Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Buckling resistance, torque, and force generation during retreatment with D-RaCe, HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo retreatment files
- Yoojin Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e10. Published online February 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e10
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
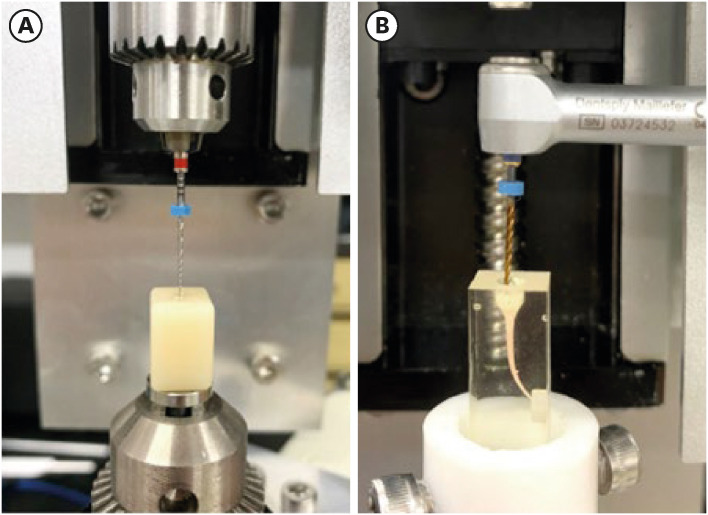
ePub Objectives This study compared the buckling resistance of 3 nickel-titanium (NiTi) retreatment file systems and the torque/force generated during retreatment.
Materials and Methods The buckling resistance was compared among the D-RaCe (DR2), HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo R25/05 retreatment systems. J-shaped canals within resin blocks were prepared with ProTaper NEXT X3 and obturated by the single-cone technique with AH Plus. After 4 weeks, 4 mm of gutta-percha in the coronal aspect was removed with Gates-Glidden drills. Retreatment was then performed using DR1 (size 30, 10% taper) followed by DR2 (size 25, 4% taper), HyFlex Remover (size 30, 7% taper), or Mtrwo R25/05 (size 25, 5% taper) (15 specimens in each group). Further apical preparation was performed with WaveOne Gold Primary. The clockwise torque and upward force generated during retreatment were recorded. After retreatment, resin blocks were examined using stereomicroscopy, and the percentage of residual filling material in the canal area was calculated. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance with the Tukey test.
Results The HyFlex Remover files exhibited the greatest buckling resistance (
p < 0.05), followed by the Mtwo R25/05. The HyFlex Remover and Mtwo R25/05 files generated the highest maximum clockwise torque and upward force, respectively (p < 0.05). The DR1 and DR2 files generated the least upward force and torque (p < 0.05). The percentage of residual filling material after retreatment was not significantly different between file systems (p > 0.05).Conclusions NiTi retreatment instruments with higher buckling resistance generated greater clockwise torque and upward force.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of three different retreatment files in removing root canal filling material: An In vitro confocal microscopy study
Meghna Sarah Abraham, Aravind R. Kudva, Prathap M. S. Nair, Shravan Kini, Samreena Kalander, Faseeh Muhammed Bin Farookh
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 136. CrossRef - Efficacy of Endodontic Files in Root Canal Retreatment: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Anna Soler-Doria, José Luis Sanz, Marcello Maddalone, Leopoldo Forner
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(8): 293. CrossRef - Postoperative Pain Following Single‐Visit Nonsurgical Retreatment Using Minimally Invasive Rotary vs. Reciprocating Nickel‐Titanium File Systems: A Two‐Arm Parallel Randomized Clinical Trial
Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, Büşra Pehlivan, Celalettin Topbaş, Abdurrahman Kerim Kul, Dursun Ali Şirin, Sivakumar Nuvvula
Pain Research and Management.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Canal Centering Ability of Single-file Retreatment System vs Multiple-file Retreatment System, with and without Gutta-Percha Solvent: An In Vitro Study
Sangkeetha Gnanasekaran, Arasappan Rajakumaran, Rajeswari Kalaiselvam, Mathan Rajan Rajendran, Seshan Rakkesh Ramesh, Manigandan Kuzhanchinathan
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(9): 898. CrossRef - Effect of Different Downward Loads and Rotational Speeds on the Removal of Gutta-Percha and Root Canal Sealer Using a Nickel-Titanium Rotary Gutta-Percha Removal System: An Ex Vivo Study
Koki Toyoda, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Satoshi Omori, Keiko Hirano, Arata Ebihara, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2025; 16(1): 446. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation and fracture resistance of endodontically retreated teeth using hyflex remover, Mtwo, and ProTaper retreatment file systems: An in vitro study
Isha Singh, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Pallavi Sharma, Kunal Bedi, Priyanka Rani, Swapnil Vats
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 56. CrossRef - Comparison of torsional, bending, and buckling resistances of different nickel-titanium glide path files
Feyyaz Çeliker, İrem Çetinkaya
Matéria (Rio de Janeiro).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the impact of obturation techniques, kinematics and irrigation protocols on apical debris extrusion and time required in endodontic retreatment
Eugenio Pedullà, Francesco Iacono, Martina Pitrolo, Giovanni Barbagallo, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Chiara Pirani
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(3): 623. CrossRef
- Comparative evaluation of the efficacy of three different retreatment files in removing root canal filling material: An In vitro confocal microscopy study
- 2,625 View
- 53 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref

- Cyclic fatigue resistance, torsional resistance, and metallurgical characteristics of M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold NiTi files
- Eugenio Pedullà, Fabio Lo Savio, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Gabriele Miccoli, Elena Bruno, Silvia Rapisarda, Seok Woo Chang, Ernesto Rapisarda, Guido La Rosa, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e25. Published online April 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the mechanical properties and metallurgical characteristics of the M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (United Dental).
Materials and Methods One hundred and sixty new M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (sizes 20/0.04 and 25/0.04) were used. Torque and angle of rotation at failure (
n = 20) were measured according to ISO 3630-1. Cyclic fatigue resistance was tested by measuring the number of cycles to failure in an artificial stainless steel canal (60° angle of curvature and a 5-mm radius). The metallurgical characteristics were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and the Student-Newman-Keuls test.Results Comparing the same size of the 2 different instruments, cyclic fatigue resistance was significantly higher in the M3 Pro Gold files than in the M3 Rotary files (
p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed between the files in the maximum torque load, while a significantly higher angular rotation to fracture was observed for M3 Pro Gold (p < 0.05). In the DSC analysis, the M3 Pro Gold files showed one prominent peak on the heating curve and 2 prominent peaks on the cooling curve. In contrast, the M3 Rotary files showed 1 small peak on the heating curve and 1 small peak on the cooling curve.Conclusions The M3 Pro Gold files showed greater flexibility and angular rotation than the M3 Rotary files, without decrement of their torque resistance. The superior flexibility of M3 Pro Gold files can be attributed to their martensite phase.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
Reyhaneh Shoorgashti, Marzie Jafari, Mohadeseh Alimohammadi, Niloofar Ebrahimi
Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health Studies.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in Niti and Glide Path Rotary System: Preparation of Canal Centering and Transportation in Double-curved Root Canals
Calvin Reinnaldi, Wiena Widyastuti, Taufiq Ariwibowo, Sri Ratna Laksmiastuti
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Cleaning Efficacy of Neolix and M3 Immatural Rotary Files in Comparison with Hand Files in Primary Molar Root Canals
Shabnam Maleki, Effat Khodadadi, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Elham Mahmoudi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(2): 88. CrossRef - Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Instrumentation Time Among ProTaper Next, Neoniti, and M3‐Pro Gold Rotary Systems: An In Vitro Study
Robab Farhang, Bita Alizadeh, Saeedeh Galledar, Sara Noorolouny, Rashin Alyali, Bahareh Pouya, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Elango Natarajan
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Continuous Rotation and Optimal Torque Reverse Kinematics on the Cyclic Fatigue Strength of Endodontic NiTi Clockwise Cutting Rotary Instruments
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Marco A. Versiani
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 317. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of WaveOne Gold in Reciprocation, ProGlider in Rotary Motion, and Manual Files in a Reciprocating Handpiece Within Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Shivangi M Pujara, Hardik B Shah, Leena H Jobanputra
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The extended finite element method in endodontics: A scoping review and future directions for cyclic fatigue testing of nickel–titanium instruments
Philip Yuan‐Ho Chien, Laurence James Walsh, Ove Andreas Peters
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Characterization of the file‐specific heat‐treated ProTaper Ultimate rotary system
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Duarte Marques, Natasha Ajuz, Mário Rito Pereira, Rui Pereira da Costa, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(4): 530. CrossRef - Influence of different heat treatments and temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments with the same design
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Maria Laura Leotta, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Eugenio Pedullà
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(4): 1793. CrossRef - Analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next rotary instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Andjelkovic-Apostolovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Radomir Barac, Marija Nikolic, Marko Igic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(3): 109. CrossRef - What Meaningful Information Are the Instruments Mechanical Testing Giving Us? A Comprehensive Review
Jorge N.R. Martins, Rui F. Martins, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(8): 985. CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Four different Contemporary NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files by Metallurgical and Mechanical Analysis with Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectrophotometry with FE-SEM and Cyclic Fatigue Resistance Evaluation
Akash Azad, Shraddha Chokshi
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2022; 14(1): 21. CrossRef - Impact of Peracetic Acid on the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Endodontic Instrument
Suhad Jabbar Hamed Al-Nasrawi, Zuha Ayad Jaber, Nibrass Talib Al-Quraine, Abtesam Imhemed Aljdaimi, Sattar Jabbar Abdul-Zahra Al-Hmedat, Saleh Zidan, Julfikar Haider, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Influence of shaft length on torsional behavior of endodontic nickel–titanium instruments
Gianluca Gambarini, Marco Seracchiani, Alessio Zanza, Gabriele Miccoli, Andrea Del Giudice, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 568. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments according to the Angle of File Access and Radius of Root Canal
Eugenio Pedullà, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Chiara Virgillito, Ernesto Rapisarda, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Luigi Generali
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 431. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on torsional resistance and surface roughness of nickel‐titanium instruments
E. J. N. L. Silva, J. F. N. Giraldes, C. O. de Lima, V. T. L. Vieira, C. N. Elias, H. S. Antunes
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1645. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
- 1,933 View
- 22 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Antifungal effects of synthetic human β-defensin 3-C15 peptide
- Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Christine Kim, Jong-Won Kum, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yu Gu, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seok Woo Chang, Seung Hyun Han, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):91-97. Published online March 17, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.91
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this
ex vivo study was to compare the antifungal activity of a synthetic peptide consisting of 15 amino acids at the C-terminus of human β-defensin 3 (HBD3-C15) with calcium hydroxide (CH) and Nystatin (Nys) againstCandida albicans (C. albicans ) biofilm.Materials and Methods C. albicans were grown on cover glass bottom dishes or human dentin disks for 48 hr, and then treated with HBD3-C15 (0, 12.5, 25, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 300 µg/mL), CH (100 µg/mL), and Nys (20 µg/mL) for 7 days at 37℃. On cover glass, live and dead cells in the biomass were measured by the FilmTracer Biofilm viability assay, and observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM). On dentin, normal, diminished and ruptured cells were observed by field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM). The results were subjected to a two-tailedt -test, a one way analysis variance and apost hoc test at a significance level ofp = 0.05.Results C. albicans survival on dentin was inhibited by HBD3-C15 in a dose-dependent manner. There were fewer aggregations ofC. albicans in the groups of Nys and HBD3-C15 (≥ 100 µg/mL). CLSM showedC. albicans survival was reduced by HBD3-C15 in a dose dependent manner. Nys and HBD3-C15 (≥ 100 µg/mL) showed significant fungicidal activity compared to CH group (p < 0.05).Conclusions Synthetic HBD3-C15 peptide (≥ 100 µg/mL) and Nys exhibited significantly higher antifungal activity than CH against
C. albicans by inhibiting cell survival and biofilm.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anti-fungal peptides: an emerging category with enthralling therapeutic prospects in the treatment of candidiasis
Jyoti Sankar Prusty, Ashwini Kumar, Awanish Kumar
Critical Reviews in Microbiology.2025; 51(5): 755. CrossRef - Current status of antimicrobial peptides databases and computational tools for optimization
Madhulika Jha, Akash Nautiyal, Kumud Pant, Navin Kumar
Environment Conservation Journal.2025; 26(1): 281. CrossRef - Harnessing antimicrobial peptides in endodontics
Xinzi Kong, Vijetha Vishwanath, Prasanna Neelakantan, Zhou Ye
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(7): 815. CrossRef - Human β-defensins and their synthetic analogs: Natural defenders and prospective new drugs of oral health
Mumian Chen, Zihe Hu, Jue Shi, Zhijian Xie
Life Sciences.2024; 346: 122591. CrossRef - Candida albicans Virulence Factors and Pathogenicity for Endodontic Infections
Yeon-Jee Yoo, A Reum Kim, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Seung Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
Microorganisms.2020; 8(9): 1300. CrossRef - Innate Inspiration: Antifungal Peptides and Other Immunotherapeutics From the Host Immune Response
Derry K. Mercer, Deborah A. O'Neil
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Human salivary proteins and their peptidomimetics: Values of function, early diagnosis, and therapeutic potential in combating dental caries
Kun Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Wei Li, Linglin Zhang
Archives of Oral Biology.2019; 99: 31. CrossRef - Endodontic biofilms: contemporary and future treatment options
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Soram Oh, A-Reum Kim, Seung-Hyun Han, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Bioactive Peptides Against Fungal Biofilms
Karen G. N. Oshiro, Gisele Rodrigues, Bruna Estéfani D. Monges, Marlon Henrique Cardoso, Octávio Luiz Franco
Frontiers in Microbiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Anticandidal Potential of Stem Bark Extract from Schima superba and the Identification of Its Major Anticandidal Compound
Chun Wu, Hong-Tan Wu, Qing Wang, Guey-Horng Wang, Xue Yi, Yu-Pei Chen, Guang-Xiong Zhou
Molecules.2019; 24(8): 1587. CrossRef - Synthetic Human β Defensin-3-C15 Peptide in Endodontics: Potential Therapeutic Agent in Streptococcus gordonii Lipoprotein-Stimulated Human Dental Pulp-Derived Cells
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Jue-Yeon Lee, Soram Oh, Yu Gu, A-Reum Kim, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 21(1): 71. CrossRef - Candida Infections and Therapeutic Strategies: Mechanisms of Action for Traditional and Alternative Agents
Giselle C. de Oliveira Santos, Cleydlenne C. Vasconcelos, Alberto J. O. Lopes, Maria do S. de Sousa Cartágenes, Allan K. D. B. Filho, Flávia R. F. do Nascimento, Ricardo M. Ramos, Emygdia R. R. B. Pires, Marcelo S. de Andrade, Flaviane M. G. Rocha, Cristi
Frontiers in Microbiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Perspectives for clinical use of engineered human host defense antimicrobial peptides
María Eugenia Pachón-Ibáñez, Younes Smani, Jerónimo Pachón, Javier Sánchez-Céspedes
FEMS Microbiology Reviews.2017; 41(3): 323. CrossRef - The synthetic human beta-defensin-3 C15 peptide exhibits antimicrobial activity against Streptococcus mutans, both alone and in combination with dental disinfectants
Ki Bum Ahn, A. Reum Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2017; 55(10): 830. CrossRef - Antibiofilm peptides against oral biofilms
Zhejun Wang, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo
Journal of Oral Microbiology.2017; 9(1): 1327308. CrossRef - Humanβ-Defensin 3 Reduces TNF-α-Induced Inflammation and Monocyte Adhesion in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
Tianying Bian, Houxuan Li, Qian Zhou, Can Ni, Yangheng Zhang, Fuhua Yan
Mediators of Inflammation.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Antifungal Effects of Synthetic Human Beta-defensin-3-C15 Peptide on Candida albicans –infected Root Dentin
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Ikyung Kwon, So-Ram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Yoon Lee, Seung-Hyun Han, Seok-Woo Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1857. CrossRef - A 15-amino acid C-terminal peptide of beta-defensin-3 inhibits bone resorption by inhibiting the osteoclast differentiation and disrupting podosome belt formation
Ok-Jin Park, Jiseon Kim, Ki Bum Ahn, Jue Yeon Lee, Yoon-Jeong Park, Kee-Yeon Kum, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Molecular Medicine.2017; 95(12): 1315. CrossRef
- Anti-fungal peptides: an emerging category with enthralling therapeutic prospects in the treatment of candidiasis
- 1,761 View
- 5 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Effect of acidic solutions on the microhardness of dentin and set OrthoMTA and their cytotoxicity on murine macrophage
- Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yoon Lee, Jae-Won Kum, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Sang-Min Lim, Seok Woo Chang, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(1):12-21. Published online December 1, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.1.12

-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effects of three acids on the microhardness of set mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) and root dentin, and cytotoxicity on murine macrophage.
Materials and Methods OrthoMTA (BioMTA) was mixed and packed into the human root dentin blocks of 1.5 mm diameter and 5 mm height. Four groups, each of ten roots, were exposed to 10% citric acid (CA), 5% glycolic acid (GA), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and saline for five minutes after setting of the OrthoMTA. Vickers surface microhardness of set MTA and dentin was measured before and after exposure to solutions, and compared between groups using one-way ANOVA with Tukey test. The microhardness value of each group was analyzed using student
t test. Acid-treated OrthoMTA and dentin was examined by scanning electron microscope (SEM). Cell viability of tested solutions was assessed using WST-8 assay and murine macrophage.Results Three test solutions reduced microhardness of dentin. 17% EDTA demonstrated severe dentinal erosion, significantly reduced the dentinal microhardness compared to 10% CA (
p = 0.034) or 5% GA (p = 0.006). 10% CA or 5% GA significantly reduced the surface microhardness of set MTA compared to 17% EDTA and saline (p < 0.001). Acid-treated OrthoMTA demonstrated microporous structure with destruction of globular crystal. EDTA exhibited significantly more cellular toxicity than the other acidic solutions at diluted concentrations (0.2, 0.5, 1.0%).Conclusions Tested acidic solutions reduced microhardness of root dentin. Five minute's application of 10% CA and 5% GA significantly reduced the microhardness of set OrthoMTA with lower cellular cytotoxicity compared to 17% EDTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
Mohammed A. Hussein, Rasha H. Jehad
Journal of Medical and Oral Biosciences.2025; : 36. CrossRef - Impact of calcium hydroxide and 2-hydroxyisocaproic acid on the microhardness of root dentine: an in vitro study
Nandini T. Niranjan, Protim Ghosh Dastidar, Raghavendra Penukonda, Galvin Sim Siang Lin, Roopa Babannavar, Arun Jaysheel, Harshada Pattar
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 711. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Effect of Chitosan-Based Irrigation Solutions on the Bond Strength of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate to Bulk-Fill Composite
Arzu Şahin Mantı, Bağdagül Helvacıoğlu Kıvanç
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2024; 15(12): 370. CrossRef - Effect of Various Acid Solutions as an Aid in Removing the OrthoMTA-Based Root Canal Filling
Naveen Chhabra, Abhishek Parolia
Materials.2023; 16(13): 4535. CrossRef - Effect of Glycolic Acid, Maleic Acid, and EDTA in the Removal of Smear Layer from Root Canal Dentin
Tarini Mullick, Nidambur Vasudev Ballal
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the effect of various chelating agents on the microhardness of root canal dentin: An in vitro study
Mineet Kaul, Zinnie Nanda, Kranthikumar Reddy, Rahul Deore, Divya Mandlecha, Esha Jaiswal
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 234. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide and niobium pentoxide treatment effects before MTA placement
Kolli Sankeerthana, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(1): 48. CrossRef - Calcium silicate and calcium aluminate cements for dentistry reviewed
Carolyn Primus, James L. Gutmann, Franklin R. Tay, Anna B. Fuks
Journal of the American Ceramic Society.2022; 105(3): 1841. CrossRef - Influence of Acidic Environmental Conditions on Push‐Out Bonding Strength of Four Calcium Silicate‐Based Materials to Root Dentin
Beliz Özel, Raif Erişen, Boonlert Kukiattrakoon
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on the microhardness of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and TotalFill Bioceramic Putty
Jacklyn H.R. Chu, Kalie Y. Chia, Alexander L. Qui, Alex Moule, William N. Ha
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(1): 33. CrossRef - Pre-application of dentin bonding agent prevents discoloration caused by mineral trioxide aggregate
Yoo-Lim Choi, Young-Eun Jang, Bom Sahn Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Yemi Kim
BMC Oral Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycolic acid as the final irrigant in endodontics: Mechanical and cytotoxic effects
Yuri Dal Bello, Hisadora Fracaro Porsch, Ana Paula Farina, Matheus Albino Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Ana Karina Bedran-Russo, Doglas Cecchin
Materials Science and Engineering: C.2019; 100: 323. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-electrolyte drinks exhibit risks for human enamel surface loss
Mary Anne Sampaio de Melo, Vanara Florêncio Passos, Juliana Paiva Marques Lima, Sérgio Lima Santiago, Lidiany Karla Azevedo Rodrigues
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 246. CrossRef
- Removal Efficiency of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate: A narrative Review of Retrieval Techniques
- 2,647 View
- 17 Download
- 13 Crossref

- The effect of MTAD as a final root canal irrigants on the coronal bacterial leakage of obturated root canals
- Tae Woo Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Dong Sung Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(4):397-404. Published online July 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.4.397
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of MTAD, EDTA and sodium hypochlorite(NaOCl) as final irrigants on coronal leakage resistance to
Enterococcus faecalis . Forty extracted human maxillary molars were used in this experiment. The teeth were randomly divided into positive control group (Group 1; n = 5), negative control group (Group 2; n = 5) and three experimental groups (n = 30). In Group 3 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite. In Group 4 (n = 10) and 5 (n = 10), the root canals were irrigated with sodium hypochlorite and rinsed with EDTA and MTAD, respectively. The teeth in each group were cleaned and shaped to #40 profile with .04 taper, and obturated with gutta-percha and AH-26 root canal sealer. The coronal portion of each tooth was placed in contact with inoculum ofEnterococcus faecalis in Brain Heart Infusion (BHI) culture media. Each root tip was placed in a vial containing sterile culture media. The vials were placed in anaerobic chamber and observed everyday for turbidity for 180 days. Statistical analysis was performed using Fisher's Exact Test. After 180 days, Group 3, 4, and 5 showed 7, 4 and 5 leaking samples respectively. The differences in leakage resistance were not statistically significant among Group 3, 4 and 5.
- 2,033 View
- 6 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


