Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of medium or high concentrations of in-office dental bleaching gel on the human pulp response in the mandibular incisors
- Douglas Augusto Roderjan, Rodrigo Stanislawczuk, Diana Gabriela Soares, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa, Michael Willian Favoreto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e12. Published online March 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e12
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
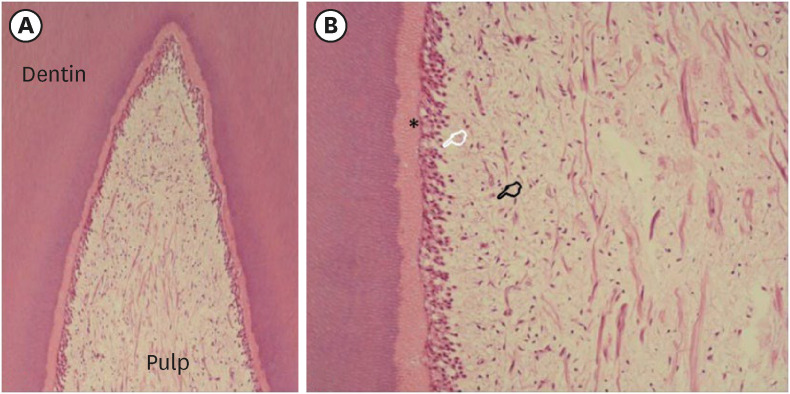
ePub Objectives The present study evaluated the pulp response of human mandibular incisors subjected to in-office dental bleaching using gels with medium or high concentrations of hydrogen peroxide (HP).
Materials and Methods The following groups were compared: 35% HP (HP35;
n = 5) or 20% HP (HP20;n = 4). In the control group (CONT;n = 2), no dental bleaching was performed. The color change (CC) was registered at baseline and after 2 days using the Vita Classical shade guide. Tooth sensitivity (TS) was also recorded for 2 days post-bleaching. The teeth were extracted 2 days after the clinical procedure and subjected to histological analysis. The CC and overall scores for histological evaluation were evaluated by the Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney tests. The percentage of patients with TS was evaluated by the Fisher exact test (α = 0.05).Results The CC and TS of the HP35 group were significantly higher than those of the CONT group (
p < 0.05) and the HP20 group showed an intermediate response, without significant differences from either the HP35 or CONT group (p > 0.05). In both experimental groups, the coronal pulp tissue exhibited partial necrosis associated with tertiary dentin deposition. Overall, the subjacent pulp tissue exhibited a mild inflammatory response.Conclusions In-office bleaching therapies using bleaching gels with 20% or 35% HP caused similar pulp damage to the mandibular incisors, characterized by partial necrosis, tertiary dentin deposition, and mild inflammation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of a bioactive desensitizing material on in-office bleaching–induced tooth sensitivity: A randomized double-blind controlled trial
Ghada A. Maghaireh, Hanan Alzraikat, Majd Y. Altarazi
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106326. CrossRef - Can pigments of different natures interfere with the cytotoxicity from in-office bleaching?
Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Beatriz Voss Martins, Marlon Ferreira Dias, Victória Peruchi, Caroline Anselmi, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Josimeri Hebling, Vanessa Cavalli, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Odontology.2025; 113(4): 1447. CrossRef - Does Patient Age Impact In-Office Tooth Bleaching Outcomes? A Parallel Clinical Trial
JL Martins, IS Araújo, JF Rabelo, CJ Soares, AL Faria-e-Silva, AD Loguercio, PCFS Filho, HL Carlo, GR da Silva
Operative Dentistry.2025; 50(3): 251. CrossRef - The pH of Bleaching Gels on the Structural and Biological Response of Dental Tissues: A Scoping Review
Jamile Menezes de Souza, Maria Olimpia Paz Alvarenga, Ana Luisa Cassiano Alves Bezerra, Gabriela Queiroz de Melo Monteiro
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(10): 2193. CrossRef - DENTA: A Dual Enzymatic Nanoagent for Self‐Activating Tooth Whitening and Biofilm Disruption
Junseok Kim, Dai‐Hwan Kim, Priyannth R. Sundharbaabu, Chae Yeon Lee, Jina Bae, Jiyu Hyun, Young‐Ju Jang, Haeni Kim, Min‐Ho Hong, Juewen Liu, Tobias Fey, Suk Ho Bhang, Jun Hyuk Heo, Jung Heon Lee
Advanced Functional Materials.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of 35 % self-mixed hydrogen peroxide In-office bleaching with reduced application time: A single-blind randomized controlled trial
Gabrielle Gomes Centenaro, Deisy Cristina Ferreira Cordeiro, Maria Alice de Matos Rodrigues, Mariah Maluf Lenhani, Roberta Micheten Dias, Cristina Gómez Polo, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 163: 106178. CrossRef - Combined catalytic strategies applied to in-office tooth bleaching: whitening efficacy, cytotoxicity, and gene expression of human dental pulp cells in a 3D culture model
Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Victória Peruchi, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Filipe Koon Wu Mon, Diana Gabriela Soares, Josimeri Hebling, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low and high hydrogen peroxide concentrations of in-office dental bleaching associated with violet light: an in vitro study
Isabela Souza Vardasca, Michael Willian Favoreto, Mylena de Araujo Regis, Taynara de Souza Carneiro, Emanuel Adriano Hul, Christiane Philippini Ferreira Borges, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Carlos Francci
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of hydrogen peroxide permeability, color change, and physical–chemical properties on the in‐office dental bleaching with different mixing tip
Michael Willian Favoreto, Sibelli Olivieri Parreiras, Michel Wendlinger, Taynara De Souza Carneiro, Mariah Ignez Lenhani, Christiane Phillipini Ferreira Borges, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2024; 36(3): 460. CrossRef - Catalysis-based approaches with biopolymers and violet LED to improve in-office dental bleaching
Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Beatriz Voss Martins, Marlon Ferreira Dias, Victória Peruchi, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Caroline Anselmi, Josimeri Hebling, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Lasers in Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Feasibility and Safety of Adopting a New Approach in Delivering a 450 nm Blue Laser with a Flattop Beam Profile in Vital Tooth Whitening. A Clinical Case Series with an 8-Month Follow-Up
Reem Hanna, Ioana Cristina Miron, Stefano Benedicenti
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(2): 491. CrossRef - Hydrogen Peroxide in the Pulp Chamber and Color Change in Maxillary Anterior Teeth After In-Office Bleaching
Alexandra Mena-Serrano, Sandra Sanchez, María G. Granda-Albuja, Michael Willian Favoreto, Taynara de Souza Carneiro, Deisy Cristina Ferreira Cordeiro, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Brazilian Dental Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of coating dental enamel with a TiF4-loaded polymeric primer on the adverse effects caused by a bleaching gel with 35% H2O2
Victória Peruchi, Rafael Antonio de Oliveira Ribeiro, Igor Paulino Mendes Soares, Lídia de Oliveira Fernandes, Juliana Rios de Oliveira, Maria Luiza Barucci Araújo Pires, Josimeri Hebling, Diana Gabriela Soares, Carlos Alberto de Souza Costa
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2024; 153: 106497. CrossRef
- Effects of a bioactive desensitizing material on in-office bleaching–induced tooth sensitivity: A randomized double-blind controlled trial
- 3,622 View
- 90 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Expression and functional characterization of odontoblast-derived gene: OD314
- Doo-Hyun Kim, Heung-Joong Kim, Moon-Jin Jeong, Ho-Hyun Son, Joo-Cheol Park
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):399-408. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.399
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Odontoblasts are responsible for the formation and maintenance of dentin. They are known to synthesize unique gene products including dentin sialophosphoprotein (DSPP). Another unique genes of the cells remain unclear.
OD314 was isolated from the odontoblasts/pulp cells of rats and partially characterized as an odontoblast-enriched gene (Dey et al., 2001). This study aimed to elucidate the biological function of OD314, relating to odontoblast differentiation and dentinogenesis. After determining the open reading frame (ORF) of OD314 by transient transfection analysis using green fluorescent protein (GFP) expression vector, mRNA
in-situ hybridization, immunohistochemistry, reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western analysis were performed.The results were as follows:
1. In
in-situ hybridization, OD314 mRNAs were expressed in odontoblasts of developing coronal and root pulp.2. OD314 was a novel protein encoding 154 amino acids, and the protein was mainly expressed in cytoplasm by transient transfection analysis.
3. Mineralized nodules were associated with multilayer cell nodules in the culture of human dental pulp cells and first detected from day 21 using alizarin-red S staining.
4. In RT-PCR analysis, OD314, osteocalcin (OC) and DSPP strongly expressed throughout 28 days of culture. Whereas, osteonectin (ON) mRNA expression stayed low up to day 14, and then gradually decreased from day 21.
5. Western blots showed an approximately 17 kDa band. OD314 protein was expressed from the start of culture and then increased greatly from day 21.
In conclusion, OD314 is considered as an odontoblast-enriched gene and may play important roles in odontoblast differentiation and dentin mineralization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of sodium fluoride on oral normal cell cultured in vitro
Byul-Bora Choi, Da-Hye Kim, Ji-Young Kim, Sang-Rye Park
Journal of Korean society of Dental Hygiene.2016; 16(3): 471. CrossRef - A study of APin-protein interactions using protein microarray
Joo-Cheol Park, Sun-Hwa Park, Heung-Joong Kim, Jong-Tae Park, Seong-Ho Youn, Ji-Woong Kim, Tae-Yeon Lee, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2007; 32(5): 459. CrossRef - Expression and function of OD314, Apin protein during ameloblast differentiation and amelogenesis
Jong-Tae Park, Yong-Seok Choi, Heung-Joong Kim, Moon-Jin Jeong, Hyun-Ju Oh, In-Cheol Shin, Joo-Cheol Park, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(6): 437. CrossRef - Expression of OD314 during ameloblast differentiation and maturation
Joo-Cheol Park, Seong-Min Ahn, Heung-Joong Kim, Moon-Jin Jeong, Min-Ju Park, In-Cheol Shin, Ho-Hyun Son
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2005; 30(5): 423. CrossRef
- The effects of sodium fluoride on oral normal cell cultured in vitro
- 947 View
- 0 Download
- 4 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


