Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Microleakage and characteristics of resin-tooth tissues interface of a self-etch and an etch-and-rinse adhesive systems
- Xuan Vinh Tran, Khanh Quang Tran
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e30. Published online May 18, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e30
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to compare the microleakage and characteristics of the resin-tooth tissue interface between self-etch and etch-and-rinse adhesive systems after 48 hours and 3 months.
Materials and Methods 40 extracted premolar teeth were randomly divided into 2 groups: 1-step self-etch adhesive system – Optibond™ All-In-One, and 2-step etch-and-rinse adhesive system - Adper™ Single Bond 2. Both groups were subjected to 500 thermocycles (5°C–55°C) before scanning electron microscope (SEM) analysis or microleakage trial at 48-hour and 3-month time periods.
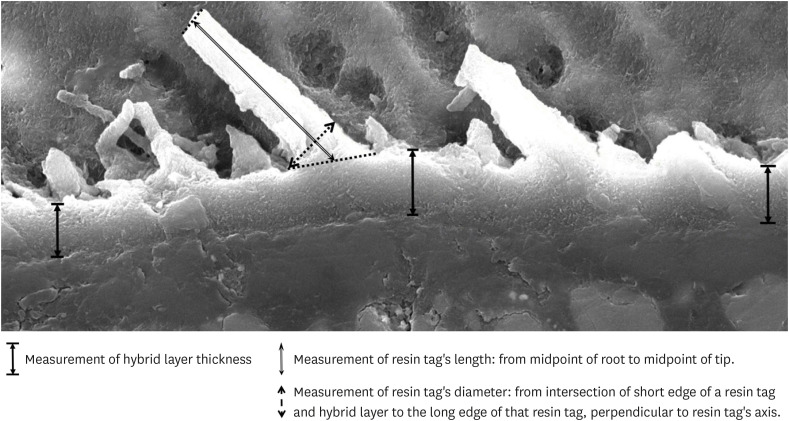
Results SEM images showed the hybrid layer thickness, diameter, and length of resin tags of the self-etch adhesive (0.42 ± 0.14 µm; 1.49 ± 0.45 µm; 16.35 ± 14.26 µm) were smaller than those of the etch-and-rinse adhesive (4.39 ± 1.52 µm; 3.49 ± 1 µm; 52.81 ± 35.81 µm). In dentin, the microleakage scores of the 2 adhesives were not different in both time periods (48 hours/3 months). However, the microleakage score of etch-and-rinse adhesive increased significantly after 3 months (0.8 ± 0.63 and 1.9 ± 0.88,
p < 0.05).Conclusions The self-etch adhesive exhibited better long-term sealing ability in dentin when compared to that of the etch-and-rinse adhesive. The greater hybrid layer thickness and dimensions of resin tags did not guarantee reliable, long-lasting sealing in the bonding area.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic review of shear bond strength of sixth- and fourth-generation adhesives in primary teeth
Maryam Hajiahmadi, Najmeh Akhlaghi, Hamid Mosleh, Ehsan Samani, Sheida Bagheri, Zohreh Salehi
Dental Research Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of different adhesive systems in bonding direct resin composite restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Ravinder S. Saini, Rajesh Vyas, Sunil Kumar Vaddamanu, Syed Altafuddin Quadri, Seyed Ali Mosaddad, Artak Heboyan
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2025; 26(2): 115. CrossRef - Characterisation of universal adhesive bonded resin-dentin interface after focused ultrasound smear layer conditioning
Cheryl Fu, Peta L. Clode, Amr S. Fawzy
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2025; 142: 104115. CrossRef - Effect of Dentin Pretreatment With Dimethyl Sulfoxide Solution on Interfacial Fracture Toughness of Composite Resin to Wet and Dry Dentin
Fatemeh Molaei, Mehrsima Ghavami-Lahiji, Seyedeh Maryam Tavangar, Hannah Wesley
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Resin tags formation by modified Renewal MI formulations in a carious dentine model
Nabih Alkhouri, Wendy Xia, Paul Ashley, Anne Young
Frontiers in Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of propolis added to single‐bottle adhesives on water permeation through the hybrid layer
Lucineide Silva da Rocha, Daniela Ferreira de Oliveira, Cinthya Luna Veloso de Lima, Ticiano Gomes do Nascimento, Johnnatan Duarte de Freitas, Jeniffer Mclaine Duarte de Freitas, Isabel Cristina Celerino de Moraes Porto
European Journal of Oral Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exploration and preliminary clinical investigation of an adhesive approach for primary tooth restoration
Xiangqin Xu, Jiansheng Zhu, May Lei Mei, Huaying Wu, Kaipeng Xie, Shoulin Wang, Yaming Chen
The Journal of Biomedical Research.2023; 37(2): 138. CrossRef - Adhesion to enamel and dentine: an update
Rana Alkattan
Primary Dental Journal.2023; 12(3): 33. CrossRef - Effects of carbodiimide combined with ethanol–wet bonding pretreatment on dentin bonding properties: an in vitro study
Xiaoxiao You, Long Chen, Jie Xu, Sihui Li, Zhenghao Zhang, Ling Guo
PeerJ.2022; 10: e14238. CrossRef - The effects of amalgam contamination and different surface modifications on microleakage of dentin bonded to bulk fill composite when using different adhesive protocols
Nojoud Alshehri, Abdullah Aljamhan, Mohammed Bin-Shuwaish
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of low-shrinkage dental adhesives via blending with spiroorthocarbonate expanding monomer and unsaturated epoxy resin monomer
Zonghua Wang, Xiaoran Zhang, Shuo Yao, Jiaxin Zhao, Chuanjian Zhou, Junling Wu
Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials.2022; 133: 105308. CrossRef - Influence of silver nanoparticles on the resin-dentin bond strength and antibacterial activity of a self-etch adhesive system
Jia Wang, Wei Jiang, Jingping Liang, Shujun Ran
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2022; 128(6): 1363.e1. CrossRef
- A systematic review of shear bond strength of sixth- and fourth-generation adhesives in primary teeth
- 2,659 View
- 41 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


