Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Isolating design variables by assessing the impact of cross-section geometry on the mechanical performance of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: a comparative in vitro study
- Anne Rafaella Tenório Vieira, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
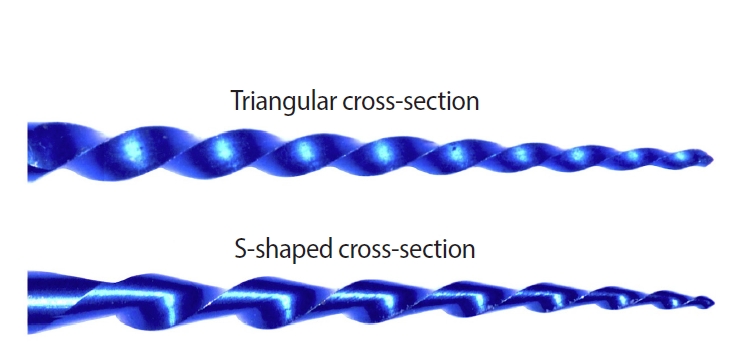
This study aimed to assess the effect of cross-section geometry on the mechanical properties of nickel-titanium (NiTi) instruments by comparing two instruments with identical tip size, taper, and thermal treatment but differing in cross-section design.
Methods
One hundred four NiTi rotary instruments, being S-shaped and triangular cross-section, manufactured with Blueish thermal treatment, were tested (n = 52 per group). Differential scanning calorimetry was employed, and the metal mass volume and cross-section area were assessed. The cyclic fatigue, torsional, and bending resistance tests were assessed. Data were analyzed using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Student t tests, and the level of significance was set at 5%.
Results
The instruments exhibited similar start and finish temperatures of phase transformation. The S-shaped instruments had significantly lower metal mass volume and cross-sectional area (p < 0.05). S-shaped instruments demonstrated superior cyclic fatigue resistance, greater angular deflection, and lower bending stiffness (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Cross-section geometry significantly influences the mechanical properties of NiTi rotary instruments.
- 2,453 View
- 91 Download

- Physical-mechanical, chemical and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements
- Tatiane Ramos dos Santos Jordão, Laura Soares Viana Fernandes, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Adílis Alexandria, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Lucianne Cople Maia, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e37. Published online October 10, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to evaluate the physical-mechanical, chemical, and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements (GICs).
Materials and Methods Different proportions of graphene powder were incorporated into 2 high-viscosity self-curing GIC, Ketac Molar (GKetac) and Fuji IX (GFuji), in 4 different concentrations: 0.5%, 1%, 2%, and 5%. The control groups included the GICs without graphene. Experiments were performed to analyze linear (Ra) and volumetric roughness (Sa), antimicrobial activity, radiopacity, fluoride release, microhardness, solubility, and water sorption. Data were analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis, Mann-Whitney, Wilcoxon, analysis of variance, and Tukey’s test (
p ≤ 0.05).Results The GKetac 0% and GFuji0% groups presented higher Ra (4.05 and 2.72) and Sa (4.76 and 5.16), respectively. No inhibition zone was observed, and the incorporation of graphene reduced radiopacity. Moreover, there was no influence on the solubility and water sorption after 21 days. A greater fluoride release was observed in the period of 7 days for most of the groups. After 21 days, GKetac 5%, 2%, and 1% presented higher releasing than 0% and 0.5% (
p ≤ 0.05).Conclusions The graphene incorporation improved the microhardness of GICs in lower concentrations. Graphene incorporation to GICs modified some physical-mechanical, and chemical, but not affected biological properties.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Laboratory-based additive modifications in glass ionomer cements: A scoping review using a systematic data mining and trend analysis framework (2015-2024)
Kenta Tsuchiya, Sharanbir K Sidhu, Salvatore Sauro, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Hidehiko Sano, Monica Yamauti, Shuhei Hoshika, James Kit Hon Tsoi, Atsushi Tomokiyo
Journal of Dentistry.2026; 166: 106349. CrossRef
- Laboratory-based additive modifications in glass ionomer cements: A scoping review using a systematic data mining and trend analysis framework (2015-2024)
- 2,832 View
- 177 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Comparative analysis of torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider, WaveOne Gold Glider, and TruNatomy Glider in simulated curved canal
- Pedro de Souza Dias, Augusto Shoji Kato, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Rina Andréa Pelegrine
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e4. Published online December 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to compare the torsional and cyclic fatigue resistance of ProGlider (PG), WaveOne Gold Glider (WGG), and TruNatomy Glider (TNG).
Materials and Methods A total of 15 instruments of each glide path system (
n = 15) were used for each test. A custom-made device simulating an angle of 90° and a radius of 5 millimeters was used to assess cyclic fatigue resistance, with calculation of number of cycles to failure. Torsional fatigue resistance was assessed by maximum torque and angle of rotation. Fractured instruments were examined by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Data were analyzed with Shapiro-Wilk and Kruskal-Wallis tests, and the significance level was set at 5%.Results The WGG group showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance than the PG and TNG groups (
p < 0.05). In the torsional fatigue test, the TNG group showed a higher angle of rotation, followed by the PG and WGG groups (p < 0.05). The TNG group was superior to the PG group in torsional resistance (p < 0.05). SEM analysis revealed ductile morphology, typical of the 2 fracture modes: cyclic fatigue and torsional fatigue.Conclusions Reciprocating WGG instruments showed greater cyclic fatigue resistance, while TNG instruments were better in torsional fatigue resistance. The significance of these findings lies in the identification of the instruments’ clinical applicability to guide the choice of the most appropriate instrument and enable the clinician to provide a more predictable glide path preparation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the remaining dentin volume following instrumentation with rotary, reciprocating, and hand files during root canal treatment in primary molars: An ex vivo study
İrem Eren, Berkant Sezer
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2126. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Evaluation of shaping ability of different glide path instruments: a micro-computed tomography study
Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Seda Falakaloğlu, Ali Keleş, Özkan Adıgüzel, Mustafa Gündoğar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
- 2,906 View
- 68 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


