Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effects of a bleaching agent on properties of commercial glass-ionomer cements
- Fernanda Lúcia Lago de Camargo, Ailla Carla Lancellotti, Adriano Fonseca de Lima, Vinícius Rangel Geraldo Martins, Luciano de Souza Gonçalves
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(3):e32. Published online July 5, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e32
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
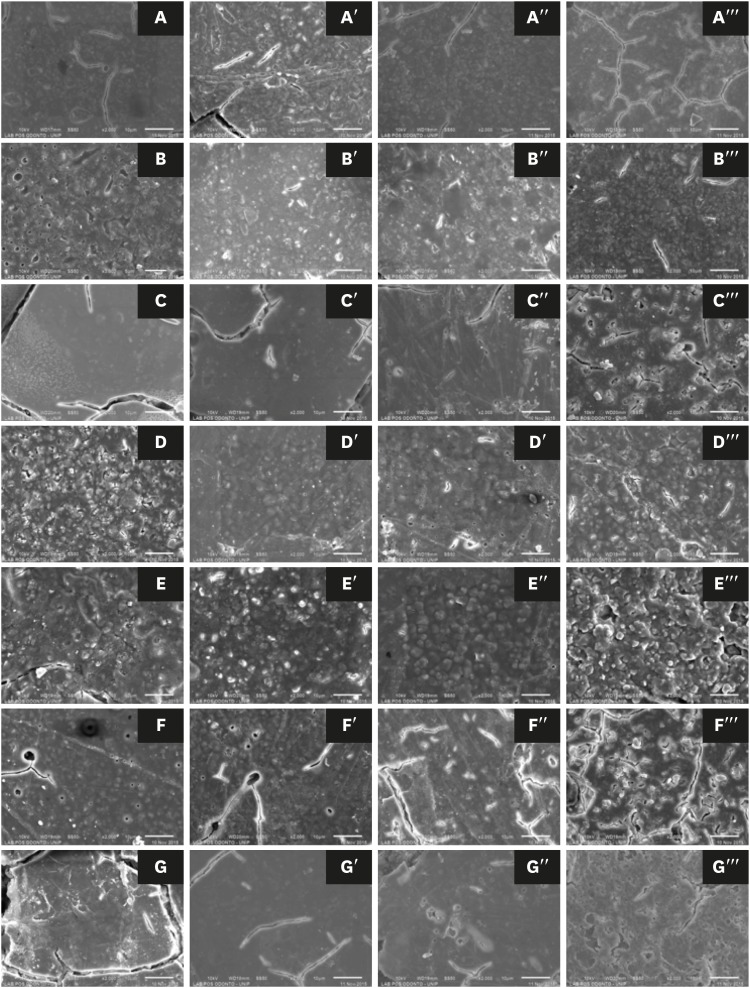
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effects of a bleaching agent on the composition, mechanical properties, and surface topography of 6 conventional glass-ionomer cements (GICs) and one resin-modified GIC.
Materials and Methods For 3 days, the specimens were subjected to three 20-minute applications of a 37% H2O2-based bleaching agent and evaluated for water uptake (WTK), weight loss (WL), compressive strength (CS), and Knoop hardness number (KHN). Changes in surface topography and chemical element distribution were also analyzed by energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. For statistical evaluation, the Kruskal-Wallis and Wilcoxon paired tests (
α = 0.05) were used to evaluate WTK and WL. CS specimens were subjected to 2-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the Tukeypost hoc test (α = 0.05), and KH was evaluated by one-way ANOVA, the Holm-Sidakpost hoc test (α = 0.05), and thet -test for independent samples (α = 0.05).Results The bleaching agent increased the WTK of Maxxion R, but did not affect the WL of any GICs. It had various effects on the CS, KHN, surface topography, and the chemical element distribution of the GICs.
Conclusions The bleaching agent with 37% H2O2 affected the mechanical and surface properties of GICs. The extent of the changes seemed to be dependent on exposure time and cement composition.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multidisciplinary conservative management of a severely discolored nonvital tooth
Álvaro Ferrando Cascales, Francesc Abella Sans, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, José Amengual Lorenzo
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2025; 133(4): 941. CrossRef - The effects of bleaching products on the color stability of ion-releasing restoratives
Jian Sheng Lee, Noor Azlin Yahya, Azwatee Abdul Aziz, Adrian U-Jin Yap
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Physical-mechanical, chemical and biological properties of graphene-reinforced glass ionomer cements
Tatiane Ramos dos Santos Jordão, Laura Soares Viana Fernandes, Karla Lorene de França Leite, Adílis Alexandria, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Lucianne Cople Maia, Tatiana Kelly da Silva Fidalgo
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An In Vitro Exploration of Interaction Mechanisms of Intracoronal Bleaching on the Compressive Strength of Conventional and Calcium Silicate–Based Self‐Adhesive Resins and Their Bonding to Composite Resin Restorative Material
Fereshteh Shafiei, Paria Dehghanian, Shadi Tivay, Yasamin Ghahramani, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharama, E. Terrer
EMC - Odontologie.2023; 39(2): 1. CrossRef - The Effect of Home and In-Office Bleaching on Microhardness and Color of Different CAD/CAM Ceramic Materials
Ruwaida Z. Alshali, Mohammed A. Alqahtani
Materials.2022; 15(17): 5948. CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharama, E. Terrer
EMC - Médecine buccale.2022; 15(4): 1. CrossRef - Éclaircissement dentaire
V. Pilliol, B. Ballester, T. Baudinet, G. Aboudharam, E. Terrer
EMC - Orthopédie dentofaciale.2022; 34(1): 1. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Two Glass Polyalkenoate Cements: An In Vivo Pilot Study Using a Sheep Model
Leyla Hasandoost, Daniella Marx, Paul Zalzal, Oleg Safir, Mark Hurtig, Cina Mehrvar, Stephen D. Waldman, Marcello Papini, Mark R. Towler
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2021; 12(3): 44. CrossRef - The Effect of Simulated Field Storage Conditions on Dental Restorative Materials for Military Field Use
David J Lemon, Wen Chen, Trevor Smith, April A Ford, Steven X Moffett, Jeffrey T Hoyle, Nicholas J Hamlin, Yoon Y Hwang
Military Medicine.2020; 185(5-6): e831. CrossRef
- Multidisciplinary conservative management of a severely discolored nonvital tooth
- 1,649 View
- 5 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Biocompatibility of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
- Min-Jae Oh, Yu-Na Jeong, In-Ho Bae, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):359-367. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.359
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of the present
in vitro study was to evaluate the biocompatibility of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) mixed with glass ionomer cement (GIC), and to compare it with that of MTA, GIC, IRM and SuperEBA.Materials and Methods Experimental groups were divided into 3 groups such as 1 : 1, 2 : 1, and 1 : 2 groups depending on the mixing ratios of MTA powder and GIC powder. Instead of distilled water, GIC liquid was mixed with the powder. This study was carried out using MG-63 cells derived from human osteosarcoma. They were incubated for 1 day on the surfaces of disc samples and examined by scanning electron microscopy. To evaluate the cytotoxicity of test materials quantitatively, XTT assay was used. The cells were exposed to the extracts and incubated. Cell viability was recorded by measuring the optical density of each test well in reference to controls.
Results The SEM revealed that elongated, dense, and almost confluent cells were observed in the cultures of MTA mixed with GIC, MTA and GIC. On the contrary, cells on the surface of IRM or SuperEBA were round in shape. In XTT assay, cell viability of MTA mixed with GIC group was similar to that of MTA or GIC at all time points. IRM and SuperEBA showed significantly lower cell viability than other groups at all time points (
p < 0.05).Conclusions In this research MTA mixed with GIC showed similar cellular responses as MTA and GIC. It suggests that MTA mixed with GIC has good biocompatibility like MTA and GIC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- In vitrocytotoxicity of four calcium silicate-based endodontic cements on human monocytes, a colorimetric MTT assay
Sedigheh Khedmat, Somayyeh Dehghan, Jamshid Hadjati, Farimah Masoumi, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 149. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
Young-Jun Lim, Sook-Hyun Nam, Sung-Ho Jung, Dong-Ryul Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 50. CrossRef
- In vitrocytotoxicity of four calcium silicate-based endodontic cements on human monocytes, a colorimetric MTT assay
- 1,620 View
- 1 Download
- 2 Crossref

- Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
- Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(5):344-352. Published online September 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.5.344
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to determine the setting time, compressive strength, solubility, and pH of mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) mixed with glass ionomer cement (GIC) and to compare these properties with those of MTA, GIC, IRM, and SuperEBA.
Materials and Methods Setting time, compressive strength, and solubility were determined according to the ISO 9917 or 6876 method. The pH of the test materials was determined using a pH meter with specified electrode for solid specimen.
Results The setting time of MTA mixed with GIC was significantly shorter than that of MTA. Compressive strength of MTA mixed with GIC was significantly lower than that of other materials at all time points for 7 days. Solubility of 1 : 1 and 2 : 1 specimen from MTA mixed with GIC was significantly higher than that of other materials. Solubility of 1 : 2 specimen was similar to that of MTA. The pH of MTA mixed with GIC was 2-4 immediately after mixing and increased to 5-7 after 1 day.
Conclusions The setting time of MTA mixed with GIC was improved compared with MTA. However, other properties such as compressive strength and pH proved to be inferior to those of MTA. To be clinically feasible, further investigation is necessary to find the proper mixing ratio in order to improve the drawbacks of MTA without impairing the pre-existing advantages and to assess the biocompatibility.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of particle size reduction on the physicochemical and mechanical properties of conventional glass ionomer cement
Nozimjon Tuygunov, Farangis Abdurahimova, Sevara Rizaeva, Zohaib Khurshid, Arief Cahyanto, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria, Bakhtinur Khudanov
Frontiers in Dental Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Setting Time, Compressive Strength, Solubility, and pH of Four Kinds of MTA
Jing-Ling Che, Jae-Hwan Kim, Seon-Mi Kim, Nam-ki Choi, Hyun-Joo Moon, Moon-Jin Hwang, Ho-Jun Song, Yeong-Joon Park
Korean Journal of Dental Materials.2016; 43(1): 61. CrossRef - Do conventional glass ionomer cements release more fluoride than resin-modified glass ionomer cements?
Maria Fernanda Costa Cabral, Roberto Luiz de Menezes Martinho, Manoel Valcácio Guedes-Neto, Maria Augusta Bessa Rebelo, Danielson Guedes Pontes, Flávia Cohen-Carneiro
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(3): 209. CrossRef - Synthesis and Properties of a New Dental Material Based on Nano‐Structured Highly Active Calcium Silicates and Calcium Carbonates
Vukoman Jokanović, Božana Čolović, Miodrag Mitrić, Dejan Marković, Bojana Ćetenović
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2014; 11(1): 57. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effect of blood contamination on the compressive strength of MTA modified with hydration accelerators
Kaveh Oloomi, Eshaghali Saberi, Hadi Mokhtari, Hamid Reza Mokhtari Zonouzi, Ali Nosrat, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 128. CrossRef - Endodontic management of a maxillary lateral incisor with dens invaginatus and external root irregularity using cone-beam computed tomography
Young-Jun Lim, Sook-Hyun Nam, Sung-Ho Jung, Dong-Ryul Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Kyung-San Min
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 50. CrossRef
- Effect of particle size reduction on the physicochemical and mechanical properties of conventional glass ionomer cement
- 1,611 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Comparison of biocompatibility of four root perforation repair materials
- Min-Kyung Kang, In-Ho Bae, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(3):192-198. Published online May 31, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.3.192
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study was carried out in order to determine in vitro biocompatibility of white mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA), and to compare it with that of the commonly used materials, i. e. calcium hydroxide liner (Dycal), glass ionomer cement (GIC), and Portland cement which has a similar composition of MTA. To assess the biocompatibility of each material, cytotoxicity was examined using MG-63 cells. The degree of cytotoxicity was evaluated by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and a colorimetric method, based on reduction of the tetrazolium salt 2,3 bis {2methoxy 4nitro 5[(sulfenylamino) carbonyl] 2H tetrazolium hydroxide} (XTT) assay.
The results of SEM revealed the cells in contact with GIC, MTA, and Portland cement at 1 and 3 days were apparently healthy. In contrast, cells in the presence of Dycal appeared rounded and detached. In XTT assay, the cellular activities of the cells incubated with all the test materials except Dycal were similar, which corresponded with the SEM observation. The present study supports the view that MTA is a very biocompatible root perforation repair material. It also suggests that cellular response of Portland cement and GIC are very similar to that of MTA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
Jeong-Ho Lee, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 222. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Min-Jae Oh, Yu-Na Jeong, In-Ho Bae, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 359. CrossRef - Physical and chemical properties of experimental mixture of mineral trioxide aggregate and glass ionomer cement
Yu-Na Jeong, So-Young Yang, Bum-Jun Park, Yeong-Joon Park, Yun-Chan Hwang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(5): 344. CrossRef
- The effect of several root-end filling materials on MG63 osteoblast-like cells
- 1,499 View
- 4 Download
- 3 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


