Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
- Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e22. Published online March 5, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
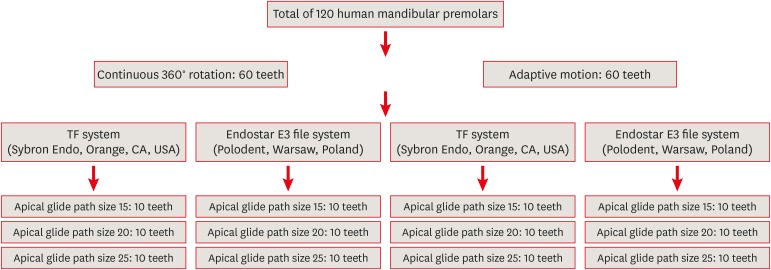
ePub Objectives This study investigated the influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on the time to reach the working length and the fracture resistance of Twisted File (TF) and Endostar E3 files.
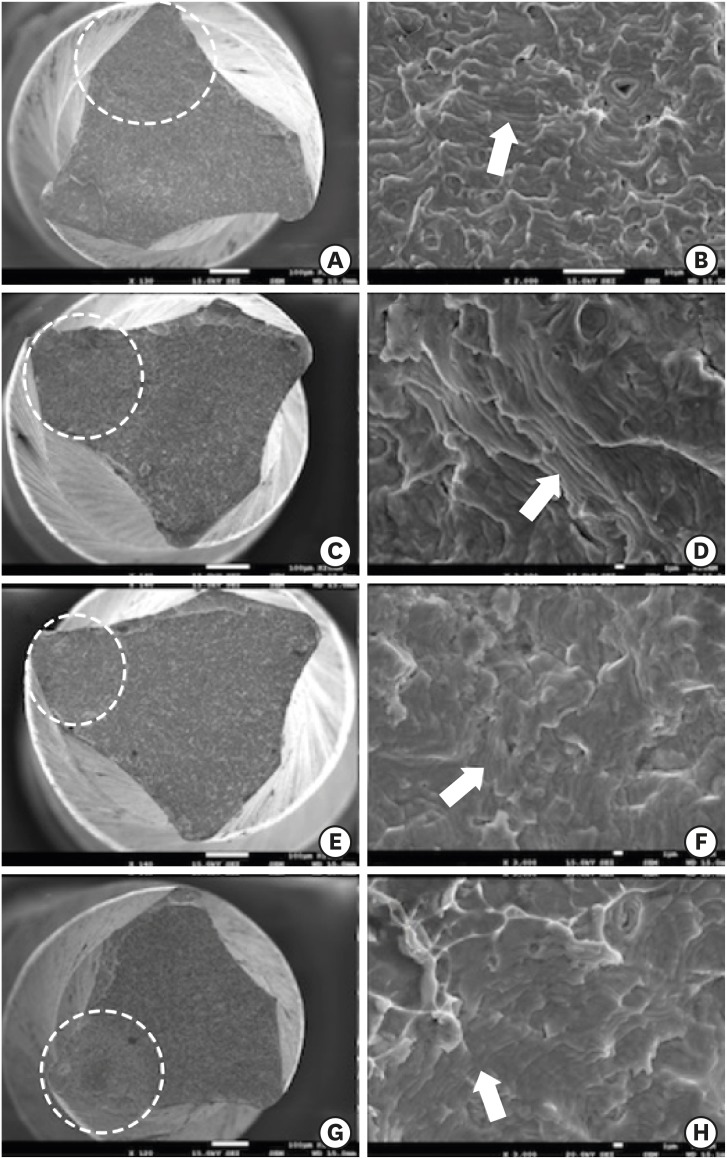
Materials and Methods A total of 120 mandibular single-rooted premolars were selected. Two methods of kinetic motion (TF adaptive and continuous rotary motion) and file systems (TF and Endostar E3) were employed. The files were used in root canals prepared to apical glide path sizes of 15, 20, and 25. The time taken to reach the working length and the number of canals used before the instrument deformed or fractured were noted. Fractured instruments were examined with scanning electron microscopy.
Results The TF system took significantly more time to reach the working length than the Endostar E3 system. Both systems required significantly more time to reach the working length at the size 15 glide path than at sizes 20 and 25. A greater number of TFs than Endostar E3 files exhibited deformation, and a higher incidence of instrument deformation was observed in adaptive than in continuous rotary motion; more deformation was also observed with the size 15 glide path. One TF was fractured while undergoing adaptive motion.
Conclusions No significant difference was observed between continuous rotary and adaptive motion. The TF system and adaptive motion were associated with a higher incidence of deformation and fracture. Apical glide path sizes of 20 and 25 required significantly less time to reach the working length than size 15.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Assessment of Different File Systems for Working Time Based on Glide Path, Operating Kinetics, and the Fracture Resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Divya Batra, Debkant Jena, Nandita Bansal, Alka Arora, Divya Gaurav Dudulwar
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(1): 69. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 1,867 View
- 13 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne nickel-titanium files
- Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e22. Published online May 9, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider nickel-titanium (NiTi) files on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne NiTi files.
Materials and Methods Forty-four WaveOne Primary files were used and divided into four groups (
n = 11). In the first group (0 WaveOne), the WaveOne Primary files served as a control group and were not used on acrylic blocks. In the 1 WaveOne Group, acrylic blocks were prepared using only WaveOne Primary files, and in the PF+WaveOne group and PG+WaveOne groups, acrylic blocks were first prepared with PathFile or ProGlider NiTi files, respectively, followed by the use of WaveOne Primary files. All the WaveOne Primary files were then subjected to cyclic fatigue testing. The number of cycles to failure was calculated and the data were statistically analyzed using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukey honest significant difference multiple-comparison test at a 5% significance level.Results The highest number of cycles to failure was found in the control group, and the lowest numbers were found in the 1 WaveOne group and the PF+WaveOne group. Significant differences were found among the 1 WaveOne, PF+WaveOne, and control groups (
p < 0.05). No statistically significant differences were found between the PG+WaveOne group and the other three groups (p > 0.05).Conclusion Glide path preparation with NiTi rotary files did not affect the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne Primary files used on acrylic blocks.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of WaveOne Gold in Reciprocation, ProGlider in Rotary Motion, and Manual Files in a Reciprocating Handpiece Within Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Shivangi M Pujara, Hardik B Shah, Leena H Jobanputra
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of glide path instruments in cyclic fatigue resistance of reciprocating instruments after three uses
André Schroder Scherer, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, José Roberto Vanni
Brazilian Dental Journal.2023; 34(2): 27. CrossRef - An Investigation of the Accuracy and Reproducibility of 3D Printed Transparent Endodontic Blocks
Martin Smutný, Martin Kopeček, Aleš Bezrouk
Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove, Czech Republic).2022; 65(2): 59. CrossRef - Evaluation of Cyclic Fatigue of Hyflex EDM, Twisted Files, and ProTaper Gold Manufactured with Different Processes: An In Vitro Study
Pooja D. Khandagale, Prashant P. Shetty, Saleem D. Makandar, Pradeep A. Bapna, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari, Anand Marya, Pietro Messina, Giuseppe Alessandro Scardina, Antonino Lo Giudice
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
- 1,730 View
- 10 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Comparison of the ability of Reciproc and Reciproc Blue instruments to reach the full working length with or without glide path preparation
- Mehmet Adıguzel, Pelin Tufenkci
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(4):e41. Published online November 1, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of the present study was to compare the mean preparation times and frequency with which Reciproc and Reciproc Blue instruments reached the full working length in mandibular molars, with or without glide path preparation.
Materials and Methods Previously untreated mesiobuccal and mesiolingual canals with completely formed apices were randomly divided into 6 groups (
n = 50) depending on the usage of Reciproc (RC; VDW), Reciproc Blue (RC Blue; VDW), C-Pilot (CP; VDW), and R-Pilot (RP; VDW) files: RC, RC Blue, RC + C-Pilot (RC-CP), RC-Blue + C-Pilot (RC Blue-CP), RC+R-Pilot (RC-RP), and RC Blue + R-Pilot (RC Blue-RP). A glide path was prepared using the hand-operated C-Pilot or the machine-operated R-Pilot instruments, respectively. The χ2 test, analysis of variance, and the Tukeypost hoc test were used for statistical comparisons.Results No statistically significant differences were observed in the distribution of the frequency of reaching the full working length in the RC (94%), RC Blue (88%), RC-CP (94%), RC Blue-CP (90%), RC-RP (96%), and RC Blue-RP (92%) groups (
p > 0.05).Conclusions Preparation of a glide path did not have a significant effect on reaching the full working length using these systems.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
Vlad Mircea Lup, Carlo Gaeta, Ashkan Tavakkoli, Andreas Louloudiadis, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 262. CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - Influence of the Brushing Motions on the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of the Reciproc Blue Instrument: In vitro Study
Juliana Borsoi Chicon, Vanessa Maria Fernandes Pavão, Maíra Henrique Gonçalves Cunha, Marcos Frozoni
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(9): 1340. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Nickel-titanium files in endodontics: Development, improvement and modifications of nickel-titanium alloy
Slavoljub Zivkovic, Milica Jovanovic-Medojevic, Jelena Neskovic, Marijana Popovic-Bajic
Vojnosanitetski pregled.2023; 80(3): 262. CrossRef - Comparison of the incidence of postoperative pain in single sitting root canal treatment after using two reciprocating systems and two continuous rotary systems: An in vivo study
VijayKumar Vijayran, Ambica Khetarpal, Asit Vats, Monika Ahlawat, Neha Singhal, Harshita
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2023; 26(1): 12. CrossRef - Effect of mode of rotation on apical extrusion of debris with four different single‐file endodontic instrumentation systems: Systematic review and meta‐analysis
Muhammad Zubair Ahmad, Durre Sadaf, Marcy McCall MacBain, Khalid A. Merdad
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 202. CrossRef - Impact of kinematics on the efficiency and safety of an engine-driven file for glide path preparation in MB2 canals of maxillary molars
Larissa B. B. Araújo, Pedro H. S. Calefi, Murilo P. Alcalde, Giulio Gavini, Rodrigo R. Vivan, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(3): 1153. CrossRef - Evaluation of type of kinematics on glide path procedures and torsional fatigue resistance after preparation of moderately curved canals
Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Victor de Moraes Cruz, Bruno Carvalho de Vasconcelos, Marcus Vinícius Reis Só, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Brazilian Oral Research.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Comparison of postoperative pain intensity following the use of three different instrumentation techniques: A randomized clinical trial
Mehmet Adiguzel, Pelin Tufenkci, ismail Ilker Pamukcu
Journal of Dental Research, Dental Clinics, Dental Prospects.2019; 13(2): 133. CrossRef
- Influence of the Adaptive Torque Control Motion on the Ability of Neolix EDMax to Reach Working Length When Used as a Single Shaping File—An In Vitro Study
- 2,718 View
- 11 Download
- 11 Crossref

- Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
- Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):123-127. Published online January 7, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.123
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Glide path preparation is recommended to reduce torsional failure of nickel-titanium (NiTi) rotary instruments and to prevent root canal transportation. This study evaluated whether the repetitive insertions of G-files to the working length maintain the apical size as well as provide sufficient lumen as a glide path for subsequent instrumentation.
Materials and Methods The G-file system (Micro-Mega) composed of G1 and G2 files for glide path preparation was used with the J-shaped, simulated resin canals. After inserting a G1 file twice, a G2 file was inserted to the working length 1, 4, 7, or 10 times for four each experimental group, respectively (
n = 10). Then the canals were cleaned by copious irrigation, and lubricated with a separating gel medium. Canal replicas were made using silicone impression material, and the diameter of the replicas was measured at working length (D0) and 1 mm level (D1) under a scanning electron microscope. Data was analysed by one-way ANOVA andpost-hoc tests (p = 0.05).Results The diameter at D0 level did not show any significant difference between the 1, 2, 4, and 10 times of repetitive pecking insertions of G2 files at working length. However, 10 times of pecking motion with G2 file resulted in significantly larger canal diameter at D1 (
p < 0.05).Conclusions Under the limitations of this study, the repetitive insertion of a G2 file up to 10 times at working length created an adequate lumen for subsequent apical shaping with other rotary files bigger than International Organization for Standardization (ISO) size 20, without apical transportation at D0 level.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
Mahima Bharat Mehta, Anupam Sharma, Aniket Jadhav, Aishwarya Handa, Abhijit Bajirao Jadhav, Ashwini A. Narayanan
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(2): 101. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive up-and-down movements on torque/force generation, surface defects and shaping ability of nickel-titanium rotary instruments: an ex vivo study
Moe Sandar Kyaw, Arata Ebihara, Yoshiko Iino, Myint Thu, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Pyae Hein Htun, Takashi Okiji
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of the Number of Pecking Motions at Working Length on the Shaping Ability of Single-file Systems in Long Oval-shaped Curved Canals
Lixiao Wang, Ruitian Lin, Hui Chen, Zihan Li, Franklin R. Tay, Lisha Gu
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(4): 548. CrossRef - Influence of pecking frequency at working length on the volume of apically extruded debris: A micro-computed tomography analysis
Li-Xiao Wang, Hui Chen, Rui-Tian Lin, Li-Sha Gu
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(3): 1274. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef
- Glide Path – An Ineluctable Route for Successful Endodontic Mechanics: A Literature Review
- 1,507 View
- 7 Download
- 9 Crossref

-
Canal preparation with nickel-titanium or stainless steel instruments without the risk of instrument fracture: preliminary observations

- Ghassan Yared
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):85-90. Published online November 13, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.85
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This report introduces a novel technique that allows a safe and predictable canal negotiation, creation of a glide path and canal preparation with reciprocating nickel-titanium or stainless steel engine-driven instruments in canals where the use of rotary and the newly developed reciprocating instruments is contraindicated. In this novel technique, the instruments are used in reciprocating motion with very small angles. Hand files are not used regardless of the complexity of the canal anatomy. It also allows achieving predictable results in canal negotiation and glide path creation in challenging canals without the risk of instrument fracture.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Analysis of the reciprocating kinematics of the VDW Silver Reciproc, E-Connect Pro, Ecom, and Endopen endodontic motors: an in vitro experimental study
Cristielly França, Juliana D. Bronzato, Dieimes Braambati, Adriana de-Jesus-Soares, Carla C. R. B. Félix, Michelle A. N. S. Ferreira, Marcos Frozoni
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2026; 51(1): e5. CrossRef - Assessing the cyclic fatigue resistance and sterilization effects on replica-like endodontic instruments compared to Reciproc Blue
Fernando Antonio Siano dos Reis, Amjad Abu Hasna, Gustavo Ragozzini, Felipe Bernardo de Moura, Tiago Moreira Bastos Campos, Alexandre Sigrist de Martin, Cláudio Antonio Talge Carvalho, Carlos Eduardo Silveira Bueno
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Middle mesial canal in mandibular first molar: A narrative review
Raghavendra Penukonda, Harshada Pattar, Phrabhakaran Nambiar, Afaf Al-Haddad
The Saudi Dental Journal.2023; 35(5): 468. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and biomechanical behavior of different access cavities of maxillary central incisors restored with different composite resins
Amjad Abu Hasna, Alana Barbosa Alves Pinto, Marcelle Simões Coelho, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Sergio Lucio Pereira de Castro Lopes, Cláudio Antonio Talge Carvalho, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 26(10): 6295. CrossRef - Reciprocating Kinematics of X-Smart Plus, VDW Silver and, iRoot Endodontic Motors: A Comparison Between Real and Set Values
Dieimes Braambati, Renata de Castro Monteiro Netto, Marcelo Santos Coelho, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Marcos Frozoni
Brazilian Dental Journal.2022; 33(6): 28. CrossRef - A Novel Root Canal Preparation Technique Hybridizing Heat-treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments
Marco Seracchiani
World Journal of Dentistry.2021; 12(3): 258. CrossRef - Effect of 2 Heat-treated Nickel-Titanium Files on Enlargement and Deformation of the Apical Foramen in Curved Canals: A Scanning Electronic Microscopic Study
Carla Daou, Roula El Hachem, Alfred Naaman, Carla Zogheib, Nada El Osta, Issam Khalil
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(10): 1478. CrossRef - Classification and cyclic fatigue evaluation of new kinematics for endodontic instruments
Gianluca Gambarini, Lucila Piasecki, Gabriele Miccoli, Gianfranco Gaimari, Roberto Di Giorgio, Dario Di Nardo, Adham A Azim, Luca Testarelli
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(2): 154. CrossRef - Association of manual or engine‐driven glide path preparation with canal centring and apical transportation: a systematic review
R. C. Hartmann, O. A. Peters, J. A. P. de Figueiredo, G. Rossi‐Fedele
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(11): 1239. CrossRef - Current Assessment of Reciprocation in Endodontic Preparation: A Comprehensive Review—Part I: Historic Perspectives and Current Applications
Nicola Maria Grande, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Stephen Cohen, Frédéric Bukiet, Gianluca Plotino
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1778. CrossRef
- Analysis of the reciprocating kinematics of the VDW Silver Reciproc, E-Connect Pro, Ecom, and Endopen endodontic motors: an in vitro experimental study
- 1,503 View
- 12 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
- Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):270-275. Published online July 16, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.270
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study compared the mechanical properties of various instruments for canal exploration and glide-path preparations.
Materials and Methods The buckling resistance, bending stiffness, ultimate torsional strength, and fracture angle under torsional load were compared for C+ file (CP, Dentsply Maillefer), M access K-file (MA, Dentsply Maillefer), Mani K-file (MN, Mani), and NiTiFlex K-file (NT, Dentsply Maillefer). The files of ISO size #15 and a shaft length of 25 mm were selected. For measuring buckling resistance (
n = 10), the files were loaded in the axial direction of the shaft, and the maximum load was measured during the files' deflection. The files (n = 10) were fixed at 3-mm from the tip and then bent 45° with respect to their long axis, while the bending force was recorded by a load cell. For measuring the torsional properties, the files (n = 10) were also fixed at 3-mm, and clockwise rotations (2-rpm) were applied to the files in a straight state. The torsional load and the distortion angle were recorded until the files succumbed to the torque.Results The CP was shown to require the highest load to buckle and bend the files, and the NT showed the least. While MA and MN showed similar buckling resistances, MN showed higher bending stiffness than MA. The NT had the lowest bending stiffness and ultimate torsional strength (
p < 0.05).Conclusions The tested instruments showed different mechanical properties depending on the evaluated parameters. CP and NT files were revealed to be the stiffest and the most flexible instruments, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
Ujjwal Das, Rajesh Kumar Das, Kallol Kumar Saha, Lugu Buru Murmu, Srimanta Banerjee, Rishila Nag
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(4): 384. CrossRef - Comparison of torsional, bending, and buckling resistances of different nickel-titanium glide path files
Feyyaz Çeliker, İrem Çetinkaya
Matéria (Rio de Janeiro).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic 0.15 Stainless-Steel K-Files: Exploring Design, Composition, and Mechanical Performance
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(2): 29. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Endodontic ISO Size 06, 08, and 10 Stainless Steel K-Files Used for Glide Path Procedures
Abayomi Omokeji Baruwa, Filipa Chasqueira, Sofia Arantes-Oliveira, João Caramês, Duarte Marques, Jaime Portugal, Jorge N. R. Martins
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(4): 98. CrossRef - Glide Path in Endodontics: A Literature Review of Current Knowledge
Vlad Mircea Lup, Giulia Malvicini, Carlo Gaeta, Simone Grandini, Gabriela Ciavoi
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(8): 257. CrossRef - Shaping Ability and Buckling Resistance of TruNatomy, WaveOne gold, and XP-Endo Shaper Single-File Systems
Neveen Ali Shaheen, Nahla Gamal Eldin Elhelbawy
Contemporary Clinical Dentistry.2022; 13(3): 261. CrossRef - A comparison of different hand and rotary endodontic glide path files for buckling resistance
Ruchika Gupta, Pramod Mohite, Suvarna Patil, Nandita Bansal
Endodontology.2021; 33(2): 102. CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on color and flexibility of nickel-titanium endodontic instruments
Bernardo Corrêa de ALMEIDA, Carlos Nelson ELIAS
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Negotiation, Glide Path, and Preflaring Procedures on Root Canal Shaping—Terminology, Basic Concepts, and a Systematic Review
Gianluca Plotino, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Frederic Bukiet, Nicola M. Grande, Sajesh K. Veettil, Gustavo De-Deus, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(6): 707. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of buckling resistance of Proglider and One-G file: An in vitro study
Priyanka Himmatrao Patil, Meenal Nitin Gulve, Swapnil Janardan Kolhe
Endodontology.2018; 30(1): 21. CrossRef - Mechanical Properties of Various Heat-treated Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments
Hye-Jin Goo, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Eugenio Pedullà, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1872. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef
- Buckling resistance of various pathfinding endodontic instruments: An in vitro study
- 2,520 View
- 46 Download
- 13 Crossref

- Influence of glide path on the screw-in effect and torque of nickel-titanium rotary files in simulated resin root canals
- Jung-Hong Ha, Sang-Shin Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):215-219. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.215
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the screw-in effect and torque generation depending on the size of glide path during root canal preparation.
Materials and Methods Forty Endo-Training Blocks (REF A 0177, Dentsply Maillefer) were used. They were divided into 4 groups. For groups 1, 2, 3, and 4, the glide path was established with ISO #13 Path File (Dentsply Maillefer), #15 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX (Dentsply Maillefer), modified #16 Path File (equivalent to #18), and #20 NiTi K-file NITIFLEX, respectively. The screw-in force and resultant torque were measured using a custom-made experimental apparatus while canals were instrumented with ProTaper S1 (Dentsply Maillefer) at a constant speed of 300 rpm with an automated pecking motion. A statistical analysis was performed using one-way analysis of variance and the Duncan
post hoc comparison test.Results Group 4 showed lowest screw-in effect (2.796 ± 0.134) among the groups (
p < 0.05). Torque was inversely proportional to the glide path of each group. In #20 glide path group, the screw-in effect and torque decreased at the last 1 mm from the apical terminus. However, in the other groups, the decrease of the screw-in effect and torque did not occur in the last 1 mm from the apical terminus.Conclusions The establishment of a larger glide path before NiTi rotary instrumentation appears to be appropriate for safely shaping the canal. It is recommended to establish #20 glide path with NiTi file when using ProTaper NiTi rotary instruments system safely.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
Taher Al Omari, Layla Hassouneh, Khawlah Albashaireh, Alaa Dkmak, Rami Albanna, Ali Al-Mohammed, Ahmed Jamleh, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
International Journal of Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Radial Lands and Alternating Cutting Edges Contribute to Reduced Screw-in and Torque in Curved Root Canals - An In Vitro Study
Greta Heimberg, Sebastian Bürklein, Edgar Schäfer, Thomas Gerhard Wolf, David Donnermeyer
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Printed Teeth in Endodontics: A New Protocol for Microcomputed Tomography Studies
Tiago Reis, Cláudia Barbosa, Margarida Franco, Ruben Silva, Nuno Alves, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Jose Martín-Cruces, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Materials.2024; 17(8): 1899. CrossRef - Evaluation of Pain Following the Use of Different Single-file Glide Path Systems: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Zeliha Danaci, Kübra Yeşildal Yeter
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 120. CrossRef - Cone-beam computed tomographic evaluation and fracture resistance of endodontically retreated teeth using hyflex remover, Mtwo, and ProTaper retreatment file systems: An in vitro study
Isha Singh, Dakshita Joy Sinha, Pallavi Sharma, Kunal Bedi, Priyanka Rani, Swapnil Vats
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(1): 56. CrossRef - Screw-in force, torque generation, and performance of glide-path files with three rotation kinetics
Jee-Yeon Woo, Ji-Hyun Jang, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 761. CrossRef - Morphological and structural variations of Nickel-Titanium endodontic instruments subjected to instrumentation loads: in vitro study
Yenny Marcela Orozco-Ocampo, César Augusto Álvarez-Vargas, Francy Nelly Jiménez-García, Daniel Escobar-Rincón, Paola Ximena Jaramillo-Gil
Revista UIS Ingenierías.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nickel ion release and surface analyses on instrument fragments fractured beyond the apex: a laboratory investigation
Sıdıka Mine Toker, Ekim Onur Orhan, Arzu Beklen
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the Efficiency to Remove the Infected Dentin via Enterococcus faecalis Bacterial Count and to Adequately Shape the Canal Using Hand Kedo-SH Files, Rotary Kedo-SG (Blue) and Pro AF Baby Gold Files in Primary Molars: An In Vitro Study
Shruthi B Patil, Kaavya Shanker
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2023; 16(S2): S142. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, torque, and force generation during retreatment with D-RaCe, HyFlex Remover, and Mtwo retreatment files
Yoojin Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Soram Oh
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cyclic and torsional fatigue resistance of a new rotary file on a rotary and reciprocating motion
Gabriel Barcelos Só, Giovana Siocheta, Pedro Calefi, Murilo Alcalde, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Marco Antônio H. Duarte, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa
Microscopy Research and Technique.2023; 86(12): 1635. CrossRef - Influence of different kinematics on stationary and dynamic torsional behavior of JIZAI nickel-titanium rotary instruments: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Satoshi Omori, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Hayate Unno, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(3): 1170. CrossRef - Dynamic torque and screw-in force of four different glide path instruments assessed in simulated single- and double-curved canals: An in vitro study
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Moe-Sandar Kyaw, Yuka Kasuga, Miki Nishijo, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(4): 1598. CrossRef - Effect of Periodic Changes in Rotation Speed on Torsional Stress and Screw-in Force by Alternative Rotation Technique
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jo, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 77. CrossRef - Effect of Rotational Modes on Torque/Force Generation and Canal Centering Ability during Rotary Root Canal Instrumentation with Differently Heat-Treated Nickel–Titanium Instruments
Satoshi Omori, Arata Ebihara, Keiko Hirano, Yuka Kasuga, Hayate Unno, Taro Nakatsukasa, Shunsuke Kimura, Keiichiro Maki, Takao Hanawa, Takashi Okiji
Materials.2022; 15(19): 6850. CrossRef - Shaping ability of rotary and reciprocating single-file systems in combination with and without different glide path techniques in simulated curved canals
Lu Shi, Yunfei Yang, Jie Wan, Wen Xie, Ruiming Yang, Ying Yao
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(4): 1520. CrossRef - Evolution and development: engine-driven endodontic rotary nickel-titanium instruments
Yuhong Liang, Lin Yue
International Journal of Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the effects from coronal pre‐flaring and glide‐path preparation on torque generation during root canal shaping procedure
Sang Won Kwak, Jung‐Hong Ha, Ya Shen, Markus Haapasalo, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Australian Endodontic Journal.2022; 48(1): 131. CrossRef - Shaping ability of ProTaper Gold and WaveOne Gold nickel-titanium rotary instruments in simulated S-shaped root canals
Lu Shi, Junling Zhou, Jie Wan, Yunfei Yang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2022; 17(1): 430. CrossRef - Endodontic Rotary Files, What Should an Endodontist Know?
Ana-Belén Dablanca-Blanco, Pablo Castelo-Baz, Ramón Miguéns-Vila, Pablo Álvarez-Novoa, Benjamín Martín-Biedma
Medicina.2022; 58(6): 719. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Canal shaping
Ana Arias, Ove A. Peters
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 637. CrossRef - Comparison of Torque, Screw-in Force, and Shaping Ability of Glide Path Instruments in Continuous Rotation and Optimum Glide Path Motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Moe Sandar Kyaw, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(1): 94. CrossRef - Analysis of Torque and Force Induced by Rotary Nickel-Titanium Instruments during Root Canal Preparation: A Systematic Review
Myint Thu, Arata Ebihara, Sherif Adel, Takashi Okiji
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(7): 3079. CrossRef - Comparison of canal transportation and centering ability of manual K-files and reciprocating files in glide path preparation: a micro-computed tomography study of constricted canals
Jing-Yi Liu, Zhi-Xiong Zhou, Wei-Ju Tseng, Bekir Karabucak
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of rotational speed on torque/force generation and shaping ability during root canal instrumentation of extracted teeth with continuous rotation and optimum torque reverse motion
M. S. Kyaw, A. Ebihara, Y. Kasuga, K. Maki, S. Kimura, P. H. Htun, T. Nakatsukasa, T. Okiji
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(9): 1614. CrossRef - Shot peening increases resistance to cyclic fatigue fracture of endodontic files
Javier Nino-Barrera, Jose Sanchez-Aleman, Manuel Acosta-Humanez, Luis Gamboa-Martinez, Carlos Cortes-Rodriguez
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Optimum glide path motion is safer than continuous rotation of files in glide path preparation
Giulio Gavini, Eduardo Akisue, Dirce Akemi Sacaguti Kawakami, Celso Luiz Caldeira, George Táccio de Miranda Candeiro, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Pedro Henrique Souza Calefi, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Húngaro Duarte
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 544. CrossRef - Root canals shaped by nickel-titanium instrumentation with automated computerized numerical control systems
Liming Wang, Wenxiang Li, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Shin Hye Chung, Soram Oh, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Kee-Yeon Kum, Yu Gu
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An Update on Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instruments in Endodontics: Mechanical Characteristics, Testing and Future Perspective—An Overview
Alessio Zanza, Maurilio D’Angelo, Rodolfo Reda, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2021; 8(12): 218. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Cleaning Efficiency and Apical Extrusion of Debris Using Two Pediatric Rotary Endodontic Files: An In Vitro Study
Nilima Thosar, Sudhindra Baliga, Faraz Ahmed, Nilesh Rathi, Shreyans A Jain, Jayati Mehta
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2021; 14(2): 196. CrossRef - Body temperature fatigue behaviour of reciprocating and rotary glide path instruments in sodium hypochlorite solutions alone or combined with etidronate
Dario Perez‐Villalba, José C. Macorra, Juan J. Perez‐Higueras, Ove A. Peters, Ana Arias
Australian Endodontic Journal.2021; 47(3): 450. CrossRef - Effect of Optimum Torque Reverse Motion on Torque and Force Generation during Root Canal Instrumentation with Crown-down and Single-length Techniques
Shunsuke Kimura, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 232. CrossRef - Ex-Vivo Comparison of Torsional Stress on Nickel–Titanium Instruments Activated by Continuous Rotation or Adaptive Motion
Joo Yeong Lee, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2020; 13(8): 1900. CrossRef - Influence of glide path size and operating kinetics on time to reach working length and fracture resistance of Twisted File adaptive and Endostar E3 nickel-titanium file systems
Tamilkumaran Ramyadharshini, Inbaraj Anand Sherwood, V Shanmugham Vigneshwar, Prakasam Ernest Prince, Murugadoss Vaanjay
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Buckling Resistance of Various Nickel-Titanium Glide Path Preparation Instruments in Dynamic or Static Mode
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Antheunis Versluis, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(8): 1125. CrossRef - Comparison of torque, force generation and canal shaping ability between manual and nickel-titanium glide path instruments in rotary and optimum glide path motion
Pyae Hein Htun, Arata Ebihara, Keiichiro Maki, Shunsuke Kimura, Miki Nishijo, Daisuke Tokita, Takashi Okiji
Odontology.2020; 108(2): 188. CrossRef - THE INFLUENCE OF DIFFERENT TORQUE SETTINGS ON THE AMOUNT OF APICALLY EXTRUDED DEBRIS DURING ROTARY INSTRUMENTATION
Demet ALTUNBAŞ, Mustafa TOYOĞLU
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2020; 23(3): 160. CrossRef - Glide Path: “Path to the successful root canal instrumentation”- Review
Anjali Mairal Oak
Journal of Indian Dental Association.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Torsional fatigue strength of reciprocating and rotary pathfinding instruments manufactured from different NiTi alloys
Rodrigo Ricci VIVAN, Murilo Priori ALCALDE, George CANDEIRO, Giulio GAVINI, Celso Luis CALDEIRA, Marco Antonio Hungaro DUARTE
Brazilian Oral Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Screw-In Forces during Movement of Endodontic Files with Different Geometries, Alloys, and Kinetics
Sang Won Kwak, Chan-Joo Lee, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Jung-Hong Ha
Materials.2019; 12(9): 1506. CrossRef - Effect of glide path preparation with PathFile and ProGlider on the cyclic fatigue resistance of WaveOne nickel-titanium files
Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Force and vibration generated in apical direction by three endodontic files of different kinematics during simulated canal preparation: An in vitro analytical study
Ankit Nayak, PK Kankar, Prashant K Jain, Niharika Jain
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2019; 233(8): 839. CrossRef - Effective Establishment of Glide-Path to Reduce Torsional Stress during Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrumentation
Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Materials.2019; 12(3): 493. CrossRef - Real‐time dynamic torque values and axial forces during preparation of straight root canals using three different endodontic motors and hand preparation
S. Bürklein, J. P. Stüber, E. Schäfer
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(1): 94. CrossRef - Comparison of glide paths created with K-files, PathFiles, and the ProGlider file, and their effects on subsequent WaveOne preparation in curved canals
Linxia Zheng, Xiongfei Ji, Chengxi Li, Lulu Zuo, Xin Wei
BMC Oral Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of cyclic fatigue resistance and bending properties of two reciprocating nickel‐titanium glide path files
T. Özyürek, G. Uslu, M. Gündoğar, K. Yılmaz, N. M. Grande, G. Plotino
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(9): 1047. CrossRef - Root Canal Shaping Effect of Instruments with Offset Mass of Rotation in the Mandibular First Molar: A Micro–computed Tomographic Study
Maung Maung Kyaw Moe, Jung Hong Ha, Myoung Uk Jin, Young Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 822. CrossRef - Evaluation of selected mechanical properties of NiTi rotary glide path files manufactured from controlled memory wires
Miki NISHIJO, Arata EBIHARA, Daisuke TOKITA, Hisashi DOI, Takao HANAWA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2018; 37(4): 549. CrossRef - Effect of the Glide Path Establishment on the Torque Generation to the Files during Instrumentation: An In Vitro Measurement
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Gary Shun-Pan Cheung, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(3): 496. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Novel Glide Path Instruments with Different Alloy Properties and Kinematics
Burcu Serefoglu, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Seniha Micoogullari Kurt, Mehmet Kemal Çalişkan
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(9): 1422. CrossRef - Cyclic fatigue resistance of R‐Pilot, HyFlex EDM and PathFile nickel‐titanium glide path files in artificial canals with double (S‐shaped) curvature
G. Uslu, T. Özyürek, K. Yılmaz, M. Gündoğar
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(5): 584. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Used and New Glide Path Files
Taha Özyürek, Gülşah Uslu, Uğur İnan
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 477. CrossRef - Comparison of apical extrusion of intracanal bacteria by various glide-path establishing systems: an in vitro study
Alberto Dagna, Rashid El Abed, Sameeha Hussain, Ibrahim H Abu-Tahun, Livia Visai, Federico Bertoglio, Floriana Bosco, Riccardo Beltrami, Claudio Poggio, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 316. CrossRef - Comparing the Centering Ability of Different Pathfinding Systems and Their Effect on Final Instrumentation by Hyflex CM
Lu Shi, Shova Wagle
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(11): 1868. CrossRef - Torsional Performance of ProTaper Gold Rotary Instruments during Shaping of Small Root Canals after 2 Different Glide Path Preparations
Ana Arias, Rafaela Andrade de Vasconcelos, Alexis Hernández, Ove A. Peters
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(3): 447. CrossRef - Dynamic Torque and Vertical Force Analysis during Nickel-titanium Rotary Root Canal Preparation with Different Modes of Reciprocal Rotation
Daisuke Tokita, Arata Ebihara, Miki Nishijo, Kana Miyara, Takashi Okiji
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1706. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Pecking Motion of Rotary Nickel-titanium Instruments with Different Pecking Depth
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Asgeir Sigurdsson, Seok Woo Chang, Sung Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(10): 1688. CrossRef -
In vitro comparison of the cyclic fatigue resistance of HyFlex EDM, One G, and ProGlider nickel titanium glide path instruments in single and double curvature canals
Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu, Taha Özyürek
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2017; 42(4): 282. CrossRef - Debris extrusion by glide-path establishing endodontic instruments with different geometries
Jung-Hong Ha, Sung Kyo Kim, Sang Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Yong Chul Bae, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Dental Sciences.2016; 11(2): 136. CrossRef - Effects of Pitch Length and Heat Treatment on the Mechanical Properties of the Glide Path Preparation Instruments
Sang Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Rashid El Abed, Ibrahim H. Abu-Tahun, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(5): 788. CrossRef - Screw-in forces during instrumentation by various file systems
Jung-Hong Ha, Sang Won Kwak, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 304. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance and Force Generated by OneShape Instruments during Curved Canal Preparation
Zhuyu Wang, Wen Zhang, Xiaolei Zhang, Luigi F. Rodella
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0160815. CrossRef - Differences in torsional performance of single- and multiple-instrument rotary systems for glide path preparation
Ana Arias, Rupinderpal Singh, Ove A. Peters
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 192. CrossRef - Effect of glide path and apical preparation size on the incidence of apical crack during the canal preparation using Reciproc, WaveOne, and ProTaper Next systems in curved root canals: A stereomicroscope study
Hüseyin Sinan Topçuoğlu, Salih Düzgün, Firdevs Akpek, Gamze Topçuoğlu
Scanning.2016; 38(6): 585. CrossRef - Geometric Optimization for Development of Glide Path Preparation Nickel-Titanium Rotary Instrument
Jung-Hong Ha, Chan-Joo Lee, Sang-Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Dongseok Ha, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(6): 916. CrossRef - Glide Path Management with Single- and Multiple-instrument Rotary Systems in Curved Canals: A Micro–Computed Tomographic Study
Alison Luís Kirchhoff, Rene Chu, Isabel Mello, Andres Dario Plazas Garzon, Marcelo dos Santos, Rodrigo Sanches Cunha
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(11): 1880. CrossRef - Safe root canal preparation using reciprocating nickel-titanium instruments
Jung-Hong Ha
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 253. CrossRef - Effect of repetitive pecking at working length for glide path preparation using G-file
Jung-Hong Ha, Hyo-Jin Jeon, Rashid El Abed, Seok-Woo Chang, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 123. CrossRef - Influence of a glide path on the dentinal crack formation of ProTaper Next system
Sevinç Aktemur Türker, Emel Uzunoğlu
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(4): 286. CrossRef - ‘Screw‐in’ tendency of rotary nickel–titanium files due to design geometry
J. H. Ha, G. S. P. Cheung, A. Versluis, C. J. Lee, S. W. Kwak, H. C. Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(7): 666. CrossRef - Comparison of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of 5 Different Rotary Pathfinding Instruments Made of Conventional Nickel-Titanium Wire, M-wire, and Controlled Memory Wire
Ismail Davut Capar, Mehmet Emin Kaval, Hüseyin Ertas, Bilge Hakan Sen
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(4): 535. CrossRef - Comparision of two different preparation protocol of Ni-Ti Rotary PathFile-ProTaper instruments in simulated s-shaped canals
Elıf Delve Başer Can, Müzeyyen Gerek, Mehmet Baybora Kayahan, Kambız Mohsenı, Hakki Sunay, Gündüz Bayirli
Acta Odontologica Scandinavica.2014; 72(1): 76. CrossRef - Torsional and cyclic fatigue resistances of glide path preparation instruments: G‐file and PathFile
Sang Yup Sung, Jung‐Hong Ha, Sang‐Won Kwak, Rashid El Abed, Kyeongmin Byeon, Hyeon‐Cheol Kim
Scanning.2014; 36(5): 500. CrossRef - Buckling resistance, bending stiffness, and torsional resistance of various instruments for canal exploration and glide path preparation
Sang-Won Kwak, Jung-Hong Ha, WooCheol Lee, Sung-Kyo Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(4): 270. CrossRef - Shaping Ability of Different Nickel-Titanium Systems in Simulated S-shaped Canals with and without Glide Path
Sebastian Bürklein, Thomas Poschmann, Edgar Schäfer
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(8): 1231. CrossRef - Stress Generation during Self-Adjusting File Movement: Minimally Invasive Instrumentation
Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Sang Yup Sung, Jung-Hong Ha, Michael Solomonov, Jung-Min Lee, Chan-Joo Lee, Byung-Min Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1572. CrossRef
- Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Preparation Time by Traverse, R‐Motion Glider C, and Other Glide Path Systems in Severely Curved Canals
- 2,459 View
- 13 Download
- 76 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


