Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- The application of “bone window technique” using piezoelectric saws and a CAD/CAM-guided surgical stent in endodontic microsurgery on a mandibular molar case
- Ukseong Kim, Sunil Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e27. Published online May 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e27
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
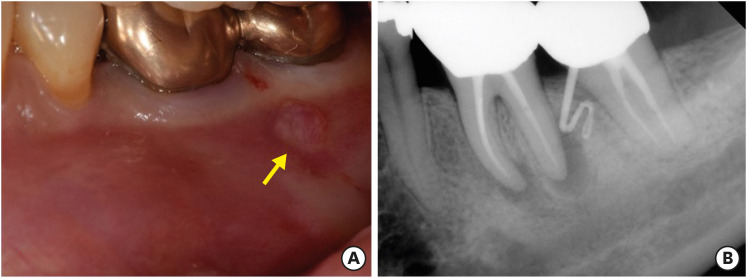
ePub Apical surgery for a mandibular molar is still challenging for many reasons. This report describes the applications of computer-guided cortical ‘bone-window technique’ using piezoelectric saws that prevented any nerve damage in performing endodontic microsurgery of a mandibular molar. A 49-year-old woman presented with gumboil on tooth #36 (previously endodontically treated tooth) and was diagnosed with chronic apical abscess. Periapical lesions were confirmed using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT). Endodontic microsurgery for the mesial and distal roots of tooth #36 was planned. Following the transfer of data of the CBCT images and the scanned cast to an implant surgical planning program, data from both devices were merged. A surgical stent was designed, on the superimposed three-dimensional model, to guide the preparation of a cortical window on the buccal side of tooth #36. Endodontic microsurgery was performed with a printed surgical template. Minimal osteotomy was required and preservation of the buccal cortical plate rendered this endodontic surgery less traumatic. No postoperative complications such as mental nerve damage were reported. Window technique guided by a computer-aided design/computer-aided manufacture based surgical template can be considerably useful in endodontic microsurgery in complicated cases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimising Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: Evidence, Uncertainties and Future Directions
Ukseong Kim, Euiseong Kim
International Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy of Guided Dual Technique in Esthetic Crown Lengthening: A Prospective Case‐Series Study
Meritxell Enfedaque‐Prat, Albert González‐Barnadas, Adrià Jorba‐García, Javi Vilarrasa, Jorge Toledano‐Serrabona, Rui Figueiredo, Eduard Valmaseda‐Castellón, Octavi Camps‐Font
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2025; 37(6): 1284. CrossRef - Guided endodontics in the application of personalized mini-invasive treatment in clinical cases: a literature review
Shuangshuang Ren, Wanping Wang, Mingyue Cheng, Wenyue Tang, Yue Zhao, Leiying Miao
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Accurately Defining the Location and Dimension of the Bony Lid Under the Guidance of Dynamic Navigation: Report on Three Cases
Kailiang Tang, Xiaole Zhang, Qibao Wang, Xinyu Zhao, Xijiao Yu, Yi Du
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025; 51(3): 785. CrossRef - Minimally Invasive Vertical Incision Subperiosteal Tunnelling Technique for Targeted Endodontic Surgery: Technical Overview and a Case Report
Francesc Abella Sans, Jaime Barragán Montes, Tomasz Zbozen, Nandini Suresh, Lalli Dharmarajan, Paul M. H. Dummer, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(11): 1799. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars with an Autonomous Robotic System
Haiying Zhang, Zi Yang, Mangnan Liu, Yaoxin Wang, Mei Fu, Benxiang Hou, Chen Zhang
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(12): 1830. CrossRef - Endodontic Microsurgery of a Mandibular Molar Using a Dynamic Navigation System (DNS) and Cortical Window Technique: A Case Report
Gustavo Castillo, Silvia Restrepo-Méndez, Oscar Zuluaga, Paola Escobar-Villegas
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2024; 3: 1. CrossRef - The bone lid technique in endodontic microsurgery
Min Zhang, He Liu, Ya Shen
Asian Journal of Surgery.2024; 47(7): 3126. CrossRef - Guided Periradicular Surgery with Er,Cr:YSGG Laser Osteotomy: A Case Report
Julian Torres Celeita, Johanna Hernández la Rotta, Amdie Chirinos Salazar, Jorge Fandiño Rodríguez, Laura López Rincón, Mauren Orduz Solorzano, Diana Parra Galvis, Oscar Jiménez Peña
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Piezoelectric Endodontic Microsurgery with Modified Cortical Window Technique: A Case Report
Rafael Fernández-Grisales, Wilder Rojas, Carolina Berruecos-Orozco
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2023; 2: 34. CrossRef - The Impact of the Preferred Reporting Items for Case Reports in Endodontics (PRICE) 2020 Guidelines on the Reporting of Endodontic Case Reports
Sofian Youssef, Phillip Tomson, Amir Reza Akbari, Natalie Archer, Fayjel Shah, Jasmeet Heran, Sunmeet Kandhari, Sandeep Pai, Shivakar Mehrotra, Joanna M Batt
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and radiological outcomes of dynamic navigation in endodontic microsurgery: a prospective study
Chen Chen, Rui Zhang, Wei Zhang, Fangzhe Li, Zan Wang, Li Qin, Yun Chen, Zhuan Bian, Liuyan Meng
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023; 27(9): 5317. CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Failure case analysis during each stage of endodontic microsurgery: A retrospective study based on clinical databases
Changwoo Ryu, Sooil Shin, Yong-Bum Cho, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2023; 13(2): 160. CrossRef - Piezoelectric Device and Dynamic Navigation System Integration for Bone Window-Guided Surgery
Frederico C. Martinho, Ina L. Griffin, Patricia A. Tordik
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(12): 1698. CrossRef - Bone Window Technique in Endodontic Microsurgery – Report of Two Cases
Spyros Floratos, Vasileios Molonis, Apostolos Tsolakis, Stylianos Kykalos, Konstantinos Kontzoglou
Journal of Endodontic Microsurgery.2022; 2: 24. CrossRef - An Update on Endodontic Microsurgery of Mandibular Molars: A Focused Review
Sun Mi Jang, Euiseong Kim, Kyung-San Min
Medicina.2021; 57(3): 270. CrossRef
- Optimising Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: Evidence, Uncertainties and Future Directions
- 1,956 View
- 37 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Development of a mouse model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research: a preliminary study
- Sunil Kim, Sukjoon Lee, Han-Sung Jung, Sun-Young Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(2):e20. Published online May 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
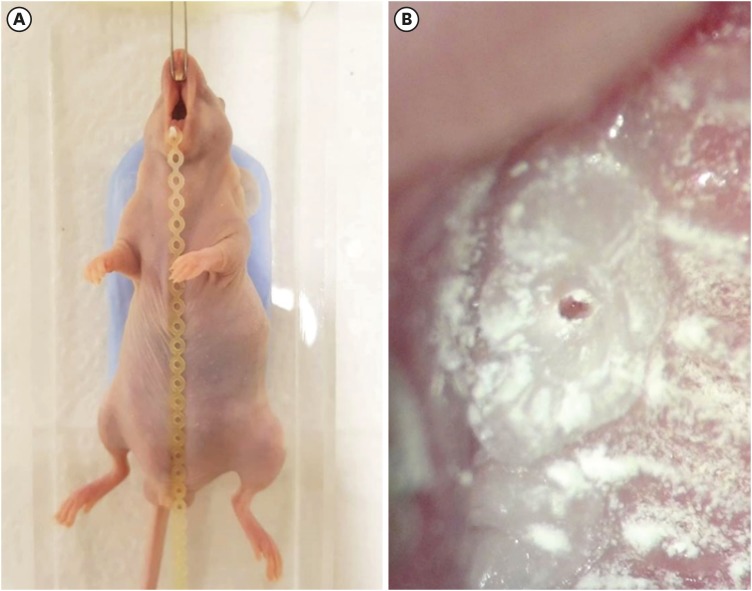
ePub Objectives To achieve pulp-dentin complex regeneration with tissue engineering, treatment efficacies and safeties should be evaluated using
in vivo orthotopic transplantation in a sufficient number of animals. Mice have been a species of choice in which to study stem cell biology in mammals. However, most pulp-dentin complex regeneration studies have used large animals because the mouse tooth is too small. The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the utility of the mouse tooth as a transplantation model for pulp-dentin complex regeneration research.Materials and Methods Experiments were performed using 7-week-old male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice; a total of 35 mice had their pulp exposed, and 5 mice each were sacrificed at 1, 2, 4, 7, 9, 12 and 14 days after pulp exposure. After decalcification in 5% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, the samples were embedded and cut with a microtome and then stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Slides were observed under a high-magnification light microscope.
Results Until 1 week postoperatively, the tissue below the pulp chamber orifice appeared normal. The remaining coronal portion of the pulp tissue was inflammatory and necrotic. After 1 week postoperatively, inflammation and necrosis were apparent in the root canals inferior to the orifices. The specimens obtained after experimental day 14 showed necrosis of all tissue in the root canals.
Conclusions This study could provide opportunities for researchers performing
in vivo orthotopic transplantation experiments with mice.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
Iago Ramirez, Igor Bassi Ferreira Petean, Francisco Wanderley Garcia de Paula-Silva, Aline Aparecida Ferraresi Tiballi, Manoel Damião Sousa-Neto, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes-Olhê, Christie Ramos Andrade Leite-Panissi, Jardel Francisco Mazzi-Chaves
Archives of Oral Biology.2025; 177: 106320. CrossRef - PRIASE 2021 guidelines for reporting animal studies in Endodontology: explanation and elaboration
V. Nagendrababu, A. Kishen, P. E. Murray, M. H. Nekoofar, J. A. P. de Figueiredo, E. Priya, J. Jayaraman, S. J. Pulikkotil, A. Jakovljevic, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(6): 858. CrossRef
- Is dental pulp inflammation capable of causing central inflammation, behavioral, and sensory alterations? A pre-clinical study
- 1,600 View
- 10 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
In vitro characterization of human dental pulp stem cells isolated by three different methods - Ji-Hyun Jang, Hyeon-Woo Lee, Kyu Min Cho, Hee-Woong Shin, Mo Kwan Kang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):283-295. Published online October 12, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we characterized human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) obtained by different culture methods to establish the most suitable methodology for dental tissue engineering and regenerative endodontic applications.
Materials and Methods HDPCs were isolated by the outgrowth method (HDPCs-OG), the enzymatic digestion method (collagenase/dispase/trypsin, HDPCs-ED), or the combination of both methods (HDPCs-Combined). The expression of mesenchymal stem cell markers (CD105, CD90, and CD73) was investigated.
In vitro differentiation capacities of HDPCs into adipogenic, osteogenic, and chondrogenic lineages were compared. Differentiation markers were analyzed by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blotting.Results Our data indicated that whole HDPCs-ED, HPDCs-OG, and HDPCs-Combined could be differentiated into adipogenic, chrondrogenic, and osteogenic cell types. However, we found that the methods for isolating and culturing HDPCs influence the differentiation capacities of cells. HDPCs-OG and HDPCs-ED were preferably differentiated into adipogenic and osteogenic cells, respectively. Differentiation markers shown by RT-PCR and western blotting analysis were mostly upregulated in the treated groups compared with the control groups.
Conclusions Our findings confirmed that cell populations formed by two different culture methods and the combined culture method exhibited different properties. The results of this study could provide an insight into regenerative endodontic treatment using HDPCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of simulated microgravity on dental pulp stem cell stemness
Huailong Hou, Zhengjun Qiu, Jingyi Che, Yanping Li, Jingxuan Sun, Weiwei Zhang, Jinjie Ma, Shuang Zhang, Mengdi Li, Yumei Niu, Lina He
Journal of Molecular Histology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validated methods for isolation and qualification of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells from different sources
Vincenzo Mattei, Francesca Santilli, Fanny Pulcini, Jessica Fabrizi, Loreto Lancia, Costantino Santacroce, Francesca Megiorni, Simona Ceccarelli, Emanuela Paldino, Roberto Gramignoli, Maria G. Roubelakis, Sadri Bahareh, Massoud Vosough, Sveva Bollini, Umb
Journal of Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - ISOLATION OF HUMAN ADULT DENTAL PULP STEM CELLS USING ENZYMATIC DIGESTION
Sehrish Khan, Saima Butt, Shumaila Usman, Sana Mirza
JOURNAL OF KHYBER COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY.2024; 14(4): 9. CrossRef - Diş Hekimliğinde Oromaksillofasiyal Bölgeden Alınabilen Mezenkimal Kök Hücreler
Sefer MAHMUTOĞLU, Ayşegül MENDİ, Derviş YILMAZ
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2022; 11(2): 184. CrossRef - Sinking Our Teeth in Getting Dental Stem Cells to Clinics for Bone Regeneration
Sarah Hani Shoushrah, Janis Lisa Transfeld, Christian Horst Tonk, Dominik Büchner, Steffen Witzleben, Martin A. Sieber, Margit Schulze, Edda Tobiasch
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(12): 6387. CrossRef - Isolation, Characterization, and Differentiation of Stem Cells From Various Dental Sources: An In Vitro Study
Sandeep S. Katti, Kishore Bhat, Chetana Bogar
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2021; 12(2): 254. CrossRef - Intra-Individual Variability of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cell Features Isolated from the Same Donor
Nela Pilbauerova, Jan Schmidt, Tomas Soukup, Jan Duska, Jakub Suchanek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13515. CrossRef - Comparison of Osteogenic Potentials of Dental Pulp and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using the New Cell Transplantation Platform, CellSaic, in a Rat Congenital Cleft-Jaw Model
Jinzhao Lyu, Yoshiya Hashimoto, Yoshitomo Honda, Naoyuki Matsumoto
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(17): 9478. CrossRef - In Vitro Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Cultured in Two Microsphere-Forming Culture Plates
Nam-Ung Bu, Hyo-Seol Lee, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Young Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 242. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Enzymatic Isolation, Amplification and Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Nela Pilbauerova, T. Soukup, T. Suchánková Kleplová, J. Suchánek
Folia Biologica.2019; 65(3): 124. CrossRef - Metabolism as an early predictor of DPSCs aging
Dannie Macrin, Ammar Alghadeer, Yan Ting Zhao, Jason W. Miklas, Abdiasis M. Hussein, Damien Detraux, Aaron M. Robitaille, Anup Madan, Randall T. Moon, Yuliang Wang, Arikketh Devi, Julie Mathieu, Hannele Ruohola-Baker
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of platelet lysate in culture of PDLSCs: anin vitrocomparative study
Duaa A. Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Raghda B. Barham, Nidaa A. Ababneh, Diana A. Shahin, Abdallah A. Al-oweidi, Hanan D. Jafar, Mazin A. Al-Salihi, Abdalla S. Awidi
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7465. CrossRef - Progress in the use of dental pulp stem cells in regenerative medicine
Eduardo Anitua, María Troya, Mar Zalduendo
Cytotherapy.2018; 20(4): 479. CrossRef - Identification of a novel heterozygous mutation of ACAN in a Korean family with proportionate short stature
Yoo-Mi Kim, Chong Kun Cheon, Han Hyuk Lim, Han-Wook Yoo
Journal of Genetic Medicine.2018; 15(2): 102. CrossRef - Conditioned medium from relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients reduces the expression and release of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS-gingivalis in THP-1 and MO3.13 cell lines
Patrizia Ballerini, Francesca Diomede, Nicola Petragnani, Simona Cicchitti, Ilaria Merciaro, Marcos F.X.B. Cavalcanti, Oriana Trubiani
Cytokine.2017; 96: 261. CrossRef
- Effects of simulated microgravity on dental pulp stem cell stemness
- 2,238 View
- 19 Download
- 16 Crossref

-
Antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment: a literature review - Part II.
in vivo studies - Dohyun Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):97-103. Published online December 9, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.97
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The first part of this study reviewed the characteristics of calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) and summarized the results of
in vitro studies related to its antimicrobial effects. The second part of this review coversin vivo studies including human clinical studies and animal studies. The use of Ca(OH)2 as an intracanal medicament represented better histological results in animal studies. However, human clinical studies showed limited antimicrobial effects that microorganisms were reduced but not eliminated through the treatment, and that some species had resistance to Ca(OH)2. Most of clinical outcome studies supported that there is no improvement in healing of periapical lesions when Ca(OH)2 was applied between appointments. Further studies are required for the antimicrobial effects of Ca(OH)2, and search for the ideal material and technique to completely clean infected root canals should be continued.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Antibacterial Efficacy of Graphene Nanoparticles against Enterococcus faecalis: In Vitro Study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Preena Sidhu, Kiran Rehman, Thiagrajan Madheswaran, Amalraj Fabian Davamani
European Journal of Dentistry.2025; 19(01): 103. CrossRef - Evaluation of antibacterial efficacy of propolis as an intercanal medicament against Enterococcus faecalis (a randomized controlled in vitro study)
Alaa Almahameed, Joul Kassis, Magd Aboud, Kinda Layous
Heliyon.2025; 11(1): e41733. CrossRef - Neoangiogenetic potential of Nd:YAG 1064 nm photobiomodulation in non-surgical healing of trauma induced periapical bone defects: a clinicalprospective pilot study
Jagruti Mutalikdesai, Rhythm Bains, Aseem P. Tikku, Ramesh Bharti, Vijay Kumar Shakya, Sukriti Kumar, Promila Verma
Lasers in Medical Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Jasminum-based Nano-reinforced Calcium Hydroxide Reduces Postoperative Pain in Symptomatic Apical Periodontitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Nehal Amir, Emaan Mansoor, Nabiha Eeman, Muhammad Nouman Ahmed, Ezza Mansoor, Efrah Mansoor, Khadim Hussain, Vera Afreixo, Afsheen Mansoor, João Filipe Brochado Martins, Paulo J. Palma
Journal of Endodontics.2025; 51(8): 996. CrossRef - Management of Enterococcus faecalis associated endodontic infection using gold nanogel: An in-vitro study
Omer Sheriff Sultan, Goh Chong Ming Jonathan, Seow Liang Lin, Fabian Davamani, Preena Sidhu, Minati Choudhury
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nano-sized Calcium Hydroxide-Zinc Oxide Intracanal Medicament: Physicochemical Characterization and Potential Endodontic Applications
Kashmiri Chowdhury, S. Delphine Priscilla Antony, Praveen Kumar Elango, Pradeep Solete, Shreshtha Muskan
Journal of International Oral Health.2025; 17(3): 196. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Tooth Discoloration Induced by an Experimental Antibiotic Paste Modified with Nano Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Mohamed Ahmed Elsayed, Md Sofiqul Islam, Safiya Ali, Zainab Hussain, Muhammed Mustahsen Rahman, Okba Mahmoud
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 307. CrossRef - An in vitro study on the antimicrobial efficacy of a calcium hydroxide versus a calcium silicate-based endodontic medicament
Dheepthi Jana, Eda Dzinovic, Ahmed Almaroof, Dipti Mehta, Sherif Elsharkawy, Sanjukta Deb, Sadia Niazi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of canal medicaments triple antibiotic paste, Bio-C Temp, and Nano-silver gel activated by visible blue light on canal dentin microhardness and extrusion bond strength of AH plus sealer: A SEM and EDX analysis
Ahoud Alshamrani, Laila AlDeeb, Thamer Almohareb, Khold Alahdal, Ahmed Maawadh, Ali Alrahlah
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2024; 47: 104088. CrossRef - Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hydrogel-Based Intracanal Medicaments in Endodontics: A Systematic Review of Development and Antibacterial Efficacy
Rathna Piriyanga, Manish Ranjan, Anand Sherwood, Swathi Priyadharshini
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(6): 449. CrossRef - The advancement in irrigation solution within the field of endodontics, A Review
Fatima Fahad , Raghad A Al-Hashimi , Munther J Hussain
Journal of Baghdad College of Dentistry.2024; 36(1): 54. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Action of Novel Panax ginseng Paste, Calcium Hydroxide and Bio-C Temp as an Intracanal Medicament Against Enterococcus faecalis and Streptococcus mutans
Zadeno Kithan, Sonali Taneja, Abhik Mukherjee
Journal of Natural Remedies.2024; : 2705. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Efficacy of Two Different Calcium Hydroxide Endodontic Dressings on the Eradication of Enterococcus faecalis in Single-Rooted Canals: An In Vitro Study
Paola G Rumhein, Kinda J Layous, Hassan Achour, Mudar Mohammad Mousa, Haya Deeb, Mohammad Y Hajeer
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of access cavity design on calcium hydroxide removal using different cleaning protocols: a confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Seda Falakaloğlu, Merve Yeniçeri Özata, Betül Güneş, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Mustafa Gündoğar, Burcu Güçyetmez Topal
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial potential of new diclofenac hydrogels for disinfection in regenerative endodontics: An in vitro and ex vivo study
Matilde Ruiz‐Linares, Javier F. Monroy‐Rojas, Carmen Solana, Pilar Baca, Beatriz Aguado, Ana Soriano‐Lerma, María Teresa Arias‐Moliz, Carmen María Ferrer‐Luque
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(1): 103. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the antibacterial effect ofAllium sativum, calcium hydroxide and their combination as intracanal medicaments in infected mature anterior teeth: A randomized clinical trial
Shaimaa Mohamed Mahfouz Omer, Dalia Abd‐Allah Mohamed, Reham Mohamed Ali Abdel Latif
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(10): 1010. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of antibiotic pastes versus calcium hydroxide intracanal dressing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ex vivo studies
Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Kamyar Khosravi, Nazanin Zargar, Armin Shirvani, MohammadHossein Nekoofar, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 463. CrossRef - Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of Lactobacilli probiotics supernatants against Enterococcus faecalis (in-vitro study)
Shymaa Shaaban, Gamal M. Hamad, Salma Genena, Marwa A. Meheissen, Sybel Moussa
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Superior Antibacterial Efficacy of Calcium Hydroxide–Propolis Paste against Enterococcus faecalis in Infected Root Canals: A Randomized Controlled In Vitro Study
Alessandro Marino, Luca De Santis, Paolo Romano
Interdisciplinary Research in Medical Sciences Specialty.2022; 2(1): 49. CrossRef - Post-operative Pain and Antibacterial Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Formulations Intracanal Medication: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study
Nermine Hassan, Alaa Diab, Geraldine Ahmed
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 248. CrossRef - EFFICACY OF VARIOUS LASER-ASSISTED IRRIGATION ACTIVATION TECHNIQUES ON CALCIUM HYDROXIDE REMOVAL
Ezgi DOĞANAY YILDIZ, Fatma DURNA YURTSEVEN, Dilek HANÇERLİOĞULLARI
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Experimental study the anti-inflammatory and osteo-regenerative qualities of the paste based on symphytum officinale tincture and calcium hydroxide
Iryna Kostyiuk, Victor Kostiuk, Halyna Kimak, Yuriy Oktysyuk, Lilia Tarnavska
Pharmacia.2021; 68(3): 585. CrossRef - Complete Obturation—Cold Lateral Condensation vs. Thermoplastic Techniques: A Systematic Review of Micro-CT Studies
Shilpa Bhandi, Mohammed Mashyakhy, Abdulaziz S. Abumelha, Mazen F. Alkahtany, Mohamed Jamal, Hitesh Chohan, A. Thirumal Raj, Luca Testarelli, Rodolfo Reda, Shankargouda Patil
Materials.2021; 14(14): 4013. CrossRef - Preserving pulp vitality: part two - vital pulp therapies
David Edwards, Simon Stone, Oliver Bailey, Phillip Tomson
British Dental Journal.2021; 230(3): 148. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Antibacterial Efficacy of Daptomycin, Gentamicin, and Calcium Hydroxide—Antibiotic Combinations on Enterococcus faecalis Dentinal Biofilm: An In Vitro Study
Arunajatesan Subbiya, Suresh Mitthra, Kesavaram Padmavathy, Krishnan Mahalakshmi, Alagarsamy Venkatesh, Kotishwaran Gayathri
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2021; 22(2): 128. CrossRef - Evaluation of the influence of sprinkling powdered slaked lime on microorganisms for the prevention of domestic animal infectious diseases
Miho Mori, Yoshikazu Sakagami, Yousuke Hamazaki, Toru Jojima
Environmental Technology.2019; 40(23): 3094. CrossRef - Efficacy of XP-Endo finisher in removal of calcium hydroxide from root canal system: A systematic review
Shruti Kamath, Rajesh Shetty, Soumya Shetty, Nikhil Nighot, Karuna Ramnani, Dhananjay Bhujbal
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2019; 11(2): 54. CrossRef - Calcium Hydroxide as Intracanal Medicament in Pulp Necrosis with Periapical Lesion : A Case Report
Elvi Sahara, Rahmi Alma Farah, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria
Key Engineering Materials.2019; 829: 226. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of clindamycin and triple antibiotic paste as root canal medicaments on tubular infection: An in vitro study
Nazanin Zargar, Motahare Rayat Hosein Abadi, Mohammad Sabeti, Zahra Yadegari, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Omid Dianat
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 86. CrossRef - 2016 ASE undergraduate essay competition candidate information
Alice Chen
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 7. CrossRef - Efficacy of self‐adjusting file, XP‐endo finisher and passive ultrasonic irrigation on the removal of calcium hydroxide paste from an artificial standardized groove
Anda Kfir, Nuphar Blau‐Venezia, Tomer Goldberger, Itzhak Abramovitz, Ronald Wigler
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 26. CrossRef - Local drug delivery in endodontics: A literature review
Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2017; 39: 334. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of Annona crassiflora Mart. against Candida albicans
de Mendonça Cavalcante Amaro, Antonio Lisboa Ribeiro Junior Karlos, CameloPessoa de Azevedo Ximenes Eulália, Porfirio Silva Zenaldo, Ivo Limeira dos Reis José, Euzebio Goulart de Santana Antonio
Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.2017; 11(13): 253. CrossRef - Antifungal effects of synthetic human β-defensin 3-C15 peptide
Sang-Min Lim, Ki-Bum Ahn, Christine Kim, Jong-Won Kum, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Yu Gu, Yeon-Jee Yoo, Seok Woo Chang, Seung Hyun Han, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Seung-Ho Baek, Qiang Zhu, Kee-Yeon Kum
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 91. CrossRef - Microbiology of Root Canal Infections
Marjut Sakko, Leo TjÄDerhane, Riina Rautemaa-Richardson
Primary Dental Journal.2016; 5(2): 84. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 2,990 View
- 34 Download
- 37 Crossref

-
Antimicrobial effect of calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment: a literature review - Part I.
In vitro studies - Dohyun Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):241-252. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.241
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The goal of endodontic treatment is the prevention and control of pulpal and periradicular infections. Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) has been widely used in endodontics as an intracanal medicament to eliminate the remaining microorganisms after chemomechanical preparation. The purpose of this article is to review the antimicrobial properties of Ca(OH)2 as an intracanal medicament in root canal treatment. The first part of this review details the characteristics of Ca(OH)2 and summarizes the results of
in vitro studies related to its antimicrobial effect. The antimicrobial effect of Ca(OH)2 results from the release of hydroxyl ions when it comes into contact with aqueous fluids. Ca(OH)2 has a wide range of antimicrobial effects against common endodontic pathogens, but is less effective againstEnterococcus faecalis andCandida albicans . The addition of vehicles or other agents might contribute to the antimicrobial effect of Ca(OH)2.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
Anu Priya Guruswamy Pandian, Depti Bellani, Ritya Mary Jibu, Varsha Agnihotri
Dental Clinics of North America.2026; 70(1): 45. CrossRef - Sustained-release medicament incorporated with cetylpyridinium chloride: An in vitro assessment of Enterococcus faecalis disinfection
Sankar Vishwanath, Sadasiva Kadandale, Revathy Parthasarathy, Srividhya Srinivasan, Sangita Ilango, Nikesh Shakthivel
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2026; 16(1): 66. CrossRef - Influence of Different Types of Intracanal Medicament and Root Canal Sealers on Root Dentine Fracture Resistance at Two Different Time Intervals
Damla Akkaya, Tugba Kosar
Journal of Endodontics.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Properties of 50% Grape Seed Extract, N-acetyl Cysteine and 5.25% Sodium Hypochlorite against Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 19433) – An In vitro Study
Nikita Vishweshwar Kurtkoti, Madhura Vivek Pawar, Vaishnavi Ketan Mathawala, Shraddha Mahadeo Shirsat
Advances in Human Biology.2025; 15(2): 237. CrossRef - Evaluation of Antimicrobial Performance of Calcium Dihydroxide (Ca(OH)2) Coating on Ti for Potential Metallic Orthopedic Implant Applications
Harald Holeczek, Michael de Wild, Jasmine Ruegg, Philipp Gruner, Walter Moser, Olivier Braissant
Antibiotics.2025; 14(1): 91. CrossRef - Synthesis of uniform core‐shell calcium hydroxide‐calcium carbonate biocidal particles via encapsulation into dry ice
Noora Darwish, Mehdi Mohammadi Ashani, Ahmed Mehairi, Ian A. Lewis, Maen M. Husein
The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering.2025; 103(10): 4774. CrossRef - PROANTHOCYANIDIN-PLGA NANOPARTICLE INFUSED CALCIUM HYDROXIDE SEALER: ADVANCING MATERIAL PERFORMANCE AND CLINICAL STABILITY IN ENDODONTICS
VANDANA SADANANDA, GOWRISH S., R. NARAYANA CHARYULU, MITHRA N. HEGDE
International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics.2025; : 126. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Assessment of Modified Triple Antibiotic Paste, Calcium Hydroxide, Chitosan-loaded Modified Triple Antibiotic Paste against Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Asiya Mujawar, Varsha Pandit, Sumaiyya Shaikh, Bilal A Shaikh
World Journal of Dentistry.2025; 16(2): 142. CrossRef - Recent advances in antibacterial nanoformulations for endodontic applications
Tiago Dionísio, Pedro Brandão, Vanessa Machado, João Botelho, José João Mendes, Pedro Fonte
Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery.2025; 22(8): 1117. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Novel Calcium Hydroxide Nanoparticles in the Different Vehicles against Mixed-species Biofilm: An In Vitro and Ex Vivo Study
Parinthron Rattanakijkamol, Patarawadee Promta, Phenphichar Wanachantararak, Warat Leelapornpisid
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2025; 26(3): 265. CrossRef - Comparison of Efficacy of Trunatomy Irrigation Needle, Sonic Irrigation Technique, and Ultrasonic Irrigation Technique in Retrievability of Rc Cal, Metapex, and Bio C Temp from Root Canals: An In-Vitro CBCT Analysis
Ajay Nevil, Faisal M. A. Gaffoor, Rethi Gopakumar, C. Sabari Girish, N. C. Sajeena, V. N. Anoop
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(Suppl 2): S1827. CrossRef - Non-surgical Management of Immature Permanent Anterior Tooth followed by Single-step Mineral Trioxide Aggregate Apexification
Harsha Haridas, K. Surya, V. Vanitha
Kerala Dental Journal.2025; 48(2): 95. CrossRef - Evaluating antimicrobial, anti-biofilm, and cytotoxic effects of titanium dioxide (TiO2) nanoparticles-coated calcium hydroxide for intracanal use
Khaled Beshr, Hisham M. Elhalabi, Heba Yehia
Advances in Traditional Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Effectiveness of Endodontic Triple Antibiotic Paste Associated With Daptomycin
Sabrina S Azevedo, Gabriela C Chianca, Bruna A Thurler, Raiane C Chamon, Helvécio C Corrêa Póvoa, Leonardo S Antunes, Natalia L Pontes Póvoa Iorio
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Enhanced penetration and antibacterial efficacy of calcium hydroxide modified with titanium dioxide nanoparticles
Teena Sheethal Dsouza, Lakshmi Nidhi Rao, Ashma Dorothy Monteiro, Heeresh Shetty
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontie – State of the Art von A bis Z
Will Qian, Andreas Bartols
Zahnmedizin up2date.2025; 19(04): 281. CrossRef - An in vitro study on the antimicrobial efficacy of a calcium hydroxide versus a calcium silicate-based endodontic medicament
Dheepthi Jana, Eda Dzinovic, Ahmed Almaroof, Dipti Mehta, Sherif Elsharkawy, Sanjukta Deb, Sadia Niazi
Clinical Oral Investigations.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Antibacterial Effect of Cannabinoids on Bacteria Associated with Persistent Endodontic Infections
Cassandra Wieczerza, Haoyan Zhai, Mazin Askar, Zheng Zhou, Susan Paurazas
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2025; 26(24): 11936. CrossRef - Effect of niobium pentoxide incorporated calcium hydroxide as an intracanal medicament on fracture resistance of root canal dentin
Nadimpalli Teja Varma, Venkatappan Sujatha, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(12): 1211. CrossRef - Anterior Palatal Radicular Cyst: A Case Report
Prasanna R Sonar, Aarati Panchbhai, Ankita Pathak, Aachal N Lande, Sandeep Kalisipudi, Osama Ahmed
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Penetration Depth and Antimicrobial Efficacy of Calcium Hydroxide, MAS Paste, Nitrofurantoin, and Levonadifloxacin against Enterococcus faecalis: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study
Nishitha Gunnam, Swathi Aravelli, Nimeshika Ramachandruni, Mounika Gandla, Swetha Kasam, Uday Kumar Podugu
Journal of International Oral Health.2024; 16(5): 394. CrossRef - The Evaluation of Anti-Osteoclastic Activity of the Novel Calcium Hydroxide Biodegradable Nanoparticles as an Intracanal Medicament
Patarawadee Promta, Patcharaporn Chaiyosang, Aussara Panya, Pongrapee Laorodphun, Warat Leelapornpisid, Napatsorn Imerb
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(5): 667. CrossRef - Garre’s osteomyelitis of the mandible managed by nonsurgical re-endodontic treatment
Heegyun Kim, Jiyoung Kwon, Hyun-Jung Kim, Soram Oh, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Glycyrrhizin on the Viability and Proliferation of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Compared to Intracanal Medicaments
Mohamed G Elbeltagy, Manal F Badawi, Amany E Badr, Mohammad A Alrashidi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2024; 25(3): 267. CrossRef - Impact of Calcium Hydroxide Particle Size on the Intracanal Medicament Penetration Efficacy
Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Achdi Afidi, Mutiara Sukma Suntana, Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria, I Made Joni, Ani Melani Maskoen
Diffusion Foundations and Materials Applications.2024; 37: 29. CrossRef - Antibiofilm efficacy of a calcium silicate-based intracanal medicament against Fusobacterium nucleatum strains
Hanan Balto, Reem Barakat, Sumaya Basudan, Ghazal Fakeeha, Sarah R. Alharbi, Rahaf Almohareb
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-surgical management of mandibular first premolar with vertucci type v root canal configuration: A case report
Mohd Faisal Azeez, Neelam Mittal, Shelly Sharma
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2024; 9(3): 146. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of an impacted migrated mandibular canine using platelet-rich fibrin and physio-dispenser system: a report of two cases
Rajmohan Shetty, Vabitha Shetty, Nikhitha Aswath, Kavitha Rai
Dental Update.2024; 51(3): 203. CrossRef - Enterococcus Phage vB_EfaS_HEf13 as an Anti-Biofilm Agent Against Enterococcus faecalis
Dongwook Lee, Jintaek Im, A Reum Kim, Woohyung Jun, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology.2024; 62(8): 683. CrossRef - In-vitro and In-silico evaluation of antimicrobial and antibiofilm effect of Neem oil and Calcium hydroxide nanoparticles against Mutans Streptococci and Enterococcus faecalis isolated from endodontic infections
Wedad M. Nageeb, Sherouk Hussein Adam, Nasr Hashem, Nelly Abdelsalam
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Effects of Formulations of Various Nanoparticles and Calcium Hydroxide as Intra-canal Medications Against Enterococcus faecalis: A Systematic Review
Seema H Bukhari, Dax Abraham, Shakila Mahesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Various Intracanal Medicaments (Curcuma longa, Honey, Nitrofurantoin, and Calcium Hydroxide) on Enterococcus faecalis: An in vitro Study
M. S. Rangareddy, Shanti Priya P., Basa Srinivas Karteek, Chigurupati Swetha, B. Sravan Kumar, Sumaiya Waheed, Jagrati Agrawal
Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics.2024; 15(1): 19. CrossRef - A Novel Control Method of Enterococcus faecalis by Co-Treatment with Protamine and Calcium Hydroxide
Yu Abe, Michiyo Honda
Pharmaceutics.2023; 15(6): 1629. CrossRef - Periapical Pathologies Treated with Conservative Approach
Mohammad Imran Khan, Khushboo Arif, Abhisheik Khare, Pradyumna Mishra
The Traumaxilla.2023; 5(1-3): 64. CrossRef - Effect of different activation methods on the intratubular penetration of CaOH2 paste: Ex‐vivo analysis by confocal laser scanning microscopy
João Pedro Gasparin Tadano, Carlos Eduardo da Silveira Bueno, Cláudia Fernandes de Magalhães Silveira, Tainara Bielecki Yamanaka, Gabriela Gonçalez Piai, Marco Antônio Húngaro Duarte, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Alexandre Sigrist De Martin
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 18. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of postoperative pain with continuous ultrasonic irrigation, laser-activated irrigation, and laser irradiation: A randomized clinical trial
Karishma Krishnakumar, Anita Sanap Tandale, Twinkle Talreja, Ridhi Dube
Endodontology.2023; 35(3): 267. CrossRef - Therapeutic Potential of Chlorhexidine-Loaded Calcium Hydroxide-Based Intracanal Medications in Endo-Periodontal Lesions: An Ex Vivo and In Vitro Study
Kadiatou Sy, Charlène Chevalier, Mickaël Maton, Ilham Mokbel, Séverine Mahieux, Isabelle Houcke, Christel Neut, Brigitte Grosgogeat, Etienne Deveaux, Kerstin Gritsch, Kevimy Agossa
Antibiotics.2023; 12(9): 1416. CrossRef - Non surgical management of a large periapical cyst like lesion using metapex, a three year followup - A case report
Subhashini Ayodhi, Ashok Laburu, Madhuram Krishnamurthy, Naveen Kumar
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2023; 7(4): 186. CrossRef - Single versus multiple visits endodontic therapy on healing rate of periapical lesions: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Athanasios Theodoridis, Nikolaos Economides
Balkan Journal of Dental Medicine.2023; 27(3): 140. CrossRef - Effect of Irrigation Solution of Sodium Hypochlorite, Ethylenediamine Tetraacetic Acid, Chitosan Oligosaccharide and Agitation Techniques on Calcium Hydroxide Removal in Root Canal: In Vitro Study
Melia Heptania, Trimurni Abidin, Widi Prasetia, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2023; : 6008. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of various types of endodontic sealers in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells
Mi-Jeong JEON, Hyunjung KO, Su-Jung SHIN, Miri KIM
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(6): 774. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Antimicrobial Efficacy of Various Antibiotic Pastes and Calcium Hydroxide Using Chitosan as a Carrier Against Enterococcus faecalis: An In Vitro Study
Srinidhi S R, Sania Singh, Ajit Hindlekar, Niranjan Desai, Nishant Vyavahare
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial Irrigation Solutions in Root Canal Treatment: A Glance at the Past, the Present, and the Future
Abubaker Qutieshat, Nutayla Al Harthy, Shima Al Busaidi, Ahmed Al Sadoon, Dima Al Sayahien, Maryam Sedqi, Sumaiya Al Rashdi, Samiya Al Ghammari
The Open Dentistry Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of different intracanal medicaments on the dislodgement resistance of mineral trioxide aggregate
Farzaneh Afkhami, Shahrzad Razavi, Sholeh Ghabraei
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibitory Effect of Medicament Camphorated Parachlorophenol to Bacteria in Chronic Apical Abscess
Diani Prisinda, Yuti Malinda
Applied Mechanics and Materials.2022; 910: 9. CrossRef - The Assessment of Quality of the Root Canal Filling and the Number of Visits Needed for Completing Primary Root Canal Treatment by Operators with Different Experience
Krystyna Pietrzycka, Mateusz Radwanski, Louis Hardan, Rim Bourgi, Davide Mancino, Youssef Haikel, Monika Lukomska-Szymanska
Bioengineering.2022; 9(9): 468. CrossRef - Evaluation of antimicrobial action and push-out bond strength and compressive strength using mineral trioxide aggregate and triple antibiotic medicament combination as root-end filling material
Rahul S. Halkai, Raeesunisa Begum, Kiran R. Halkai, Kiran Ghatole, Ashwini Hambire, Amaan Ahmed
Endodontology.2022; 34(1): 61. CrossRef - Propionate Attenuates Growth of Oral Streptococci through Enhancing Methionine Biosynthesis
Taehwan Park, Jintaek Im, A Reum Kim, Dongwook Lee, Sungho Jeong, Cheol-Heui Yun, Seung Hyun Han
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2022; 32(10): 1234. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of two different intercanal medicaments on human gingival fibroblasts - A Laboratory study
Behnaz Barakatein, Alireza Farhad, Elham Shadmehr, Hamidreza Mohammad Sharifi, Masoud Mohammadi Hamidreza Mohamad Sharif, Amin Davoudi
Endodontology.2022; 34(2): 76. CrossRef - The efficacy of EndoActivator, passive ultrasonic irrigation, and Ultra X in removing calcium hydroxide from root canals: an in-vitro study
Alireza Adl, Alireza Razavian, Fateme Eskandari
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of Calcium Hydroxide with Vehicles Relate to the pH Change, Calcium Ion Diffusion, Roughness, and Frequency of Chemical Compound in Root Canal
Dwi Yani Sastika, Trimurni Abidin, Harry Agusnar, Basri A. Gani
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2022; : 2976. CrossRef - Influence of different calcium hydroxide removal protocols on the bond strength of epoxy resin‐based sealer in long oval root canals
Patrícia Maria Escobar, Fabiane Carneiro Lopes, Kleber Carvalho, Vicente Fretes, Gabriela Gavilán Hadid, Jardel Francisco Mazzi‐Chaves, Manoel Damião Sousa‐Neto
Microscopy Research and Technique.2022; 85(2): 781. CrossRef - Antibacterial efficacy of antibiotic pastes versus calcium hydroxide intracanal dressing: A systematic review and meta-analysis of ex vivo studies
Mohammadreza Vatankhah, Kamyar Khosravi, Nazanin Zargar, Armin Shirvani, MohammadHossein Nekoofar, Omid Dianat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(5): 463. CrossRef - EFFICACY OF VARIOUS LASER-ASSISTED IRRIGATION ACTIVATION TECHNIQUES ON CALCIUM HYDROXIDE REMOVAL
Ezgi DOĞANAY YILDIZ, Fatma DURNA YURTSEVEN, Dilek HANÇERLİOĞULLARI
Atatürk Üniversitesi Diş Hekimliği Fakültesi Dergisi.2021; : 1. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity, cytocompatibility and effect of Bio‐C Temp bioceramic intracanal medicament on osteoblast biology
J. C. M. Guerreiro, V. M. Ochoa‐Rodrígez, E. M. Rodrigues, G. M. Chavez‐Andrade, M. Tanomaru‐Filho, J. M. Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, G. Faria
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(7): 1155. CrossRef - Comparison of Antibacterial Effects of Heracleum persicum and Ziziphora tenuior L. Extracts, Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine on Enterococcus faecalis as Intracanal Medicaments in Root Canal Therapy – An In Vitro Study
Aida Mehdipour, Maryam Akbarzadeh, Somayeh Kermani, Saeed Shams, Alireza Karimi
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(38): 3395. CrossRef - Interdisciplinary management of a maxillary central incisor with a palato‐radicular groove: A case report with 27 years follow‐up
David P. Mathews, David E. Hansen
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2021; 33(8): 1077. CrossRef - How Adding Chlorhexidine or Metallic Nanoparticles Affects the Antimicrobial Performance of Calcium Hydroxide Paste as an Intracanal Medication: An In Vitro Study
Kadiatou Sy, Kevimy Agossa, Mickaël Maton, Henry Chijcheapaza-Flores, Bernard Martel, Florence Siepmann, Etienne Deveaux, Nicolas Blanchemain, Christel Neut
Antibiotics.2021; 10(11): 1352. CrossRef - Selenium intracanal dressing: effects on the periapical immune response
Marcela Carvalho Espaladori, Julia Mourão Braga Diniz, Luciana Carla Neves de Brito, Warley Luciano Fonseca Tavares, Toshihisa Kawai, Leda Quercia Vieira, Antônio Paulino Ribeiro Sobrinho
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(5): 2951. CrossRef - Post-operative Pain and Antibacterial Efficacy of Silver Nanoparticles Formulations Intracanal Medication: A Randomized Controlled Clinical Study
Nermine Hassan, Alaa Diab, Geraldine Ahmed
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(D): 248. CrossRef - Comparative Assessment of Role of Intracanal Medicaments in Pain Reduction during Endodontic Treatment
Sadashiv G. Daokar, Aishwarya Rajesh Mantri, Kalpana S. Patil, Kapil D. Wahane, Suraj V. Rathi, Shivangi Shashikant Sharma
Journal of Interdisciplinary Dentistry.2021; 11(2): 73. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of Asphaline Temp, Triple antibiotic Paste and Ultracal XS against Enterococcus faecalis – An in vitro study
Siddhesh Bandekar, Aditi Amin, Shirin Kshirsagar, N Vathsala, Vyas Chinmay, Anjum Sayyad
Endodontology.2021; 33(1): 6. CrossRef - Antibacterial evaluation of guava leaves extract and its effect on reactive oxygen species formed by calcium hydroxide and chlorhexidine mixture
KarmaDeepak Chandran, Kittappa Karthikeyan, Venkatappan Sujatha, Sekar Mahalaxmi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(4): 389. CrossRef - The Effects of Intracanal Irrigants and Medicaments on Dental-Derived Stem Cells Fate in Regenerative Endodontics: An update
Sara Ayoub, Ali Cheayto, Sanaa Bassam, Mehdi Najar, Antoine Berbéri, Mohammad Fayyad-Kazan
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2020; 16(4): 650. CrossRef - Nonsurgical management of persistent periapical lesions in the anterior region - A systematic review
SayaliAnil Maral, AnamikaChetan Borkar, AnitaBabasaheb Tandale, NikhilBabaji Nighot, SanchitVilas Mujumdar, ShrutiSudhakar Khade
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2020; 12(1): 8. CrossRef - Nonsurgical Removal of Overextended Gutta-Percha Root Canal Filling in a Permanent Maxillary Central Incisor with Apical Root Resorption - A Case Report
Gaurav Umesh Chaudhari, Sumanthini Venkatsubramanyam Margasahayam, Vanitha Umesh Shenoy, Akash Kiran More, Anuradha Bhausaheb Patil
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2020; 9(42): 3159. CrossRef - Oroactive dental biomaterials and their use in endodontic therapy
Ebrahim Patel, Priyamvada Pradeep, Pradeep Kumar, Yahya E. Choonara, Viness Pillay
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2020; 108(1): 201. CrossRef - The Use of Calcium Hydroxide as an Intracanal Medicament in the Treatment of Large Periapical Lesions. A Review
Timea Dako, Mihai Pop, Julia Fulop, Janos Kantor, Monica Monea
Acta Medica Transilvanica.2020; 25(2): 58. CrossRef - Facile synthesis of highly tunable monodispersed calcium hydroxide composite particles by using a two-step ion exchange reaction
Chih-Hui Yang, Ya-Chin Wang, Ta-Chen Wang, Yi-Ching Chang, Yun-Chul Lin, Pei-Fan Chen, Wei-Jie Huang, Hsin-Yi Wen, Yu-Mei Lin, Wen-Shuo Kuo, Yi-Ting Wang, Keng-Shiang Huang
RSC Advances.2020; 10(23): 13700. CrossRef - The Comparison of Different Irrigation Systems to Remove Calcium Hydroxide from the Root Canal: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Samira Jamali, Golchin Jabbari, Elnaz Mousavi, Hashem Ahmadizadeh, Mohammad Khorram, Azad Jamee
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Detection, treatment and prevention of endodontic biofilm infections: what’s new in 2020?
Sumaya Abusrewil, Om Alkhir Alshanta, Khawlah Albashaireh, Saeed Alqahtani, Christopher J. Nile, James Alun Scott, William McLean
Critical Reviews in Microbiology.2020; 46(2): 194. CrossRef - Antimicrobial efficacy of clindamycin and triple antibiotic paste as root canal medicaments on tubular infection: An in vitro study
Nazanin Zargar, Motahare Rayat Hosein Abadi, Mohammad Sabeti, Zahra Yadegari, Alireza Akbarzadeh Baghban, Omid Dianat
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(1): 86. CrossRef - Antibacterial activity of various calcium hydroxide solvents against Fusobacterium nucleatum and Enterococcus faecalis
Siti Rusdiana Puspa Dewi, Riki Agung Santoso, Billy Sujatmiko, Ickman Seto Wibowo
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2019; 1246(1): 012010. CrossRef - Efficacy of XP-Endo finisher in removal of calcium hydroxide from root canal system: A systematic review
Shruti Kamath, Rajesh Shetty, Soumya Shetty, Nikhil Nighot, Karuna Ramnani, Dhananjay Bhujbal
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2019; 11(2): 54. CrossRef - Antibacterial power effectiveness of calcium hydroxide and propolis mixture on Fusobacterium nucleatum bacteria
Ira Widjiastuti, S. Sukaton, Agnes Melinda Wong, Nanik Zubaidah
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2019; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - Antimicrobial Potential of Calcium Hydroxide Chlorhexidine, Octenidol, Endoseptone and Combination of Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine against Enterococcus faecalis as Intracanal Medicament
Aakriti Aakriti, Dildeep Bali, Preeti Sharma, Vijaya Dhar Bhatt, Prashant Bhasin, Era Arora, Suhrab Singh, Pradeep Kumar
Journal of Pure and Applied Microbiology.2019; 13(3): 1725. CrossRef - Efficacy of self‐adjusting file, XP‐endo finisher and passive ultrasonic irrigation on the removal of calcium hydroxide paste from an artificial standardized groove
Anda Kfir, Nuphar Blau‐Venezia, Tomer Goldberger, Itzhak Abramovitz, Ronald Wigler
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 26. CrossRef - Triple antibiotic paste: momentous roles and applications in endodontics: a review
Ardavan Parhizkar, Hanieh Nojehdehian, Saeed Asgary
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Antimicrobial properties of calcium hydroxide dressing when used for long‐term application: A systematic review
Garima Sharma, Hany Mohamed Aly Ahmed, Peter S. Zilm, Giampiero Rossi‐Fedele
Australian Endodontic Journal.2018; 44(1): 60. CrossRef - Influence of dental materials on cells of the equine periodontium
H. Ringeisen, A. Pöschke, B. Krähling, C. Schröck, M. Stoll, J. Vogelsberg, K. Failing, C. Staszyk
Equine Veterinary Journal.2018; 50(3): 363. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Hydroxide Dressing on the Dentinal Tubule Penetration of 2 Different Root Canal Sealers: A Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopic Study
Emel Uzunoglu-Özyürek, Özge Erdoğan, Sevinç Aktemur Türker
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(6): 1018. CrossRef - Synthesis and Characterization of Calcium Hydroxide from Indonesian Limestone as Endodontic Intracanal Medicament
Myrna Nurlatifah Zakaria, Atia Nurul Sidiqa, Ira Artilia, Arief Cahyanto
Key Engineering Materials.2018; 782: 268. CrossRef - Slightly acidic electrolyzed water combined with chemical and physical treatments to decontaminate bacteria on fresh fruits
Charles Nkufi Tango, Imran Khan, Paul-François Ngnitcho Kounkeu, Rubab Momna, Mohammad Shakhawat Hussain, Deog-Hwan Oh
Food Microbiology.2017; 67: 97. CrossRef - Antimicrobial activity of Annona crassiflora Mart. against Candida albicans
de Mendonça Cavalcante Amaro, Antonio Lisboa Ribeiro Junior Karlos, CameloPessoa de Azevedo Ximenes Eulália, Porfirio Silva Zenaldo, Ivo Limeira dos Reis José, Euzebio Goulart de Santana Antonio
Journal of Medicinal Plants Research.2017; 11(13): 253. CrossRef - Comparison of ozone gas and sodium hypochlorite/chlorhexidine two-visit disinfection protocols in treating apical periodontitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial
Stefan Kist, Maximilian Kollmuss, Jette Jung, Sören Schubert, Reinhard Hickel, Karin Christine Huth
Clinical Oral Investigations.2017; 21(4): 995. CrossRef - Cytotoxicities and genotoxicities of cements based on calcium silicate and of dental formocresol
Hyunjung Ko, Youngdan Jeong, Miri Kim
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2017; 815: 28. CrossRef - Local drug delivery in endodontics: A literature review
Shin Hye Chung, Young-Seok Park
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2017; 39: 334. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Mixture of Calcium Hydroxide and Chlorhexidine, with Triple Antibiotic Paste and Combination of Calcium Hydroxide, Chlorhexidine, and Lycopene on Incidence of Interappointment Flare-up: An in vivo Study
Priyanka S Bilgi, Jash Mehta
International Journal of Clinical Dentistry and Research.2017; 1(1): 10. CrossRef - Antibacterial effectiveness in vitro of different formulations of calcium hydroxide paste
Israel Alexandre De Araujo SENA, Isaac Jordão De Souza ARAÚJO, Marquiony Marques Dos SANTOS, Isabela Pinheiro Cavalcanti LIMA
RGO - Revista Gaúcha de Odontologia.2017; 65(4): 293. CrossRef - Challenges in developing valid techniques for equine endodontic treatment of apically infected cheek teeth
R. M. Baratt
Equine Veterinary Education.2016; 28(11): 609. CrossRef - Discuss the role of microorganisms in the aetiology and pathogenesis of periapical disease
Vincent Aw
Australian Endodontic Journal.2016; 42(2): 53. CrossRef - Lesion Sterilization and Tissue Repair (LSTR): A Review
Anila B, Murali H, Cheranjeevi J, Kapil RS
Journal of Scientific Dentistry.2014; 4(2): 49. CrossRef
- Endodontic Intracanal Medicaments and Agents
- 6,849 View
- 78 Download
- 92 Crossref

- Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
- Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):79-88. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.79
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Appropriate use of local hemostatic agent is one of the important factors on the prognosis of endodontic microsurgery. However, most investigations to date focus on the hemostatic efficacy of the agents, whereas their biologic characteristics have not received enough attention. The purpose of this paper was to review the biologic response of local hemostatic agents, and to provide clinical guidelines on their use during endodontic microsurgery. Electronic database (PUBMED) was screened to search related studies from 1980 to 2013, and 8 clinical studies and 18 animal studies were identified. Among the materials used in these studies, most widely-investigated and used materials, epinephrine, ferric sulfate (FS) and calcium sulfate (CS), were thoroughly discussed. Influence of these materials on local tissue and systemic condition, such as inflammatory and foreign body reaction, local ischemia, dyspigmentation, delayed or enhanced bone and soft tissue healing, and potential cardiovascular complications were assessed. Additionally, biological property of their carrier materials, cotton pellet and absorbable collagen, were also discussed. Clinicians should be aware of the biologic properties of local hemostatic agents and their carrier materials, and should pay attention to the potential complications when using them in endodontic microsurgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A drug-carrying, multiscene, absorbable biological suture from fish swim bladder
Peng Sun, Hao Cui, Jinwei Zhang, Jingan Li, Changwei Ren, Yongqiang Lai
International Journal of Surgery.2025; 111(10): 6663. CrossRef - Assessing the efficacy of apicoectomy without retrograde filling in treating periapical inflammatory cysts
Jeong-Kui Ku, Woo-Young Jeon, Seung-O Ko, Ji-Young Yoon
Journal of the Korean Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons.2024; 50(3): 140. CrossRef - Functional and structural neurodegenerative activities of Ankaferd BloodStopper in a mouse sciatic nerve model
Ramazan Üstün, Elif Oğuz, Ayşe Şeker, Filiz Taspinar
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Local and Systemic Hemostatic Agents: A Comprehensive Review
Bardia Jamali, Saeed Nouri, Salimeh Amidi
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - PLGA Nanoparticle Rapamycin- or Necrostatin-1-Coated Sutures Inhibit Inflammatory Reactions after Arterial Closure in Rats
Liwei Zhang, Wang Wang, Boao Xie, Peng Sun, Shunbo Wei, Haoliang Wu, Cong Zhang, Jingan Li, Zhuo Li, Hualong Bai
ACS Applied Bio Materials.2022; 5(4): 1501. CrossRef - COMPARING THE CLINICAL AND RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES OF PULPOTOMIES IN PRIMARY MOLARS USING BIOACTIVE ENDODONTIC MATERIALS AND FERRIC SULFATE – A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS OF RANDOMIZED CLINICAL TRIALS
VELLORE KANNAN GOPINATH, SHAJU JACOB PULIKKOTIL, SAJESH K VEETTIL, LALLI DHARMARAJAN, PONNUDURAI SAMUEL GNANA PRAKASH, VINEET DHAR, JAYAKUMAR JAYARAMAN
Journal of Evidence-Based Dental Practice.2022; 22(4): 101770. CrossRef - Perioperative Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Management with Endodontic Microsurgical Techniques
Anita Aminoshariae, Mark Donaldson, Michael Horan, James C. Kulild, Dale Baur
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(10): 1557. CrossRef - Effect of blood contamination and various hemostatic procedures on the push-out bond strength of Biodentine when used for furcation perforation repair
Shanthana Reddy, Ramya Shenoy, LohithReddy Mandadi, Ishani Saluja, ManuelS Thomas
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2021; 24(3): 260. CrossRef - Endodontic Perforation Closure by Five Mineral Oxides Silicate-Based Cement with/without Collagen Sponge Matrix
Talal Al-Nahlawi, Maisour Ala Rachi, Amjad Abu Hasna, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Hemostatic agents in periapical surgery: The systematic review
Z. S. Khabadze, D. A. Nazarova, E. S. Shilyaeva, A. P. Kotelnikova, Yu. A. Bakayev, S. M. Abdulkerimova, Kh. O. Omarova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(3): 184. CrossRef - An Innovative Bioceramic Bone Graft Substitute for Bone Defect Treatment: In Vivo Evaluation of Bone Healing
Syamsiah Syam, Yung-Chieh Cho, Chung-Ming Liu, Mao-Suan Huang, Wen-Chien Lan, Bai-Hung Huang, Takaaki Ueno, Chi-Hsun Tsai, Takashi Saito, May-Show Chen, Keng-Liang Ou
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(22): 8303. CrossRef - Trial finds better haemostasis with aluminium chloride during periapical surgery
Niall Mc Goldrick, Carly Ross, James Nelson
Evidence-Based Dentistry.2017; 18(2): 50. CrossRef - Comparison of the Hemostatic Activity of Quercus persica Jaub. & Spach. (Oak) With Ferric Sulfate in Bony Crypts
Mohammad Reza Nabavizadeh, Arman Zargaran, Fariborz Moazami, Fatemeh Askari, Safoora Sahebi, Alireza Farhadpoor, Pouya Faridi
Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine.2016; 21(1): 34. CrossRef - Effect of the plant-based hemostatic agent Ankaferd Blood Stopper® on the biocompatibility of mineral trioxide aggregate
Muzaffer Emir Dinçol, Hakan Ozbas, Bulent Yılmaz, Handan Ersev, Selcuk Gokyay, Vakur Olgac
BMC Oral Health.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 2,511 View
- 14 Download
- 15 Crossref

- Cytotoxicity of newly developed pozzolan cement and other root-end filling materials on human periodontal ligament cell
- Minju Song, Tae-Sun Yoon, Sue-Youn Kim, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(1):39-44. Published online January 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.1.39
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate
in vitro cytotoxicity of the pozzolan cement and other root-end filling materials using human periodontal ligament cell.Materials and Methods Endocem (Maruchi), white ProRoot MTA (Dentsply), white Angelus MTA (Angelus), and Super EBA (Bosworth Co.) were tested after set completely in an incubator at 37℃ for 7 days, Endocem was tested in two ways: 1) immediately after mixing (fresh specimens) and 2) after setting completely like other experimental materials. The methods for assessment included light microscopic examination, cell counting and WST-1 assay on human periodontal ligament cell.
Results In the results of microscopic examination and cell counting, Super EBA showed significantly lower viable cell than any other groups (
p < 0.05). As the results of WST-1 assay, compared with untreated control group, there was no significant cell viability of the Endocem group. However, the fresh mixed Endocem group had significantly less cell viability. The cells exposed to ProRoot MTA and Angelus MTA showed the highest viability, whereas the cells exposed to Super EBA displayed the lowest viability (p < 0.05).Conclusions The cytotoxicity of the pozzolan cement (Endocem) was comparable with ProRoot MTA and Angelus MTA. Considering the difficult manipulation and long setting time of ProRoot MTA and Angelus MTA, Endocem can be used as the alternative of retrofilling material.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of Three Retrograde Filling Materials on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Resorbing Mediators
Samaneh Arab, Marjan Bahraminasab, Masoumeh Motamedi, Jamshid Hadjati, Alaviye Vahid
Journal of Microbiota.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Physicochemical Properties, Cytocompatibility, and Biocompatibility of a Bioactive Glass Based Retrograde Filling Material
Kazumasa Murata, Ayako Washio, Takahiko Morotomi, Thira Rojasawasthien, Shoichiro Kokabu, Chiaki Kitamura
Nanomaterials.2021; 11(7): 1828. CrossRef - Cell migration and osteo/odontogenesis stimulation of iRoot FS as a potential apical barrier material in apexification
Y. Liu, X. M. Liu, J. Bi, S. Yu, N. Yang, B. Song, X. Chen
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(4): 467. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of Biodentine™ ® with Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells: In Vitro Study
Duaa Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Hanan Jafar, Zakariya Abu Harfil, Abdalla Awidi
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(1): 17. CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study of remaining filling materials of two bioceramic sealers and epoxy resin sealer after retreatment
KyungJae Kim, Da Vin Kim, Sin-Young Kim, SungEun Yang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Gap Volume after Retrofilling Using 4 Different Filling Materials: Evaluation by Micro–computed Tomography
Sue Youn Kim, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(4): 635. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory and Mineralization Effects of ProRoot MTA and Endocem MTA in Studies of Human and Rat Dental Pulps In Vitro and In Vivo
Do-Hee Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Sun-Hun Kim, Kyung-San Min, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1534. CrossRef - Effects of Three Calcium Silicate Cements on Inflammatory Response and Mineralization-Inducing Potentials in a Dog Pulpotomy Model
Chung-Min Kang, Jiwon Hwang, Je Seon Song, Jae-Ho Lee, Hyung-Jun Choi, Yooseok Shin
Materials.2018; 11(6): 899. CrossRef - Cytocompatibility of Biodentine and iRoot FS with human periodontal ligament cells: an in vitro study
T. Luo, J. Liu, Y. Sun, Y. Shen, L. Zou
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(7): 779. CrossRef - Biological response of commercially available different tricalcium silicate‐based cements and pozzolan cement
Serhat Köseoğlu, Tuğba Pekbağr?yan?k, Ebru Kucukyilmaz, Mehmet Sağlam, Sukru Enhos, Ayşe Akgün
Microscopy Research and Technique.2017; 80(9): 994. CrossRef - Biological efficacy of two mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA)-based materials in a canine model of pulpotomy
Myeongyeon LEE, Chung-Min KANG, Je Seon SONG, Yooseok SHIN, Seunghye KIM, Seong-Oh KIM, Hyung-Jun CHOI
Dental Materials Journal.2017; 36(1): 41. CrossRef - Cytotoxicities and genotoxicities of cements based on calcium silicate and of dental formocresol
Hyunjung Ko, Youngdan Jeong, Miri Kim
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2017; 815: 28. CrossRef - Bioactive-glass in Endodontic Therapy and Associated Microsurgery
Andrea Corrado Profeta, Gian Marco Prucher
The Open Dentistry Journal.2017; 11(1): 164. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Super Ethoxybenzoic Acid as Root-end Filling Materials in Endodontic Microsurgery: Long-term Outcomes
Sunil Kim, Minju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(7): 997. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting calcium-silicate cements on cell viability and angiogenic factor release in human pulp-derived cells
Chooryung J. Chung, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 143. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and Initial Biocompatibility of Endodontic Biomaterials (MTA and Biodentine™) Used as Root-End Filling Materials
Diana María Escobar-García, Eva Aguirre-López, Verónica Méndez-González, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
BioMed Research International.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - In Vitro Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Three Root-End Filling Materials in Human Periodontal Ligament Fibroblasts
Hernán Coaguila-Llerena, Abraham Vaisberg, Zulema Velásquez-Huamán
Brazilian Dental Journal.2016; 27(2): 187. CrossRef - Dynamic intratubular biomineralization following root canal obturation with pozzolan‐based mineral trioxide aggregate sealer cement
Yeon‐Jee Yoo, Seung‐Ho Baek, Kee‐Yeon Kum, Won‐Jun Shon, Kyung‐Mi Woo, WooCheol Lee
Scanning.2016; 38(1): 50. CrossRef - A Randomized Controlled Study of the Use of ProRoot Mineral Trioxide Aggregate and Endocem as Direct Pulp Capping Materials
Minju Song, Minji Kang, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(1): 11. CrossRef - Comparative Analysis of Selected Physicochemical Properties of Pozzolan Portland and MTA-Based Cements
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha, Alex Semenoff-Segundo, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Alvaro Henrique Borges
International Scholarly Research Notices.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Surgical endodontics: past, present, and future
James L. Gutmann
Endodontic Topics.2014; 30(1): 29. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 201. CrossRef
- Effects of Three Retrograde Filling Materials on Production of Inflammatory Cytokines and Resorbing Mediators
- 1,477 View
- 1 Download
- 22 Crossref

- Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
- Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(4):187-193. Published online November 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.4.187
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Epinephrine is one of the most widely-used vasoconstrictors in dental treatment including endodontic microsurgery. However, the systemic safety of epinephrine has been in debate for many years because of its potential risk to cause cardiovascular complications. The purpose of this review was to assess the cardiovascular effect of epinephrine use in endodontic microsurgery. Endodontic microsurgery directly applies epinephrine into the bone cavity, and the amount is reported to be much larger than other dental surgeries. Moreover, when considering that systemic potency of intraosseous application is reported to be comparable to intravenous application, the systemic influence of epinephrine could be increased in endodontic microsurgery. Besides, pre-existing cardiovascular complications or drug interactions can enhance its systemic influence, resulting in increased susceptibility to cardiovascular complications. Although clinical studies have not reported significant complications for patients without severe systemic complications, many epinephrine-induced emergency cases are warning the cardiovascular risk related with pre-existing systemic disease or drug interactions. Epinephrine is a dose-sensitive drug, and its hypersensitivity reaction can be fatal to patients when it is related to cardiovascular complications. Therefore, clinicians should recognize the risk, and the usage of pre-operative patient evaluation, dose control and patient monitoring are required to ensure patient's safety during endodontic microsurgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Local Hemostatic Agents in Minor Oral Surgical Procedures: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Kshitija Patil, Jay N Goyal, Saurabh Dudhe, Janice John, Simona Joseph, Sanchi Kadbe, Seema Gupta
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacological Interactions of Epinephrine at Concentrations Used in Dental Anesthesiology: An Updated Narrative Review
Maria Aikaterini Saraga, Ioannis Fotopoulos, Vasileios Zisis, Athanasios Poulopoulos, Nikolaos Dabarakis, Theodoros Lillis
Reports.2025; 8(4): 224. CrossRef - Effects of nasal desmopressin spray versus topical epinephrine on surgical field clarity and hemodynamics in endonasal dacryocystorhinostomy: a randomized clinical study
Mohamed G.M. El Sayed, Marwa M. Medhat, Dina A.E. Salem, Marwa A.M. Khedr, Alshaimaa A.F. Kamel
Research and Opinion in Anesthesia & Intensive Care.2024; 11(1): 1. CrossRef - Is 1:1000 adrenaline as a topical haemostat an effective alternative to control bleeding in dentistry and oral surgery?
Raj D. Aslam, Jonathan Liew, Eleni Besi
British Dental Journal.2023; 235(1): 29. CrossRef - Effect of Flumazenil on Emergence Agitation after Orthognathic Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Young Hyun Koo, Geun Joo Choi, Hyun Kang, Yong Hun Jung, Young Cheol Woo, Young-Jun Choi, Chong Wha Baek
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(3): 416. CrossRef - Hemostatic agents in periapical surgery: The systematic review
Z. S. Khabadze, D. A. Nazarova, E. S. Shilyaeva, A. P. Kotelnikova, Yu. A. Bakayev, S. M. Abdulkerimova, Kh. O. Omarova
Endodontics Today.2021; 19(3): 184. CrossRef - THE EFFECT OF ADRENALINE ON DYNAMICS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM INDICES IN RATS
S. Shkurashivska, H. Ersteniuk
Visnyk of Lviv University. Biological series.2017; (75): 151. CrossRef - The Correlation between the Blood Sugar and Allergy of the Trauma Patient
Jeong Soo Lee, Sung Hee Hyun, Ji-Sook Lee, In Sik Kim
Korean Journal of Clinical Laboratory Science.2014; 46(1): 22. CrossRef - Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 1,802 View
- 5 Download
- 10 Crossref

- Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
- Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):113-118. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.113
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Nowadays, oral anticoagulants are commonly prescribed to numerous patients for preventing cardiovascular accident such as thromboembolism. An important side effect of anticoagulant is anti-hemostasis. In a major surgery, the oral anticoagulant therapy (OAT) regimen must be changed before the surgery for proper post-operative bleeding control. However, in a minor dental surgery and endodontic surgery, the necessity for changing or discontinuing the OAT is open to debate. In this study, risks of the consequences were weighed and analyzed. In patients who stop the OAT, the occurrence of thromboembolic complication is rare but the result is fatal. In patients who continuing the OAT, post-operative bleeding can be controlled well with the local hemostatic measures. In the endodontic surgery, there are almost no studies about this issue. The intra-operative bleeding control is particularly important in the endodontic surgery because of its delicate and sensitive procedures such as inspection of resected root surface using dental microscope and retrograde filling. Further studies are necessary about this issue in the viewpoint of endodontic surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Patients Receiving Anticoagulation Therapy in Dental Practice: A Systematic Review
Francesco Inchingolo, Angelo Michele Inchingolo, Fabio Piras, Laura Ferrante, Antonio Mancini, Andrea Palermo, Alessio Danilo Inchingolo, Gianna Dipalma
Healthcare.2024; 12(15): 1537. CrossRef - Hemostatic Alginate/Nano-Hydroxyapatite Composite Aerogel Loaded with Tranexamic Acid for the Potential Protection against Alveolar Osteitis
Mai El Halawany, Randa Latif, Mohamed H. H. AbouGhaly
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(10): 2255. CrossRef - Perioperative Antiplatelet and Anticoagulant Management with Endodontic Microsurgical Techniques
Anita Aminoshariae, Mark Donaldson, Michael Horan, James C. Kulild, Dale Baur
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(10): 1557. CrossRef - Administration of Coagulation-Altering Therapy in the Patient Presenting for Oral Health and Maxillofacial Surgery
Thomas M. Halaszynski
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America.2016; 28(4): 443. CrossRef - Biologic response of local hemostatic agents used in endodontic microsurgery
Youngjune Jang, Hyeon Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 79. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effect of epinephrine in endodontic microsurgery: a review
Youngjune Jang, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 187. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 1,989 View
- 5 Download
- 7 Crossref

- Does apical root resection in endodontic microsurgery jeopardize the prosthodontic prognosis?
- Sin-Yeon Cho, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(2):59-64. Published online May 28, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.2.59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Apical surgery cuts off the apical root and the crown-to-root ratio becomes unfavorable. Crown-to-root ratio has been applied to periodontally compromised teeth. Apical root resection is a different matter from periodontal bone loss. The purpose of this paper is to review the validity of crown-to-root ratio in the apically resected teeth. Most roots have conical shape and the root surface area of coronal part is wider than apical part of the same length. Therefore loss of alveolar bone support from apical resection is much less than its linear length.The maximum stress from mastication concentrates on the cervical area and the minimum stress was found on the apical 1/3 area. Therefore apical root resection is not so harmful as periodontal bone loss. Osteotomy for apical resection reduces longitudinal width of the buccal bone and increases the risk of endo-perio communication which leads to failure. Endodontic microsurgery is able to realize 0 degree or shallow bevel and precise length of root resection, and minimize the longitudinal width of osteotomy. The crown-to-root ratio is not valid in evaluating the prosthodontic prognosis of the apically resected teeth. Accurate execution of endodontic microsurgery to preserve the buccal bone is essential to avoid endo-perio communication.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
Hanguo Wang, Xin Xu, Zhuan Bian, Jingping Liang, Zhi Chen, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Xi Wei, Kaijin Hu, Qintao Wang, Zuhua Wang, Jiyao Li, Dingming Huang, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Liuyan Meng, Chen Zhang, Fangfang Xie, Di Yang, Jinhua Yu
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Approaches in apical microsurgery: conventional vs. guided. A systematic review
Germán Sánchez-Herrera, Matteo Facchera, Cristina Palma-Carrió, Martín Pérez-Leal
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of apical root resection level and filling technique on the fracture resistance of endodontically treated teeth: a biomechanical study
Guilherme Pauletto, Sidnei Flores de Pellegrin, Yasmin Padoin, Andressa Weber Vargas, Duvan Cala Castillo, Gabriel Kalil Rocha Pereira, Carlos Alexandre Souza Bier, Renata Dornelles Morgental
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistence of horizontal bone loss and dehiscence with the bundle and conventional fiber post: a finite element analysis
Deniz Yanık, Nurullah Türker, Ahmet Mert Nalbantoğlu
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; : 1. CrossRef - The tooth survival of non‐surgical root‐filled posterior teeth and the associated prognostic tooth‐related factors: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
S. R. Patel, F. Jarad, E. Moawad, A. Boland, J. Greenhalgh, Maria Liu, Michelle Maden
International Endodontic Journal.2024; 57(10): 1404. CrossRef - New-designed 3D printed surgical guide promotes the accuracy of endodontic microsurgery: a study of 14 upper anterior teeth
Dan Zhao, Weige Xie, Tianguo Li, Anqi Wang, Li Wu, Wen Kang, Lu Wang, Shiliang Guo, Xuna Tang, Sijing Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multifactorial Analysis of Endodontic Microsurgery Using Finite Element Models
Raphael Richert, Jean-Christophe Farges, Jean-Christophe Maurin, Jérôme Molimard, Philippe Boisse, Maxime Ducret
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(6): 1012. CrossRef - Mid‐term outcomes and periodontal prognostic factors of autotransplanted third molars: A retrospective cohort study
Ernest Lucas‐Taulé, Marc Llaquet, Jesús Muñoz‐Peñalver, José Nart, Federico Hernández‐Alfaro, Jordi Gargallo‐Albiol
Journal of Periodontology.2021; 92(12): 1776. CrossRef - Effect of length of apical root resection on the biomechanical response of a maxillary central incisor in various occlusal relationships
S. J. Ran, X. Yang, Z. Sun, Y. Zhang, J. X. Chen, D. M. Wang, B. Liu
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(1): 111. CrossRef - Changes of Root Length and Root-to-Crown Ratio after Apical Surgery: An Analysis by Using Cone-beam Computed Tomography
Thomas von Arx, Simon S. Jensen, Michael M. Bornstein
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(9): 1424. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Root Resection on the Biomechanical Response of a Single-rooted Tooth—Part 2: Apical Root Resection Combined with Periodontal Bone Loss
Youngjune Jang, Hyoung-Taek Hong, Heoung-Jae Chun, Byoung-Duck Roh
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(3): 412. CrossRef - Influence of Apical Root Resection on the Biomechanical Response of a Single-rooted Tooth: A 3-dimensional Finite Element Analysis
Youngjune Jang, Hyoung-Taek Hong, Byoung-Duck Roh, Heoung-Jae Chun
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(9): 1489. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on apical microsurgery
- 1,985 View
- 14 Download
- 12 Crossref

- Hypoesthesia after IAN block anesthesia with lidocaine: management of mild to moderate nerve injury
- Sungjoo Moon, Seung-Jong Lee, Euiseong Kim, Chan-Young Lee
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):232-235. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.232
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Hypoesthesia after an inferior alveolar nerve (IAN) block does not commonly occur, but some cases are reported. The causes of hypoesthesia include a needle injury or toxicity of local anesthetic agents, and the incidence itself can cause stress to both dentists and patients. This case presents a hypoesthesia on mental nerve area followed by IAN block anesthesia with 2% lidocaine. Prescription of steroids for a week was performed and periodic follow up was done. After 1 wk, the symptoms got much better and after 4 mon, hypoesthesia completely disappeared. During this healing period, only early steroid medication was prescribed. In most cases, hypoesthesia is resolved within 6 mon, but being aware of etiology and the treatment options of hypoesthesia is important. Because the hypoesthesia caused by IAN block anesthesia is a mild to moderate nerve injury, early detection of symptom and prescription of steroids could be helpful for improvement of the hypoesthesia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Botulinum Toxin-A, Generating a Hypothesis for Orofacial Pain Therapy
Yair Sharav, Rafael Benoliel, Yaron Haviv
Toxins.2025; 17(8): 389. CrossRef - Intranasal CRMP2-Ubc9 inhibitor regulates NaV1.7 to alleviate trigeminal neuropathic pain
Santiago I. Loya-Lopez, Heather N. Allen, Paz Duran, Aida Calderon-Rivera, Kimberly Gomez, Upasana Kumar, Rory Shields, Rui Zeng, Akshat Dwivedi, Saumya Saurabh, Olga A. Korczeniewska, Rajesh Khanna
Pain.2024; 165(3): 573. CrossRef - İMPLANT CERRAHİSİ SONRASI HİPOESTEZİ-6 AYLIK TAKİP: VAKA SERİSİ
Sefa AYDINDOĞAN, Emine Elif MUTAFCİLAR VELİOĞLU, Yunus Emre BALABAN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2023; 10(4): 350. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of Post-Traumatic Trigeminal Neuropathic Pain
Olga A. Korczeniewska, Divya Kohli, Rafael Benoliel, Sita Mahalakshmi Baddireddy, Eli Eliav
Biomolecules.2022; 12(12): 1753. CrossRef - Shape and anatomical relationship of the mental foramen to the mandibular premolars in an Indian sub-population: a retrospective CBCT analysis
Komal Sheth, Kulvinder Singh Banga, Ajinkya M. Pawar, James L. Gutmann, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Trigeminal neuralgia and persistent idiopathic facial pain (atypical facial pain)
Gary W. Jay, Robert L. Barkin
Disease-a-Month.2022; 68(6): 101302. CrossRef - Differential roles of NMDAR subunits 2A and 2B in mediating peripheral and central sensitization contributing to orofacial neuropathic pain
Yan-Yan Zhang, Fei Liu, Zhong-Han Fang, Yue-Ling Li, Hong-Lin Liao, Qin-Xuan Song, Cheng Zhou, Jie-Fei Shen
Brain, Behavior, and Immunity.2022; 106: 129. CrossRef - Visualization of Inferior Alveolar and Lingual Nerve Pathology by 3D Double-Echo Steady-State MRI: Two Case Reports with Literature Review
Adib Al-Haj Husain, Daphne Schönegg, Silvio Valdec, Bernd Stadlinger, Thomas Gander, Harald Essig, Marco Piccirelli, Sebastian Winklhofer
Journal of Imaging.2022; 8(3): 75. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms of painful traumatic trigeminal neuropathy—Evidence from animal research and clinical correlates
Olga A. Korczeniewska, Junad Khan, Eli Eliav, Rafael Benoliel
Journal of Oral Pathology & Medicine.2020; 49(6): 580. CrossRef - Behavioral changes in calves 11 days after cautery disbudding: Effect of local anesthesia
Sarah J.J. Adcock, Danielle M. Cruz, Cassandra B. Tucker
Journal of Dairy Science.2020; 103(9): 8518. CrossRef - Frequency of Lower Lip Paresthesia in Patients Receiving Implant-Supported Mandibular Dentures in Tabriz, Iran in 2017-2018
Farrokh Farhadi, Reza Khorshidi-Khiavi, Fereshteh Taheri, Milad Ghanizadeh
Avicenna Journal of Dental Research.2019; 11(1): 26. CrossRef - Persistent idiopathic facial pain
Rafael Benoliel, Charly Gaul
Cephalalgia.2017; 37(7): 680. CrossRef - Painful Traumatic Trigeminal Neuropathy
Rafael Benoliel, Sorin Teich, Eli Eliav
Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery Clinics of North America.2016; 28(3): 371. CrossRef - Neuropathy of Trigeminal Nerve Branches After Oral and Maxillofacial Treatment
Jimoh Olubanwo Agbaje, Elke Van de Casteele, Marjolein Hiel, Ciska Verbaanderd, Ivo Lambrichts, Constantinus Politis
Journal of Maxillofacial and Oral Surgery.2016; 15(3): 321. CrossRef - The Enigma of the Mental Foramen as It Relates to Plastic Surgery
Raphael Alves Chu, Fabio Xerfan Nahas, Marcello Di Martino, Fernanda Abibi Soares, Neil Ferreira Novo, Ricardo Luiz Smith, Lydia Masako Ferreira
Journal of Craniofacial Surgery.2014; 25(1): 238. CrossRef - Mental nerve paresthesia secondary to initiation of endodontic therapy: a case report
Syed Mukhtar-Un-Nisar Andrabi, Sharique Alam, Afaf Zia, Masood Hasan Khan, Ashok Kumar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(3): 215. CrossRef - Pain Sensation and Postsurgical Complications in Posterior Mandibular Implant Placement Using Ridge Mapping, Panoramic Radiography, and Infiltration Anesthesia
Ali Saad Thafeed AlGhamdi
ISRN Dentistry.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef
- Botulinum Toxin-A, Generating a Hypothesis for Orofacial Pain Therapy
- 2,084 View
- 8 Download
- 17 Crossref

- Invasive cervical resorption: treatment challenges
- Yookyung Kim, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim, Byoung-Duck Roh
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):228-231. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.228
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Invasive cervical resorption is a relatively uncommon form of external root resorption. It is characterized by invasion of cervical region of the root by fibrovascular tissue derived from the periodontal ligament. This case presents an invasive cervical resorption occurring in maxillary lateral incisor, following damage in cervical cementum from avulsion and intracoronal bleaching procedure. Flap reflection, debridement and restoration with glass ionomer cement were performed in an attempt to repair the defect. But after 2 mon, more resorption extended apically. Considering root stability and recurrence potential, we decided to extract the tooth. Invasive cervical resorption in advanced stages may present great challenges for clinicians. Therefore, prevention and early detection must be stressed when dealing with patients presenting history of potential predisposing factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - The Outcome of Decoronation in Severe Cases of External Cervical Root Resorption in Young Patients
Dina Moss, Eyal Nuni, Hagay Slutzky, Daniel Moreinos, Iris Slutzky-Goldberg
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Surgical repair of external cervical resorption - Prognosis and prognostic factors
Po-Yuan Jeng, Shu-Hui Chang, Chen-Ying Wang, Li-Deh Lin, Jiiang-Huei Jeng, Yi-Ling Tsai
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(1): 377. CrossRef - The Disease Process, Diagnosis and Treatment of Invasive Cervical Resorption: A Review
Olivia Rotondi, PhiAnh Waldon, Sahng G. Kim
Dentistry Journal.2020; 8(3): 64. CrossRef - Combined endodontic and periodontal management of a class 3 invasive cervical resorption in a mandibular first molar
Takayoshi Nagahara, Katsuhiro Takeda, Yusuke Aida, Tomoyuki Iwata, Ryoichi Yagi, Hidemi Kurihara, Hideki Shiba
Clinical Case Reports.2018; 6(10): 2005. CrossRef - External cervical resorption: a three‐dimensional classification
S. Patel, F. Foschi, F. Mannocci, K. Patel
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(2): 206. CrossRef - Invasive cervical resorption and the oro-facial cleft patient: a review and case series
A. O'Mahony, C. McNamara, A. Ireland, J. Sandy, J. Puryer
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(9): 677. CrossRef - Characteristics and treatment of invasive cervical resorption in vital teeth. A narrative review and a report of two cases
P. Tsaousoglou, E. Markou, N. Efthimiades, I. Vouros
British Dental Journal.2017; 222(6): 423. CrossRef - Fifteen-year Clinical Follow-up of Restoration of Extensive Cervical Resorption in a Maxillary Central Incisor
EG Reston, RPR Bueno, LQ Closs, J Zettermann
Operative Dentistry.2017; 42(2): E55. CrossRef - The Assessment and Management of External Cervical Resorption with Periapical Radiographs and Cone-beam Computed Tomography: A Clinical Study
Kreena Patel, Francesco Mannocci, Shanon Patel
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(10): 1435. CrossRef - Management of invasive cervical resorption in a maxillary central incisor
SSenthil Kumar, NS Mohan Kumar, JV Karunakaran, S Nagendran
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2015; 7(6): 712. CrossRef
- Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
- 2,048 View
- 14 Download
- 11 Crossref

- A survey of experience-based preference of Nickel-Titanium rotary files and incidence of fracture among general dentists
- WooCheol Lee, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim, Hyojin Lee, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):201-206. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.201
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose was to investigate the preference and usage technique of NiTi rotary instruments and to retrieve data on the frequency of re-use and the estimated incidence of file separation in the clinical practice among general dentists.
Materials and Methods A survey was disseminated via e-mail and on-site to 673 general dentists. The correlation between the operator's experience or preferred technique and frequency of re-use or incidence of file fracture was assessed.
Results A total of 348 dentists (51.7%) responded. The most frequently used NiTi instruments was ProFile (39.8%) followed by ProTaper. The most preferred preparation technique was crown-down (44.6%). 54.3% of the respondents re-used NiTi files more than 10 times. There was a significant correlation between experience with NiTi files and the number of reuses (
p = 0.0025). 54.6% of the respondents estimated experiencing file separation less than 5 times per year. The frequency of separation was significantly correlated with the instrumentation technique (p = 0.0003).Conclusions A large number of general dentists in Korea prefer to re-use NiTi rotary files. As their experience with NiTi files increased, the number of re-uses increased, while the frequency of breakage decreased. Operators who adopt the hybrid technique showed less tendency of separation even with the increased number of re-use.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
Chiaki Akiba Katz, Misaki Fujimoto, Hidetaka Kuroda, Koichiro Muromachi
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Adoption of rotary instrumentation among general practitioners in Qassim region, Saudi Arabia: A cross-sectional survey
Badi B. Alotaibi
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 181. CrossRef - Undergraduate Endodontic Training and Its Relation to Contemporary Practice: Multicenter Cross-Sectional Study in Saudi Arabia
Fahda N. Algahtani, Reem M. Barakat, Lujain M. Alqarni, Alanoud F. Alqabbani, Manal F. Alkadi, Rahaf A. Almohareb, André Luiz Ferreira Costa
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Fracture Incidence of Kedo-S Square Pediatric Rotary Files: A Prospective Clinical Study
Lakshimi Lakshmanan, Ganesh Jeevanandan, Prabhadevi C Maganur, Satish Vishwanathaiah
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 594. CrossRef - Prevention and management of fractured instruments in endodontic treatment
Wei-Rong Tang
World Journal of Surgical Procedures.2015; 5(1): 82. CrossRef - Influence of operator's experience level on lifespan of the WaveOne Primary file in extracted teeth
Abdulrahman Mohammed Saleh, Saeid Tavanafar, Pouyan Vakili-Gilani, Noor Jamal Al Sammerraie, Faahim Rashid
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(4): 222. CrossRef
- Migration of a Separated Endodontic File Into the Mandibular Canal: An 8-Year Follow-up Case Report
- 1,880 View
- 9 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Minimizing the extra-oral time in autogeneous tooth transplantation: use of computer-aided rapid prototyping (CARP) as a duplicate model tooth
- Seung-Jong Lee, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):136-141. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.136
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The maintenance of the healthy periodontal ligament cells of the root surface of donor tooth and intimate surface contact between the donor tooth and the recipient bone are the key factors for successful tooth transplantation. In order to achieve these purposes, a duplicated donor tooth model can be utilized to reduce the extra-oral time using the computer-aided rapid prototyping (CARP) technique.
Materials and Methods Briefly, a three-dimensional digital imaging and communication in medicine (DICOM) image with the real dimensions of the donor tooth was obtained from a computed tomography (CT), and a life-sized resin tooth model was fabricated. Dimensional errors between real tooth, 3D CT image model and CARP model were calculated. And extra-oral time was recorded during the autotransplantation of the teeth.
Results The average extra-oral time was 7 min 25 sec with the range of immediate to 25 min in cases which extra-oral root canal treatments were not performed while it was 9 min 15 sec when extra-oral root canal treatments were performed. The average radiographic distance between the root surface and the alveolar bone was 1.17 mm and 1.35 mm at mesial cervix and apex; they were 0.98 mm and 1.26 mm at the distal cervix and apex. When the dimensional errors between real tooth, 3D CT image model and CARP model were measured in cadavers, the average of absolute error was 0.291 mm between real teeth and CARP model.
Conclusions These data indicate that CARP may be of value in minimizing the extra-oral time and the gap between the donor tooth and the recipient alveolar bone in tooth transplantation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- American Dental Association and American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology patient selection for dental radiography and cone-beam computed tomography
Erika Benavides, Joseph R. Krecioch, Trishul Allareddy, Allison Buchanan, Martha Ann Keels, Ana Karina Mascarenhas, Mai-Ly Duong, Kelly K. O’Brien, Kathleen M. Ziegler, Ruth D. Lipman, Roger T. Connolly, Lucia Cevidanes, Kitrina Cordell, Satheesh Elangova
The Journal of the American Dental Association.2026; 157(1): 20. CrossRef - American Dental Association and American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology patient selection for dental radiography and cone-beam computed tomography
Erika Benavides, Josep R. Krecioch, Trishul Allareddy, Allison Buchanan, Martha Ann Keels, Ana Karina Mascarenhas, Mai-Ly Duong, Kelly K. O'Brien, Kathleen M. Ziegler, Ruth D. Lipman, Roger T. Connolly, Lucia Cevidanes, Kitrina Cordell, Satheesh Elangovan
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - 13-year follow-up of autotransplantation using an immature third molar: a case report
Hojin Moon
Journal of Dental Rehabilitation and Applied Science.2025; 41(1): 72. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Printing in Dentistry: A Scoping Review of Clinical Applications, Advantages, and Current Limitations
Mi-Kyoung Jun, Jong-Woo Kim, Hye-Min Ku
Oral.2025; 5(2): 24. CrossRef - Template-Guided Autogenous Tooth Transplantation Using a CAD/CAM Dental Replica in a Complex Anatomical Scenario: A Case Report
Michael Alfertshofer, Florian Gebhart, Dirk Nolte
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(7): 281. CrossRef - Autogenous Transplantation of Teeth Across Clinical Indications: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Martin Baxmann, Karin Christine Huth, Krisztina Kárpáti, Zoltán Baráth
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(14): 5126. CrossRef - Effect of 3D printed replicas on the duration of third molar autotransplantation surgery: A controlled clinical trial
Miks Lejnieks, Ilze Akota, Gundega Jākobsone, Laura Neimane, Oskars Radzins, Sergio E. Uribe
Dental Traumatology.2024; 40(2): 221. CrossRef - Use of 3D printing models for donor tooth extraction in autotransplantation cases
Rui Hou, Xiaoyong Hui, Guangjie Xu, Yongqing Li, Xia Yang, Jie Xu, Yanli Liu, Minghui Zhu, Qinglin Zhu, Yu Sun
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Autologous Transplantation Tooth Guide Design Based on Deep Learning
Lifen Wei, Shuyang Wu, Zelun Huang, Yaxin Chen, Haoran Zheng, Liping Wang
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2024; 82(3): 314. CrossRef - Anterior tooth autotransplantation: a case series
DC‐V Ong, P Goh, G Dance
Australian Dental Journal.2023; 68(3): 202. CrossRef - Dental Auto Transplantation Success Rate Increases by Utilizing 3D Replicas
Peter Kizek, Marcel Riznic, Branislav Borza, Lubos Chromy, Karolina Kamila Glinska, Zuzana Kotulicova, Jozef Jendruch, Radovan Hudak, Marek Schnitzer
Bioengineering.2023; 10(9): 1058. CrossRef - Planificación digital y guía de fresado para autotrasplante de tercer molar
Silvio Llanos, Henry García, Carlos Manresa, Carolina Bonilla, Alessandra Baasch
Reporte Imagenológico Dentomaxilofacial.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Una alternativa a los implantes dentarios: manejo quirúrgico y endodóntico con planificación digital y guía de fresado de autotrasplantes de terceros molares. Reporte de un caso
Silvio Llanos, Henry García, Carlos Manresa, Carolina Bonilla, Julio Tebres, Stefanía Requejo, Alessandra Baasch
Latin American Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2023; 3(2): 80. CrossRef - Extraoral Root-End Resection May Promote Pulpal Revascularization in Autotransplanted Mature Teeth—A Retrospective Study
Petra Rugani, Barbara Kirnbauer, Irene Mischak, Kurt Ebeleseder, Norbert Jakse
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(23): 7199. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional (3D) Stereolithographic Tooth Replicas Accuracy Evaluation: In Vitro Pilot Study for Dental Auto-Transplant Surgical Procedures
Filiberto Mastrangelo, Rossella Battaglia, Dario Natale, Raimondo Quaresima
Materials.2022; 15(7): 2378. CrossRef - Surgical Management of Impacted Lower Second Molars: A Comprehensive Review
Diane Isabel Selvido, Nattharin Wongsirichat, Pratanporn Arirachakaran, Dinesh Rokaya, Natthamet Wongsirichat
European Journal of Dentistry.2022; 16(03): 465. CrossRef - Application effect of computer-aided design combined with three-dimensional printing technology in autologous tooth transplantation: a retrospective cohort study
Shuang Han, Hui Wang, Jue Chen, Jihong Zhao, Haoyan Zhong
BMC Oral Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Application of Virtual Simulation Technology and 3-Dimensional-Printed Computer-Aided Rapid Prototyping in Autotransplantation of a Mature Third Molar
Hui Zhang, Min Cai, Zhiguo Liu, He Liu, Ya Shen, Xiangya Huang
Medicina.2022; 58(7): 953. CrossRef - Present status and future directions: Surgical extrusion, intentional replantation and tooth autotransplantation
Gianluca Plotino, Francesc Abella Sans, Monty S. Duggal, Nicola M. Grande, Gabriel Krastl, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Gianluca Gambarini
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S3): 827. CrossRef - Review on 3D printing in dentistry: conventional to personalized dental care
Shadaan Ahmad, Nazeer Hasan, Fauziya, Akash Gupta, Arif Nadaf, Lubna Ahmad, Mohd. Aqil, Prashant Kesharwani
Journal of Biomaterials Science, Polymer Edition.2022; 33(17): 2292. CrossRef - Three-dimensional printing in endodontics: A review of literature
Jyoti Chauhan, Ida de Noronha de Ataide, Marina Fernandes
IP Indian Journal of Conservative and Endodontics.2021; 6(4): 198. CrossRef - Pre- and peri-operative factors influence autogenous tooth transplantation healing in insufficient bone sites
Thanapon Suwanapong, Aurasa Waikakul, Kiatanant Boonsiriseth, Nisarat Ruangsawasdi
BMC Oral Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - European Society of Endodontology position statement: Surgical extrusion, intentional replantation and tooth autotransplantation
G. Plotino, F. Abella Sans, M. S. Duggal, N. M. Grande, G. Krastl, V. Nagendrababu, G. Gambarini
International Endodontic Journal.2021; 54(5): 655. CrossRef - Successful pulp revascularization of an autotransplantated mature premolar with fragile fracture apicoectomy and plasma rich in growth factors: a 3‐year follow‐up
J. F. Gaviño Orduña, M. García García, P. Dominguez, J. Caviedes Bucheli, B. Martin Biedma, F. Abella Sans, M. C. Manzanares Céspedes
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(3): 421. CrossRef - Clinical procedures and outcome of surgical extrusion, intentional replantation and tooth autotransplantation – a narrative review
G. Plotino, F. Abella Sans, M. S. Duggal, N. M. Grande, G. Krastl, V. Nagendrababu, G. Gambarini
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(12): 1636. CrossRef - 3D printing in dentistry – Exploring the new horizons
Praveen Vasamsetty, Tejaswini Pss, Divya Kukkala, Madhavi Singamshetty, Shashivardhan Gajula
Materials Today: Proceedings.2020; 26: 838. CrossRef - The use of 3D additive manufacturing technology in autogenous dental transplantation
Pau Cahuana-Bartra, Abel Cahuana-Cárdenas, Lluís Brunet-Llobet, Marta Ayats-Soler, Jaume Miranda-Rius, Alejandro Rivera-Baró
3D Printing in Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Autotransplantation of mature impacted tooth to a fresh molar socket using a 3D replica and guided bone regeneration: two years retrospective case series
Ye Wu, Jiaming Chen, Fuping Xie, Huanhuan Liu, Gang Niu, Lin Zhou
BMC Oral Health.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Transplantations, réimplantations
M.-A. Fauroux, E. Malthiéry, C. Favre de Thierrens, M. Zanini, J.-H. Torres
EMC - Chirurgie orale et maxillo-faciale.2019; 32(2): 1. CrossRef - Endodontic applications of 3D printing
J. Anderson, J. Wealleans, J. Ray
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(9): 1005. CrossRef - Applications of additive manufacturing in dentistry: A review
Aishwarya Bhargav, Vijayavenkatraman Sanjairaj, Vinicius Rosa, Lu Wen Feng, Jerry Fuh YH
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2018; 106(5): 2058. CrossRef - Virtual Simulation of Autotransplantation Using 3-dimensional Printing Prototyping Model and Computer-assisted Design Program
Soram Oh, Sehoon Kim, Ha Seon Lo, Joo-Young Choi, Hyun-Jung Kim, Gil-Joo Ryu, Sun-Young Kim, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(12): 1883. CrossRef - Computer-aided autotransplantation of teeth with 3D printed surgical guides and arch bar: a preliminary experience
Wei He, Kaiyue Tian, Xiaoyan Xie, Enbo Wang, Nianhui Cui
PeerJ.2018; 6: e5939. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of teeth using computer-aided rapid prototyping of a three-dimensional replica of the donor tooth: a systematic literature review
J.P. Verweij, F.A. Jongkees, D. Anssari Moin, D. Wismeijer, J.P.R. van Merkesteyn
International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2017; 46(11): 1466. CrossRef - Contemporary Approach to Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Roots Using 3D-printing Technology
Jungha Park, Sangho Lee, Nanyoung Lee, Myoungkwan Jih, Hyeran Cheong
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2017; 44(4): 461. CrossRef - 3D-printing techniques in a medical setting: a systematic literature review
Philip Tack, Jan Victor, Paul Gemmel, Lieven Annemans
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic Factors for Clinical Outcomes in Autotransplantation of Teeth with Complete Root Formation: Survival Analysis for up to 12 Years
Youngjune Jang, Yoon Jeong Choi, Seung-Jong Lee, Byoung-Duck Roh, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(2): 198. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of an Impacted Premolar Using Collagen Sponge after Cyst Enucleation
Jae-Hyung Lim, Jong-Ki Huh, Kwang-Ho Park, Su-Jung Shin
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(3): 417. CrossRef - Vertical Bone Growth after Autotransplantation of Mature Third Molars: 2 Case Reports with Long-term Follow-up
Sunil Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Yooseok Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(8): 1371. CrossRef - Autotransplantation of mesiodens for missing maxillary lateral incisor with cone‐beam CT‐fabricated model and orthodontics
Y. Lee, S. W. Chang, H. Perinpanayagam, Y. J. Yoo, S. M. Lim, S. R. Oh, Y. Gu, S. J. Ahn, K.‐Y. Kum
International Endodontic Journal.2014; 47(9): 896. CrossRef - Optimizing Third Molar Autotransplantation: Applications of Reverse-Engineered Surgical Templates and Rapid Prototyping of Three-Dimensional Teeth
Ji-Man Park, Jacquiline Czar I. Tatad, Maria Erika A. Landayan, Seong-Joo Heo, Sun-Jong Kim
Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.2014; 72(9): 1653. CrossRef - Immediate autotransplantation of third molars: an experience of 57 cases
Shakil Ahmed Nagori, Ongkila Bhutia, Ajoy Roychoudhury, Ravinder Mohan Pandey
Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine, Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology.2014; 118(4): 400. CrossRef
- American Dental Association and American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology patient selection for dental radiography and cone-beam computed tomography
- 1,681 View
- 10 Download
- 42 Crossref

- Success and failure of endodontic microsurgery
- Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):66-66. Published online February 4, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.66
- 767 View
- 3 Download

- Subcutaneous emphysema during fracture line inspection: case report
- Min-Young Kim, Sung-Ho Park, Yoo-Seok Shin, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):506-509. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.506
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The development of subcutaneous emphysema is a well-known complication that has been reported after dental extraction, endodontic treatment, or restorative preparation. Gaseous invasion, leading to swelling, crepitus on palpation, is commonly restricted to the connective tisssues immediately adjacent to the entry site. However, the use of compressed air- and water-cooled turbines may allow large amounts of air and water to be driven through the fascial planes into the mediastinum, pleural space, or even the retroperitoneum.
This case report is about the patient who presented with subcutaneous emphysema that occurred after fracture line inspection. Possible cause, treatment, and prevention of emphysema will be discussed.
- 906 View
- 4 Download

- Success and failure of endodontic microsurgery
- Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(6):465-476. Published online November 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.6.465
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub In current endodontic practice, introduction of operating microscope, ultrasonic instruments, and microinstruments has induced a big change in the field of surgical retreatment. In this study, we aimed to offer key steps of endodontic microsurgery procedure compared with traditional root-end surgery, and to evaluate factors influencing success and failure based on published articles.
Endodontic microsurgery is a surgical procedure performed with the aid of a microscope, ultrasonic instruments and modern microsurgical instruments. The microscope provides magnification and illumination - essential for identifying minute details of the apical anatomy. Ultrasonic instruments facilitate the precise root-end preparation that is within the anatomical space of the canal. Modern endodontics can therefore be performed with precision and predictability, thus eliminating the disadvantages inherent in traditional periapical surgery such as large osteotomy, beveled apicoectomy, inaccurate root-end preparation and the inability to observe isthmus.
Factors influencing the outcomes of endodontic microsurgery may be diverse, but standardization of procedures can minimize its range. Among patient and tooth-related factors, periodontal status and tooth position are known to be prognostic, but there are only few articles concerning this matter. High-evidence randomized clinical trials or prospective cohort studies are needed to confirm these findings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Treatment-Related Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery and the Influence of GTR on Radiographic Healing—A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jarosław Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(19): 6382. CrossRef - Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
Daniel Bieszczad, Jaroslaw Wichlinski, Tomasz Kaczmarzyk
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(14): 3991. CrossRef - Comparison of Clinical Outcomes of Endodontic Microsurgery: 1 Year versus Long-term Follow-up
Minju Song, Taekjin Nam, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(4): 490. CrossRef - The Influence of Bone Tissue Deficiency on the Outcome of Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Su-Jung Shin, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(11): 1341. CrossRef - Prognostic Factors of Clinical Outcomes in Endodontic Microsurgery: A Prospective Study
Minju Song, Sahng Gyoon Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Baekil Kim, Euiseong Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(12): 1491. CrossRef - Is stopping of anticoagulant therapy really required in a minor dental surgery? - How about in an endodontic microsurgery?
Yong-Wook Cho, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 113. CrossRef
- Treatment-Related Factors Affecting the Success of Endodontic Microsurgery and the Influence of GTR on Radiographic Healing—A Cone-Beam Computed Tomography Study
- 2,246 View
- 28 Download
- 6 Crossref

- Evaluation of canal preparation for apical sealing with various Ni-Ti rotary instruments
- Yooseok Shin, Su-Jung Shin, Minju Song, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(4):300-305. Published online July 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.4.300
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim of this study was to evaluate the various NiTi rotary instruments regarding their ability to provide a circular apical preparation.
Materials and Methods 50 single canal roots were selected, cut at the cementodentinal junction and the coronal 1/3 of the canals was flared using Gates Glidden burs. Samples were randomly divided into 5 experimental groups of 10 each. In group I, GT files, Profile 04 and Quantec #9 and #10 files were used. In Group II Lightspeed was used instead of Quantec. In Group III, Orifice shaper, Profile .06 series and Lightspeed were used. In Group IV, Quantec #9 and #10 files were used instead of Lightspeed. In Group V, the GT file and the Profile .04 series were used to prepare the entire canal length. All tooth samples were cut at 1 mm, 3 mm and 5 mm from the apex and were examined under the microscope.
Results Groups II and III (Lightspeed) showed a more circular preparation in the apical 1mm samples than the groups that used Quantec (Group I & IV) or GT files and Profile .04 series.(Group V)(
p < 0.05) There was no significant difference statistically among the apical 3, 5 mm samples. In 5 mm samples, most of the samples showed complete circularity and none of them showed irregular shape.Conclusions Lightspeed showed circular preparation at apical 1 mm more frequently than other instruments used in this study. However only 35% of samples showed circularity even in the Lightspeed Group which were enlarged 3 ISO size from the initial apical binding file (IAF) size. So it must be considered that enlarging 3 ISO size isn't enough to make round preparation.
- 719 View
- 5 Download

- Partial pulp necrosis caused by excessive orthodontic force
- Min-Young Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Il-Young Jung, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):149-153. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.149
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub As the dental pulp is encased with a rigid, noncompliant shell, changes in pulpal blood flow or vascular tissue pressure can have serious implication for the health of pulp. Numerous studies have demonstrated that orthodontic force application may influence both blood flow and cellular metabolism, leading degenerative and/or inflammatory responses in the dental pulp. The aim of this case report is to present a case about tooth with chronic periapical abscess which showed normal vital responses. Excessive orthodontic force is thought to be the prime cause of partial pulp necrosis. Owing to remaining vital tissue, wrong dianosis can be made, and tooth falsely diagnosed as vital may be left untreated, causing the necrotic tissue to destroy the supporting tissuses. Clinician should be able to utilize various diagnostic tools for the precise diagnosis, and be aware of the endodontic-orthodontic inter-relationship.
- 1,688 View
- 26 Download

- Patients' perception and satisfaction with apicoectomy
- Euiseong Kim, Seung-Jong Lee, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(2):114-118. Published online March 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.2.114
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was aimed to examine the patients' perception and satisfaction with the results of endodontic microsurgery which was apicoectomy with retrofilling.
Materials and Methods A questionnaire was given to 109 patients, who were recalled after a minimum of 3 months upon endodontic microsurgery in the Department of Conservative Dentistry, Yonsei University. A contingency table and correlation analysis were used to determine if there were any correlations between age/gender and the patients' responses (
p = 0.05).Results Approximately 60% of respondents answered they had never heard of surgical endodontic procedures. 63.3% of respondents chose the surgical option because they wanted to keep their natural teeth. If the patient required the same procedure on another tooth later, 100 out of 109 respondents answered they would choose microsurgery instead of extraction. Most patients (82.57%) appeared to be satisfied with the surgical procedure.
Conclusions Endodontic microsurgery consisting of apicoectomy and retrofilling seems to appeal to majority of patients as a satisfactory and valuable treatment choice.
- 1,161 View
- 9 Download

- Comparison of apical transportation and change of working length in K3, NRT AND PROFILE rotary instruments using transparent resin block
- Min-Jung Yoon, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(1):59-65. Published online January 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.1.59
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study is to compare the apical transportation and working length change in curved root canals created in resin blocks, using 3 geometrically different types of Ni-Ti files, K3, NRT, and Profile.
Materials and Methods The curvature of 30 resin blocks was measured by Schneider technique and each groups of Ni-Ti files were allocated with 10 resin blocks at random. The canals were shaped with Ni-Ti files by Crown-down technique. It was analyzed by Double radiograph superimposition method (Backman CA 1992), and for the accuracy and consistency, specially designed jig, digital X-ray, and CAD/CAM software for measurement of apical transportation were used. The amount of apical transportation was measured at 0, 1, 3, 5 mm from 'apical foramen - 0.5 mm' area, and the alteration of the working length before and after canal shaping was also measured. For statistics, Kruskal-Wallis One Way Analysis was used.
Results There was no significant difference between the groups in the amount of working length change and apical transportation at 0, 1, and 3 mm area (
p = 0.027), however, the amount of apical transportation at 5 mm area showed significant difference between K3 and Profile system (p = 0.924).Conclusions As a result of this study, the 3 geometrically different Ni-Ti files showed no significant difference in apical transportation and working length change and maintained the original root canal shape.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
Ki-Won Kim, Kyung-Mo Cho, Se-Hee Park, Ki-Yeol Choi, Bekir Karabucak, Jin-Woo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(1): 7. CrossRef
- A comparison of dimensional standard of several nickel-titanium rotary files
- 964 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Pulp vitality and coronal discoloration following traumatic injuries
- Tae-Sun Yoon, Hyung-Gyu Kong, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):492-496. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.492
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Coronal discoloration is a common sequela to traumatic injuries. In subluxation cases, although the injury is not strong enough to rupture the apical vessels, discoloration may appear by tearing thin walls or occluding small capillaries. In absence of infection pulpal regeneration can occur, and as a result discoloration may completely or partially subside. But judging pulpal status by coronal discoloration can be dangerous and it may lead to unnecessary treatment.
This case presents coronal discoloration and recovery following traumatic injury of maxillary anterior teeth. In diagnosing traumatized teeth routine cold tests or electric pulp tests are known to be unreliable, but with the aid of ultrasound doppler imaging, assessing pulp vitality of traumatized teeth can be more accurate.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulp necrosis following luxated injury to teeth in a patient with uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus: a case report
Haneol Shin, Seung-Jong Lee, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(1): 61. CrossRef
- Pulp necrosis following luxated injury to teeth in a patient with uncontrolled type II diabetes mellitus: a case report
- 1,284 View
- 10 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Biocompatibility of bioaggregate cement on human pulp and periodontal ligament (PDL) derived cells
- Choo-Ryung Chung, Euiseong Kim, Su-Jung Shin
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):473-478. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.473
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was performed to investigate the biocompatibility of newly introduced Bioaggregate on human pulp and PDL cells.
Materials and Methods Cells were collected from human pulp and PDL tissue of extracted premolars. Cell culture plate was coated either with Bioaggregate or white MTA, then the same number of cells were poured to cell culture dishes. Cell attachment and growth was examined under a phase microscope after 1,3 and 7 days of seeding. Cell viability was measured and the data was analyzed using Student
t -test and one way ANOVA.Results Both types of cells used in this study were well attached and grew healthy on Bioaggregate and MTA coated culture dishes. No cell inhibition zone was observed in Bioaggregate group. There was no statistical difference of viable cells between bioaggreagte and MTA groups.
Conclusions Bioaggregate appeared to be biocompatible compared with white MTA on human pulp and PDL cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of tricalcium silicate bone cement modified with wollastonite/ fluorapatite glass and glass-ceramic
H.K. Abd El-Hamid, A.M. Fayad, R.L. Elwan
Ceramics International.2024; 50(14): 25322. CrossRef - Influence of insulin on the healing of exposed dental pulp after pulp capping: An experimental study in a dog model
Mokhtar A. Al‐Anesi, Ashraf M. Abu‐Seida, Salma H. El Ashry, Abeer H. Mahran, Ehab S. Abd‐Elhamid
Special Care in Dentistry.2021; 41(1): 49. CrossRef - ROOT END FILLING MATERIALS – A REVIEW
Bynagari Chandra Shekar, Veerendra Uppin, Madhu Pujar
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 5. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting calcium-silicate cements on cell viability and angiogenic factor release in human pulp-derived cells
Chooryung J. Chung, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 143. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity and physical properties of tricalcium silicate-based endodontic materials
Young-Eun Jang, Bin-Na Lee, Jeong-Tae Koh, Yeong-Joon Park, Nam-Eok Joo, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2014; 39(2): 89. CrossRef - Biocompatibility of root-end filling materials: recent update
Payal Saxena, Saurabh Kumar Gupta, Vilas Newaskar
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 119. CrossRef
- Evaluation of bioactivity, biocompatibility, and antibacterial properties of tricalcium silicate bone cement modified with wollastonite/ fluorapatite glass and glass-ceramic
- 1,319 View
- 3 Download
- 6 Crossref

- In vivo evaluation of accuracy and consistency of two electronic apex locators
- Chien-Yun Pi, Euiseong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):453-460. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.453
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the accuracy and consistency of two different apex locators at both the Apex and 0.5 marks.
Materials and Methods Twenty-six root canals was scheduled for extraction for periodontal or prosthodontic reasons. Thirteen canals were measured using Root ZX and the rest by i-ROOT. The root canal length was measured both the at 0.5 mark and the Apex mark. The file was then fixed to the tooth, and the distance from the file tip to the major foramen of each canal was measured after removing the root dentin under the microscope so that the major foramen and the file tip were seen.
Results When the Apex mark was used, 100% of both the Root ZX and i-ROOT groups were within 0.5 mm of the major foramen.
When 0.5 mark was used, 100% of the Root ZX group and 77% of the i-ROOT group were within 0.5 mm of the major foramen.
In terms of standard deviation and quartile value, the Apex mark was more consistent than 0.5 mark in the Root ZX group, and 0.5 mark was more consistent in the i-ROOT group, but there was no statistically significant difference when compared with
t -test.The root canal length difference between the Apex mark and 0.5 mark was 0.22 mm and 0.46 mm in the Root ZX and i-ROOT groups, respectively.
Conclusions In this study, the Apex mark was the more consistent mark. Therefore, it is recommended to subtract 0.5 mm, which is the average length between the apex and apical constriction, from the root canal length at the Apex mark to obtain the working length clinically.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Apical Periodontitis on the Accuracy of 3 Electronic Root Canal Length Measurement Devices: An In Vivo Study
Masoud Saatchi, Mohammad Ghasem Aminozarbian, Seyed Mohsen Hasheminia, Amin Mortaheb
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(3): 355. CrossRef
- Influence of Apical Periodontitis on the Accuracy of 3 Electronic Root Canal Length Measurement Devices: An In Vivo Study
- 1,136 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Comparison of viability of oral epithelial cells stored by different freezing methods
- Do-Young Baek, Seung-Jong Lee, Han-Sung Jung, EuiSeong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2009;34(6):491-499. Published online November 30, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2009.34.6.491
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study examined the influence of the storage methods on the viability of oral epithelial cells using conventional cell freezing storage, slow freezing preservation, rapid freezing preservation, and slow freezing preservation with a pressure of 2 Mpa or 3 Mpa. The cell viability was evaluated by cell counting, WST-1 and the clonogenic capacity after 6 days of freezing storage. After 6 days, the frozen cells were thawed rapidly, and the cell counting, WST-1, and clonogenic capacity values were measured and compared.
The results from cell counting demonstrated that conventional cryopreservation, slow freezing under a 2 Mpa pressure and slow freezing under a 3 Mpa pressure showed significantly higher values than slow freezing preservation and rapid freezing preservation (p<0.05).
The results from the optical density by WST-1 demonstrated that slow freezing under a 2 Mpa pressure showed significantly higher values than slow freezing preservation and rapid freezing preservation (p<0.05).
The clonogenic capacity demonstrated that slow freezing under a 2 Mpa pressure showed significantly higher values than slow freezing preservation and rapid freezing preservation (p<0.05).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of the Viability of Rat Periodontal Ligament Cells after Storing at 0℃/2 MPa Condition up to One Week: In Vivo MTT Method
Sun Mi Jang, Sin-Yeon Cho, Eui-Seong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Dental Science.2016; 9(1): 1. CrossRef - The evaluation of periodontal ligament cells of rat teeth after low-temperature preservation under high pressure
Jin-Ho Chung, Jin Kim, Seong-Ho Choi, Eui-Seong Kim, Jiyong Park, Seung-Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 285. CrossRef
- Evaluation of the Viability of Rat Periodontal Ligament Cells after Storing at 0℃/2 MPa Condition up to One Week: In Vivo MTT Method
- 1,261 View
- 2 Download
- 2 Crossref

-
Selective detection of viable
Enterococcus faecalis using propidium monoazide in combination with real-time PCR - Sinyoung Kim, Seungjong Lee, Euiseong Kim, Deoggyu Seo, Yoonjung Song, Ilyoung Jung
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(6):537-544. Published online November 30, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.6.537
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can detect bacteria more rapidly than conventional plate counting. However DNA-based assays cannot distinguish between viable and dead cells due to persistence of DNA after cells have lost their vitality. Recently, propidium monoazide (PMA) treatment has been introduced. The purpose of this study is to evaluate the applicability of the PMA treatment and real-time PCR method for cell counting in comparison with plate counting and to evaluate the antibacterial efficacy of 2% CHX on
E. faecalis using PMA treatment in combination with real-time PCR.Firstly, to elucidate the relationship between the proportion of viable cells and the real-time PCR signals after PMA treatment, mixtures with different ratios of viable and dead cells were used. Secondly, relative difference of viable cells using PMA treatment in combination with real-time PCR was compared with CFU by plate counting. Lastly, antibacterial efficacy of 2% CHX on
E. faecalis was measured using PMA treatment in combination with real-time PCR.The results were as follows :
Ct value increased with decreasing proportion of viable
E. faecalis .There was correlation between viable cells measured by real-time PCR after PMA treatment and CFU by plate counting until Optical density (OD) value remains under 1.0. However, viable cells measured by real-time PCR after PMA treatment have decreased at 1.5 of OD value while CFU kept increasing.
Relative difference of viable
E. faecalis decreased more after longer application of 2% CHX.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by-
Effects of sodium hypochlorite on the potential infectivity of human norovirus
GII
.4 using propidium monoazide with
RT‐qPCR
and quality assessments in Manila clams (
Ruditapes phili
Min Gyu Song, Eun Bi Jeon, Ji Yoon Kim, Shin Young Park
Journal of Food Processing and Preservation.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of temperature and medium on the viability ofMycobacterium lepraeduring long term-storage
Jin-Ho Park, Yun-Ji Kim, Jong-Pill Kim
Korean Leprosy Bulletin.2019; 52(1): 41. CrossRef - In Vivo Quantitative Evaluation of Live and Dead Bacteria in Root Canal Infection by Using Propidium Monoazide with Real-Time PCR
Sin-Young Kim, Yooseok Shin, Chan-Young Lee, Il-Young Jung
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(11): 1359. CrossRef
-
Effects of sodium hypochlorite on the potential infectivity of human norovirus
GII
.4 using propidium monoazide with
RT‐qPCR
and quality assessments in Manila clams (
Ruditapes phili
- 1,291 View
- 14 Download
- 3 Crossref

- Evaluation of the influence of apical sizes on the apical sealing ability of the modified continuous wave technique
- Muhyun Ryu, Ilyoung Jung, Seungjong Lee, Sujung Shin, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):66-75. Published online January 31, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.066
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study examined the influence of the apical sizes on the sealing ability of a root canal filling.
Thirty-six single rooted teeth with a single canal were divided into 3 groups (n = 12) and instrumented with either the Profile® or LightSpeed® system to achieve three different apical sizes (master apical file [MAF] of #25, #40, or #60). The teeth were filled with gutta percha using a modified continuous wave technique. The level of microleakage was determined by immersing ten teeth from each group into India ink for 1 week followed by clearing with nitric acid, ethyl-alcohol, and methylsalicylate. The microleakage was measured using vernier calipers. The data was analyzed statistically using Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA and a Student-Newman-Keuls Method. Two teeth from each group were sectioned horizontally at 1, 2, 3 and 4 mm from the apex in order to observe a cross section.
The apical size was significantly (p < .05) influenced the level of microleakage. In the Student-Newman-Deuls Method, MAF sizes of #25 and #40; and MAF sizes of #25 and #60, respectively showed a statistically significant difference. There was no significant difference between #40 and #60. In most cross sections, oval-shaped canals were observed, and the irregularity of the internal surface increased with decreasing apical size. There was also an increase in the area of recess, which is the area where the canal space is not filled with either gutta-percha or sealer.
When the root canals are filled using a modified continuous wave technique, canal filling with more consistent and predictable outcome may be expected as the apical preparation size is increased.
- 993 View
- 9 Download

- CYCLIC FATIGUE OF THE SODIUM HYPOCHLORITE TREATED AND /OR STEAM AUTOCLAVED NICKEL-TITANIUM ENDODONTIC FILES
- Hye-Young Cho, Il-Young Jung, Chan-Young Lee, Euiseong Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2008;33(1):54-65. Published online January 14, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.054
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Abstract The purpose of this study was to determine the effect of sodium hypochlorite and steam autoclaving on the cyclic fatigue of nickel-titanium endodontic files.
Two types of files with a .06 taper and #30 were used, K3® (SybronEndo, Glendora, California, USA) and Hero642®(Micro-Mega, Besançon, France).
The files were divided into 6 experimental groups containing 10 files each group depending the soaking time in 6% sodium hypochlorite solution and number of cycles of steam autoclave. After sterilization, a cyclic fatigue test was performed on each file, and the fracture time was recorded in seconds. The control group underwent the cyclic fatigue test only. After the test, the surface characteristics of the files were observed using scanning electron microscopy (SEM).
All groups containing the Hero 642® files showed a similar cyclic fatigue fracture time. However, the cyclic fatigue fracture time with the K3® files was significantly shorter in groups which were treated with sodium hypochlorite than in the control group (P < 0.05). SEM revealed both Hero642® and K3® files to have significant corrosion on the file surface in groups treated with sodium hypochlorite, compared with the sharp and regular blades of the control group. K3® files showed more corrosion than the Hero642® files. Bluntness of the blades of the K3® file was observed in groups treated with steam autoclave. Although there was no obvious destruction on the surface of steam autoclaved Hero642® files, slight bluntness was observed.
Sterilizing with a steam autoclave is much less destructive to K3® files than sodium hypochlorite. The longer time exposed to sodium hypochlorite, the more destructive pattern was shown on the blades of the files. Therefore, when using sodium hypochlorite solution, the exposure time should be as short as possible in order to prevent corrosion and increase the cyclic fatigue fracture time.
- 750 View
- 1 Download

-
The effect of canal filling with gutta-percha or resilon on
Enterococcus faecalis in bovine dentinal tubules - Sang-Wook Jee, Euiseong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Yun-Jung Yoo
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(5):385-392. Published online September 30, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.5.385
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to observe the effect of canal filling on the bacteria left in the dentinal tubules and to compare the sealing ability between Gutta-percha and Resilon. The bovine dentin block models were prepared.
E. faecalis was inoculated to dentin blocks and incubated. The dentin blocks were divided into 5 groups.Group 1 was the negative control. Group 2 was the positive control. Group 3 was filled with ZOE based sealer and Gutta-percha, Group 4 with resin based sealer and Gutta-percha, and Group 5 with resin based sealer and Resilon. After 24 hour, the blocks were incubated at 37℃ for 1, 2, 3 and 4 weeks on BHI agar plates.
The internal dentin portion of the blocks was removed using ISO 027, 029, 031, 035 round burs and the dentin chips were incubated at 37℃ for 24 hour. Following incubation, the optical density of the medium was measured. The data were statistically analysed using repeated measures ANOVA and one-way ANOVA.
The results were as follows,
1. There was statistically significant reduction in the number of E. faecalis of the group where dentinal tubules were completely sealed with nail varnish in comparison with the groups obturated with gutta-percha or resilon (p < 0.05).
2. In group 5, the number of E. faecalis in the dentinal tubules decreased significantly with time (p < 0.05), whereas in Group 3 and 4, there was no reduction in its number (p > 0.05).
3. Under the conditions of this experiment,
E. faecalis survived up to 4 weeks after obturation with gutta-percha or resilon (p > 0.05).-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation ofEnterococcus faecalisremoval efficacy of the EndoVac® and EndoActivator® intracanal irrigation methods
Seung-Gon Song, Se-Hee Park, Kyung-Mo Cho, Jin-Woo Kim
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2009; 34(5): 390. CrossRef
- Evaluation ofEnterococcus faecalisremoval efficacy of the EndoVac® and EndoActivator® intracanal irrigation methods
- 973 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The effect of the endodontic access cavity on the marginal leakage of crowns
- Euiseong Kim, Jinho Chung, Yongkun Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2002;27(4):389-393. Published online July 31, 2002
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2002.27.4.389
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The marginal integrity of the crown can be broken during endodontic access cavity preparation due to the vibration of burs. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of endodontic access cavity preparation on the marginal leakage of full veneer gold crowns. 24 intact molars were mounted in acrylic resin blocks and prepared for crowns by a restorative dentist and crowns were cast with gold alloy. 20 Crowns were cemented with glass ionomer cement and 2 crowns were not cemented for positive control. 200 thermo-cycles from 5℃ to 50℃ with a travel time of 20s were completed. Then samples were randomly divided into 2 experimental groups of 9 each. Endodontic access preparation and zinc-oxide eugenol temporary fillings were done in Group 1. Teeth in Group 2 were not treated. Samples were coated with 2 layers of nail varnish and were immersed in 1% methylene blue dye for 20 hrs. Endodontic access was prepared in 2 samples, which were coated with nail varnish on all surfaces for negative control. After washing in running water, gold crowns were cut with a #330 bur. Four buccolingual sections, 2 mm apart, were cut from the central section of each tooth and were examined and scored under the microscope for dye leakage. Score 1: leakage to the cervical 1/3 of the axial wall, Score 2: leakage to the middle 1/3 of the axial wall, Score 3: leakage to the coronal 1/3 of the axial wall, Score 4: leakage to the occlusal surface. The median value for Group 1 is 4 and for Group 2 is 2. The result of this study showed that samples in Group 1 leaked more than those in Group 2. This finding was significant(P<0.001).
- 870 View
- 3 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


