Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
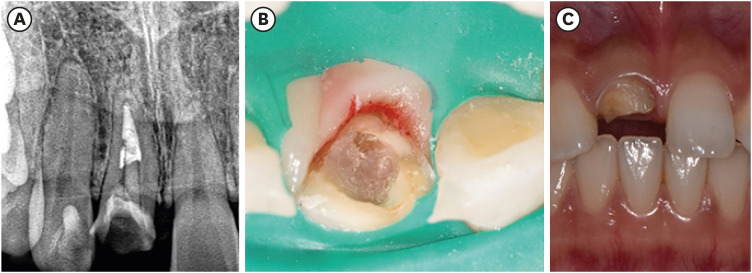
- Fiber-reinforced composite post removal using guided endodontics: a case report
- Changgi Cho, Hyo Jin Jo, Jung-Hong Ha
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e50. Published online September 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e50
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Although several techniques have been proposed to remove fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) post, no safe and efficient technique has been established. Recently, a guided endodontics technique has been introduced in cases of pulp canal obliteration. This study describes 2 cases of FRC post removal from maxillary anterior teeth using this guided endodontics technique with a dental operating microscope. Optically scanned data set from plaster cast model was superimposed with the data set of cone-beam computed tomography. By implant planning software, the path of a guide drill was selected. Based on them, a customized stent was fabricated and utilized to remove the FRC post. Employing guided endodontics, the FRC post was removed quickly and safely with minimizing the loss of the remaining tooth structure. The guided endodontics was a useful option for FRC post removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparing the Effectiveness of a Robotic and Dynamic Navigation System in Fiber Post removal: An In Vitro Study
Duo Zhou, Fulu Xu, Jiayun Dai, Xingyang Wang, Yifan Ping, Juan Wang
Journal of Endodontics.2026; 52(2): 261. CrossRef - Application of 3D-printed resin guides for the removal of molar fiber posts
Yumin Wu, Lumei Huang, Bing Ge, Yuhang Zhang, Juan Zhang, Haifeng Xie, Ye Zhu, Chen Chen
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 153: 105462. CrossRef - Guided Removal of Long and Short Fiber Posts Using Endodontic Static Guides: A Case Report
Sahar Shafagh, Mamak Adel, Atiyeh Sabzpai
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Guided versus non-guided fiber post removal: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the accuracy, efficiency, and dentin preservation of static navigation techniques in the removal of fiber posts
Mohamad Elabdalla, Farshad Khosraviani, Shahryar Irannejadrankouhi, Niloofar Ghadimi, Turgut Yağmur Yalçın, Shaheen Wathiq Tawfeeq Al Hajaj, Mahmood Dashti
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 134(3): 630.e1. CrossRef - Top 100 Most-cited Scientific Articles in Guided Endodontic 2018–2024: A Bibliometric Analysis
Gustavo Adrián Morales Valladares, Raquel Esmeralda Guillén Guillén, Martha Elena Gallegos Intriago, Mary Yussely Burgos Barreiro, Claudia Jhelissa Campos Vélez, Andrés Alexander Castillo Chacón, Silvana Beatriz Terán Ayala
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management of a Tooth With Intracanal Fiber Post and Periapical Lesion Using Guided Endodontic Technique
Mamak Adel, Zohreh Asgari
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Guided Endodontics on the Success of Endodontic Treatment: An Umbrella Review of Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Aakansha Puri, Dax Abraham, Alpa Gupta
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontia guiada por tomografia computadorizada de feixe cônico
Maysa Gaudereto Laurindo, Celso Neiva Campos, Anamaria Pessoa Pereira Leite, Paola Cantamissa Rodrigues Ferreira
Cadernos UniFOA.2024; 19(54): 1. CrossRef - Removal of fiber posts using conventional versus guided endodontics: a comparative study of dentin loss and complications
R. Krug, F. Schwarz, C. Dullin, W. Leontiev, T. Connert, G. Krastl, F. Haupt
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy and Efficiency of the Surgical-Guide-Assisted Fiber Post Removal Technique for Anterior Teeth: An Ex Vivo Study
Ryota Ito, Satoshi Watanabe, Kazuhisa Satake, Ryuma Saito, Takashi Okiji
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 333. CrossRef - Endodontic management of severely calcified mandibular anterior teeth using guided endodontics: A report of a case and a review of the literature
Mina Davaji, Sahar Karimpour
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 245. CrossRef - A laboratory study comparing the static navigation technique using a bur with a conventional freehand technique using ultrasonic tips for the removal of fibre posts
Francesc Abella Sans, Zeena Tariq Alatiya, Gonzalo Gómez Val, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Paul Michael Howell Dummer, Fernando Durán‐Sindreu Terol, Juan Gonzalo Olivieri
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(3): 355. CrossRef - A three‐dimensional printed assembled sleeveless guide system for fiber‐post removal
Yang Xue, Lei Zhang, Ye Cao, Yongsheng Zhou, Qiufei Xie, Xiaoxiang Xu
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(2): 178. CrossRef - Accuracy of a 3D printed sleeveless guide system used for fiber post removal: An in vitro study
Siyi Mo, Yongwei Xu, Lei Zhang, Ye Cao, Yongsheng Zhou, Xiaoxiang Xu
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 128: 104367. CrossRef - Expert consensus on digital guided therapy for endodontic diseases
Xi Wei, Yu Du, Xuedong Zhou, Lin Yue, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Zhi Chen, Jingping Liang, Wenxia Chen, Lihong Qiu, Xiangya Huang, Liuyan Meng, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Yu Tian, Zisheng Tang, Qi Zhang, Leiying Miao, Jin Zhao, Deqin Yang, Jian Yang, Junqi
International Journal of Oral Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Knowledge, attitude, practice and perception survey on post and core restorations
Aruna Kumari Veronica, Shamini Sai, Anand V Susila
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 228. CrossRef
- Comparing the Effectiveness of a Robotic and Dynamic Navigation System in Fiber Post removal: An In Vitro Study
- 4,411 View
- 91 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref

- Effect of ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal
- Anny Carine Barros Aguiar, Daniely Amorim de Meireles, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Angela Delfina Bitencourt Garrido, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):265-269. Published online July 17, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.265
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the effect of different ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal.
Materials and Methods The crowns of forty human canine teeth were removed, and after biomechanical preparation and filling, the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. The post spaces were made, and root canal molding was performed with self-cured acrylic resin. After casting (Cu-Al), the posts were cemented with zinc phosphate cement. The specimens were randomly separated into 4 groups (
n = 10), as follows: G1 - no ultrasonic vibration (control); G2 - ultrasonic vibration using an elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip; G3 - ultrasonic vibration with a flattened convex and linear active tip; G4 - ultrasonic vibration with active semicircular tapered tip. Ultrasonic vibration was applied for 15 seconds on each post surface and tensile test was performed in a Universal Testing Machine (Instron 4444 - 1 mm/min).Results G4 presented the highest mean values, however, with no statistically significant difference in comparison to G3 (
P > 0.05). G2 presented the lowest mean values with statistically significant difference to G3 and G4 (P < 0.05).Conclusions Ultrasonic vibration with elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip was most effective in reducing force required for intraradicular post removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
Giulliano C. Serpa, Orlando A. Guedes, Neurinelma S. S. Freitas, Julio A. Silva, Carlos Estrela, Daniel A. Decurcio
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 190. CrossRef - Activación ultrasónica durante la preparación bio químico mecánica del tratamiento endodóntico no quirúrgico. Revisión de la literatura
Gisselle Cantanzaro, Nelsin Villaroel, Diana Dorta
ODOUS Científica .2022; 22(2): 135. CrossRef - Endodontic Retreatment Using Dynamic Navigation: A Case Report
Jonathan Bardales-Alcocer, Marco Ramírez-Salomón, Elma Vega-Lizama, María López-Villanueva, Gabriel Alvarado-Cárdenas, Kenneth S. Serota, Jorgeraul Ramírez-Wong
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(6): 1007. CrossRef - Assessment of a Cavity to Optimize Ultrasonic Efficiency to Remove Intraradicular Posts
Izabela Araujo Aguiar Graça, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, André Augusto Franco Marques, Leandro de Moura Martins, Ângela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1350. CrossRef - REMOVAL ALLOY CAST ROOT INLAY BY LOWPOWER ULTRASONIC AND STANDARD TIP
L. D. Vejsgejm, T. N. Gomenjuk
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2017; 14(4): 37. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef
- The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
- 1,647 View
- 15 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


