Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cytotoxicity of two self-adhesive resin cements and their interference in the phagocytic activity of murine macrophages
- Danilo Couto da Silva, Leonardo Gomes Vaz, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares, Leda Quercia Vieira, Ricardo Reis de Oliveira, Antônio Paulino Ribeiro Sobrinho
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e31. Published online July 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
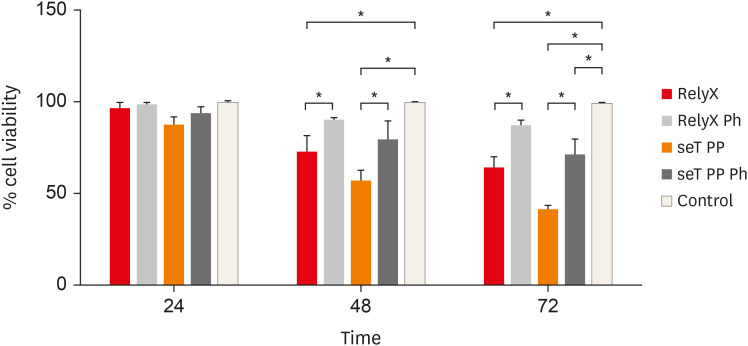
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate
in vitro the effects of the self-adhesive resin cements RelyX U200 (3M ESPE) and seT PP (SDI Limited) on murine macrophages and the interference of the photoactivation.Materials and Methods Cell viability assays, cell adherence, yeast phagocytosis of
Saccharomyces boulardii and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) were performed in the presence of capillaries containing the respective self-adhesive cement when photoactivated or not.Results After long periods of contact, both types of cements, when not photoactivated, are more cytotoxic for macrophages. The seT PP cement when only chemically activated seems to interfere more negatively in the process of phagocytosis of yeasts
S. boulardii. Both types of cements interfere in the cell adhesion process, independent of photoactivation. None of the types of cements tested was able to induce the production of ROS.Conclusions Our results highlight the great importance of the photoactivation of self-adhesive resin cements in the dental clinic, since RelyX U200, when photoactivated, presented the best results within the evaluated parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Preheating Self-Adhesive Cements on the Degree of Conversion, Cell Migration, and Cell Viability
Henrique Cantarelli, Fernando Antonio Costa Xavier, Fernando Freitas Portella, Keiichi Hosaka, Eduardo Galia Reston, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Celso Afonso Klein-Junior
Applied Mechanics.2024; 5(3): 553. CrossRef - Dental Luting Cements: An Updated Comprehensive Review
Artak Heboyan, Anna Vardanyan, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Tatevik Avagyan, Hamid Tebyaniyan, Mohammed Mustafa, Dinesh Rokaya, Anna Avetisyan
Molecules.2023; 28(4): 1619. CrossRef
- Influence of Preheating Self-Adhesive Cements on the Degree of Conversion, Cell Migration, and Cell Viability
- 1,979 View
- 21 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


