Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
- Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(3):e33. Published online August 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
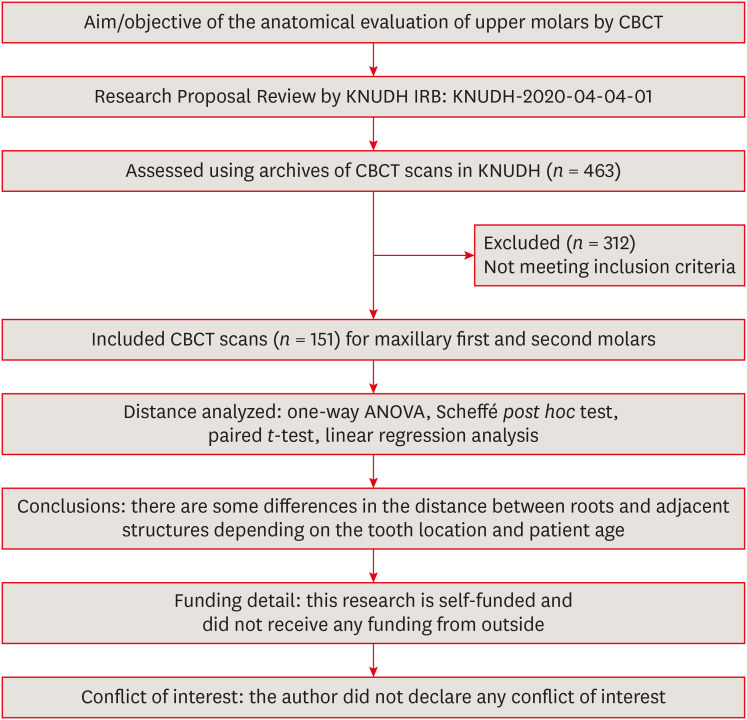
ePub Objectives This study aimed to analyze the proximity of maxillary molar roots to their overlying cortical bone surfaces and the maxillary sinus.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomographic images of 151 patients with completely erupted upper molars that had 3 separate roots were studied. The following distances were measured: from the root apex to the cortical plate and maxillary sinus floor, and from the apical 3-mm level of the root to the cortical plate. Differences between groups were analyzed with 1-way analysis of variance and the Scheffé
post hoc test, the significance of differences between cone-beam computed tomography views with the pairedt -test, and the significance of differences among age groups with linear regression analysis. The significance level was set atp < 0.05.Results The mesiobuccal and distobuccal root apexes of maxillary second molars were more distant from the buccal cortical plate than the maxillary first molars (
p < 0.05). The apical 3-mm level of the mesiobuccal root of the first molar was closer to the buccal cortical bone than the second molar (p < 0.05). In the maxillary first molars, the thickness of the buccal cortical bone decreased in all roots with age (p < 0.05). In all root apexes of both molars, the difference in the vertical level between the maxillary sinus floor and the root apex increased with age (p < 0.05).Conclusions Awareness of the anatomical profile of maxillary molar apices in relation to the cortical bones and maxillary sinus will be beneficial for apical surgery.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Proximity of maxillary molar palatal roots to adjacent structures for endodontic microsurgery: a cone-beam computed tomography study
Xiaoxiang Huang, Jun Xu, Benxiang Hou, Ying Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Periapical bone loss configuration in sub-Saudi patients afflicted with periapical abscesses: A 3D cone-beam computed tomography analysis
Swati A. Srivastava, Rahaf A. Alawajy, Rehab Abdelaziz, Elzahraa A. Eldwakhly, Selma A. Saadaldin, Rahaf A. Almohareb, Fahda Nabeel Algahtani, Mai Salah Soliman, Manal M. Abdelhafeez
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2025; 15(2): 144. CrossRef
- Proximity of maxillary molar palatal roots to adjacent structures for endodontic microsurgery: a cone-beam computed tomography study
- 3,028 View
- 28 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Involvement of TRPA1 in the cinnamaldehyde-induced pulpal blood flow change in the feline dental pulp
- Dokyung Kim, Moon-Hwan Lee, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):202-209. Published online July 29, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.202
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to investigate the involvement of TRPA1 in the cinnamaldehyde-induced pulpal blood flow (PBF) change in the feline dental pulp.
Materials and Methods Mandibles of eight cats were immobilized and PBF was monitored with a laser Doppler flowmetry at the mandibular canine tooth. To evaluate the effect of cinnamaldehyde on PBF, cinnamaldehyde was injected into the pulp through the lingual artery at a constant rate for 60 seconds. As a control, a mixture of 70% ethanol and 30% dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, vehicle) was used. To evaluate the involvement of transient receptor potential ankyrin 1 (TRPA1) in PBF change, AP18, a specific TRPA1 antagonist, was applied into the pulp through the Class V dentinal cavity followed by cinnamaldehyde-administration 3 minutes later. The paired variables of experimental data were statistically analyzed using paired
t -test. Ap value of less than 0.05 was considered as statistically significant.Results Administration of cinnamaldehyde (0.5 mg/kg, intra-arterial [i.a.]) induced significant increases in PBF (
p < 0.05). While administration of a TRPA1 antagonist, AP18 (2.5 - 3.0 mM, into the dentinal cavity [i.c.]) caused insignificant change of PBF (p > 0.05), administration of cinnamaldehyde (0.5 mg/kg, i.a.) following the application of AP18 (2.5 - 3.0 mM, i.c.) resulted in an attenuation of PBF increase from the control level (p < 0.05). As a result, a TRPA1 antagonist, AP18 effectively inhibited the vasodilative effect of cinnamaldehyde (p < 0.05).Conclusions The result of the present study provided a functional evidence that TRPA1 is involved in the mechanism of cinnamaldehyde-induced vasodilation in the feline dental pulp.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A simple model for the assessment of the agonistic activity of dibenzazepine derivatives by molecular moieties
Mohammad Hossein Keshavarz, Hossein Fakhraian, Norollah Saedi
Medicinal Chemistry Research.2021; 30(1): 215. CrossRef
- A simple model for the assessment of the agonistic activity of dibenzazepine derivatives by molecular moieties
- 2,038 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Proximity of the mandibular molar root apex from the buccal bone surface: a cone-beam computed tomographic study
- Dokyung Kim, Jung-Hong Ha, Myoung-Uk Jin, Young-Kyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(3):182-188. Published online July 14, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.3.182
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the proximity of the mandibular molar apex to the buccal bone surface in order to provide anatomic information for apical surgery.
Materials and Methods Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) images of 127 mandibular first molars and 153 mandibular second molars were analyzed from 160 patients' records. The distance was measured from the buccal bone surface to the root apex and the apical 3.0 mm on the cross-sectional view of CBCT.
Results The second molar apex and apical 3 mm were located significantly deeper relative to the buccal bone surface compared with the first molar (
p < 0.01). For the mandibular second molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the root apex was significantly shorter in patients over 70 years of age (p < 0.05). Furthermore, this distance was significantly shorter when the first molar was missing compared to nonmissing cases (p < 0.05). For the mandibular first molars, the distance to the distal root apex of one distal-rooted tooth was significantly greater than the distance to the disto-buccal root apex (p < 0.01). In mandibular second molar, the distance to the apex of C-shaped roots was significantly greater than the distance to the mesial root apex of non-C-shaped roots (p < 0.01).Conclusions For apical surgery in mandibular molars, the distance from the buccal bone surface to the apex and apical 3 mm is significantly affected by the location, patient age, an adjacent missing anterior tooth, and root configuration.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
Zhengmei Lin, Dingming Huang, Shuheng Huang, Zhi Chen, Qing Yu, Benxiang Hou, Lihong Qiu, Wenxia Chen, Jiyao Li, Xiaoyan Wang, Zhengwei Huang, Jinhua Yu, Jin Zhao, Yihuai Pan, Shuang Pan, Deqin Yang, Weidong Niu, Qi Zhang, Shuli Deng, Jingzhi Ma, Xiuping
International Journal of Oral Science.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcome of intentional replantation of endodontically treated teeth with periapical pathosis: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Faizan Javed, Kamil Zafar, Farhan R. Khan
Australian Endodontic Journal.2023; 49(S1): 494. CrossRef - Proximity of maxillary molar apexes to the cortical bone surface and the maxillary sinus
Han Shin Lee, Dokyung Kim, Sung Kyo Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Alveolar bone thickness overlying healthy maxillary and mandibular teeth: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Marziyeh Shafizadeh, Azita Tehranchi, Armin Shirvani, Saeed Reza Motamedian
International Orthodontics.2021; 19(3): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between the anatomic structures and mandibular posterior teeth for endodontic surgery in a Turkish population: a cone-beam computed tomographic analysis
Zeliha Uğur Aydın, Duygu Göller Bulut
Clinical Oral Investigations.2019; 23(9): 3637. CrossRef
- Expert consensus on intentional tooth replantation
- 1,973 View
- 4 Download
- 5 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


