Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
- Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e18. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
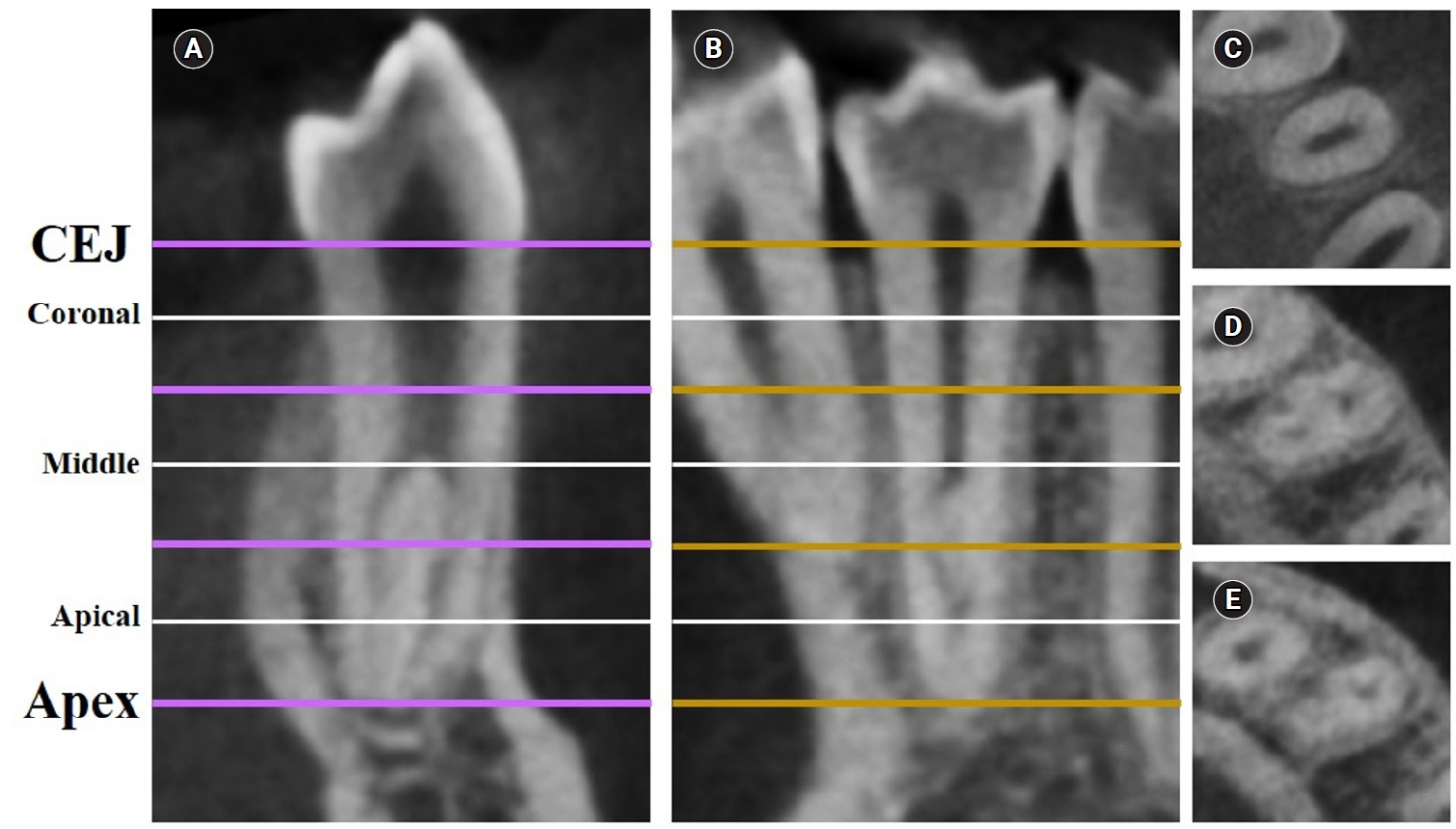
This study aimed to measure the dentin thickness of C-shaped canals in mandibular first and second premolars at coronal, middle, and apical root levels using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
Dentin thicknesses of buccal, lingual, mesial, and distal root walls of 41 C-shaped premolars were measured at three different root levels on axial CBCT slices. The measurements were made at the midpoint of each third, along with 1 mm below and above the midpoint. C-shape configurations of the premolar root canals were also recorded. Analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis, and the independent samples t-tests were used for the comparisons (p = 0.05).
Results
The thickest walls for both premolars were buccal and lingual walls at all three root levels (p < 0.05). The thinnest walls for the first premolar teeth were mesial and distal walls of the lingual canal, while it was the mesial end of the buccal and lingual canals for the second premolars (p < 0.05). Dentin wall thicknesses at the mesial end of buccal and lingual canals of C1-shaped first premolars were thinner than C2-shaped first premolars at the apical level (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Danger zones for C-shaped mandibular first and second premolars are predominantly mesial walls facing the radicular groove and distal wall of the lingual canal. CBCT imaging during endodontic treatment is recommended to avoid complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
- 3,613 View
- 135 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen to the mandibular premolars in an Indian sub-population: a retrospective CBCT analysis
- Komal Sheth, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, James L. Gutmann, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e1. Published online December 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e1
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study assessed the shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen (MF) to mandibular posterior teeth in an Indian sub-population.
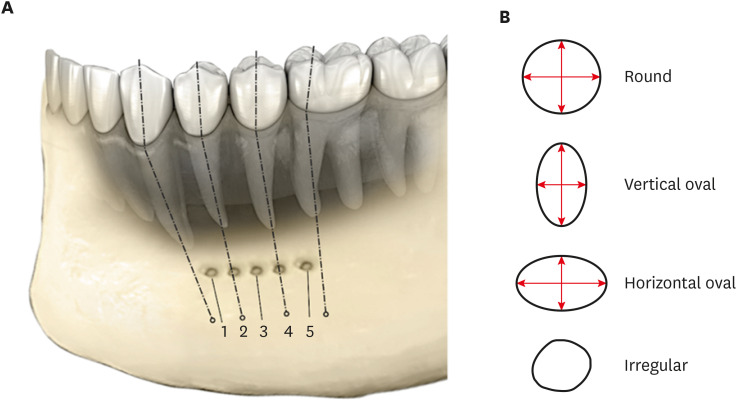
Materials and Methods In total, 475 existing cone-beam computed tomography records exhibiting 950 MFs and including the bilateral presence of mandibular premolars and first molars were assessed. Images were evaluated 3-dimensionally to ascertain the position, shape, and anatomical proximity of MFs to mandibular teeth. The position and shape of MFs were measured and calculated. The Pythagorean theorem was used to calculate the distance between the root apex of the mandibular teeth and the MF.
Results MFs exhibited a predominantly round shape (left: 67% and right: 65%) followed by oval (left: 30% and right: 31%) in both males and females and in different age groups. The root apices of mandibular second premolars (left: 71% and right: 62%) were closest to the MF, followed by distal to the first premolars and mesial to the second premolars. The mean vertical distance between the MF and the nearest tooth apex calculated on sagittal sections was 2.20 mm on the right side and 2.32 mm on the left side; no significant difference was found according to sex or age. The distance between the apices of the teeth and the MF was ≥ 4 mm (left; 4.09 ± 1.27 mm and right; 4.01 ± 1.15 mm).
Conclusions These findings highlight the need for clinicians to be aware of the location of the MF in treatment planning and while performing non-surgical and surgical endodontic procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical and radiographic assessment of variations of the mental foramen and their impact on success of local anaesthesia administration
Isratul Jannat, M. Ummay Salma, Nipu Rani Chowdhury, Kulsum Nahar, Dilruba Binte Mostafa, Khandokar Emanuzzaman Emon, Shahela Sarmin
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2026; 14(3): 823. CrossRef - Clinical Implications of the Localization and Morphological Variability of the Mental Foramen—A Systematic Review
Mariola Krzykawska-Krupska, Janusz Pach, Piotr Regulski, Jacek Tomczyk, Izabela Strużycka, Kazimierz Szopiński, Katarzyna Osipowicz, Anna Pogorzelska
Diagnostics.2026; 16(5): 779. CrossRef - Optimising Treatment Strategies: Labial versus Labio-inferior Plating Using Three-dimensional Miniplates for Mandibular Symphysis and Parasymphysis Fractures
Akash P Muralidharan, Kalyani Bhate, K Mithun Nilgiri, Sumithra S Nair, Lakshmi Shetty, Rose Johnson
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(2): 242. CrossRef - Morphometric analysis of mental foramen in retained cadaveric specimens of mandibles of Sri Lankan population
Dadallage Tharanga De Silva, Usliyanage Clifford Priyantha Perera
Anatomical Science International.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional CBCT Study of Anterior Loop, Accessory Mental Foramen, and Lingual Foramina in Patients’ Mandibles: Implications for Safer Implant Planning
Abbas Shokri, Mohammad Mahdi Maleki, Leili Tapak
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radiographic Recognition of Mental Nerve for Secured Dental Implant Placement by Cone-Beam Computed Tomography in Mosul City Population
Asmaa B. Al-Saffar, Mekdad H. Alrigbo, Rawaa Y. Al-Rawee
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2024; 35(7): 2049. CrossRef - Accuracy of Implant Size Prediction Based on Edentulous Ridge Dimension on Cone-beam Computed Tomography - A Retrospective Study
Hunter R. Jolicoeur, Gerard A. Camargo, Tamara G. Stephenson, Wenjian Zhang
Annals of Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Mental Foramenin Panoramik Radyografi ve Konik Işınlı Bilgisayarlı Tomografi Görüntüleri Üzerinde Morfolojik Analizi
Ezgi UZUN, Burak Kerem APAYDIN, Ayşen TİL
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(3): 540. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Possible Relationship between the Curvature and
Horizontal Course of the Inferior Alveolar Canal
Cansu G. Koca, M. Fatih Çiçek, Sanaz Sadry, Ozan Yenidünya, Fatma Akkoca Kaplan, Aras Erdil
Current Medical Imaging Formerly Current Medical Imaging Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Anatomical and radiographic assessment of variations of the mental foramen and their impact on success of local anaesthesia administration
- 3,052 View
- 51 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


