Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The clinical success of ART restorations and Hall technique in primary molars: a randomized 18-month follow-up study
- Esra Oz, Zuhal Kırzıoglu, Canan Kale
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e19. Published online May 1, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
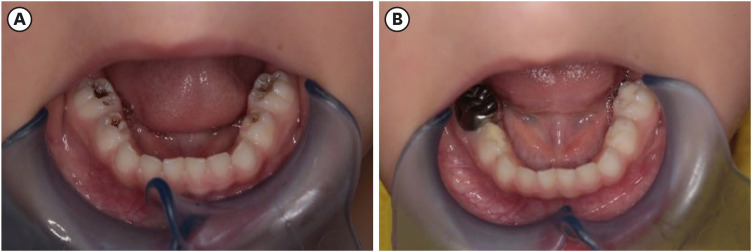
ePub Objectives The aim of the study was to evaluate the clinical and radiographic success of the Hall technique (HT) and atraumatic restorative treatment (ART) restorations using high-viscosity glass-ionomer cement for the management of occlusal carious lesions in primary molars.
Materials and Methods This randomized clinical study observed 40 children (aged 5–6 years). For each child, one tooth was treated with HT and one with ART. The primary outcome measures for HT restorations were successful, minor, and major failure rates. Clinical evaluations of ART restorations were performed according to the modified United States Public Health Service criteria during 18-month follow-up. McNemar test was used for statistical analysis.
Results Thirty of 40 (75%) participants returned for 18 months of follow-up. In the clinical evaluations of teeth that were treated with HT, the patients did not have complaints of pain or other symptoms, all crowns remained in the oral cavity, the gums were healthy, and the teeth were functional in all evaluations. At the end of the 18-month follow-up, the surface texture and marginal integrity criteria of ART restorations were recorded as 26.7% and 33.3%, respectively. In the radiographic evaluation of 30 patients treated with ART and HT, all restorations were considered successful.
Conclusions The 18-month clinical and radiographic results after treatments applied to single-surface cavities in anxious children showed that both treatment methods were successful.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Two-year outcomes of hall technique and modified hall technique in deep carious lesions of primary molars: a randomized clinical trial
Sumeyye Konukman Turker, Ayse Isil Cihan
BMC Oral Health.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Success rate of Hall Technique for restoring carious primary molars - systematic review and meta-analysis
Tamara Kerber Tedesco, Nicola Patricia Innes, Claudia Lopez Gallegos, Gabriela Seabra Silva, Thais Gimenez, Mariana Minatel Braga, Mariana Pinheiro Araujo, Jayakumar Jayaraman, Waraf Al-yaseen, Daniela Prócida Raggio
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(1): 65. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Dental Restorative Materials in the Atraumatic Treatment of Carious Primary Teeth in Pediatric Dentistry: A Systematic Review
Gianna Dipalma, Angelo Michele Inchingolo, Lucia Casamassima, Paola Nardelli, Danilo Ciccarese, Paolo De Sena, Francesco Inchingolo, Andrea Palermo, Marco Severino, Cinzia Maria Norma Maspero, Alessio Danilo Inchingolo
Children.2025; 12(4): 511. CrossRef - Clinical, radiographic, and microhardness evaluation of caries in primary molars managed with modified Hall technique
Eman El Sayed El Bedewy, Nahed A.A. Abohamila, Shereen A. M. Ali, Shimaa M.M. Hadwa
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(1): 133. CrossRef - Pain Perception During Minimally Invasive Caries Removal in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial Comparing Chemo-Mechanical Caries Removal
Dhirja Goel, Neha Awasthi, Yanina Singh, Sukhdeep Singh, Nenung Yirang
Journal of International Society of Preventive and Community Dentistry.2025; 15(4): 348. CrossRef - Clinical and histological evaluation of hall technique with and without silver diamine fluoride in the treatment of carious primary molars
Marwa M.A.Z. Abd-Elhaleium, Fatma A.-A. El-Hendawy, Lamis A. El-Ghareb, Sara Y. AboAli
Tanta Dental Journal.2025; 22(2): 351. CrossRef - Comparative success of minimally invasive treatments for cavitated caries in primary teeth: a network meta-analysis
Rasoul Sahebalam, Mahsa Ghorbani, Alireza Sarraf Shirazi, Motahareh Khosrojerdi, Mana Mowji
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Two-year outcomes of hall technique and modified hall technique in deep carious lesions of primary molars: a randomized clinical trial
- 6,514 View
- 115 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Chair-side CAD/CAM fabrication of a single-retainer resin bonded fixed dental prosthesis: a case report
- Carlos Alberto Jurado, Akimasa Tsujimoto, Hidehiko Watanabe, Jose Villalobos-Tinoco, Jorge Luis Garaicoa, Mark David Markham, Wayne Walter Barkmeier, Mark Andrew Latta
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e15. Published online February 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
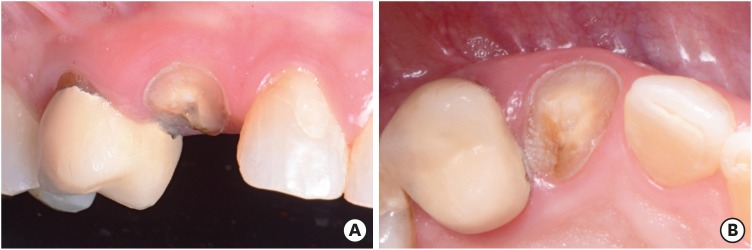
ePub This clinical report describes designing and fabricating a single-retainer resin-bonded fixed dental prosthesis with a chair-side computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacturing system. The whole procedure, from tooth extraction to final placement of the prosthesis, was completed in one day, and a single clinic visit. No clinical complications were found at the 2-year follow-up after placement of the restoration, and satisfactory functional and esthetic results were achieved.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Using the foundation restoration as a blueprint: An uncomplicated approach to retrofitting crowns to existing removable partial dentures using CAD-CAM technology
Jae-Hoon Lee, Juliana Pfeffer, Carlos A. Jurado, Francisco X. Azpiazu-Flores
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(6): 1416. CrossRef - Fracture load of chairside CAD‐CAM veneers fabricated with pre‐and fully crystalized lithium disilicate ceramics
Carlos A. Jurado, Jacquelyn S. Yeh, Cristina M. P. Vidal, Seok‐Hwan Cho, Salahaldeen Abuhammoud
Journal of Prosthodontics.2025; 34(4): 429. CrossRef - Clinical Efficacy of Anterior Ceramic Materials in Resin-Bonded Fixed Dental Prostheses with Different Bridge Designs—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Nutsongsak Panyasuksri, Pattarika Angkasith, Apichai Yavirach, Pisaisit Chaijareenont, Surasak Saokaew, Sukrit Kanchanasurakit
Prosthesis.2025; 7(2): 41. CrossRef - Full Zirconia Resin‐Bonded Fixed Dental Prosthesis: A Clinical Report
Majda Lemrichi, Amal El Yamani
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimizing Hard and Soft‐Tissue Esthetics With Anterior Cantilever Zirconia Ceramic Resin‐Bonded Fixed Dental Prostheses
Markus B. Blatz, Tony Rotondo, Szabi Hant, Lea S. Prott
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Thickness on Light Transmission for Pre- and Fully Crystallized Chairside CAD/CAM Lithium Disilicate Ceramics
Franciele Floriani, Salahaldeen Abuhammoud, Silvia Rojas-Rueda, Amit Unnadkat, Nicholas G. Fischer, Chin-Chuan Fu, Carlos A. Jurado
Materials.2024; 17(9): 2045. CrossRef - Microstructural and flexural strength of various CAD‐CAM lithium disilicate ceramics
Joissi Ferrari Zaniboni, Amanda Soares Silva, Aryvelto Miranda Silva, João Felipe Besegato, Oscar Fernando Muñoz‐Chávez, Edson Alves de Campos
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture resistance of zirconia surveyed crowns with four different occlusal rest seat designs
Carlos Alberto Jurado, Akram Sayed Ahmed, Nathaniel C. Lawson, Francisco X. Azpiazu‐Flores, Conley Green, Seok‐Hwan Cho
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(5): 484. CrossRef - Effect of incisal preparation design on the fracture strength of monolithic zirconia‐reinforced lithium silicate laminate veneers
Carlos A. Jurado, Ramtin Sadid‐Zadeh, Hidehiko Watanabe, Craig E. Robbins, Kelvin I. Afrashtehfar, Nicholas G. Fischer, Damian J. Lee
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(3): 281. CrossRef - Fracture resistance of CAD/CAM provisional crowns with two different designs: an in vitro study
Salwa Mekled, Mark Iskander, Belinda Rodriguez, Paige Hodges, Jasleen Bhogal, Joan Adechoubou, Geraldine Weinstein
Exploration of Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Glazing and Polishing Systems for Novel Chairside CAD/CAM Lithium Disilicate and Virgilite Crowns
CA Jurado, K Arndt, FX Azpiazu-Flores, F Faddoul, R França, NG Fischer, H Watanabe
Operative Dentistry.2023; 48(6): 689. CrossRef - Traditional versus conservative endodontic access impact on fracture resistance of chairside CAD‐CAM lithium disilicate anterior crowns: An in vitro study
Carlos A. Jurado, Clarisa Amarillas‐Gastelum, Bruna Santos Honório Tonin, Gentry Nielson, Kelvin I. Afrashtehfar, Nicholas G. Fischer
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(8): 728. CrossRef - Digital Full-Mouth Reconstruction Assisted by Facial and Intraoral Scanners: A Case Report and Technique Description
Jorge Garaicoa, Carlos A. Jurado, Kelvin I. Afrashtehfar, Abdulaziz Alhotan, Nicholas G. Fischer
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(3): 1917. CrossRef - Students’ perception of digital waxing software for dental anatomy education
Amira Elgreatly, Ahmed Mahrous, Wendy A. Clark, Ingeborg J. De Kok, Fang Qian, Akimasa Tsujimoto
Journal of Oral Science.2022; 64(2): 178. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Different Polishing Kits for Chairside CAD/CAM Provisional Restorative Materials
CA Jurado, WW Barkmeier, A Alshabib, SS Alresayes, C-C Fu, EC Teixeira, AG Baruth, A Tsujimoto
Operative Dentistry.2022; 47(6): 670. CrossRef - Fatigue bond strength of dental adhesive systems: Historical background of test methodology, clinical considerations and future perspectives
Akimasa Tsujimoto, Wayne W. Barkmeier, Erica C. Teixeira, Toshiki Takamizawa, Masashi Miyazaki, Mark A. Latta
Japanese Dental Science Review.2022; 58: 193. CrossRef - Diagnostic Mock-Up as a Surgical Reduction Guide for Crown Lengthening: Technique Description and Case Report
Carlos A. Jurado, Venkata Parachuru, Jose Villalobos Tinoco, Gerardo Guzman-Perez, Akimasa Tsujimoto, Ramya Javvadi, Kelvin I. Afrashtehfar
Medicina.2022; 58(10): 1360. CrossRef - Color stability of fully- and pre-crystalized chair-side CAD-CAM lithium disilicate restorations after required and additional sintering processes
Carlos Alberto Jurado, Tamer El-Gendy, Jared Hyer, Akimasa Tsujimoto
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2022; 14(1): 56. CrossRef - Comparison of Fracture Resistance for Chairside CAD/CAM Lithium Disilicate Crowns and Overlays with Different Designs
Carlos Alberto Jurado, Zinaida Kaleinikova, Akimasa Tsujimoto, Daniel Alberto Cortés Treviño, Robert R. Seghi, Damian J. Lee
Journal of Prosthodontics.2022; 31(4): 341. CrossRef - Light Transmission for a Novel Chairside CAD/CAM Lithium Disilicate Ceramic
Carlos A Jurado, Akimasa Tsujimoto, Clarisa Amarillas-Gastelum, Saad Alresayes, Kennedee French, Hamid Nurrohman
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2022; 22(12): 1365. CrossRef - Intraoral Scanning with Rubber Dam Isolation in Place for Fabrication of a Chairside Computer-assisted Design and Computer-assisted Manufacture Ceramic Restoration
Rachel Lederman, Jeffrey Cohen, Akimasa Tsujimoto
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(8): 943. CrossRef
- Using the foundation restoration as a blueprint: An uncomplicated approach to retrofitting crowns to existing removable partial dentures using CAD-CAM technology
- 2,094 View
- 26 Download
- 21 Crossref

- Three dimensional reconstruction of teeth using x-ray microtomography
- Dong-Hoon Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2003;28(6):485-490. Published online November 30, 2003
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2003.28.6.485
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Complete understanding of the exterior and interior structure of the tooth would be prerequisite to the successful clinical results, especially in the restorative and endodontic treatment.
Although three-dimensional reconstruction method using x-ray microtomography could not be used in clinical cases, it may be the best way to reconstruct the morphologic characteristics of the tooth structure in detail without destructing the tooth itself. This study was done to three dimensionally reconstruct every teeth in the arch in order to increase the understanding about the endodontic treatment and to promote the effective restorative treatment by upgrading the knowledge of the tooth morphology.
After placing tooth between the microfocus x-ray tube and the image intensifier to obtain two-dimensional images of each level, scanning was done under the condition of 80 keV, 100 µA, 16.8 magnification with the spot size of 8 µm. Cross-section pixel size of 16.28 µm and 48.83 cross-section to cross-section distance were also used.
From the results of this study, precise three dimensional reconstructed images of every teeth could be obtained. Furthermore, it was possible to see image that showed interested area only, for example, enamel portion only, pulp and dentin area without enamel structure, pulp only, combination image of enamel and pulp, etc.
It was also possible to see transparent image without some part of tooth structure. This image might be used as a guide when restoring and preparing the full and partial crown by showing the positional and morphological relationship between the pulp and the outer tooth structure.
Another profit may be related with the fact that it would promote the understanding of the interior structure by making observation of the auto-rotating image of .AVI file from the various direction possible.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fracture Flow of Radionuclides in Unsaturated Conditions at LILW Disposal Facility
Won-Seok Kim, Jungjin Kim, Jinmo Ahn, Seongsik Nam, Wooyong Um
Journal of Korean Society of Environmental Engineers.2015; 37(8): 465. CrossRef
- Fracture Flow of Radionuclides in Unsaturated Conditions at LILW Disposal Facility
- 1,061 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


