Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
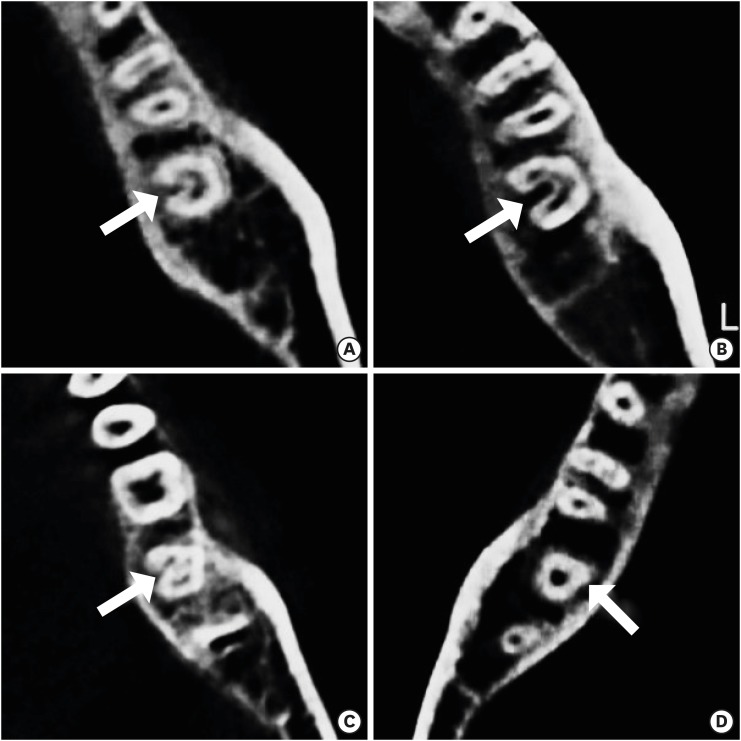
- C-shaped root canals of mandibular second molars in a Korean population: a CBCT analysis
- Hee-Sun Kim, Daun Jung, Ho Lee, Yoon-Sic Han, Sohee Oh, Hye-Young Sim
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e42. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the C-shaped root canal anatomy of mandibular second molars in a Korean population.
Materials and Methods A total of 542 teeth were evaluated using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). The canal shapes were classified according to a modified version of Melton's method at the level where the pulp chamber floor became discernible.
Results Of the 542 mandibular second molars, 215 (39.8%) had C-shaped canals, 330 (53%) had 3 canals, 17 (3.3%) had 2 canals, 12 (2.2%) had 4 canals, and 8 (1.7%) had 1 canal. The prevalence of C-shaped canals was 47.8% in females and 28.4% in males. Seventy-seven percent of the C-shaped canals showed a bilateral appearance. The prevalence of C-shaped canals showed no difference according to age or tooth position. Most teeth with a C-shaped canal system presented Melton's type II (45.6%) and type III (32.1%) configurations.
Conclusions There was a high prevalence of C-shaped canals in the mandibular second molars of the Korean population studied. CBCT is expected to be useful for endodontic diagnosis and treatment planning of mandibular second molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A cone-beam computed tomography-based morphometric comparison of mandibular molars between Han Chinese and Malays
Jacob John, Wei Cheong Ngeow, Ting-Chun Shen, Lih-Jyh Fuh, Phrabhakaran Nambiar, Yen-Wen Shen, Jui-Ting Hsu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2026; 21(1): 265. CrossRef - Prevalence of C‐Shaped Canals in Maxillary Molars in an Iranian Population: A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Analysis
Amin Salem Milani, Shahin Namvar Asl Amirkhizi, Tahmineh Razi, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Pouya Sabanik, Nikhat Kaura
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of mandibular and maxillary second molar root canal anatomy in a Turkish subpopulation using CBCT: comparison of Briseno-Marroquin and Vertucci classifications
Hüseyin Gürkan Güneç, İpek Öreroğlu, Kemal Çağlar, Kader Cesur Aydin
BMC Medical Imaging.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2025; 50(2): e18. CrossRef - Prevalence of c-shaped canal morphology in premolar and molar teeth assessed by cone-beam computed tomography: systematic review and meta-analysis
Faezeh Yousefi, Younes Mohammadi, Elham Shokri
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging Findings of Clinical Significance in Endodontics During Cone Beam Computed Tomography Scanning of the Upper Airway—The Anterior, Bilateral, C-Shaped, Dual of Mandibular Root Canals: A Brief Case Report
Edgar García-Torres, Diana Laura Grissel Guerrero-Falcón, Hugo Alejandro Bojórquez-Armenta, Oscar Eduardo Almeda-Ojeda, Víctor Hiram Barajas-Pérez, Luis Javier Solís-Martínez
Diagnostics.2025; 15(24): 3157. CrossRef - Frequency of C-Shaped Root Canals in Permanent Mandibular Second Molars in a Sample of Pakistani Population using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Syed Nabeel Ahmed, Muhammad Mansoor Majeed, Sakina Kazmi, Muhammad Omar Ansari
Pakistan Journal of Health Sciences.2024; : 109. CrossRef - ANÁLISE DAS VARIAÇÕES ANATÔMICAS DE CANAIS C-SHAPED NOS MOLARES INFERIORES: UMA REVISÃO INTEGRATIVA DA LITERATURA
Larissa Eulália Pereira, Thayana Karla Guerra Lira dos Santos
Revista Contemporânea.2024; 4(5): e4264. CrossRef - External Validation of the Effect of the Combined Use of Object Detection for the Classification of the C-Shaped Canal Configuration of the Mandibular Second Molar in Panoramic Radiographs: A Multicenter Study
Sujin Yang, Kee-Deog Kim, Yoshitaka Kise, Michihito Nozawa, Mizuho Mori, Natsuho Takata, Akitoshi Katsumata, Yoshiko Ariji, Wonse Park, Eiichiro Ariji
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 627. CrossRef - A Cone‐Beam Computed Tomography Evaluation of C‐Shaped Canal Configuration in Maxillary Molars Among an Iranian Population
Nafiseh Nikkerdar, Mohammad Moslehi, Amin Golshah, Mario Dioguardi
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Root and canal morphology of mandibular second molars in an Egyptian subpopulation: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Shehabeldin Mohamed Saber, Mohammed abou El Seoud, Shaimaa Mohamed Abu el Sadat, Nawar Naguib Nawar
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive evaluation of root and root canal morphology of mandibular second molars in a Saudi subpopulation evaluated by cone-beam computed tomography
Moazzy I. Almansour, Saad M. Al‑Zubaidi, Abdulmjeed S. Enizy, Ahmed A. Madfa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of C-Shaped Canal Morphology in Mandibular and Maxillary Second Molars in an Iraqi Subpopulation Using Cone-Beam Computed Tomography
Kazhan Abdalrahman, Ranjdar Talabani, Sara Kazzaz, Dlsoz Babarasul, Berndt Koslowski
Scanning.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomography evaluation of C-shaped root canal system in mandibular second molars in kuwaiti sub-population
AbdullahJassim Alenezi, Saad Al-Nazhan, Nassr Al-Maflehi, MazenA Aldosimani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2022; 12(3): 283. CrossRef - Prevalence and morphology of C‐shaped and non‐C‐shaped root canal systems in mandibular second molars
T Fenelon, P Parashos
Australian Dental Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of C-shaped canals in mandibular second molars of a selected patient group using cone beam computed tomography: prevalence, configuration and radicular groove types
Sema Sönmez Kaplan, Tuna Kaplan, Güzide Pelin Sezgin
Odontology.2021; 109(4): 949. CrossRef - Prevalência estimada de canais “C- Shaped”: Uma revisão sistemática e meta-análise
Natália Pereira da Silva Falcão, Sandro Junio de Oliveira Tavares, Ludmila Silva Guimarães, Katherine Azevedo Batistela Rodrigues Thuller, Leonardo dos Santos Antunes, Estefano Borgo Sarmento, Fellipe Navarro Azevedo de Azevedo, Cinthya Cristina Gomes, Ca
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2020; : 91. CrossRef - Preferred Reporting Items for Epidemiologic Cross-sectional Studies on Root and Root Canal Anatomy Using Cone-beam Computed Tomographic Technology: A Systematized Assessment
Jorge N.R. Martins, Anil Kishen, Duarte Marques, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, João Caramês, António Mata, Marco A. Versiani
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(7): 915. CrossRef - Clinical and radiological assessment of the anatomical and topographic structure of the root canals of teeth in patients of different age groups
N.B. Petrukhina, O.A. Zorina, O.A. Boriskina, I.S. Berkutova, V.A. Venediktova, R.R. Saltovets
Stomatologiya.2020; 99(5): 32. CrossRef
- A cone-beam computed tomography-based morphometric comparison of mandibular molars between Han Chinese and Malays
- 2,354 View
- 13 Download
- 20 Crossref

- The effect of different fluoride application methods on the remineralization of initial carious lesions
- Seon Mi Byeon, Min Ho Lee, Tae Sung Bae
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(2):121-129. Published online May 10, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.2.121
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the effect of single and combined applications of fluoride on the amount of fluoride release, and the remineralization and physical properties of enamel.
Materials and Methods Each of four fluoride varnish and gel products (Fluor Protector, FP, Ivoclar Vivadent; Tooth Mousse Plus, TM, GC; 60 Second Gel, A, Germiphene; CavityShield, CS, 3M ESPE) and two fluoride solutions (2% sodium fluoride, N; 8% tin(ii) fluoride, S) were applied on bovine teeth using single and combined methods (10 per group), and then the amount of fluoride release was measured for 4 wk. The electron probe microanalysis and the Vickers microhardness measurements were conducted to assess the effect of fluoride application on the surface properties of bovine teeth.
Results The amount of fluoride release was higher in combined applications than in single application (
p < 0.05). Microhardness values were higher after combined applications of N with FP, TM, and CS than single application of them, and these values were also higher after combined applications of S than single application of A (p < 0.05). Ca and P values were higher in combined applications of N with TM and CS than single application of them (p < 0.05). They were also increased after combined applications of the S with A than after single application (p < 0.05).Conclusions Combined applications of fluoride could be used as a basis to design more effective methods of fluoride application to provide enhanced remineralization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
Soumyashri Das, Mansi Jain, HP Suma Sogi, Sonali Sukesh K, Apurva Gambhir, FNU Gagandeep
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2025; 18(11): 1365. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of ozone gel on the initial carious lesions
Maha A. Alsharqawy, Wedad M Etman, Mirvat M Salama, Reda G. Saleh
Tanta Dental Journal.2023; 20(3): 203. CrossRef - Evaluation of Remineralization Potential of Natural Substances on Artificially Induced Carious Lesions in Primary Teeth: An In Vitro Study
Kavitha Ramar, Pooja V Ravi, Rajakumar Sekar
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(2): 244. CrossRef - Upaya Preventif Kesehatan Gigi dan Mulut dengan Aplikasi Fluor pada Gigi Siswa SMPN 77 Jakarta
Agus Ardinansyah, Mochammad Atmaji Windrianto, Nur Hidayati Nosi Prastiyani
Info Abdi Cendekia.2023; 6(2): 74. CrossRef - Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Enamelast® and Fluor defender® fluoride varnishes against Streptococcus mutans biofilm: an in vitro study in primary teeth
M. A. Matar, S. S. Darwish, R. S. Salma, W. A. Lotfy
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2023; 24(5): 549. CrossRef - In-vitro evaluation of the anti-cariogenic effect of a hybrid coating associated with encapsulated sodium fluoride and stannous chloride in nanoclays on enamel
Sávio José Cardoso BEZERRA, Ítallo Emídio Lira VIANA, Idalina Vieira AOKI, Simone DUARTE, Anderson Takeo HARA, Taís SCARAMUCCI
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Salivary Fluoride Concentration after Topical Application of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Sodium Fluoride: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nidhi Agarwal, V Vishnu Priya, Zohra Jabin, Iffat Nasim
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2022; 15(3): 371. CrossRef - Release and Recharge of Fluoride Ions from Acrylic Resin Modified with Bioactive Glass
Zbigniew Raszewski, Danuta Nowakowska, Wlodzimierz Wieckiewicz, Agnieszka Nowakowska-Toporowska
Polymers.2021; 13(7): 1054. CrossRef - Enamel remineralisation-inducing materials for caries prevention
Sri Kunarti, Widya Saraswati, Dur Muhammad Lashari, Nadhifa Salma, Tasya Nafatila
Dental Journal.2021; 54(3): 165. CrossRef - Fluoride Concentration in Saliva following Professional Topical Application of 2% Sodium Fluoride Solution
Manjit Talwar, Amrit Tewari, H. S. Chawla, Vinod Sachdev, Suresh Sharma
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2019; 10(3): 423. CrossRef - Clinical and laboratory evaluation of the Elgydium Protection caries toothpaste effectiveness in patients with high intensity of dental caries
O. A. Zorina, N. B. Petruhina, A. Z. M, O. A. Boriskina, A. A. Tupicin, V. A. Prohodnaja
Stomatologiya.2019; 98(3): 21. CrossRef - Bleaching of simulated stained-remineralized caries lesions in vitro
Sarah S. Al-Angari, Frank Lippert, Jeffrey A. Platt, George J. Eckert, Carlos González-Cabezas, Yiming Li, Anderson T. Hara
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(4): 1785. CrossRef - Short-Time Antibacterial Effects of Dimethylaminododecyl Methacrylate on Oral Multispecies Biofilm In Vitro
Yujie Zhou, Suping Wang, Xuedong Zhou, Yiran Zou, Mingyun Li, Xian Peng, Biao Ren, Hockin H. K. Xu, Michael D. Weir, Lei Cheng, Yu Chen, Qi Han
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the Application of Different Fluoride Supplements on Enamel Demineralization Adjacent to Orthodontic Brackets: An In Vitro Study
Arman Mohammadi Shayan, Monireh Rassouli, Soodabeh Kimyai, Hadi Valizadeh, Mohammad Hossein Ahangar Atashi, Sahand Rikhtegaran
Iranian Journal of Orthodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of nicomethanol hydrofluoride on dental enamel and synthetic apatites: a role for anti-caries protection
N. Sharkov
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2017; 18(6): 411. CrossRef - Intérêt prophylactique et thérapeutique des chewing-gums sans sucre en orthodontie. Une étude menée auprès de professionnels de santé et de patients
Pauline Ferney, François Clauss, Damien Offner, Delphine Wagner
L'Orthodontie Française.2017; 88(3): 275. CrossRef - Silver Diamine Fluoride Has Efficacy in Controlling Caries Progression in Primary Teeth: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ana Cláudia Chibinski, Letícia Maíra Wambier, Juliana Feltrin, Alessandro Dourado Loguercio, Denise Stadler Wambier, Alessandra Reis
Caries Research.2017; 51(5): 527. CrossRef - Dental Caries Management of a Patient with a High Caries Risk Based on the Caries Risk Assessment: a Case Peport
Dong-Hyun Lee, Sung-Ok Hong, Seok-Ryun Lee
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(3): 231. CrossRef
- Effect of Different Topical Fluorides on the Microhardness of Bleached Enamel: In Vitro Study
- 2,250 View
- 13 Download
- 18 Crossref

- Evaluation of apical canal shapes produced sequentially during instrumentation with stainless steel hand and Ni-Ti rotary instruments using Micro-computed tomography
- Woo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Ho Lee, Kyung-A Chun, Min-Seock Seo, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(3):231-237. Published online May 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.3.231
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the optimal master apical file size with minimal transportation and optimal efficiency in removing infected dentin. We evaluated the transportation of the canal center and the change in untouched areas after sequential preparation with a #25 to #40 file using 3 different instruments: stainless steel K-type (SS K-file) hand file, ProFile and LightSpeed using microcomputed tomography (MCT).
Materials and Methods Thirty extracted human mandibular molars with separated orifices and apical foramens on mesial canals were used. Teeth were randomly divided into three groups: SS K-file, Profile, LightSpeed and the root canals were instrumented using corresponding instruments from #20 to #40. All teeth were scanned with MCT before and after instrumentation. Cross section images were used to evaluate canal transportation and untouched area at 1- , 2- , 3- , and 5- mm level from the apex. Data were statistically analyzed according to' repeated nested design'and Mann-Whitney test (
p = 0.05).Results In SS K-file group, canal transportation was significantly increased over #30 instrument. In the ProFile group, canal transportation was significantly increased after preparation with the #40 instrument at the 1- and 2- mm levels. LightSpeed group showed better centering ability than ProFile group after preparation with the #40 instrument at the 1 and 2 mm levels.
Conclusions SS K-file, Profile, and LightSpeed showed differences in the degree of apical transportation depending on the size of the master apical file.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the shaping abilities of three nickel–titanium instrumentation systems using micro-computed tomography
Jin Yi Baek, Hyun Mi Yoo, Dong Sung Park, Tae Seok Oh, Kee Yeon Kum, Seung Yun Shin, Seok Woo Chang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2014; 9(2): 111. CrossRef
- Comparison of the shaping abilities of three nickel–titanium instrumentation systems using micro-computed tomography
- 1,075 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
- Jeong-Ho Lee, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(3):222-228. Published online May 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.3.222
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA; Dentsply, Tulsa Dental, Tulsa, OK, USA), which is widely used as root-end filling material, with DiaRoot BioAggregate (DB; Innovative BioCaramix Inc, Vancouver, BC, Canada), newly developed product, by using MG63 osteoblast-like cells. MTA, DB, and Intermediate Restorative Material (IRM; Dentsply Caulk, Milford, DE, USA) were used for root-end filling material while tissue culture plastic was used for control group. Each material was mixed and, the mixtures were left to set for 24 hours. MG63 cells were seeded to each group and then they were cultured for attachment for 4 hours. Following the attachment of cells to the root-end filling material, early cellular response was observed. After another 12 hours'culture, the level of attachment between cells and material was observed and in order to identify the effect of each material to bone formation, transforming growth factor beta1 (TGFβ1) and osteocalin (OC) were estimated by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), and the amount of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) was also measured. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA. As a result, only at OC and the number of cells which were attached to materials, there was no statistical difference between MTA and DB. At other items, there was statistically significant difference in all groups. Although DB has not shown exactly the same cellular response like that of MTA, the number of attached cells shows that biocompatibility of the material and OC indicates bone formation rate. Therefore, if DB is used for root end filling material, it is expected to lead to similar results to MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef - Bone regeneration in a periodontally challenged hopeless tooth
Jammula Surya Prasanna, Parupalli Karunakar, Dasari Rajashree, Raji V. Solomon
Journal of Dr. NTR University of Health Sciences.2013; 2(4): 296. CrossRef
- Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
- 1,364 View
- 1 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Evaluation of canal preparation with Ni-Ti rotary files by micro computed tomography
- Jeong-Ho Lee, Mi-Ja Kim, Chang-In Seok, Woo-Cheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(4):378-385. Published online July 31, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.4.378
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to compare the effects of preparation with GT files and profiles .04 in shaping of root canals and reconstruct the three-dimensional root canal system using micro computed tomography.
40 canals of the extracted human mandibular molars were used, and randomly distributed into two experimental groups. In group 1, canals were prepared by GT files. In group 2, Profiles .04. were used. Apical preparation size was #30.
For each tooth pre and post operative cross-sectional images were obtained by the micro CT at 50 micron intervals. Pre and post operative cross-sectional images of 1, 2, 3, 5, and 8mm from the apex were compared. For each section, canal area and centering ratio were determined. For each tooth pre- and post-operative root canal volume from the furcation to the apex of the roots was calculated by three-dimensional image software. Following results were obtained:
1. At 8mm from the apex, area of dentin removed by GT rotary file was significantly larger than that by Profile .04. And at the other levels there was not a significant difference.
2. There was a trend for GT rotary file to remain more centered in the canals than Profile .04 at all levels. But at 3mm level, there was a statistically significant difference.
3. In root canal volume increments after instrumentation, there was no significant difference between two groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of apical canal shapes produced sequentially during instrumentation with stainless steel hand and Ni-Ti rotary instruments using Micro-computed tomography
Woo-Jin Lee, Jeong-Ho Lee, Kyung-A Chun, Min-Seock Seo, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 231. CrossRef - Comparative study on morphology of cross-section and cyclic fatigue test with different rotary NiTi files and handling methods
Jae-Gwan Kim, Kee-Yeon Kum, Eui-Seong Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2006; 31(2): 96. CrossRef
- Evaluation of apical canal shapes produced sequentially during instrumentation with stainless steel hand and Ni-Ti rotary instruments using Micro-computed tomography
- 1,405 View
- 4 Download
- 2 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


