Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
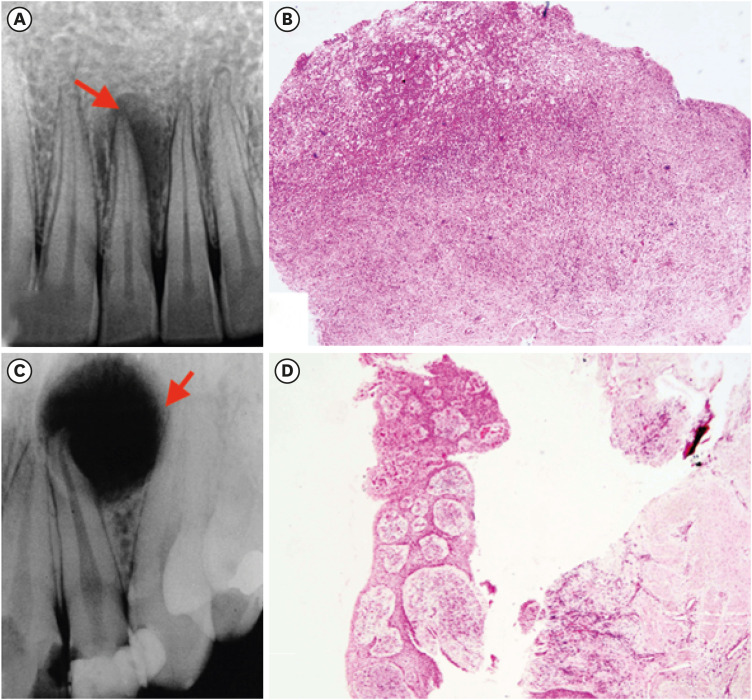
- Interplay of collagen and mast cells in periapical granulomas and periapical cysts: a comparative polarizing microscopic and immunohistochemical study
- Deepty Bansal, Mala Kamboj, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi, Nisha Marwah
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e12. Published online February 14, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This pilot study aimed to establish the interrelationship between collagen and mast cells in periapical granulomas and periapical cysts.
Materials and Methods An observational cross-sectional study was conducted on the paraffin-embedded tissue sections of 68 specimens (34 periapical granulomas and 34 periapical cysts). The specimens were stained with picrosirius to observe collagen fiber birefringence and anti-tryptase antibody to evaluate the mast cell count immunohistochemically. The mean number and birefringence of collagen fibers, as well as the mean number of mast cells (total, granulated, and degranulated), and the mean inflammatory cell density were calculated. The data obtained were analyzed using the Kruskal Wallis test, Mann Whitney
U test, and Spearman correlation test (p < 0.05).Results The mean number of thick collagen fibers was higher in periapical cysts, while that of thin fibers was higher in granulomas (
p = 0.00). Cysts emitted orange-yellow to red birefringence, whereas periapical granulomas had predominantly green fibers (p = 0.00). The mean inflammatory cell density was comparable in all groups (p = 0.129). The number of total, degranulated, and granulated mast cells exhibited significant results (p = 0.00) in both groups. Thick cyst fibers showed significant inverse correlations with inflammation and degranulated mast cells (p = 0.041, 0.04 respectively).Conclusions Mast cells and inflammatory cells influenced the nature of collagen fiber formation and its birefringence. This finding may assist in the prediction of the nature, pathogenesis, and biological behavior of periapical lesions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Mystifying Role of Mast Cells in the Pathogenesis of Periapical Pathologies - A Systematic Review
Mala Kamboj, Shashibala Malik, R. Keerthika, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi, Gopikrishnan Vijayakumar, Adarsh Kumar
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(7): 845. CrossRef - Immunohistochemical Analysis of CD117 in the Mast Cells of Odontogenic Keratocysts
Sujatha Varma, Shameena PM, Plakkil Viswanathan Deepthi, Indu G
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Immunohistochemical evaluation of cyclooxygenase‐2 and mast cell density in periapical lesions
Shashibala Malik, Mala Kamboj, Anjali Narwal, Anju Devi
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(8): 980. CrossRef
- The Mystifying Role of Mast Cells in the Pathogenesis of Periapical Pathologies - A Systematic Review
- 2,342 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- The relationship of radiographic lesion size and characteristics to diagnosis of periapical cysts and granulomas
- Ho-Sik Choi, Woo-Cheol Lee, Won-Jun Shon, Kee-Yeon Kum, Kwang-Shik Bae, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):24-29. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.024
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to find out the relationship of radiographic lesion size, gender, age of patients and radiographic character to the diagnosis of periapical cyst and granuloma.
The data was collected from 187 periapical lesions of 167 patients who undergone apical surgery at Department of Conservative Dentistry, Seoul National University Dental Hospital from 2003 to 2005. The lesion were surgically removed and send for biopsy to the Oral Pathology Laboratory. From the initial radiograph, lesion size was calculated using PiViewSTAR® (INFINITT, Korea) program. The obtained data were statistically evaluated using SPSS (p < 0.05).
The result were as followings:
From 187 biopsy samples, the incidence of periapical cyst was 28.34% and granuloma was 65.24%.
There was a significant correlation between periapical cyst and the size of radiographic lesion (p < 0.01).
There were no significant correlations between age, gender, location of lesion and the final diagnosis (p > 0.05).
There was a significant correlation between the non-demarcation of the lesion and the incidence of periapical granuloma (p < 0.01).
- 2,199 View
- 24 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


