Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption based on cone-beam computed tomographic imaging: a cross-sectional study
- Matheus Diniz Ferreira, Matheus Barros-Costa, Felipe Ferreira Costa, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e39. Published online October 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study investigated the prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption (ECR) regarding sex, age, tooth, stages of progression, and portal of entry, using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans.
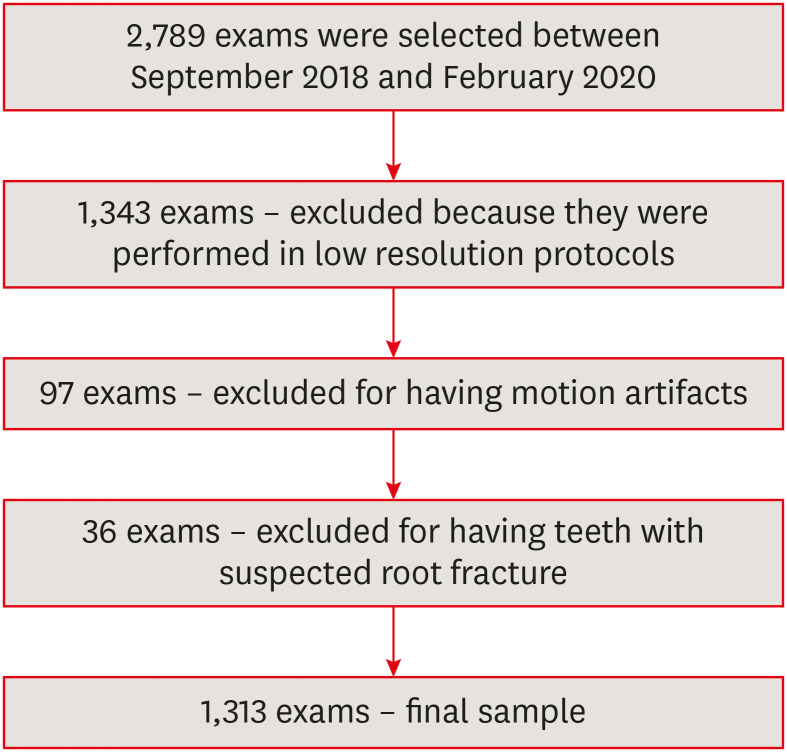
Materials and Methods CBCT scans of 1,313 patients from a Brazilian subpopulation comprising 883 female and 430 male patients (mean age, 55.2 years), acquired using a PreXion 3D CBCT unit, were evaluated. All permanent teeth included in the scans were evaluated for the presence of ECR according to the 3-dimensional classification and the portal of entry. The association between the presence of ECR and the factors studied was assessed using the χ2 test. Intra-observer agreement was analyzed with the kappa test (
α = 0.05).Results In total, 6,240 teeth were analyzed, of which 84 (1.35%) were affected by ECR. A significant association was found between the presence of ECR and sex, with a higher prevalence in male patients (
p = 0.002). The most frequently affected teeth were the mandibular and maxillary central incisors. The most common height was the mid-third of the root. For the portal of entry, 44% of cases were on the proximal surfaces, 40.5% on the lingual/palatal surface and 15.5% on the buccal surface. Intra-observer agreement was excellent.Conclusions The prevalence of ECR was 1.35%, with a higher prevalence in male patients and a wide age distribution. The mandibular and maxillary central incisors were the most commonly affected teeth, and cases of ECR most frequently showed a height into the mid-third of the root and proximal entry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
Terrell F. Pannkuk
Dental Traumatology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Prise en charge des lésions cervicales
C. Mocquot, L. Detzen, I. Fontanille, B. Orlik, F. Decup
EMC - Médecine buccale.2025; 18(3): 1. CrossRef - Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Characterization of External Cervical Resorption Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Isadora Carneiro Pereira Machado, Marilia Oliveira Morais, Adriana Lustosa Pereira Bicalho, Patricia Helena Pereira Ferrari, Juliano Martins Bueno, José Luiz Cintra Junqueira, Mariana Quirino Silveira Soares
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 164. CrossRef - Influence of tube current and metal artifact reduction on the diagnosis of external cervical resorption in teeth adjacent to a dental implant in CBCT: an ex-vivo study
Thamiles Gonzalez-Passos, Matheus Barros-Costa, Matheus L Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Maxillary anterior teeth with extensive root resorption treated with multidisciplinary approach: A case report
Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho, Carollyne Souza Campello, Juliana Pires Abdelnur, Vivian Ronquete, Carlos Henrique Sardenberg Pereira, Marilia F Marceliano-Alves
International Journal of Case Reports and Images.2023; 14(1): 8. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic features of external cervical resorption – An observational study
Shanon Patel, Francesc Abella, Kreena Patel, Paul Lambrechts, Nassr Al‐Nuaimi
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(12): 1475. CrossRef
- External Cervical Resorption Treatment: A Single‐Center Retrospective Cohort Study of Cases Treated Over a 20‐Year Period
- 3,723 View
- 55 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref

- Invasive cervical resorption: treatment challenges
- Yookyung Kim, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):228-231. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.228
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Invasive cervical resorption is a relatively uncommon form of external root resorption. It is characterized by invasion of cervical region of the root by fibrovascular tissue derived from the periodontal ligament. This case presents an invasive cervical resorption occurring in maxillary lateral incisor, following damage in cervical cementum from avulsion and intracoronal bleaching procedure. Flap reflection, debridement and restoration with glass ionomer cement were performed in an attempt to repair the defect. But after 2 mon, more resorption extended apically. Considering root stability and recurrence potential, we decided to extract the tooth. Invasive cervical resorption in advanced stages may present great challenges for clinicians. Therefore, prevention and early detection must be stressed when dealing with patients presenting history of potential predisposing factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Outcome of Decoronation in Severe Cases of External Cervical Root Resorption in Young Patients
Dina Moss, Eyal Nuni, Hagay Slutzky, Daniel Moreinos, Iris Slutzky-Goldberg
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical repair of external cervical resorption - Prognosis and prognostic factors
Po-Yuan Jeng, Shu-Hui Chang, Chen-Ying Wang, Li-Deh Lin, Jiiang-Huei Jeng, Yi-Ling Tsai
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 377. CrossRef - The Disease Process, Diagnosis and Treatment of Invasive Cervical Resorption: A Review
Olivia Rotondi, PhiAnh Waldon, Sahng G. Kim
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(3): 64. CrossRef - Combined endodontic and periodontal management of a class 3 invasive cervical resorption in a mandibular first molar
Takayoshi Nagahara, Katsuhiro Takeda, Yusuke Aida, Tomoyuki Iwata, Ryoichi Yagi, Hidemi Kurihara, Hideki Shiba
Clinical Case Reports.2018; 6(10): 2005. CrossRef - External cervical resorption: a three‐dimensional classification
S. Patel, F. Foschi, F. Mannocci, K. Patel
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 206. CrossRef - Invasive cervical resorption and the oro-facial cleft patient: a review and case series
A. O'Mahony, C. McNamara, A. Ireland, J. Sandy, J. Puryer
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(9): 677. CrossRef - Characteristics and treatment of invasive cervical resorption in vital teeth. A narrative review and a report of two cases
P. Tsaousoglou, E. Markou, N. Efthimiades, I. Vouros
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(6): 423. CrossRef - Fifteen-year Clinical Follow-up of Restoration of Extensive Cervical Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor
EG Reston, RPR Bueno, LQ Closs, J Zettermann
Operative Dentistry.2017; 42(2): E55. CrossRef - The Assessment and Management of External Cervical Resorption with Periapical Radiographs and Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Clinical Study
Kreena Patel, Francesco Mannocci, Shanon Patel
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1435. CrossRef - Management of invasive cervical resorption in a maxillary central incisor
SSenthil Kumar, NS Mohan Kumar, JV Karunakaran, S Nagendran
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2015; 7(6): 712. CrossRef
- Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
- 2,299 View
- 14 Download
- 11 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


