Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
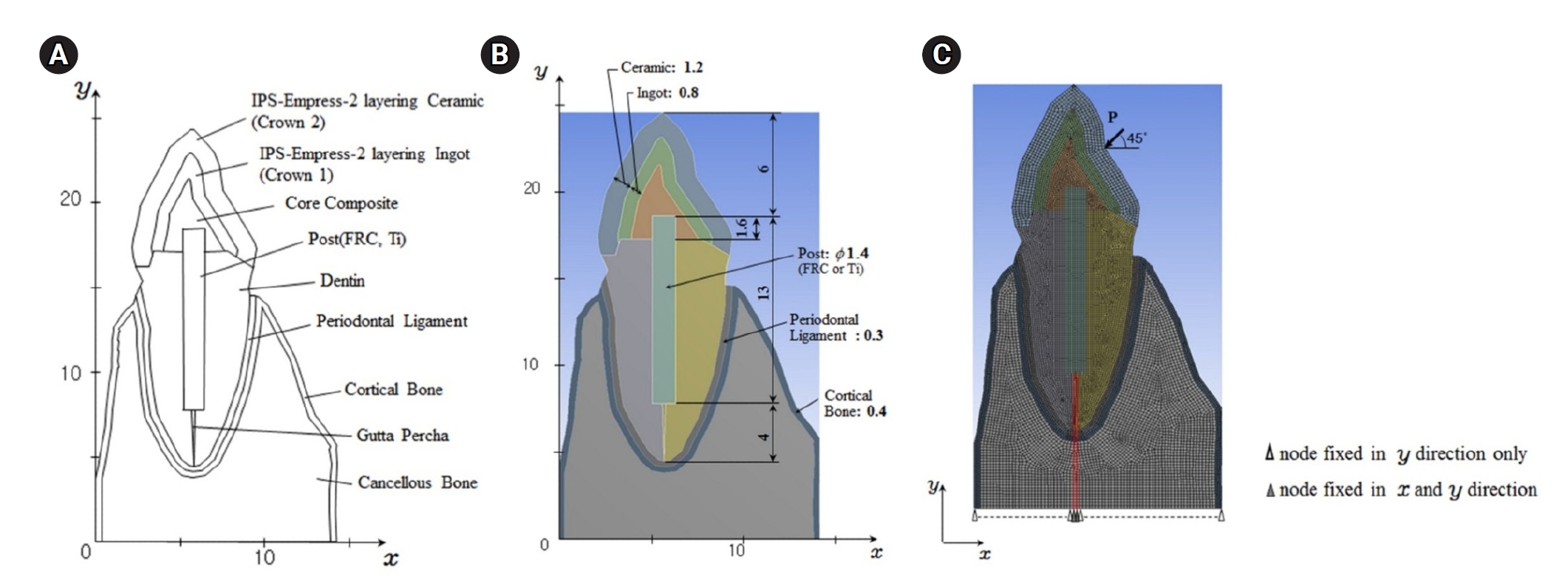
- Impact of post adhesion on stress distribution: an in silico study
- Kkot-Byeol Bae, Jae-Yoon Choi, Young-Tae Cho, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e19. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the stress distribution in teeth restored with different post materials and bonding conditions using finite element analysis (FEA).
Methods
A two-dimensional FEA model of a maxillary central incisor restored with IPS-Empress-2 crown (Ivoclar Vivadent), composite resin core, and posts were created. The model simulated bonded and non-bonded conditions for both fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) and titanium (Ti) posts. Stress distribution was analyzed using ANSYS 14.0 software under a 100-N load applied at a 45° angle to the long axis of the tooth.
Results
The results revealed that stress concentration was significantly higher in non-bonded posts compared to bonded ones. FRC posts exhibited stress values closer to those of dentin, whereas Ti posts demonstrated higher stress concentration, particularly in non-bonded states, increasing the potential risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
Conclusions
FRC posts, with elastic properties similar to dentin and proper adhesion, minimize stress concentration and potential damage to surrounding tissues. Conversely, materials with higher elastic modulus like Ti, can cause unfavorable stress concentrations if not properly bonded, emphasizing the importance of post adhesion in tooth restoration. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Ecofriendly and High-Strength Dental Composites: Structural and Functional Perspectives
Sayem A. Mulla, Amit Patil, Himmat Jaiswal, Bhavani Sangala Nagendra, Ashima Jakhar, Waseem Z. Khan
European Journal of General Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in Ecofriendly and High-Strength Dental Composites: Structural and Functional Perspectives
- 2,408 View
- 93 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Influence of post types and sizes on fracture resistance in the immature tooth model
- Jong-Hyun Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Jeong-Won Park, Il-Young Jung
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(4):257-266. Published online July 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.4.257
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of post types and sizes on fracture resistance in immature tooth model with various restorative techniques. Bovine incisors were sectioned 8 mm above and 12 mm below the cementoenamel junction to simulate immature tooth model. To compare various post-and-core restorations, canals were restored with gutta-percha and resin core, or reinforced dentin wall with dual-cured resin composite, followed by placement of D.T. LIGHT-POST, ParaPost XT, and various sizes of EverStick Post individually. All of specimens were stored in the distilled water for 72 hours and underwent 6,000 thermal cycles. After simulation of periodontal ligament structure with polyether impression material, compressive load was applied at 45 degrees to the long axis of the specimen until fracture was occurred.
Experimental groups reinforced with post and composite resin were shown significantly higher fracture strength than gutta-percha group without post placement (p < 0.05). Most specimens fractured limited to cervical third of roots. Post types did not influence on fracture resistance and fracture level significantly when cement space was filled with dual-cured resin composite. In addition, no statistically significant differences were seen between customized and standardized glass fiber posts, which cement spaces were filled with resin cement or composite resin individually. Therefore, root reinforcement procedures as above in immature teeth improved fracture resistance regardless of post types and sizes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Dental Posts used in Restoring Badly Broken Primary teeth
Tebra Alkayakh, Abdulrahim Aldarewesh
Libyan Journal of Medical Research.2024; 18(1): 65. CrossRef - An in vitro comparison of fracture resistance of immature teeth subjected to apexification using three different bioactive materials
Aarshati Vyas, Shilpa Shah, Nishtha K Patel, Krushnangi Yagnik, Vyoma Hirpara, Rajvi Shah
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 7(4): 172. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Fracture Resistance of Simulated Immature Teeth Reinforced with a Novel Anatomic Post and MTA or Biodentine as an Apical Barrier: An In Vitro Study
Shivani H Dholakia, Mrunalini J Vaidya
Journal of Operative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020; 4(2): 62. CrossRef - Rehabilitation of compromised permanent incisors with anatomically adjustable fiber post
Talat M. Beltagy
Tanta Dental Journal.2018; 15(1): 52. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of upper central incisors restored with different posts and cores
Maryam Rezaei Dastjerdi, Kamran Amirian Chaijan, Saeid Tavanafar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 229. CrossRef - Retentive strength of different intracanal posts in restorations of anterior primary teeth: anin vitrostudy
Mahtab Memarpour, Fereshteh Shafiei, Maryam Abbaszadeh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 215. CrossRef
- Effect of Dental Posts used in Restoring Badly Broken Primary teeth
- 1,519 View
- 5 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


