Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A 3-year retrospective study of clinical durability of bulk-filled resin composite restorations
- Muhittin Ugurlu, Fatmanur Sari
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e5. Published online December 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e5
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to assess the clinical longevity of a bulk-fill resin composite in Class II restorations for 3-year.
Materials and Methods Patient record files acquired from the 40 patients who were treated due to needed 2 similar sizes Class II composite restorations were used for this retrospective study. In the experimental cavity, the flowable resin composite SDR was inserted in the dentinal part as a 4 mm intermediate layer. A 2 mm coverage layer with a nano-hybrid resin composite (CeramX) was placed on SDR. The control restoration was performed by an incremental technique of 2 mm using the nano-hybrid resin composite. The restorations were blindly assessed by 2 calibrated examiners using modified United States Public Health Service criteria at baseline and 1, 2, and 3 years. The data were analyzed using non-parametric tests (
p = 0.05).Results Eighty Class II restorations were evaluated. After 3-years, 4 restorations (5%) failed, 1 SDR + CeramX, and 3 CeramX restorations. The annual failure rate (AFR) of the restorations was 1.7%. The SDR + CeramX group revealed an AFR of 0.8%, and the CeramX group an AFR of 2.5% (
p > 0.05). Regarding anatomical form and marginal adaptation, significant alterations were observed in the CeramX group after 3-years (p < 0.05). The changes in the color match were observed in each group over time (p < 0.05).Conclusions The use of SDR demonstrated good clinical durability in deep Class II resin composite restorations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Bond Strength of Bulk-Fill Resin Repairs: Impact of Surface and Adhesive Protocols
Samuel Eleutério Paiva Sousa, Fiorella Elizabeth Arévalo Tarrillo, Maria Paula Novaes Camargo Manna, Sandra Ribeiro de Barros da Cunha, Maria Ângela Pita Sobral
Odovtos - International Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 1(1): 291. CrossRef - Evaluation of Surface Roughness and Microhardness of New Generation Bulk-Fill Composites
Zehra SÜSGÜN YILDIRIM, Ezgi SONKAYA, Zeliha Gonca BEK KÜRKLÜ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(2): 180. CrossRef - Damping Behaviour and Mechanical Properties of Restorative Materials for Primary Teeth
Thomas Niem, Roland Frankenberger, Stefanie Amend, Bernd Wöstmann, Norbert Krämer
Materials.2022; 15(21): 7698. CrossRef
- Bond Strength of Bulk-Fill Resin Repairs: Impact of Surface and Adhesive Protocols
- 4,008 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

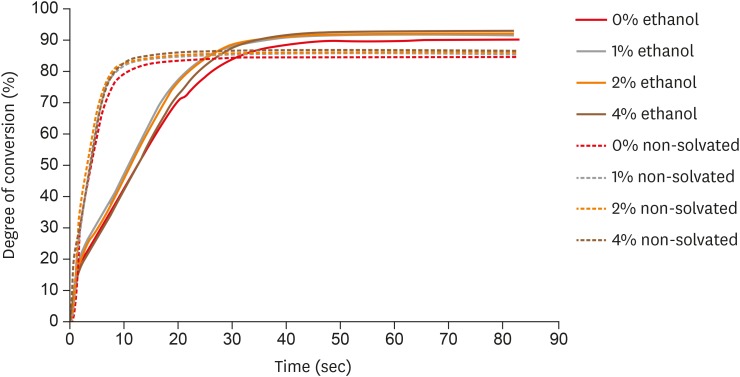
- The influence of nanofillers on the properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives
- Leonardo Bairrada Tavares da Cruz, Marcelo Tavares Oliveira, Cintia Helena Coury Saraceni, Adriano Fonseca Lima
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e28. Published online July 24, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e28
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the influence of different concentrations of nanofillers on the chemical and physical properties of ethanol-solvated and non-solvated dental adhesives.
Materials and Methods Eight experimental adhesives were prepared with different nanofiller concentrations (0, 1, 2, and 4 wt%) and 2 solvent concentrations (0% and 10% ethanol). Several properties of the experimental adhesives were evaluated, such as water sorption and solubility (
n = 5, 20 seconds light activation), real-time degree of conversion (DC;n = 3, 20 and 40 seconds light activation), and stability of cohesive strength at 6 months (CS;n = 20, 20 seconds light activation) using the microtensile test. A light-emitting diode (Bluephase 20i, Ivoclar Vivadent) with an average light emittance of 1,200 mW/cm2 was used.Results The presence of solvent reduced the DC after 20 seconds of curing, but increased the final DC, water sorption, and solubility of the adhesives. Storage in water reduced the strength of the adhesives. The addition of 1 wt% and 2 wt% nanofillers increased the polymerization rate of the adhesives.
Conclusions The presence of nanofillers and ethanol improved the final DC, although the DC of the solvated adhesives at 20 seconds was lower than that of the non-solvated adhesives. The presence of ethanol reduced the strength of the adhesives and increased their water sorption and solubility. However, nanofillers did not affect the water sorption and strength of the tested adhesives.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In Vitro Comparison of Gingival Epithesis Materials: Color Stability, Surface Properties, and Microbial Adhesion After Staining
Ellen Pick, Andrea Gubler, Thomas Attin, Patrick R. Schmidlin
Dentistry Journal.2026; 14(3): 142. CrossRef - Effect of boric acid on the color stability and mechanical properties of 3D-printed permanent resins
Dalndushe Abdulai, Rafat Sasany, Raghib Suradi, Mehran Moghbel, Seyed Ali Mosaddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Boron Nitride-Filled Dental Adhesive System
Senthilguru Kulanthaivel, Jeremiah Poppen, Sandra Ribeiro Cunha, Benjamin Furman, Kyumin Whang, Erica C. Teixeira
Polymers.2023; 15(17): 3512. CrossRef - Analyses of Experimental Dental Adhesives Based on Zirconia/Silver Phosphate Nanoparticles
Abdul Khan, Yasmin Alhamdan, Hala Alibrahim, Khalid Almulhim, Muhammad Nawaz, Syed Ahmed, Khalid Aljuaid, Ijlal Ateeq, Sultan Akhtar, Mohammad Ansari, Intisar Siddiqui
Polymers.2023; 15(12): 2614. CrossRef - Mechanical characterization and adhesive properties of a dental adhesive modified with a polymer antibiotic conjugate
Camila Sabatini, Russell J. Aguilar, Ziwen Zhang, Steven Makowka, Abhishek Kumar, Megan M. Jones, Michelle B. Visser, Mark Swihart, Chong Cheng
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 129: 105153. CrossRef
- In Vitro Comparison of Gingival Epithesis Materials: Color Stability, Surface Properties, and Microbial Adhesion After Staining
- 1,505 View
- 9 Download
- 5 Crossref

- The effect of clinical performance on the survival estimates of direct restorations
- Kyou-Li Kim, Cheol Namgung, Byeong-Hoon Cho
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(1):11-20. Published online February 26, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.1.11
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In most retrospective studies, the clinical performance of restorations had not been considered in survival analysis. This study investigated the effect of including the clinically unacceptable cases according to modified United States Public Health Service (USPHS) criteria into the failed data on the survival analysis of direct restorations as to the longevity and prognostic variables.
Materials and Methods Nine hundred and sixty-seven direct restorations were evaluated. The data of 204 retreated restorations were collected from the records, and clinical performance of 763 restorations in function was evaluated according to modified USPHS criteria by two observers. The longevity and prognostic variables of the restorations were compared with a factor of involving clinically unacceptable cases into the failures using Kaplan-Meier survival analysis and Cox proportional hazard model.
Results The median survival times of amalgam, composite resin and glass ionomer were 11.8, 11.0 and 6.8 years, respectively. Glass ionomer showed significantly lower longevity than composite resin and amalgam. When clinically unacceptable restorations were included into the failure, the median survival times of them decreased to 8.9, 9.7 and 6.4 years, respectively.
Conclusions After considering the clinical performance, composite resin was the only material that showed a difference in the longevity (
p < 0.05) and the significantly higher relative risk of student group than professor group disappeared in operator groups. Even in the design of retrospective study, clinical evaluation needs to be included.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Decision‐Making of Repair vs. Replacement of Defective Direct Dental Restorations: A Multinational Cross‐Sectional Study With Meta‐Analysis
Ömer Hatipoğlu, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Nessrin Taha, Thiyezen Abdullah Aldhelai, Daoud M. Ayyad, Ahmed A. Madfa, Benjamin Martin‐Biedma, Rafael Fernández‐Grisales, Bakhyt A. Omarova, Wen Yi Lim, Suha Alfirjani, Kacper Nijak
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(4): 977. CrossRef - Clinical Performance of Lithium Disilicate Ceramic Veneers Cemented With Light-Cured Resin Cements: An Observational Study
Nguyen Thi Minh Hien, Tran Hung Lam, Do Thi Thao, Hoang Viet
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Failure Risk of Composite Resin and Amalgam Restorations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Woroud Al-Sulimmani, Asmaa Al-Rasheed, Hebah Al-Daraan, Muna Al-Mutairi, Yash Brahmbhatt, Hesham Al-Hazmi, Hend Al-Qaderi
International Dental Journal.2025; 75(4): 100871. CrossRef - The Effect of Polishing on the Clinical Performance of Amalgam Restorations Using the Mahler’s Scale and Modified United States Public Health Service Criteria: A Prospective Clinical Study
Soham Suraj Wadke, Dipali Y. Shah
Journal of Indian Association of Public Health Dentistry.2025; 23(3): 282. CrossRef - Navigating the practical-knowledge gap in deep margin elevation: A step towards a structured case selection – a review
Eman H. Ismail, Saba S. Ghazal, Rahaf D. Alshehri, Hajar N. Albisher, Rana S. Albishri, Abdulrahman A. Balhaddad
The Saudi Dental Journal.2024; 36(5): 674. CrossRef - A review of dental antibacterial agents and antibacterial modification of composite resins and dentin adhesives
Hojin Moon
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2024; 51(4): 189. CrossRef - Er:YAG laser in selective caries removal and dentin treatment with chitosan: a randomized clinical trial in primary molars
Rai Matheus Carvalho Santos, Renata Siqueira Scatolin, Sérgio Luiz de Souza Salvador, Aline Evangelista Souza-Gabriel, Silmara Aparecida Milori Corona
Lasers in Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Longevity of composite restorations is definitely not only about materials
Flávio Fernando Demarco, Maximiliano Sergio Cenci, Anelise Fernandes Montagner, Verônica Pereira de Lima, Marcos Britto Correa, Rafael R. Moraes, Niek J.M. Opdam
Dental Materials.2023; 39(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of different adhesive systems on dental defects and sensitivity to teeth in composite resin restoration: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Keda Fang, Kenan Chen, Mengqi Shi, Liang Wang
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(6): 2495. CrossRef - Survival of direct resin composite onlays and indirect tooth-coloured adhesive onlays in posterior teeth: a systematic review
Colin E. McGrath, Stephen J. Bonsor
British Dental Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A 2-year clinical evaluation of direct and semi-direct resin composite restorations in non-carious cervical lesions: a randomized clinical study
Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele, Laura Célia Fernandes Meirelles, Rafael Santos Rocha, Lucélia Lemes Gonçalves, Daniele Mara Silva Ávila, Sérgio Eduardo de Paiva Gonçalves, Eduardo Bresciani
Clinical Oral Investigations.2020; 24(3): 1321. CrossRef - Treatment options for large posterior restorations: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Bruna M. Vetromilla, Niek J. Opdam, Ferdinan L. Leida, Rafael Sarkis-Onofre, Flavio F. Demarco, Mark P.J. van der Loo, Maximiliano S. Cenci, Tatiana Pereira-Cenci
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2020; 151(8): 614. CrossRef - Effect of a novel prime‐and‐rinse approach on short‐ and long‐term dentin bond strength of self‐etch adhesives
Mingxing Li, Jingqiu Xu, Ling Zhang, Chaoyang Wang, Xiaoting Jin, Yan Hong, Baiping Fu, Matthias Hannig
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2019; 127(6): 547. CrossRef - Longevity of resin-bonded fixed partial dental prostheses made with metal alloys
Naomi Tanoue
Clinical Oral Investigations.2016; 20(6): 1329. CrossRef - Amalgam vs Composite Restoration, Survival, and Secondary Caries
Muhanad Alhareky, Mary Tavares
Journal of Evidence Based Dental Practice.2016; 16(2): 107. CrossRef - Seal, replacement or monitoring amalgam restorations with occlusal marginal defects? Results of a 10-year clinical trial
G. Moncada, E. Fernández, K. Mena, J. Martin, P. Vildósola, O.B. De Oliveira, J. Estay, I.A. Mjör, V.V. Gordan
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(11): 1371. CrossRef - Longitudinal Results of a 10-year Clinical Trial of Repair of Amalgam Restorations
G Moncada, P Vildósola, E Fernández, J Estay, OB de Oliveira Júnior, MF de Andrade, J Martin, IA Mjör, VV Gordan
Operative Dentistry.2015; 40(1): 34. CrossRef - Amalgam and resin composite longevity of posterior restorations: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Vittorio Moraschini, Cheung Ka Fai, Raphael Monte Alto, Gustavo Oliveira dos Santos
Journal of Dentistry.2015; 43(9): 1043. CrossRef - Aumento de longevidad de restauraciones de resinas compuestas y de su unión adhesiva. Revisión de tema
Gustavo Moncada, Patricio Vildósola, Eduardo Fernandez, Juan Estay, Osmir B de Oliveira Junior, Javier Martin
Revista Facultad de Odontología.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparison of resin-modified glass-ionomer and resin composite polymerisation shrinkage stress in a wet environment
Joshua J. Cheetham, Joseph E.A. Palamara, Martin J. Tyas, Michael F. Burrow
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2014; 29: 33. CrossRef - Factors affecting the placement or replacement of direct restorations in a dental school
Samara Silvani, Roberta Ferreira Trivelato, Ruchele Dias Nogueira, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo-Martins
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2014; 5(1): 54. CrossRef
- Clinical Decision‐Making of Repair vs. Replacement of Defective Direct Dental Restorations: A Multinational Cross‐Sectional Study With Meta‐Analysis
- 1,685 View
- 4 Download
- 21 Crossref

- The evaluation of clinical efficacy and longevity of home bleaching without combined application of In-office bleaching
- Byunk-Gyu Shin, Sung-Eun Yang
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):387-394. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.387
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the whitening efficacy and longevity of home bleaching.
Materials and Methods A total of 28 patients were divided into either experimental group (Opalescence F; 15% carbamide peroxide) or control group randomly. The patients in experimental group were instructed to wear individual trays applied with bleaching gel for 2 hours a day for 4 weeks. Any treatments weren't applied to the patients in control group. The color measurements of central incisors, lateral incisors & canines of upper and lower arch were recorded at base line, immediately after the finishment of treatmemt (4 weeks), 8 weeks and 12 weeks using Colorimeter (Chroma Meter, 2600d Konica Minolta co.) and Vitapan classical shade guide (Vita Zahnfabrik).
Results A significantly stronger color change was observed for overall teeth samples in experimental group immediately after treatment (at 4 weeks) compared to ones in control group (
p < 0.05). There was also a significant difference between baseline and 8 weeks or 12 weeks separately though color rebouncing phenomenon occurred as time went by (p < 0.05).Conclusions The clinical effecacy and longevity of home bleaching without combined application of in-office bleaching was observed through this experiment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of at-home bleaching agents and concentrations on tooth sensitivity: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Renata Maria Oleniki Terra, Michael Willian Favoreto, Tom Morris, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105891. CrossRef - Effect of at-home agents and concentrations on bleaching efficacy: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Renata Maria Oleniki Terra, Michael Willian Favoreto, Tom Morris, Alessandro D. Loguercio, Alessandra Reis
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 160: 105857. CrossRef - Effects of Citrus limon Extract on Oxidative Stress-Induced Nitric Oxide Generation and Bovine Teeth Bleaching
Soon-Jeong Jeong
Journal of Dental Hygiene Science.2021; 21(2): 96. CrossRef - Efficacy of a self - applied paint - on whitening gel combined with wrap
Soo-Yeon Kim, Jae-Hyun Ahn, Ji-Young Kim, Jin-Woo Kim, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2018; 34(3): 175. CrossRef - Home-based chemically-induced whitening (bleaching) of teeth in adults
Prashanti Eachempati, Sumanth Kumbargere Nagraj, Salian Kiran Kumar Krishanappa, Puneet Gupta, Ibrahim Ethem Yaylali
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of preference drinks on tooth color reduction after tooth bleaching: A 12-momth follow-up study
Hyo Jin Goo, Min Jeong Cho, Yun Sook Jung, Ji Hye Kim, Fan Dong, Keun Bae Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2016; 40(1): 55. CrossRef - Tooth color reduction and consequent patient satisfaction after office and home bleaching: a 6-month follow-up study
Hyo-Jin Goo, Hyeon-Sook Kwun, Jeong-Hee Park, Min-Jeong Cho, Eun-Kyong Kim, Youn-Hee Choi, Keun-Bae Song
Journal of Korean Academy of Oral Health.2015; 39(1): 3. CrossRef
- Effect of at-home bleaching agents and concentrations on tooth sensitivity: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
- 1,214 View
- 2 Download
- 7 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


