioxide aggregate on osteo/odontogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cells: a comprehensive and systematic literature review
Danial Babaki, Sanam Yaghoubi, Maryam M. Matin
Biomaterial Investigations in Dentistry.2020; 7(1): 175. CrossRef - APICAL MICROLEAKAGE OF VARIOUS BIOMATERIALS IN SIMULATED IMMATURE APICES
Fatih TULUMBACI, Volkan ARIKAN, Aylin AKBAY OBA, İşıl SÖNMEZ ŞAROĞLU
Selcuk Dental Journal.2019; 6(3): 247. CrossRef - Effects of the exposure site on histological pulpal responses after direct capping with 2 calcium-silicate based cements in a rat model
Panruethai Trongkij, Supachai Sutimuntanakul, Puangwan Lapthanasupkul, Chitpol Chaimanakarn, Rebecca Wong, Danuchit Banomyong
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Histopathological evaluation of periodontium after repairing furcation perforation with MTA and biodentine
Nehal Youssef Youssef Abdelati, Ibrahim Hassan Elkalla, Salwa Mohamed Awad, Hanaa Mahmoud Shalan
Pediatric Dental Journal.2018; 28(1): 33. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the antibacterial activity of two Biocompatible materials i.e. Biodentine and MTA when used as a direct pulp capping agent against streptococcus mutans and Enterococcus faecalis- An in vitro study
Aditi Subodh Jain, Asmita Singh Gupta, Rupika Agarwal
Endodontology.2018; 30(1): 66. CrossRef - Superfast Set, Strong and Less Degradable Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Cement
Abdullah Alqedairi, Carlos A. Muñoz-Viveros, Eugene A. Pantera, Marc Campillo-Funollet, Hussam Alfawaz, Ensanya Ali Abou Neel, Tariq S. Abuhaimed
International Journal of Dentistry.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of physicochemical properties of root-end filling materials using conventional and Micro-CT tests
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves TORRES, Roberta BOSSO-MARTELO, Camila Galletti ESPIR, Joni Augusto CIRELLI, Juliane Maria GUERREIRO-TANOMARU, Mario TANOMARU-FILHO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2017; 25(4): 374. CrossRef - Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 12. CrossRef - In vivo evaluation of the effects of hydraulic calcium silicate dental cements on plasma and liver aluminium levels in rats
Kadriye Demirkaya, Birsen Can Demirdöğen, Zeynep Öncel Torun, Onur Erdem, Serdar Çetinkaya, Cemal Akay
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2016; 124(1): 75. CrossRef - Healing of Large Periapical with Tricalcium Silicate-based Root End Filling Material
Snehal S Sonarkar, Rucheet Purba, Rajesh Podar
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2016; 1(2): 41. CrossRef - The Effect of Blood Contamination on the Chemical Characterization of Hydrated Mineral Trioxide Aggregates and Their Dentin-Interface: A Comparative Study
Sawsan T. Abu Zeid, Lubna A. Shafie, Abeer A. Mokeem Saleh, Monazah G. Khafagi
Spectroscopy Letters.2015; 48(9): 631. CrossRef - A review of the physical, chemical properties of MTA
Yong-Bum Cho
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2015; 42(1): 51. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials
Young-Eun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yeong-Joon Park, Nam-Eok Joo, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 89. CrossRef - Study on Biocompatibility and Mineralization Potential of Capseal
Kwang Shik Bae, Seok Woo Chang, Kee Yeon Kum, Woo Cheol Lee
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2014; 7(1): 1. CrossRef - Surface microhardness of three thicknesses of mineral trioxide aggregate in different setting conditions
Noushin Shokouhinejad, Leila Jafargholizadeh, Mehrfam Khoshkhounejad, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Maryam Raoof
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 253. CrossRef - Biodentine-a novel dentinal substitute for single visit apexification
Gurudutt Nayak, Mohammad Faiz Hasan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 120. CrossRef - Tooth Discoloration after the Use of New Pozzolan Cement (Endocem) and Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and the Effects of Internal Bleaching
Ji-Hyun Jang, Minji Kang, Soyeon Ahn, Soyeon Kim, Wooksung Kim, Yaelim Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1598. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength of MTA modified with hydration accelerators
Kaveh Oloomi, Eshaghali Saberi, Hadi Mokhtari, Hamid Reza Mokhtari Zonouzi, Ali Nosrat, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 128. CrossRef - Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 113. CrossRef - Washout resistance of fast-setting pozzolan cement under various root canal irrigants
Ga-Yeon Jang, Su-Jung Park, Seok-Mo Heo, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kwang-Won Lee, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 248. CrossRef - A preliminary report on histological outcome of pulpotomy with endodontic biomaterials vs calcium hydroxide
Ali Nosrat, Ali Peimani, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 227. CrossRef - Conservative approach of a symptomatic carious immature permanent tooth using a tricalcium silicate cement (Biodentine): a case report
Cyril Villat, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Dominique Seux, Pierre Farge
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 258. CrossRef
- Discoloration, radiopacity, and push-out bond strength of bismuth-based radiopacifiers in endodontic sealers
- 2,721 View
- 24 Download
- 44 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


