Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Assessment of mechanical allodynia in healthy teeth adjacent and contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth: a clinical study
- Vaishnavi Ratnakar Patankar, Ashish K Jain, Rahul D Rao, Prajakta R Rao
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e31. Published online July 29, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
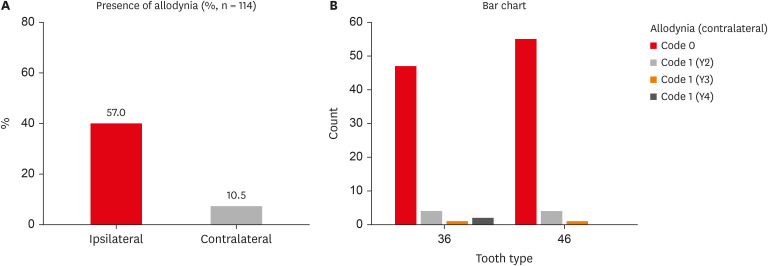
ePub Objectives The present study investigated the prevalence of mechanical allodynia (MA) in healthy teeth adjacent and contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth.
Materials and Methods This cross-sectional study included 114 patients with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis and apical periodontitis in permanent mandibular first molars who possessed healthy teeth adjacent and contralateral to the endodontically diseased tooth. The mechanical sensitivity of the teeth was determined by percussion testing. The presence or absence of pain on percussion in the teeth adjacent and contralateral to the endodontically diseased tooth and the tooth distal to the contralateral symmetrical tooth was recorded according to coding criteria. The prevalence of MA was computed as a percentage, and binary logistic regression analysis was done. The Fisher exact test and Mann-Whitney
U test were used for binary and ordinal data.Results Age and sex did not influence the prevalence of MA. An increased prevalence of MA was found in patients with higher levels of spontaneous pain (
p < 0.001). The prevalence of allodynia was 57% in teeth adjacent to endodontically diseased teeth and 10.5% in teeth contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth. In addition, on the ipsilateral side, there were more painful sensations distal to the diseased tooth than mesially.Conclusions Despite being disease-free, teeth adjacent and contralateral to endodontically diseased teeth exhibited pain on percussion. There was a direct association between the severity of the patient’s pain and the presence of MA.
- 2,807 View
- 89 Download

- The prevalence of apical periodontitis in patients prior to hematopoietic cell transplantation: a systematic review
- Letícia Tainá de Oliveira Lemes, Carolina Horn Troian-Michel, Theodoro Weissheimer, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e22. Published online May 9, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
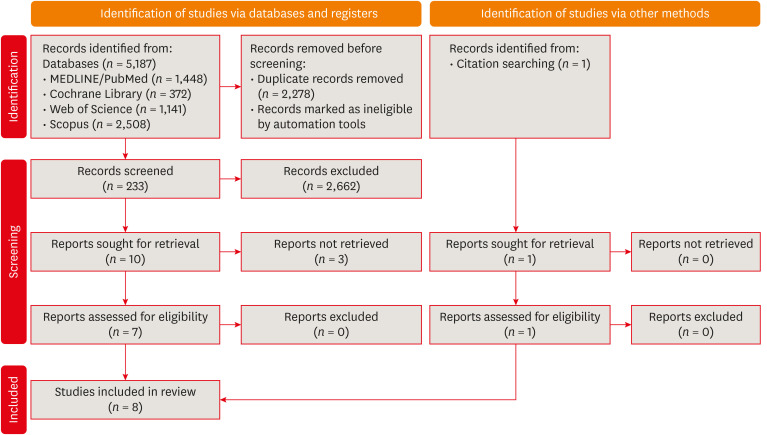
ePub Objectives This systematic review addressed the question: “What is the prevalence of apical periodontitis in patients prior to hematopoietic cell transplantation?”
Materials and Methods A systematic search was conducted in MEDLINE/PubMed, Cochrane Library, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Grey Literature Report. Eligibility criteria were based on the condition, content, and population strategy: the condition was the radiographic prevalence of apical periodontitis, the content comprised patients scheduled for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, and the population consisted of adult and pediatric patients. The revised Risk of Bias in Nonrandomized Studies of Exposure tool was used to assess the quality of studies. The Grading Recommendations Assessments, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) tool was used to assess the quality of evidence.
Results Eight studies were included in this review. The average number of patients with apical periodontitis was 15.65% (range, 2.1%–43.34%). One study was classified as having a very high risk of bias, 1 with a high risk of bias, and 6 with some concern for bias. GRADE analysis showed a very low certainty of evidence. Significant limitations concerning the absence of control over confounding variables were identified.
Conclusions With the caveat of the very low quality of evidence in the studies reviewed, there was a low to moderate prevalence of apical periodontitis in patients prior to undergoing hematopoietic cell transplantation.
- 1,929 View
- 50 Download

- Prevalence of apical periodontitis and quality of root canal treatment in an adult Kuwaiti sub-population: a cross-sectional study
- Abdulrahman A. Alhailaa, Saad A Al-Nazhan, Mazen A Aldosimani
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(2):e16. Published online March 22, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This cross-sectional study evaluated the prevalence of apical periodontitis (AP) and the technical quality of root canal fillings in an adult Kuwaiti subpopulation using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images.
Materials and Methods Two experienced examiners analyzed 250 CBCT images obtained from Kuwaiti patients aged 15–65 years who attended government dental specialist clinics between January 2019 and September 2020. The assessment followed the radiographic scoring criteria proposed by De Moor for periapical status and the technical quality of root canal filling. Chi-square and Fisher’s exact tests were used for statistical analysis, with significance level set at
p < 0.05.Results Among the 2,762 examined teeth, 191 (6.91%) exhibited radiographic signs of AP, and 176 (6.37%) had undergone root canal filling. AP prevalence in root canal-treated teeth was 32.38%, with a significant difference between males and females. Most of the endodontically treated teeth exhibited adequate root canal filling (71.5%).
Conclusions The study demonstrated a comparable prevalence of AP and satisfactory execution of root canal treatment compared to similar studies in different countries.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Retrospective Study of CBCT-Based Detection of Endodontic Failures and Periapical Lesions in a Romanian Cohort
Oana Andreea Diaconu, Lelia Mihaela Gheorghiță, Anca Gabriela Gheorghe, Mihaela Jana Țuculină, Maria Cristina Munteanu, Cătălina Alexandra Iacov, Virginia Maria Rădulescu, Mihaela Ionescu, Adina Andreea Mirea, Carina Alexandra Bănică
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(18): 6364. CrossRef
- A Retrospective Study of CBCT-Based Detection of Endodontic Failures and Periapical Lesions in a Romanian Cohort
- 4,657 View
- 81 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Radiographic patterns of periosteal bone reactions associated with endodontic lesions
- Poorya Jalali, Jessica Riccobono, Robert A. Augsburger, Mehrnaz Tahmasbi-Arashlow
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e23. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e23
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
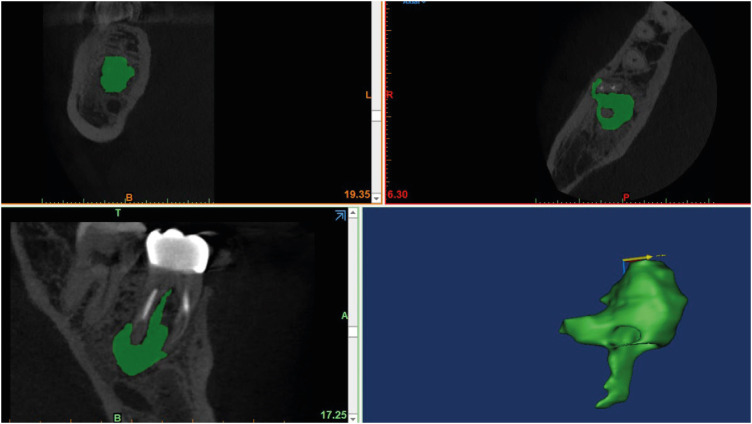
ePub Objectives The formation of new bone by periosteum due to an insult is called periosteal bone reaction (PBR). This study assessed the cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) patterns of periosteal bone reactions associated with periapical inflammatory lesion (apical periodontitis/periapical rarefying osteitis).
Materials and Methods Twenty-two small field of view CBCT images of patients with PBR were selected from a database of a private practice limited to endodontics. The volume of the periapical inflammatory lesion, the presence of cortical fenestration, the distance of the root apices to the affected cortex, and the location, pattern, and longest diameter of the periosteal reaction were recorded. Statistical analysis was performed using Wilcoxon Ranksum, Fischer’s exact, Spearman Correlation Coefficient, and paired
t -test.Results In all cases, periosteal bone reaction manifested as either parallel (90.9%) or irregular (9.1%). No correlation was found between periapical inflammatory lesion volume and the periosteal reaction's longest diameter (
p > 0.05). Cortical fenestration was noted in 72.7% of the cases. In addition, the findings showed that periosteal reactions were located mostly on the buccal and were present 53.8% and 100% of the time in the mandible and maxilla, respectively.Conclusions The periosteal reactions of endodontic origin had a nonaggressive form (
i.e ., parallel or irregular), and none of the lesions resulted in a periosteal reaction with an ominous Codman’s triangle or spicule pattern.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The influence of endodontic treatment quality on periapical lesions' architecture in cone‐beam computed tomography
Ewa Mackiewicz, Tobias Bonsmann, Krzysztof Safranow, Patrycja Nowicka, Janusz Kołecki, Alicja Nowicka
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(1): 36. CrossRef - Novel radiographic pattern of maxillary periostitis induced by endodontic inflammation: A case report
Pai-Chun Huang, I-Hao Su, Meng-Ling Chiang, Jyh-Kwei Chen
Journal of Dental Sciences.2025; 20(3): 1982. CrossRef - Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- The influence of endodontic treatment quality on periapical lesions' architecture in cone‐beam computed tomography
- 4,798 View
- 79 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Apical periodontitis in mesiobuccal roots of maxillary molars: influence of anatomy and quality of root canal treatment, a CBCT study
- Samantha Jannone Carrion, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Marcos Frozoni
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e37. Published online September 19, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
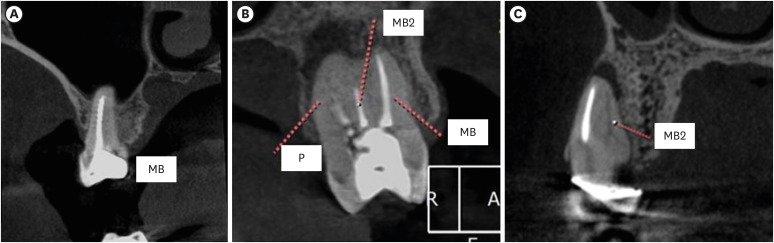
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of apical periodontitis (AP) in the mesiobuccal roots of root canal-treated maxillary molars.
Materials and Methods One thousand cone-beam computed tomography images of the teeth were examined by 2 dental specialists in oral radiology and endodontics. The internal anatomy of the roots, Vertucci’s classification, quality of root canal treatment, and presence of missed canals were evaluated; additionally, the correlation between these variables and AP was ascertained.
Results A total of 1,000 roots (692 first molars and 308 second molars) encompassing 1,549 canals were assessed, and the quality of the root canal filling in the majority (56.9%) of the canals was satisfactory. AP was observed in 54.4% of the teeth. A mesiolingual canal in the mesiobuccal root (MB2 canal) was observed in 54.9% of the images, and the majority (83.5%) of these canals were not filled. Significant associations were observed between the presence of an MB2 canal and the quality of the root canal filling and the presence of AP.
Conclusions AP was detected in more than half of the images. The MB2 canals were frequently missed or poorly filled.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical Configuration of the MB2 Canal Using High-Resolution Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Luciana Magrin Blank-Gonçalves, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Monikelly do Carmo Chagas Nascimento, Ana Grasiela Limoeiro, Luiz Roberto Coutinho Manhães-Jr
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(5): 609. CrossRef - The Effect of Age and Gender on the Distance Between the Maxillary Sinus Cortical Bone and Maxillary Molars: A Cone-Beam Tomography Analysis
Thaysa Menezes Constantino, Marília Fagury Videira Marceliano-Alves, Vivian Ronquete, Ana Grasiela da Silva Limoeiro, Pablo Andres Amoroso-Silva, Mariano Simon Pedano, Tchilalo Boukpessi, Fábio Vidal, Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho
Sinusitis.2025; 9(1): 9. CrossRef - Retrospective study of the morphology of third maxillary molars among the population of Lower Silesia based on analysis of cone beam computed tomography
Anna Olczyk, Barbara Malicka, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299123. CrossRef - Relationship between apical periodontitis and missed canals in mesio-buccal roots of maxillary molars: CBCT study
Badi B. Alotaibi, Kiran I. Khan, Muhammad Q. Javed, Smita D. Dutta, Safia S. Shaikh, Nawaf M. Almutairi
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2024; 19(1): 18. CrossRef - APICAL PERIODONTITIS IN MAXILLARY MOLARS WITH MISSED SECOND MESIO-BUCCAL ROOT CANAL: A CBCT STUDY
Cristina Coralia Nistor, Ioana Suciu , Ecaterina Ionescu , Anca Dragomirescu , Elena Coculescu , Andreea Baluta
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation.2024; 16(3): 100. CrossRef - Anatomic Comparison of Contralateral Maxillary Second Molars Using High-Resolution Micro-CT
Ghassan Dandache, Umut Aksoy, Mehmet Birol Ozel, Kaan Orhan
Symmetry.2023; 15(2): 420. CrossRef
- Anatomical Configuration of the MB2 Canal Using High-Resolution Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
- 3,199 View
- 51 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref

- Association between cigarette smoking and the prevalence of post-endodontic periapical pathology: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Néstor Ríos-Osorio, Hernan Darío Muñoz-Alvear, Fabio Andrés Jiménez-Castellanos, Sara Quijano-Guauque, Oscar Jiménez-Peña, Herney Andrés García-Perdomo, Javier Caviedes-Bucheli
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e27. Published online June 13, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to assess the association of cigarette smoking with the prevalence of post-endodontic apical periodontitis in humans.
Materials and Methods We searched through PubMed/Medline, Web of Science, and Scopus from inception to December 2020. Risk of bias was performed by using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale for cross-sectional, cohort, and case-control studies. We performed the statistical analysis in Review Manager 5.3 (RevMan 5.3).
Results 6 studies met the inclusion criteria for qualitative and quantitative synthesis. Statistical analysis of these studies suggests that there were no differences in the prevalence of post endodontic apical periodontitis (AP) when comparing non-smokers
vs smoker subjects regarding patients (odds ratio [OR], 0.68; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.31–1.49; I2 = 58%) and teeth (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 0.99–2.93; I2 = 72%).Conclusions Our findings suggest that there was no association between cigarette smoking and post-endodontic apical periodontitis, as we did not find statistical differences in the prevalence of post-endodontic AP when comparing non-smokers
vs smoker subjects. Therefore, smoking should not be considered a risk factor associated with endodontic failure.
- 2,568 View
- 36 Download

- Revitalization of necrotic mature permanent incisors with apical periodontitis: a case report
- Emre Nagas, M. Ozgur Uyanik, Zafer C. Cehreli
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e31. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e31
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
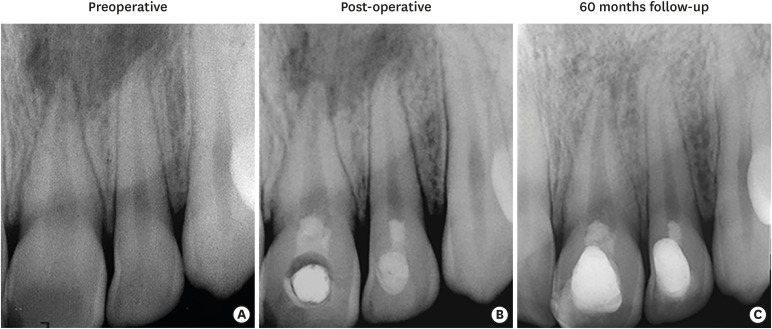
ePub Despite considerable focus on the regenerative endodontic treatment of immature teeth with necrotic infected pulps and apical periodontitis, little data exist with regard to its possible implementation in necrotic permanent teeth with complete apical and radicular development. The present report describes the procedures and outcome of a regenerative endodontic treatment approach in 2 previously-traumatized incisors with closed apex with apical periodontitis. A 2-visit treatment procedure was employed. At initial visit, the root canals were copiously irrigated, followed by placement of a triple antibiotic paste containing ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, and clindamycin into the root canals. After 4 weeks, the antibiotic paste was removed, and apical bleeding was initiated with size 10 hand files beyond the apices. The root canals were coronally sealed with mineral trioxide aggregate, and the access cavities were restored with bonded resin composite. At post-operative 60 months, both teeth were remained asymptomatic, with the recall radiographs showing complete resolution of apical radiolucency and reestablishment of periradicular tissues. In both teeth, the dimensions of root space remained unchanged as verified by image analysis. The revitalization protocol utilizing root canal disinfection and induced apical bleeding in necrotic, closed-apex incisors may offer a clinically acceptable alternative to conventional root canal treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Regenerative potential of concentrated growth factor compared to platelet-rich fibrin in treatment of necrotic mature teeth: a randomized clinical trial
Taghreed Salah, Wael Hussein, Heba Abdelkafy
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Pulp Revascularization in the Treatment of Apical Periodontitis in Mature Necrotic Teeth: An Umbrella Review
Wanderson Limeira de Sousa Barbosa, Luiz Renato Paranhos, Márcia Valente de Brito Dantas, Rômulo Dias Jesuino, João Marcos da Costa Ribeiro, Walbert A. Vieira, Felipe de Souza Matos
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(2): 495. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic outcomes of non-surgical retreatment of mature maxillary incisors using two regenerative endodontic techniques in adolescents: a 24-month randomized clinical trial
Ahmad Abdel Hamid Elheeny, Sherif Shafik EL Bahnasy, Yassmin Mohamed ElMakawi, Mohammed Turky, Eman Farouk Ahmed, Norhan Khaled Omar Wahba
BDJ Open.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of chitosan medicaments loaded with green-synthesized silver nanoparticles on basic fibroblast growth factor release from infected dentin
Dilek Hancerliogullari, Zehra Gun Gok, Nebahat Aytuna Cerci, Eray Ceylanoglu, Bengisu Ozturk, Ozum Hekim Harput, Sevda Durust Baris, Filiz Kiper, Ali Erdemir
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Revolutionizing Endodontics: Innovative Approaches for Treating Mature Teeth With Closed Apices and Apical Lesions: A Report of Two Cases
Claudia Brizuela, Gastón Meza, Maroun Khoury
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 596. CrossRef - Current Aspects of Regenerative Endodontics: A Systematic Review
A. V. Mitronin, K. A. Archakov, D. A. Ostanina, Yu. A. Mitronin, T. V. Khizrieva
Endodontics Today.2024; 21(4): 287. CrossRef - Correlation between pulp sensibility and magnetic resonance signal intensity following regenerative endodontic procedures in mature necrotic teeth- a retrospective cohort study
Noha Mohamed El-Kateb, Amr Mohamed Abdallah, Rania Noaman ElBackly
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of periapical lesion size on healing outcome following regenerative endodontic procedures: a clinical investigation
Noha Mohamed El Kateb, Mahmoud Mostafa Fata
Oral Radiology.2022; 38(4): 480. CrossRef - Do alternative scaffolds used in regenerative endodontics promote better root development than that achieved with blood clots?
Letícia de Araújo, Taynara Santos Goulart, Ana Clara Kuerten Gil, Daniela Peressoni Vieira Schuldt, Beatriz Serrato Coelho, Daniela de Rossi Figueiredo, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(2): 22. CrossRef - Endodontic Regenerative Procedures in Necrotic Adult Teeth
Sara Garrido-Parada, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Nancy Feijoo-Pato, José Gaviño-Orduña, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(9): 4212. CrossRef - Combined conventional and regenerative treatment in molars with coexistent closed and open apices: A case series
Zafer C. Cehreli, Gizem Erbas Unverdi, Pinar Eymirli, Irem Mergen, Ezgihan Arslan, Gulce Esenturk
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 197. CrossRef - Regenerative Endodontic Procedures for the Treatment of Necrotic Mature Teeth with Apical Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Antonios Glynis, Federico Foschi, Ismini Kefalou, Despina Koletsi, Giorgos N. Tzanetakis
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(6): 873. CrossRef - Different Approaches to the Regeneration of Dental Tissues in Regenerative Endodontics
Anna M. Krupińska, Katarzyna Skośkiewicz-Malinowska, Tomasz Staniowski
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(4): 1699. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Intracanal Regenerated Tissues after Regenerative Endodontic Procedures in Mature Teeth Using Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial
Noha Mohamed El-Kateb, Rania Noaman El-Backly, Wessam Mohamed Amin, Amr Mohamed Abdalla
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(5): 563. CrossRef
- Regenerative potential of concentrated growth factor compared to platelet-rich fibrin in treatment of necrotic mature teeth: a randomized clinical trial
- 2,264 View
- 26 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Management of large class II lesions in molars: how to restore and when to perform surgical crown lengthening?
- Ana Belén Dablanca-Blanco, Juan Blanco-Carrión, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, Purificación Varela-Patiño, Alba Bello-Castro, Pablo Castelo-Baz
- Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):240-252. Published online August 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The restoration of endodontic tooth is always a challenge for the clinician, not only due to excessive loss of tooth structure but also invasion of the biological width due to large decayed lesions. In this paper, the 7 most common clinical scenarios in molars with class II lesions ever deeper were examined. This includes both the type of restoration (direct or indirect) and the management of the cavity margin, such as the need for deep margin elevation (DME) or crown lengthening. It is necessary to have the DME when the healthy tooth remnant is in the sulcus or at the epithelium level. For caries that reaches the connective tissue or the bone crest, crown lengthening is required. Endocrowns are a good treatment option in the endodontically treated tooth when the loss of structure is advanced.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Awareness and Practice of Deep Margin Elevation among Dental Practitioners in India: A Cross-Sectional Survey
Mythri Padaru, Preethesh Shetty, Namith Rai, Raksha Bhat
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Rubber dam isolation to optimise intraoral scanning and the restoration of teeth with subgingival margins
Renato Lardin Sartori Sanchez, Gisele Lie Fukuoka, Nathália Pereira Censi Stapani, Isabella Neme Ribeiro dos Reis
BMJ Case Reports.2025; 18(4): e264082. CrossRef - Impact of spacers and thermocycling on porosity and gaps in class II endodontic temporary restorations evaluated by microcomputed tomography
Fahda N. Algahtani, Manal Alkadi, Hiba R. Talic, Sarah S. AlShalawi, Lujain M. Alqarni, Reem M. Barakat, Rasha Haridy, Sara M. ElKhateeb, Rahaf A. Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Margin Elevation: Current Evidence and a Critical Approach to Clinical Protocols—A Narrative Review
Athanasios Karageorgiou, Maria Fostiropoulou, Maria Antoniadou, Eftychia Pappa
Adhesives.2025; 1(3): 10. CrossRef - Deep margin elevation in restorative dentistry: A scoping review
Anna Taylor, Lorna Burns
Journal of Dentistry.2024; 146: 105066. CrossRef - Effect of cervical margin relocation on marginal adaptation and microleakage of indirect ceramic restorations
Marwa Adel, Amina Hamdy, Ahmed Sabet, Kamal Ebeid
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(4): 374. CrossRef - Application of one-piece endodontic crowns fabricated with CAD-CAM system to molars
Haruto Hiraba, Kensuke Nishio, Yoshimasa Takeuchi, Takashi Ito, Tetsuo Yamamori, Atsushi Kamimoto
Japanese Dental Science Review.2024; 60: 81. CrossRef - Structurally compromised teeth. Part II: A novel approach to peripheral build up procedures
Guido Fichera, Claudia Mazzitelli, Vincenzo Picciariello, Tatjana Maravic, Uros Josic, Annalisa Mazzoni, Lorenzo Breschi
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 20. CrossRef - Biomimetic Restorative Dentistry: an evidence-based discussion of common myths
Alessandra REIS, Victor Pinheiro FEITOSA, Ana Cláudia CHIBINSKI, Michael Willian FAVORETO, Mario Felipe GUTIERREZ, Alessandro Dourado LOGUERCIO
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative clinical evaluation of correct anatomic contour and tight contact in Class II direct composite restoration using two newer contact forming instruments
Jaimini Patel, Nimisha C. Shah, Meetkumar Dedania, Deebah Choudhary, Nidhi Bharti, Aishwarya Jain
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2024; 27(11): 1135. CrossRef - Effect of Deep Margin Elevation on the Pulpal and Periodontal Health of Teeth: A Systematic Review
S Srirama, S Jain, B Arul, K Prabakar, V Natanasabapathy
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(4): 388. CrossRef - New Technique for Wedge Selection in Direct Class II Restorations: A Pilot Study
Tania Gancedo-Gancedo, Benjamín Martín-Biedma, Javier Domínguez-Cachón, Sara Garrido-Parada, Victoria Ababii, Patricia Pereira-Lores, Sandra García-Varela, Pablo Castelo-Baz
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(5): 1324. CrossRef - Different Designs of Deep Marginal Elevation and Its Influence on Fracture Resistance of Teeth with Monolith Zirconia Full-Contour Crowns
Ali Robaian, Abdullah Alqahtani, Khalid Alanazi, Abdulrhman Alanazi, Meshal Almalki, Anas Aljarad, Refal Albaijan, Ahmed Maawadh, Aref Sufyan, Mubashir Baig Mirza
Medicina.2023; 59(4): 661. CrossRef - M-i-M for DME: matrix-in-a-matrix technique for deep margin elevation
Pascal Magne
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2023; 130(4): 434. CrossRef - A New Concept of Posterior Mini-invasive Restorations: Clinical Procedures and Requirements—Case Report
Zeineb Riahi, Belhassen Harzallah, Mounir Cherif, Dalenda Hadyaoui, Imen Kalghoum, Oumayma Mejri
CODS - Journal of Dentistry.2023; 14(2): 61. CrossRef - Evaluation of biologic width re-establishment using CHU aesthetic gauges in crown lengthening cases- a clinical study
Avantika Rani, Shiva Shankar Gummaluri, Hirak S. Bhattacharya, Preeti Bhattacharya, Sumbul Saifi, saummya singh
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2023; 13(2): 138. CrossRef - Interfacial integrity of bulk-fill resin composite restorations in deep Class-II cavities
Rana Abdelrehim SEDKY, Hooi Pin CHEW, Khaled Aly NOUR, Shaimaa Mohamed ABUELSADAT, Dina ELSHERBINI, Alex Siu Lun FOK
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(5): 692. CrossRef - Biological evaluation of indirect restorations in endodontically treated posterior teeth with deeply located proximal margins following deep margin elevation versus surgical crown lengthening: a randomized controlled trial
Ahmed Tarek Farouk, Olfat El Sayed Hassanein, Ola Ibrahim Fahmy, Ahmed M. Elkady, Hani ElNahass
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep Margin Elevation: Current Concepts and Clinical Considerations: A Review
Majed Aldakheel, Khalid Aldosary, Shatha Alnafissah, Rahaf Alaamer, Anwar Alqahtani, Nora Almuhtab
Medicina.2022; 58(10): 1482. CrossRef - Deep Margin Elevation: A Literature Review
Theodora Kalliopi Samartzi, Dimokritos Papalexopoulos, Panagiotis Ntovas, Christos Rahiotis, Markus B. Blatz
Dentistry Journal.2022; 10(3): 48. CrossRef - Examination of caries‐affected dentin and composite‐resin interface after different caries removal methods: A scanning electron microscope study
Nazmiye Donmez, Magrur Kazak, Zeynep Buket Kaynar, Yesim Sesen Uslu
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(6): 2212. CrossRef - Clinical performance of indirect restorations with cervical margin relocation in posterior teeth: A systematic review
Ghaida Alhumaidan, Raghad Alammar, Dhafer Al Asmari, Ali Alenezi
Dentistry Review.2022; 2(1): 100034. CrossRef - Current Strategies to Control Recurrent and Residual Caries with Resin Composite Restorations: Operator- and Material-Related Factors
Moataz Elgezawi, Rasha Haridy, Moamen A. Abdalla, Katrin Heck, Miriam Draenert, Dalia Kaisarly
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6591. CrossRef - Survival and success of endocrowns: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Raghad A. Al-Dabbagh
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(3): 415.e1. CrossRef - The Relationships Between Tooth‐Supported Fixed Dental Prostheses and Restorations and the Periodontium
Carlo Ercoli, Dennis Tarnow, Carlo E. Poggio, Alexandra Tsigarida, Marco Ferrari, Jack G. Caton, Konstantinos Chochlidakis
Journal of Prosthodontics.2021; 30(4): 305. CrossRef - Placement of Posterior Composite Restorations: A Cross-Sectional Study of Dental Practitioners in Al-Kharj, Saudi Arabia
Mohamed M. Awad, Mansour Alradan, Nawaf Alshalan, Ali Alqahtani, Feras Alhalabi, Mohammed Ali Salem, Ahmed Rabah, Ali Alrahlah
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(23): 12408. CrossRef - Microleakage of Direct Restorations-Comparisonbetween Bulk-Fill and Traditional Composite Resins:Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Francesca Zotti, Edoardo Falavigna, Giorgia Capocasale, Daniele De Santis, Massimo Albanese
European Journal of Dentistry.2021; 15(04): 755. CrossRef - Assessment of knowledge, attitude, and practice regarding Deep Margin Elevation (DME) among dental practitioners in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Sultan R. Binalrimal, Weam M. Banjar, Sara H. Alyousef, Mada I. Alawad, Ghalia I. Alawad
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2021; 10(5): 1931. CrossRef - Treatment Prognosis of Restored Teeth with Crown Lengthening vs. Deep Margin Elevation: A Systematic Review
Maryam H. Mugri, Mohammed E. Sayed, Binoy Mathews Nedumgottil, Shilpa Bhandi, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Zohaib Khurshid, Saurabh Jain, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(21): 6733. CrossRef - Direct resin composite restoration of endodontically-treated permanent molars in adolescents: bite force and patient-specific finite element analysis
Monise de Paula RODRIGUES, Priscilla Barbosa Ferreira SOARES, Márcio Alex Barros GOMES, Renata Afonso PEREIRA, Daranee TANTBIROJN, Antheunis VERSLUIS, Carlos Jose SOARES
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Up to 12 years clinical evaluation of 197 partial indirect restorations with deep margin elevation in the posterior region
R.A. Bresser, D. Gerdolle, I.A. van den Heijkant, L.M.A. Sluiter-Pouwels, M.S. Cune, M.M.M. Gresnigt
Journal of Dentistry.2019; 91: 103227. CrossRef - How biomechanics can affect the endodontic treated teeth and their restorative procedures?
Carlos José Soares, Monise de Paula Rodrigues, André Luis Faria-e-Silva, Paulo Cesar Freitas Santos-Filho, Crisnicaw Veríssimo, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Antheunis Versluis
Brazilian Oral Research.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Awareness and Practice of Deep Margin Elevation among Dental Practitioners in India: A Cross-Sectional Survey
- 2,953 View
- 100 Download
- 32 Crossref

- Epigenetics: general characteristics and implications for oral health
- Ji-Yun Seo, Yoon-Jung Park, Young-Ah Yi, Ji-Yun Hwang, In-Bog Lee, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Ho-Hyun Son, Deog-Gyu Seo
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):14-22. Published online November 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Genetic information such as DNA sequences has been limited to fully explain mechanisms of gene regulation and disease process. Epigenetic mechanisms, which include DNA methylation, histone modification and non-coding RNAs, can regulate gene expression and affect progression of disease. Although studies focused on epigenetics are being actively investigated in the field of medicine and biology, epigenetics in dental research is at the early stages. However, studies on epigenetics in dentistry deserve attention because epigenetic mechanisms play important roles in gene expression during tooth development and may affect oral diseases. In addition, understanding of epigenetic alteration is important for developing new therapeutic methods. This review article aims to outline the general features of epigenetic mechanisms and describe its future implications in the field of dentistry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Embracing change: Chemical modifications of nucleic acid bases as epigenetic marks
Nishu Nain, Shoaib Khan, Priyanka Phogat, Aparna Bansal, Shrikant Kukreti
Next Research.2026; 5: 101292. CrossRef - Conversation between skin microbiota and the host: from early life to adulthood
Jimin Cha, Tae-Gyun Kim, Ji-Hwan Ryu
Experimental & Molecular Medicine.2025; 57(4): 703. CrossRef - Identification of two novel variants in homeodomain of
MSX1 associated with oligodontia
Ting Zeng, Xiuyou Wang, Li Xu, Xin Dong, Xili Qiu, Zhiyuan Deng, Saimin Pei, Rong Lei, Yuehong Wang, Ling Peng
Oral Science and Homeostatic Medicine.2025; 1(2): 9610029. CrossRef - DNA Methylation of COX‐2, IFN‐γ, TNF‐α, and LINE‐1 in Clinically Stable Periodontal Tissues Following Periodontal Therapy
Giulio Rasperini, Koki Yoshida, Alessandro Martinotti, Valentina Bollati, Letizia Tarantini, Farah Asa'ad
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Long Non-coding RNA and DNA Methylation on Gene Expression in Dental Fluorosis
Xiaoyan Hu, Huiru Li, Minzhi Yang, Yujiong Chen, Ailin Zeng, Jiayuan Wu, Jian Zhang, Yuan Tian, Jing Tang, Shengyan Qian, Mingsong Wu
Biological Trace Element Research.2024; 202(1): 221. CrossRef - MicroRNAs: Mighty Mite RNAs in Oral Diseases
Devapriya Appukuttan, P. S. G. Prakash
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2024; 14(3): 145. CrossRef - Role of epigenetics in OSCC: an understanding above genetics
Priyanka P. Vatsa, Yogita Jindal, Janhavi Bhadwalkar, Ambika Chamoli, Vinal Upadhyay, Amit Mandoli
Medical Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Downregulation of miRNA‐26 in chronic periodontitis interferes with innate immune responses and cell migration by targeting phospholipase C beta 1
Juhi R. Uttamani, Afsar R. Naqvi, Araceli Maria Valverde Estepa, Varun Kulkarni, Maria F. Brambila, Gloria Martínez, Gabriela Chapa, Christine D. Wu, Wei Li, Sona Rivas‐Tumanyan, Salvador Nares
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2023; 50(1): 102. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Epigenetic Modifications on Different Facets in the Periodontal Pathogenesis
Samuel Laberge, Daniel Akoum, Piotr Wlodarczyk, Jean-Daniel Massé, Dominique Fournier, Abdelhabib Semlali
Genes.2023; 14(6): 1202. CrossRef - The Role of Histone Acetylation Modification in Dental Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Odontogenesis
Haoling Chen, Zijing Huang, Chuxiao Chen
Cellular Reprogramming.2023; 25(1): 11. CrossRef - Your health is in your mouth: A comprehensive view to promote general wellness
Antonia Barranca-Enríquez, Tania Romo-González
Frontiers in Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Brief Landscape of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Dental Pathologies
Wojciech Tynior, Joanna Katarzyna Strzelczyk
Cytology and Genetics.2022; 56(5): 475. CrossRef - Influence of epigenetics on periodontitis and peri‐implantitis pathogenesis
Lena Larsson, Nolan M. Kavanagh, Trang V. N. Nguyen, Rogerio M. Castilho, Tord Berglundh, William V. Giannobile
Periodontology 2000.2022; 90(1): 125. CrossRef - DNA methylation alterations and their potential influence on macrophage in periodontitis
Yiyang Jiang, Jingfei Fu, Juan Du, Zhenhua Luo, Lijia Guo, Junji Xu, Yi Liu
Oral Diseases.2022; 28(2): 249. CrossRef - Stabilizing and Anti-Repressor Elements Effectively Increases Transgene Expression in Transfected CHO Cells
Qin Li, Rui-Fang Yan, Yong-Xiao Yang, Chun-liu Mi, Yan-long Jia, Tian-Yun Wang
Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis and Anticancer Potential of New Hydroxamic Acid Derivatives as Chemotherapeutic Agents
Işıl Nihan Korkmaz, Hasan Özdemir
Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.2022; 194(12): 6349. CrossRef - Impact of Epigenetic Alterations in the Development of Oral Diseases
Rodopi Emfietzoglou, Evangelos Pachymanolis, Christina Piperi
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 28(6): 1091. CrossRef - Basics of Epigenetics and Role of Epigenetics in Diabetic Complications
Andamuthu Yamunadevi, Ramani Pratibha, Muthusamy Rajmohan, Sengottaiyan Mahendraperumal, Nalliappan Ganapathy
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2021; 13(Suppl 1): S336. CrossRef - Effects of Epigenetic Regulation on Cancer
Muhammet Mesut Nezir ENGİN, Esra ÖZEN ENGİN, Recep ERÖZ, Gorkem DULGER, Hüseyin YÜCE
Journal of Biotechnology and Strategic Health Research.2021; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation therapy improves human dental pulp stem cell viability and migration in vitro associated to upregulation of histone acetylation
Ivana M. Zaccara, Letícia B. Mestieri, Emily F. S. Pilar, Maria S. Moreira, Fabiana S. Grecca, Manoela D. Martins, Patrícia Maria Poli Kopper
Lasers in Medical Science.2020; 35(3): 741. CrossRef - The Biology of Social Adversity Applied to Oral Health
N. Gomaa, H. Tenenbaum, M. Glogauer, C. Quiñonez
Journal of Dental Research.2019; 98(13): 1442. CrossRef - The effect of DNA methylation on the miRNA expression pattern in lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in human dental pulp cells
Zehuan Mo, Qimeng Li, Luhui Cai, Minkang Zhan, Qiong Xu
Molecular Immunology.2019; 111: 11. CrossRef - One-Carbon Metabolism Links Nutrition Intake to Embryonic Development via Epigenetic Mechanisms
Si Wu, Jun Zhang, Feifei Li, Wei Du, Xin Zhou, Mian Wan, Yi Fan, Xin Xu, Xuedong Zhou, Liwei Zheng, Yachuan Zhou
Stem Cells International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulation in dental pulp inflammation
T Hui, C Wang, D Chen, L Zheng, D Huang, L Ye
Oral Diseases.2017; 23(1): 22. CrossRef - Current Concepts of Epigenetics and Its Role in Periodontitis
Lena Larsson
Current Oral Health Reports.2017; 4(4): 286. CrossRef - The periodontal war: microbes and immunity
Jeffrey L. Ebersole, Dolph Dawson, Pinar Emecen‐Huja, Radhakrishnan Nagarajan, Katherine Howard, Martha E. Grady, Katherine Thompson, Rebecca Peyyala, Ahmad Al‐Attar, Kathryn Lethbridge, Sreenatha Kirakodu, Octavio A. Gonzalez
Periodontology 2000.2017; 75(1): 52. CrossRef - Epigenetic regulatory elements: Recent advances in understanding their mode of action and use for recombinant protein production in mammalian cells
Niamh Harraghy, David Calabrese, Igor Fisch, Pierre‐Alain Girod, Valérie LeFourn, Alexandre Regamey, Nicolas Mermod
Biotechnology Journal.2015; 10(7): 967. CrossRef - Protocol for assessing maternal, environmental and epigenetic risk factors for dental caries in children
Surani Fernando, David J. Speicher, Mahmoud M. Bakr, Miles C. Benton, Rodney A. Lea, Paul A. Scuffham, Gabor Mihala, Newell W. Johnson
BMC Oral Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef
- Embracing change: Chemical modifications of nucleic acid bases as epigenetic marks
- 2,408 View
- 26 Download
- 28 Crossref

- Necrosis of intact premolar caused by an adjacent apical infection: a case report
- Saeed Asgary, Laleh Alim Marvasti
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):90-92. Published online May 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.90
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Although periapical inflammatory lesions are usually resulted by infection in the root canal system, this rare case showed that a periapical lesion related to an infected tooth may cause pulpal necrosis in adjacent intact tooth, with no history or clinical signs of caries, disease, trauma or developmental anomaly. This case also suggests that the periapical lesion can be treated conservatively, without surgical intervention. Furthermore, this case highlights the importance of prompt treatment of apical periodontitis before the lesion becomes extensive as well as follows up of large lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accidentally Extruded Calcium Hydroxide Into a Cystic Lesion Associated With an Adjacent Tooth—A Case Report
Emmanuel Mazinis, Nikolaos Tsanidis, Vasilios Thomaidis
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Atypically grown large periradicular cyst affecting adjacent teeth and leading to confounding diagnosis of non‐endodontic pathology
Domenico Ricucci, Massimiliano Amantea, Christian Girone, José F. Siqueira
Australian Endodontic Journal.2020; 46(2): 272. CrossRef
- Accidentally Extruded Calcium Hydroxide Into a Cystic Lesion Associated With an Adjacent Tooth—A Case Report
- 2,178 View
- 18 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Effects of canal enlargement and irrigation needle depth on the cleaning of the root canal system at 3 mm from the apex
- Ho-Jin Moon, Chan-Ui Hong
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):24-28. Published online March 2, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.24
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to test the hypothesis, that the effectiveness of irrigation in removing smear layer in the apical third of root canal system is dependent on the depth of placement of the irrigation needle into the root canal and the enlargement size of the canal.
Materials and Methods Eighty sound human lower incisors were divided into eight groups according to the enlargement size (#25, #30, #35 and #40) and the needle penetration depth (3 mm from working length, WL-3 mm and 9 mm from working length, WL-9 mm). Each canal was enlarged to working length with Profile.06 Rotary Ni-Ti files and irrigated with 5.25% NaOCl. Then, each canal received a final irrigation with 3 mL of 3% EDTA for 4 min, followed by 5 mL of 5.25% NaOCl at different level (WL-3 mm and WL-9 mm) from working length. Each specimen was prepared for the scanning electron microscope (SEM). Photographs of the 3mm area from the apical constriction of each canal with a magnification of ×250, ×500, ×1,000, ×2,500 were taken for the final evaluation.
Results Removal of smear layer in WL-3 mm group showed a significantly different effect when the canal was enlarged to larger than #30. There was a significant difference in removing apical smear layer between the needle penetration depth of WL-3 mm and WL-9 mm.
Conclusions Removal of smear layer from the apical portion of root canals was effectively accomplished with apical instrumentation to #35/40 06 taper file and 3 mm needle penetration from the working length.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Numerical Evaluation of Flow Pattern for Root Canal Irrigation Including icrobubbles
Joon Hyun Kim, Chan U Lee, Inwhan Lee, Jaeyong Sung
Journal of the Korean Society of Manufacturing Technology Engineers.2023; 32(5): 251. CrossRef
- Numerical Evaluation of Flow Pattern for Root Canal Irrigation Including icrobubbles
- 1,073 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Microbial profile of asymptomatic and symptomatic teeth with primary endodontic infections by pyrosequencing
- Sang-Min Lim, Tae-Kwon Lee, Eun-Jeong Kim, Jun-Hong Park, Yoon Lee, Kwang-Shik Bae, Kee-Yeon Kum
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):498-505. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.498
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this
in vivo study was to investigate the microbial diversity in symptomatic and asymptomatic canals with primary endodontic infections by using GS FLX Titanium pyrosequencing.Materials and Methods Sequencing was performed on 6 teeth (symptomatic, n = 3; asymptomatic, n = 3) with primary endodontic infections. Amplicons from hypervariable region of the small-subunit ribosomal RNA gene were generated by polymerized chain reaction (PCR), and sequenced by means of the GS FLX Titanium pyrosequencing.
Results On average, 10,639 and 45,455 16S rRNA sequences for asymptomatic and symptomatic teeth were obtained, respectively. Based on Ribosomal Database Project Classifier analysis, pyrosequencing identified the 141 bacterial genera in 13 phyla. The vast majority of sequences belonged to one of the seven phyla:
Actinobacteria ,Bacteroidetes ,Firmicutes ,Fusobacteria ,Proteobacteria ,Spirochetes , andSynergistetes . In genus level,Pyramidobacter ,Streptococcus , andLeptotrichia constituted about 50% of microbial profile in asymptomatic teeth, whereasNeisseria ,Propionibacterium , andTessaracoccus were frequently found in symptomatic teeth (69%). Grouping the sequences in operational taxonomic units (3%) yielded 450 and 1,997 species level phylotypes in asymptomatic and symptomatic teeth, respectively. The total bacteria counts were significantly higher in symptomatic teeth than that of asymptomatic teeth (p < 0.05).Conclusions GS FLX Titanium pyrosequencing could reveal a previously unidentified high bacterial diversity in primary endodontic infections.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Root Canal Microbiome Associated With Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis as Determined by High-Throughput Sequencing
Rodrigo Rodrigues Amaral, Tiago Braga, José F. Siqueira, Isabela N. Rôças, Caio Tavora Coelho da Costa Rachid, Anna Gabriella Guimarães Oliveira, Maria Ilma de Souza Côrtes, Robert Mattew Love
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(4): 487. CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study the root canal microbiome
José F. Siqueira, Isabela N. Rôças
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 46. CrossRef - Oral microbiomes in children with asthma and dental caries
Sergey V. Cherkasov, Larisa Yu. Popova, Tatyana V. Vivtanenko, Rimma R. Demina, Yuri A. Khlopko, Alexander S. Balkin, Andrey O. Plotnikov
Oral Diseases.2019; 25(3): 898. CrossRef - Insights into the human oral microbiome
Digvijay Verma, Pankaj Kumar Garg, Ashok Kumar Dubey
Archives of Microbiology.2018; 200(4): 525. CrossRef - Solving the etiology of dental caries
Aurea Simón-Soro, Alex Mira
Trends in Microbiology.2015; 23(2): 76. CrossRef - Present status and future directions in endodontic microbiology
José F. Siqueira, Isabela N. Rôças
Endodontic Topics.2014; 30(1): 3. CrossRef - Application of high-throughput sequencing in understanding human oral microbiome related with health and disease
Hui Chen, Wen Jiang
Frontiers in Microbiology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef
- Root Canal Microbiome Associated With Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis as Determined by High-Throughput Sequencing
- 1,271 View
- 4 Download
- 7 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


