Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of dentin surface preparations on bonding of self-etching adhesives under simulated pulpal pressure
- Chantima Siriporananon, Pisol Senawongse, Vanthana Sattabanasuk, Natchalee Srimaneekarn, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e4. Published online December 28, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
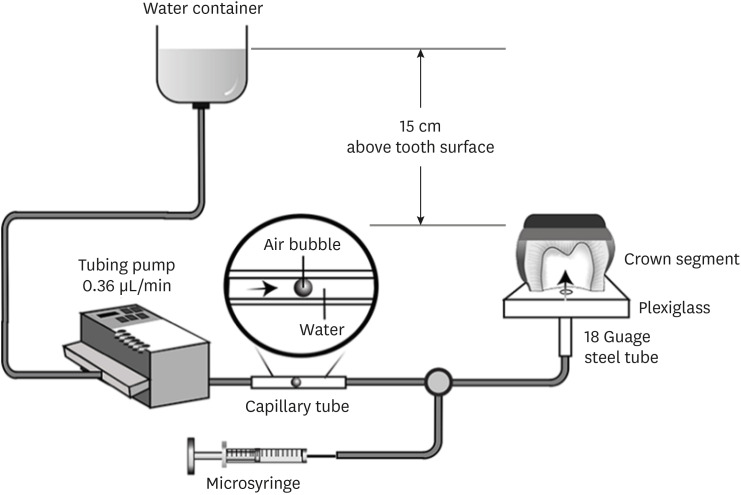
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of different smear layer preparations on the dentin permeability and microtensile bond strength (µTBS) of 2 self-etching adhesives (Clearfil SE Bond [CSE] and Clearfil Tri-S Bond Universal [CTS]) under dynamic pulpal pressure.
Materials and Methods Human third molars were cut into crown segments. The dentin surfaces were prepared using 4 armamentaria: 600-grit SiC paper, coarse diamond burs, superfine diamond burs, and carbide burs. The pulp chamber of each crown segment was connected to a dynamic intra-pulpal pressure simulation apparatus, and the permeability test was done under a pressure of 15 cmH2O. The relative permeability (%P) was evaluated on the smear layer-covered and bonded dentin surfaces. The teeth were bonded to either of the adhesives under pulpal pressure simulation, and cut into sticks after 24 hours water storage for the µTBS test. The resin-dentin interface and nanoleakage observations were performed using a scanning electron microscope. Statistical comparisons were done using analysis of variance and
post hoc tests.Results Only the method of surface preparation had a significant effect on permeability (
p < 0.05). The smear layers created by the carbide and superfine diamond burs yielded the lowest permeability. CSE demonstrated a higher µTBS, with these values in the superfine diamond and carbide bur groups being the highest. Microscopic evaluation of the resin-dentin interface revealed nanoleakage in the coarse diamond bur and SiC paper groups for both adhesives.Conclusions Superfine diamond and carbide burs can be recommended for dentin preparation with the use of 2-step CSE.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
Chavakorn Atsavathavornset, Pipop Saikaew, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Hidehiko Sano
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Universal adhesive systems in dentistry: A narrative review
Svetlana N. Razumova, Anzhela S. Brago, Oxana R. Ruda, Zoya A. Guryeva, Elvira V. Adzhieva
Russian Journal of Dentistry.2024; 28(5): 512. CrossRef - Delayed light activation of resin composite affects the bond strength of adhesives under dynamic simulated pulpal pressure
Nattaporn Sukprasert, Choltacha Harnirattisai, Pisol Senawongse, Hidehiko Sano, Pipop Saikaew
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(11): 6743. CrossRef
- The effect of different adhesive strategies and diamond burs on dentin bond strength of universal resin cements
- 3,106 View
- 48 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The effects of total-etch, wet-bonding, and light-curing of adhesive on the apical seal of a resin-based root canal filling system
- Won-Il Ryu, Won-Jun Shon, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Han Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):385-396. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of adhesion variables such as the priming concepts of canal wall and the curing modes of adhesives on the sealing ability of a resin-based root canal filling system.
Materials and Methods Apical microleakage of the Resilon-RealSeal systems filled with 3 different combinations of adhesion variables was compared with the conventional gutta-percha filling using a dye penetration method. Experimental groups were SEDC, Resilon (Resilon Research LLC) filling with self-etch RealSeal (SybronEndo) primer and dual-cure RealSeal sealer; NELC, Resilon filling with no etching, Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (3M ESPE) primer application and light-curing adhesive; and TELC, Resilon filling with Scotchbond Multi-Purpose primer and adhesive used under total etch / wet bonding and light-cure protocols. GPCS, gutta-percha filling with conventional AH26 plus sealer, was the control group.
Results The median longitudinal dye penetration length of TELC was significantly shorter than those of GPCS and SEDC (Kruskal-Wallis test,
p < 0.05). In the cross-sectional microleakage scores, TELC showed significant differences from other groups at 2 to 5 mm from the apical foramen (Kruskal-Wallis test,p < 0.05).Conclusions When a resin-based root canal filling material was used, compared to the self-etching primer and the dual-cure sealer, the total etch/wet-bonding with primer and light-curing of adhesive showed improved apical sealing and was highly recommended.
- 1,282 View
- 1 Download

- Influence of application methods of one-step self-etching adhesives on microtensile bond strength
- Chul-Kyu Choi, Sung-Ae Son, Jin-Hee Ha, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Yong-Hun Kwon, Jeong-Kil Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):203-210. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.203
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of various application methods of one-step self-etch adhesives to microtensile resin-dentin bond strength.
Materials and Methods Thirty-six extracted human molars were used. The teeth were assigned randomly to twelve groups (
n = 15), according to the three different adhesive systems (Clearfil Tri-S Bond, Adper Prompt L-Pop, G-Bond) and application methods. The adhesive systems were applied on the dentin as follows: 1) The single coating, 2) The double coating, 3) Manual agitation, 4) Ultrasonic agitation. Following the adhesive application, light-cure composite resin was constructed. The restored teeth were stored in distilled water at room temperature for 24 hours, and prepared 15 specimens per groups. Then microtensile bond strength was measured and the failure mode was examined.Results Manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating and double coating did. Double coating of adhesive significantly increased the microtensile bond strength than single coating did and there was no significant difference between the manual agitation and ultrasonic agitation group. There was significant difference in microtensile bonding strength among all adhesives and Clearfil Tri-S Bond showed the highest bond strength.
Conclusions In one-step self-etching adhesives, there was significant difference according to application methods and type of adhesives. No matter of the material, the manual or ultrasonic agitation of the adhesive showed significantly higher microtensile bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
Nuray Zulkadir Ergin, Aslı Seçilmiş
Süleyman Demirel Üniversitesi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2025; 16(3): 356. CrossRef - The Classification and Selection of Adhesive Agents; an Overview for the General Dentist
Naji Ziad Arandi
Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry.2023; Volume 15: 165. CrossRef
- Effect of Baicalein on Bond Strength of Indirect Ceramic Restoration
- 2,039 View
- 13 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


