Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Determination of optimal horizontal beam angulations for canal separation in mandibular molars using cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective image-based analysis
- Benedikt Schneider, Tamina Tepe, Daniel Rapp, Wilhelm Frank, Maria Lessani, Constantin von See, Sebastian Fitzek, Jörg Philipp Tchorz
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e9. Published online February 26, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e9
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
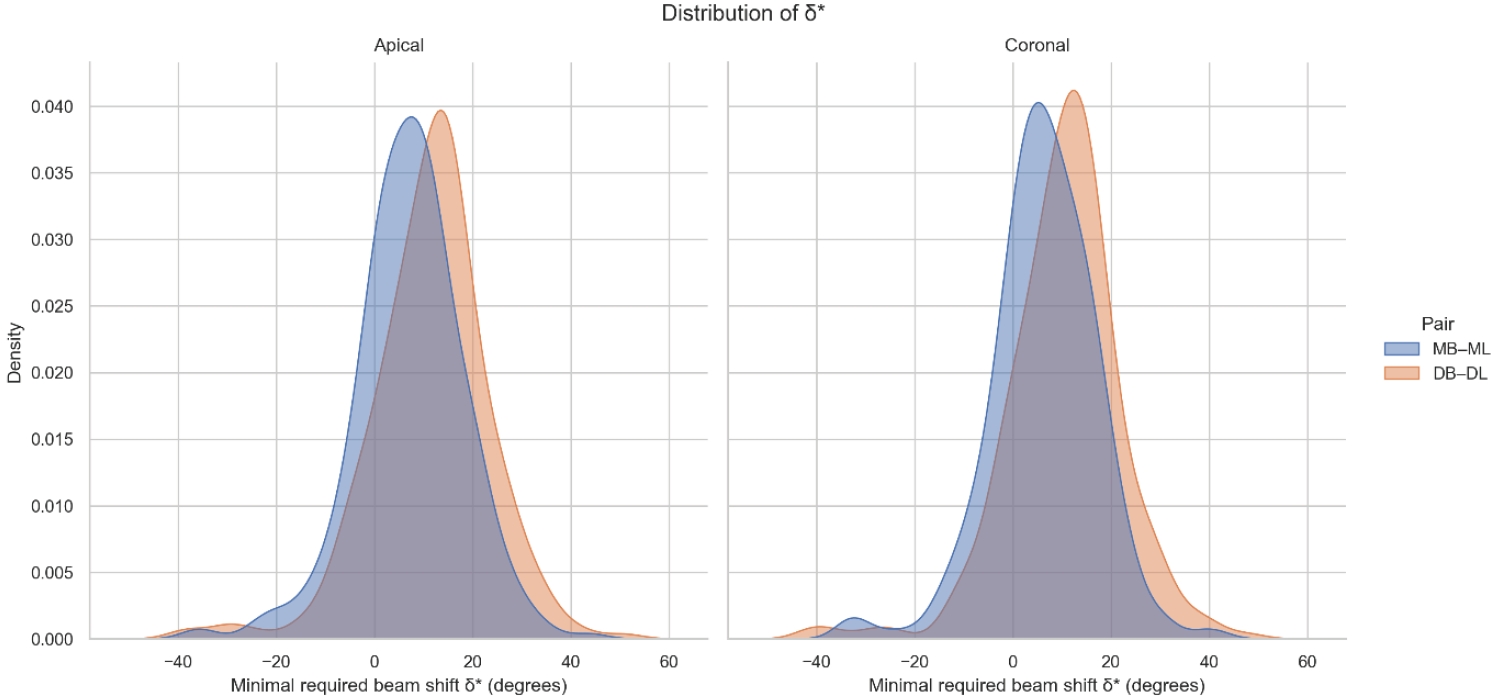
Two-dimensional intraoral radiographs often obscure canals due to superimposition, especially in mandibular molars with complex anatomy. This cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) study identified the horizontal beam angles at which first and second molar canals overlap and derived clinically applicable angulations for enhanced canal separation.
Methods
Eighty-five CBCT datasets from 100 patients met the inclusion criteria, yielding 318 mandibular molars (160 first, 158 second). Using ImageJ, absolute horizontal overlap angles (α) were measured to determine the corresponding theoretical separation angles defined as δ* = 90° – α. Separability was modeled across horizontal beam angulation increments from −45° to +45° in five steps, and Wilson’s 95% confidence intervals were computed. Group comparisons used the Mann-Whitney U and independent t-tests (p ≤ 0.05)
Results
Minimal mesial beam angulations for effective canal separability (δ* = 90° − α) ranged from approximately 7° to 15° for mesial roots and approximately 10° to 13° for distal roots. No significant mesial differences were observed between first and second molars (p > 0.30). Distal roots of second molars exhibited significantly higher angulations (p = 0.003 coronal, p < 0.001 apical). Mesial canals achieved ≥95% separability at approximately 25° and ≥99% at approximately 35°; distal canals required approximately 30° and approximately 40°.
Conclusions
A mesial beam angulation of 30° to 35° provides probable canal differentiation in mandibular molars, separating mesial canals in ≥99% and distal canals in ≥95% of cases. This range refines previous recommendations and supports the as low as reasonably achievable (ALARA) principle.
- 443 View
- 16 Download

- Which factors related to apical radiolucency may influence its radiographic detection? A study using CBCT as reference standard
- Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Eduarda Helena Leandro Nascimento, Hugo Gaêta-Araujo, Laís Oliveira de Araujo Cardelli, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e43. Published online July 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e43
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
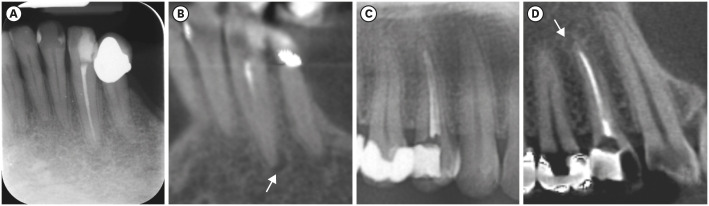
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the detection rate of apical radiolucencies in 2-dimensional images using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) as the reference standard, and to determine which factors related to the apical radiolucencies and the teeth could influence its detection.
Materials and Methods The sample consisted of exams of patients who had panoramic (PAN) and/or periapical (PERI) radiography and CBCT. The exams were assessed by 2 oral radiologists and divided into PAN+CBCT (227 teeth–285 roots) and PERI+CBCT (94 teeth–115 roots). Radiographic images were evaluated for the presence of apical radiolucency, while CBCT images were assessed for presence, size, location, and involvement of the cortical bone (thinning, expansion, and destruction). Diagnostic values were obtained for PERI and PAN.
Results PERI and PAN presented high accuracy (0.83 and 0.77, respectively) and specificity (0.89 and 0.91, respectively), but low sensitivity, especially for PAN (0.40 vs. 0.65 of PERI). The size of the apical radiolucency was positively correlated with its detection in PERI and PAN (
p < 0.001). For PAN, apical radiolucencies were 3.93 times more frequently detected when related to single-rooted teeth (p = 0.038). The other factors did not influence apical radiolucency detection (p > 0.05).Conclusions PERI presents slightly better accuracy than PAN for the detection of apical radiolucency. The size is the only factor related to radiolucency that influences its detection, for both radiographic exams. For PAN, apical radiolucency is most often detected in single-rooted teeth.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Radiomics-based classification of pediatric dental trauma in periapical radiographs: a preliminary study
Mengtian Peng, Bin Yu, Juan Hu, Xiaoxin Xie, Jihong He
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Increasing Diagnostic Acumen in Endodontics
Shilpa Thakkar, Dana Mominkhan
Dental Clinics of North America.2025; 69(4): 479. CrossRef - Three-dimensional clinical assessment for MRONJ risk in oncologic patients following tooth extractions
Catalina Moreno Rabie, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Nicolly Oliveira Santos, Fernanda Nogueira Reis, Tim Van den Wyngaert, Reinhilde Jacobs
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quality of techniques used to assess clinical outcomes of regenerative endodontic treatment in necrotic mature teeth
Roy George
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2022; 23(3): 98. CrossRef
- Radiomics-based classification of pediatric dental trauma in periapical radiographs: a preliminary study
- 2,974 View
- 21 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
- Shashirekha Govind, Amit Jena, Satabdi Pattanaik, Mahaprasad Anarasi, Satyajit Mohapatra, Vinay Shivagange
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e33. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
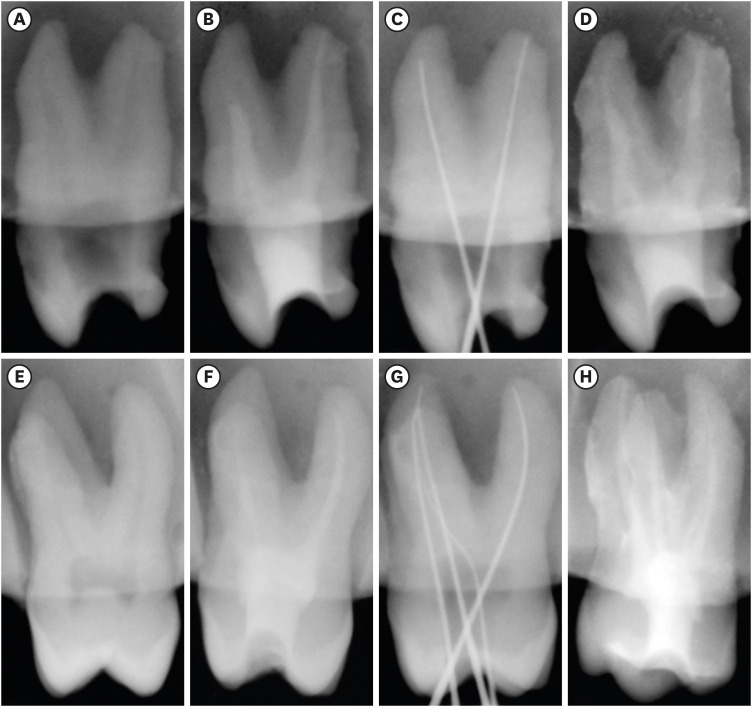
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of ionic and non-ionic-based contrast media (
in vitro study) and the combinatorial effect of chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution (CERS) (in vivo study) for visualization of the root canal anatomy.Materials and Methods In vitr o study (120 teeth): The root canal of maxillary premolars and molars (in vitro group 1 and 2 respectively,n = 60 each) were analyzed using 4 different contrast media (subgroups: Omnipaque 350, Iopamidol, Xenetix 350, and Urografin 76;n = 15 each) in combination with 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Based on the results of thein vitro study,in vivo study (80 teeth) was done to compare Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl with CERS (in vivo group 1 and 2 respectively,n = 40 each) on maxillary and mandibular premolars and molars. Two endodontists used radiovisiography to assess the depth of ingress and identify the aberrant root anatomy after access cavity preparation, and after initial cleaning and shaping of canals. Kruskal-Wallis test was used forin vitro comparison (p < 0.05), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Mann-WhitneyU test forin vivo analysis (p < 0.01).Results In vitro study, Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl facilitated a significant higher visualization (p < 0.05). Forin vivo study, CERS had a statistically significant depth of ingress (p < 0.01), and was efficient in identifying the aberrant root canal anatomy of premolars and molars.Conclusions CERS facilitates better visualization of the root canal anatomy of human premolars and molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Improving Endodontic Radiograph Interpretation with TV-CLAHE for Enhanced Root Canal Detection
Barbara Obuchowicz, Joanna Zarzecka, Michał Strzelecki, Marzena Jakubowska, Rafał Obuchowicz, Adam Piórkowski, Elżbieta Zarzecka-Francica, Julia Lasek
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(15): 5554. CrossRef - Efficacy of sonic and ultrasonic activation on irrigant penetration in different tapered preparations: An in vitro study
M. Rama Sowmya, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Pradeep Solete, Sahil Choudhari, S Delphine Priscilla Antony, Mohammed Mustafa
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 370. CrossRef - Analysis of the value of visualized root canal technique in the clinical treatment of endodontics
Nana SUN, Nannan WANG, Xin QIAN
Panminerva Medica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
- 1,793 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- Detection of root perforations using conventional and digital intraoral radiography, multidetector computed tomography and cone beam computed tomography
- Abbas Shokri, Amir Eskandarloo, Maruf Noruzi-Gangachin, Samira Khajeh
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):58-67. Published online November 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.58
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the accuracy of conventional intraoral (CI) radiography, photostimulable phosphor (PSP) radiography, cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) and multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) for detection of strip and root perforations in endodontically treated teeth.
Materials and Methods Mesial and distal roots of 72 recently extracted molar were endodontically prepared. Perforations were created in 0.2, 0.3, or 0.4 mm diameter around the furcation of 48 roots (strip perforation) and at the external surface of 48 roots (root perforation); 48 roots were not perforated (control group). After root obturation, intraoral radiography, CBCT and MDCT were taken. Discontinuity in the root structure was interpreted as perforation. Two observers examined the images. Data were analyzed using Stata software and Chi-square test.
Results The sensitivity and specificity of CI, PSP, CBCT and MDCT in detection of strip perforations were 81.25% and 93.75%, 85.42% and 91.67%, 97.92% and 85.42%, and 72.92% and 87.50%, respectively. For diagnosis of root perforation, the sensitivity and specificity were 87.50% and 93.75%, 89.58% and 91.67%, 97.92% and 85.42%, and 81.25% and 87.50%, respectively. For detection of strip perforation, the difference between CBCT and all other methods including CI, PSP and MDCT was significant (
p < 0.05). For detection of root perforation, only the difference between CBCT and MDCT was significant, and for all the other methods no statistically significant difference was observed.Conclusions If it is not possible to diagnose the root perforations by periapical radiographs, CBCT is the best radiographic technique while MDCT is not recommended.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationship between radiographic measurements of alveolar bone in posterior single-tooth edentulous regions and non-alveolar jawbones using multidetector computed tomography
Imad Barngkgei, Leen Khattash, Samar Kakhia
Oral Radiology.2025; 41(1): 10. CrossRef - Prevention, Diagnostic Challenges, and Management of Endodontic Perforations: A Narrative Review
Taylor M. DeVine, Nora L. Paisner, Adeyinka F. Dayo
Complications.2025; 2(3): 17. CrossRef - Extrusion of debris during retreatment using various nickel-titanium files in teeth with simulated lateral root perforation
Hatice Harorlı, Simay Koç, Alper Kuştarcı
Journal of Oral Science.2024; 66(3): 189. CrossRef - The importance of cone-beam computed tomography in endodontic therapy: A review
Shaul Hameed Kolarkodi
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(7): 780. CrossRef - Assessment of the diagnostic accuracy of strip and furcal perforations in different sizes by cone beam computed tomography
Zahra Ghoncheh, Hanieh Kaviani, Sara Soleimani, Shifteh Nasri, Fatemeh Malekpour, Farzaneh Afkhami
Oral Radiology.2023; 39(4): 654. CrossRef - Konik Işınlı Bilgisayarlı Tomografinin Endodontik Uygulamalarda Kullanımı
Gülsün AKAY, Kahraman GÜNGÖR
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2022; 11(1): 8. CrossRef - CBCT Visualization of Furcation Perforation Repair Materials Using Different Voxel Sizes
Ayse Isıl ORHAN, Pelin TUFENKCİ, Aysenur ONCU, Sevinc SEVGI, Berkan CELİKTEN, Kaan ORHAN
Clinical and Experimental Health Sciences.2021; 11(4): 654. CrossRef - Accuracy of Conventional Periapical Radiography in Diagnosing Furcation Repair after Perforation Treatment
Stephanie Díaz Huamán, Maria Gerusa Brito Aragão, Ana Paula Dias Moreno, Alexandra Mussolino de Queiroz, Raquel Assed Bezerra da Silva, Francisco Wanderley Garcia de Paula-Silva, Léa Assed Bezerra da Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 827. CrossRef - Association between marginal bone loss and bone quality at dental implant sites based on evidence from cone beam computed tomography and periapical radiographs
Amir Eskandarloo, Reza Arabi, Mohsen Bidgoli, Faezeh Yousefi, Jalal Poorolajal
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(1): 36. CrossRef - Effect of exposure parameters of cone beam computed tomography on metal artifact reduction around the dental implants in various bone densities
Abbas Shokri, Mohammad Reza Jamalpour, Atefeh Khavid, Zeinab Mohseni, Masoud Sadeghi
BMC Medical Imaging.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhancing the three-dimensional visualization of a foreign object using Mimics software
Muhammad Khan Asif, Phrabhakaran Nambiar, Iqra Muhammad Khan, Zeti Adura Binti Che Ab Aziz, Nora Sakina Binti Mohd Noor, Palasuntharam Shanmuhasuntharam, Norliza Ibrahim
Radiology Case Reports.2019; 14(12): 1545. CrossRef - Diagnostic Accuracy of Three Cone Beam Computed Tomography Systems and Periapical Radiography for Detection of Fenestration Around Dental Implants
Amir Eskandarloo, Samira Saati, Mahbubeh Purabdolahi Ardakani, Mohamadreza Jamalpour, Naser Mohammad Gholi Mezerji, Vahid Akheshteh
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2018; 9(3): 376. CrossRef - Evidence-based decision-making in endodontics
Eyal Rosen, Igor Tsesis
Clinical Dentistry Reviewed.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence of pulp sensibility loss of anterior teeth after paramedian insertion of orthodontic mini-implants in the anterior maxilla
Jan Hourfar, Dirk Bister, Jörg A. Lisson, Björn Ludwig
Head & Face Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Image analysis for dental bone quality assessment using CBCT imaging
Suprijanto, L Epsilawati, M S Hajarini, E Juliastuti, H Susanti
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2016; 694: 012065. CrossRef - Identification of the Procedural Accidents During Root Canal Preparation Using Digital Intraoral Radiography and Cone Beam Computed Tomography
K.-Ivácson A.- Csinszka, Monea Adriana Maria, Monea Monica, Pop Mihai, Borda Angela
Acta Medica Marisiensis.2016; 62(3): 326. CrossRef
- The relationship between radiographic measurements of alveolar bone in posterior single-tooth edentulous regions and non-alveolar jawbones using multidetector computed tomography
- 2,293 View
- 11 Download
- 16 Crossref

- The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
- Wook-Jin Seong, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Soocheol Jeong, Youngcheul Heo, Woo-Bin Song, Mansur Ahmad
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):146-153. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Aluminum step wedge (ASW) equivalent radiodensity (eRD) has been used to quantify restorative material's radiodensity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of image acquisition control (IAC) of a digital X-ray system on the radiodensity quantification under different exposure time settings.
Materials and Methods Three 1-mm thick restorative material samples with various opacities were prepared. Samples were radiographed alongside an ASW using one of three digital radiographic modes (linear mapping (L), nonlinear mapping (N), and nonlinear mapping and automatic exposure control activated (E)) under 3 exposure time settings (underexposure, normal-exposure, and overexposure). The ASW eRD of restorative materials, attenuation coefficients and contrasts of ASW, and the correlation coefficient of linear relationship between logarithms of gray-scale value and thicknesses of ASW were compared under 9 conditions.
Results The ASW eRD measurements of restorative materials by three digital radiographic modes were statistically different (
p = 0.049) but clinically similar. The relationship between logarithms of background corrected grey scale value and thickness of ASW was highly linear but attenuation coefficients and contrasts varied significantly among 3 radiographic modes. Varying exposure times did not affect ASW eRD significantly.Conclusions Even though different digital radiographic modes induced large variation on attenuation of coefficient and contrast of ASW, E mode improved diagnostic quality of the image significantly under the under-exposure condition by improving contrasts, while maintaining ASW eRDs of restorative materials similar. Under the condition of this study, underexposure time may be acceptable clinically with digital X-ray system using automatic gain control that reduces radiation exposure for patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is the radiopacity of CAD/CAM aesthetic materials sufficient?
Rua S. Babaier, Modi S. Aldeeb, Nick Silikas, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2022; 38(6): 1072. CrossRef
- Is the radiopacity of CAD/CAM aesthetic materials sufficient?
- 1,663 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The reduction methods of operator's radiation dose for portable dental X-ray machines
- Jeong-Yeon Cho, Won-Jeong Han
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):160-164. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.160
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was aimed to investigate the methods to reduce operator's radiation dose when taking intraoral radiographs with portable dental X-ray machines.
Materials and Methods Two kinds of portable dental X-ray machines (DX3000, Dexcowin and Rextar, Posdion) were used. Operator's radiation dose was measured with an 1,800 cc ionization chamber (RadCal Corp.) at the hand level of X-ray tubehead and at the operator's chest and waist levels with and without the backscatter shield. The operator's radiation dose at the hand level was measured with and without lead gloves and with long and short cones.
Results The backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the hand level of X-ray tubehead to 23 - 32%, the lead gloves to 26 - 31%, and long cone to 48 - 52%. And the backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the operator's chest and waist levels to 0.1 - 37%.
Conclusions When portable dental X-ray systems are used, it is recommended to select X-ray machine attached with a backscatter shield and a long cone and to wear the lead gloves.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the Occupational Radiation Dose from a Handheld Portable X-ray Unit During Full-mouth Intraoral Dental Radiographs in the Dog and the Cat – A Pilot Study
Lenin A. Villamizar-Martinez, Jeannie Losey
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2024; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - Seguridad y protección radiológica con el uso de rayos X portátiles. Revisión de literatura
Francisco Javier Marichi-Rodríguez, Janeth Serrano-Bello, Marine Ortiz-Magdaleno, Febe Carolina Vázquez-Vázquez
Revista Odontológica Mexicana Órgano Oficial de la Facultad de Odontología UNAM.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Operator and Patient Doses after Irradiation with Handheld X-ray Devices
Ali Altındağ, Hakan Eren, Kaan Orhan, Sebahat Görgün
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(18): 10414. CrossRef - Hand-held dental X-ray device: Attention to correct use
Guilherme Ceschia Martins, Thaíza Gonçalves Rocha, Thaís de Lima Azeredo, Andréa de Castro Domingos, Maria Augusta Visconti, Eduardo Murad Villoria
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2023; 53(3): 265. CrossRef - Effect of cranium structure on dose distribution during intraoral radiography
Takeru Ishii, Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Atsuharu Nitanda, Akihiro Ochiai, Shinji Kito, Hirofumi Aboshi, Hideki Saka
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2022; 64(1): 131. CrossRef - Application of the Monte Carlo Method for the Evaluation of Scattered Radiation Dose Due to the Use of Handheld X-Ray in Dentistry
A Cc Gonzales, M R Soares, W O G Batista, A R Cardeña, J P Marquez, J R Vega
Radiation Protection Dosimetry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ASSESSMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL RADIATION DOSE FROM CAMERA MODEL INTRAORAL HANDHELD X-RAY DEVICE WITHOUT STRAY RADIATION PROTECTION SHIELD
Mahkameh Moshfeghi, Yaser Safi, Alireza Afzalan, Mitra Ghazizadeh Ahsaie
Radiation Protection Dosimetry.2022; 198(1-2): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of radiation exposure to operators of portable hand-held dental X-ray units
Justin Leadbeatter, Jennifer Diffey
Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine.2021; 44(2): 377. CrossRef - Comparison of air dose and operator exposure from portable X-ray units
Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Ruri Asami, Takeru Ishii, Shinji Kito, Yuichi Tamatsu, Hirofumi Aboshi, Hideki Saka
Legal Medicine.2020; 47: 101787. CrossRef - Dental research using intraoral techniques with portable digital radiography adapted for fieldwork in Qubbet el-Hawa (Egypt)
Sandra López-Lázaro, Violeta C. Yendreka, Alejandro Jiménez-Serrano, José Alba-Gómez, Gabriel M. Fonseca
Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of stray radiation to the operator for five hand-held dental X-ray devices
Richard Smith, Richard Tremblay, Graeme M Wardlaw
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2019; 48(5): 20180301. CrossRef - Assessment of image quality and exposure parameters of an intraoral portable X-rays device
Elton G Zenóbio, Madelon AF Zenóbio, Carolina DB Azevedo, Maria do Socorro Nogueira, Cláudio D Almeida, Flávio R Manzi
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2019; 48(3): 20180329. CrossRef - The study of protection of operators and surrounding workers at the time of using portable intraoral X-ray unit
Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Ruri Asami, Tomonori Ozawa, Maki Izawa, Hideki Saka
Legal Medicine.2018; 33: 66. CrossRef - The effects of device position on the operator's radiation dose when using a handheld portable X-ray device
Jimmy Makdissi, Ravikiran R Pawar, Ben Johnson, Bun S Chong
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2016; 45(3): 20150245. CrossRef - Patient and staff dosimetry during radiographic procedures in an intensive care unit
Rosario Fernández, Miguel Moreno-Torres, Antonia M Contreras, María I Núñez, Damián Guirado, Luis Peñas
Journal of Radiological Protection.2015; 35(3): 727. CrossRef - The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
Wook-Jin Seong, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Soocheol Jeong, Youngcheul Heo, Woo-Bin Song, Mansur Ahmad
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 146. CrossRef
- Assessment of the Occupational Radiation Dose from a Handheld Portable X-ray Unit During Full-mouth Intraoral Dental Radiographs in the Dog and the Cat – A Pilot Study
- 5,687 View
- 33 Download
- 16 Crossref

- The efficacy of chemo-mechanical removal of dentin carious lesion
- Soon-Bin Lim, Kyung-Kyu Choi, Sang-Jin Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(3):149-157. Published online May 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.3.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Mechanical removals in decayed teeth have been performed using drill and sharp hand instruments. These methods have some disadvantages such as pain, local anesthesia and overextended cavities. Therefore chemo-mechanical excavation of dentin carious lesions has been introduced. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the efficacy of traditional mechanical methods using burs and chemo-mechanical methods (Carisolv) of caries dentin.
Mechanical caries removal was carried with low speed round bur. Chemo-mechanical caries excavation was performed with Carisolv (Medi-team), using the Carisolv hand instruments. The mean time to remove caries with two different methods was evaluated and the data analyzed with SPSS software (ver 11.5) by t-test (p < 0.05). For histomorphometry of caries removal were also carried with mechanical or chemo-mechanical (Carisolv) methods from 20 extracted caries permanent molars. Complete caries removal was verified with a #23 sharp explorers, Caries Detector (Kuraray Co. Japan), and standard apical radiography.
1. Chemo-mechanical method was taken more times than mechanical method (1.5 fold) (p < 0.05).
2. Excavation for caries took more time for molar lesion than premolar lesion, and the least time was taken to remove the caries in incisor lesion (p < 0.05).
3. There were no significant differences to remove the caries between the maxilla and mandible (p > 0.05).
4. The remaining carious dentin was detected after the chemo-mechanical removal of the carious dentin, and no smear layer were seen after the mechanical and chemo-mechanical removal of the carious dentin.
- 843 View
- 2 Download

-
In vivo quantitative analysis of remineralization effect of remineralization solution "R" of incipient enamel dental caries - Myung-Eun Kim, Il-young Jung, Kee-Yeon Kum, Chang-young Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(2):175-182. Published online March 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.2.175
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Dental caries is a chronic disease that causes the destruction of tooth structure by the interaction of plaque bacteria, food debris, and saliva.
There has been attempts to induce remineralization by supersaturating the intra-oral environment around the surface enamel, where there is incipient caries.
In this study, supersaturated remineralized solution "R" was applied to specimens with incipient enamel caries, and the quantitative ananlysis of remineralization was evaluated using microradiography. Thirty subjects volunteered to participate in this study. Removable appliances were constructed for the subjects, and the enamel specimen with incipient caries were embedded in the appliances. The subjects wore the intra-oral appliance for 15 days except while eating and sleeping.
The removable appliance were soaked in supersaturated solution "R", saline, or Senstime® to expose the specimen to those solutions three times a day, 5 minutes each time. After 15 days, microradiography was retaken to compare and evaluate remineralization.
The results were as the following:
1. The ratio of remineralized area to demineralized area was significantly higher in the supersaturated solution "R" and Senstime® than in the saline. (p<0.05)
2. Remineralization in the supersaturated buffer solution "R" occurred in the significantly deeper parts of the tooth, compared to the Senstime® group containing high concentration of fluoride.(p<0.05)
As in the above results, the remineralization effect of remineralized buffer solution "R" on incipient enamel caries has been proven. For clinical utilization, further studies on soft tissue reaction and the effect on dentin and cementum are necessary.
In conclusion compared to commercially available fluoride solution, remineralization solution "R" showed better remineralization effect on early enamel caries lesion, so it is considered as effecient solution for clinical application.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
Ji-Hoon Kim, Ho-Hyun Son, Juhea Chang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 90. CrossRef - Changes in surface content and crystal structure after fluoride gel or hydroxyapatite paste application on stripped enamel
Sang-Cheol Kim, Hyun-Sil Hong, Young-Cheol Hwang
The Korean Journal of Orthodontics.2008; 38(6): 407. CrossRef
- Color and hardness changes in artificial white spot lesions after resin infiltration
- 1,236 View
- 9 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


