Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of combined application of premixed bioceramic paste and diode laser in vital pulp therapy: an immunohistochemical randomized controlled split-mouth in vivo animal experiment
- Mo’men A. Salama, Dalia M. Fayyad, Mohamed I. Rabie, Manar A. A. Selim, Mahmoud F. Ahmed
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e4. Published online January 20, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e4
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
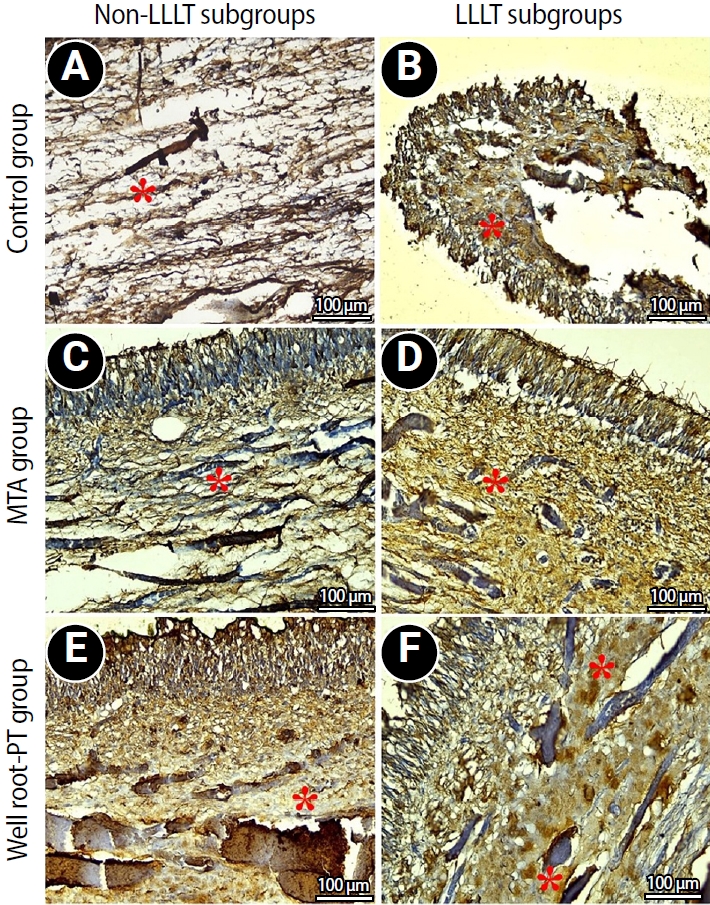
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of premixed bioceramic paste (Well-Root PT; Vericom) compared to mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) on the expression of the mineralization-related marker dentin sialoprotein (DSP) in dental pulp following direct pulp capping, with or without prior diode laser application.
Methods
Direct pulp exposures were performed in the upper and lower incisors of eight dogs (n = 96 teeth). Cavities (Class V) were created and received pulp capping with either Well-Root PT (n = 32), MTA (n = 32), or no capping material (polytetrafluoroethylene disc only) (n = 32), with or without the application of a diode laser. Immunohistochemical analysis of DSP expression was conducted and quantified as the mean area percentage using ImageJ software at 2 and 8 weeks posttreatment.
Results
Both the Well-Root PT and MTA groups showed significantly increased DSP expression compared to the control group at both 2 and 8 weeks (p < 0.05). No significant difference in the mean area percentage of DSP expression was found between the Well-Root PT and MTA groups. The diode laser application did not produce a significant effect on DSP expression. Within-group comparison revealed a significant increase in DSP expression between the 2- and 8-week follow-up periods (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Well-Root PT demonstrated comparable efficacy to MTA in promoting DSP expression, supporting its use as an effective direct pulp capping material. Diode laser application prior to capping had no effect on DSP expression in this experimental model.
- 549 View
- 30 Download

- Success rate of direct pulp capping on permanent teeth using bioactive materials: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Karem Paula Pinto, Gabriela Ribeiro da Silva, Cláudio Malizia Alves Ferreira, Luciana Moura Sassone, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(4):e34. Published online September 6, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This systematic review and meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the success rate of direct pulp capping (DPC) on permanent teeth, comparing the use of MTA with calcium hydroxide and calcium silicate-based cements. A systematic search was carried out in 4 databases until July 2023. The selection was based on PICOS criteria and only randomized clinical trials were included. The risk of bias was assessed using RoB-2 tool, and meta-analyses were performed using RevMan 5.3 software. The overall quality of evidence was determined using the GRADE tool. Thirteen studies were included. Meta-analyses indicated significantly higher success rate for DPC using MTA compared to calcium hydroxide, while no significant difference was observed between MTA and Biodentine, showing a success rate from 80% to 100% even after 3 years of follow-up. Five studies were classified as having high risk of bias and the GRADE assessment revealed low certainty of evidence. DPC is highly effective for permanent teeth when using MTA or Biodentine. There is a need for future well-designed randomized clinical trials to evaluate the efficacy of DPC using newer bioceramic materials.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
Njwan Fadhel SHEHAB
Dental Materials Journal.2026; 45(1): 92. CrossRef - Photobiomodulation-assisted pulp capping using nano-hydroxyapatite and mineral trioxide aggregate: Report of two cases
Priya Pal, Rhythm Bains, Promila Verma, Vivek Kumar Bains
Journal of Healthcare Research and Education.2026; 2: 2. CrossRef - Histological Tissue Response to Calcium Silicate-Based Cements Assessed in Human Tooth Culture Models: A Systematic Review
Alberto Cabrera-Fernández, Hebertt Gonzaga dos Santos Chaves, Aránzazu Díaz-Cuenca, Juan J. Segura-Egea, Jenifer Martín-González, João Peça, Diana B. Sequeira, João Miguel Marques dos Santos
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2026; 17(2): 78. CrossRef - Indian Association of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics consensus statement on deep caries management
Deepak Kumar Sharma, R. S. Mohan Kumar, Shishir Singh, Suparna Ganguly Saha, Meenal Nithin Gulve, Dipali Y. Shah, Sathish Abraham, Shruthi Nagaraja, Raksha Bhat
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 714. CrossRef
- Physicochemical effects of nano type-B bone substitute on pulp protective cement formulations
- 19,177 View
- 569 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

-
Hard tissue formation after direct pulp capping with osteostatin and MTA
in vivo - Ji-Hye Yoon, Sung-Hyeon Choi, Jeong-Tae Koh, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(2):e17. Published online February 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In recent
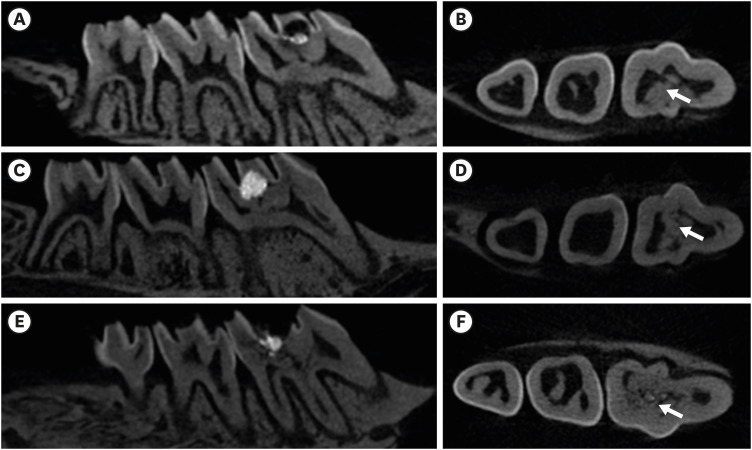
in vitro study, it was reported that osteostatin (OST) has an odontogenic effect and synergistic effect with mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) in human dental pulp cells. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate whether OST has a synergistic effect with MTA on hard tissue formationin vivo .Materials and Methods Thirty-two maxillary molars of Spraque-Dawley rats were used in this study. An occlusal cavity was prepared and the exposed pulps were randomly divided into 3 groups: group 1 (control; ProRoot MTA), group 2 (OST 100 μM + ProRoot MTA), group 3 (OST 10 mM + ProRoot MTA). Exposed pulps were capped with each material and cavities were restored with resin modified glass ionomer. The animals were sacrificed after 4 weeks. All harvested teeth were scanned with micro-computed tomography (CT). The samples were prepared and hard tissue formation was evaluated histologically. For immunohistochemical analysis, the specimens were sectioned and incubated with primary antibodies against dentin sialoprotein (DSP).
Results In the micro-CT analysis, it is revealed that OST with ProRoot MTA groups showed more mineralized bridge than the control (
p < 0.05). In the H&E staining, it is showed that more quantity of the mineralized dentin bridge was formed in the OST with ProRoot MTA group compared to the control (p < 0.05). In all groups, DSP was expressed in newly formed reparative dentin area.Conclusions OST can be a supplementary pulp capping material when used with MTA to make synergistic effect in hard tissue formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pulpal responses to mineral trioxide aggregate with and without zinc oxide addition in mature canine teeth after full pulpotomy
Behnam Bolhari, Neda Kardouni Khouzestani, Hadi Assadian, Saeed Farzad-Mohajeri, Mohammad Mehdi Dehghan, Soheil Niavarzi, Behnam Dorost, Venkateshbabu Nagendrababu, Henry F. Duncan, Artak Heboyan, Antonio Signore, Stefano Benedicenti
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Advancements in Peptides for Promoting Reparative Dentin Regeneration in Direct Pulp Capping: A Narrative Review
Jiawen Wang, Shuwei Qiao, Tianjia Huang, Junjie Lian, Song Zhu
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and pro-mineralization effects of premixed calcium silicate-based materials on human dental pulp stem cells: An in vitro and in vivo study
Nyein Chan KO, Sonoko NODA, Yamato OKADA, Kento TAZAWA, Nobuyuki KAWASHIMA, Takashi OKIJI
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(5): 729. CrossRef - Osteostatin, a peptide for the future treatment of musculoskeletal diseases
Daniel Lozano, Arancha R. Gortazar, Sergio Portal-Núñez
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 223: 116177. CrossRef - Comparison of bioactive material failure rates in vital pulp treatment of permanent matured teeth – a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Péter Komora, Orsolya Vámos, Noémi Gede, Péter Hegyi, Kata Kelemen, Adél Galvács, Gábor Varga, Beáta Kerémi, János Vág
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hard tissue formation in pulpotomized primary teeth in dogs with nanomaterials MCM-48 and MCM-48/hydroxyapatite: an in vivo animal study
Sahar Talebi, Nosrat Nourbakhsh, Ardeshir Talebi, Amir Abbas Nourbakhsh, Abbas Haghighat, Maziar Manshayi, Hamid Reza Bakhsheshi, Razieh Karimi, Rahman Nazeri, Kenneth J.D. Mackenzie
BMC Oral Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Reparative Mineralized Tissue Characterization by Different Bioactive Direct Pulp-capping Agents
Mrunal Shinde, Varsha Pandit, Sarita Singh, Aniket Jadhav, Sarah Marium, Smita Patil
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2024; 16(1): 8. CrossRef - Effects of mineral trioxide aggregate and methyl sulfonyl methane on pulp exposure via RUNX2 and RANKL pathways
Altar Ateş, Ayca Kurt, Tolga Mercantepe
Odontology.2024; 112(3): 895. CrossRef - Effects of barium titanate on the dielectric constant, radiopacity, and biological properties of tricalcium silicate-based bioceramics
Yoorina CHOI, Yun-Chan HWANG, Mi-Kyung YU, Kwang-Won LEE, Kyung-San MIN
Dental Materials Journal.2023; 42(1): 55. CrossRef - Bioactive potential of Bio‐C Pulpo is evidenced by presence of birefringent calcite and osteocalcin immunoexpression in the rat subcutaneous tissue
Marcela Borsatto Queiroz, Rafaela Nanami Handa Inada, Camila Soares Lopes, Juliane Maria Guerreiro‐Tanomaru, Estela Sasso‐Cerri, Mário Tanomaru‐Filho, Paulo Sérgio Cerri
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2022; 110(10): 2369. CrossRef - The Influence of New Bioactive Materials on Pulp–Dentin Complex Regeneration in the Assessment of Cone Bone Computed Tomography (CBCT) and Computed Micro-Tomography (Micro-CT) from a Present and Future Perspective—A Systematic Review
Mirona Paula Palczewska-Komsa, Bartosz Gapiński, Alicja Nowicka
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(11): 3091. CrossRef - A Breakthrough in the Era of Calcium Silicate-Based Cements: A Critical Review
Payal S Chaudhari, Manoj G Chandak, Akshay A Jaiswal, Nikhil P Mankar, Priyanka Paul
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Direct Pulp Capping Bioactive Materials in Dentin Regeneration: A Systematic Review
Ermin Nie, Jiali Yu, Rui Jiang, Xiangzhen Liu, Xiang Li, Rafiqul Islam, Mohammad Khursheed Alam
Materials.2021; 14(22): 6811. CrossRef
- Pulpal responses to mineral trioxide aggregate with and without zinc oxide addition in mature canine teeth after full pulpotomy
- 2,942 View
- 38 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref

- Considerations during crown reattachment procedure over the pulpal exposure: case report
- Bona Kim, Yoon Lee, Min-Ju Song, Su-Jung Shin, Jeong-Won Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(4):240-244. Published online November 21, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.4.240
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Crown reattachment is the most conservative treatment which can be used to restore fractured tooth, presumably with sufficient strength, while maintaining original contour, incisal translucency, and reducing chair time and cost.
However, in case of crown fracture with pin-point pulp exposure, we should cautiously minimize the irritation to the pulp and consider pre-treatment pulpal status, choice of pulp capping materials, choice of bonding system and treatment sequence during crown reattachment procedures. This case reports the considerations while crown reattachment with direct pulp capping using calcium hydroxide (Dycal, Dentsply Caulk).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Conservative Approach to the Management of a Dental Trauma for Immediate Natural Esthetics
Pallav Mahesh Patni, Pradeep Jain, Mona Jain Patni
Archives of Trauma Research.2016;[Epub] CrossRef
- A Conservative Approach to the Management of a Dental Trauma for Immediate Natural Esthetics
- 1,416 View
- 7 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Pulp response of beagle dog to direct pulp capping materials: Histological study
- Ji-Hyun Bae, Young-Gyun Kim, Pil-Young Yoon, Byeong-Hoon Cho, Yong-Hoon Choi
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(1):5-12. Published online January 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.1.005
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the pulp tissue reaction to direct pulp capping of mechanically exposed beagle dogs'pulp with several capping materials. A total of 36 teeth of 2 healthy beagle dongs were used. The mechanically exposed pulps were capped with one of the followings: (1) Mineral Trioxide Aggregate (MTA: ProRoot® MTA, Dentsply, Tulsa, USA), (2) Clearfil SE Bond (Dentin adhesive system: Kuraray, Osaka, Japan), (3) Ultra-Blend (Photo-polymerized Calcium hydroxide: Ultradent, South Jordan, USA), (4) Dycal (Quick setting Calcium hydroxide: LD Caulk Co., Milford, USA) at 7, 30, and 90 days before sacrificing. The cavities were restored with Z350 flowable composite resin (3M ESPE, St. Paul. MN, USA). After the beagle dogs were sacrificed, the extracted teeth were fixed, decalcified, prepared for histological examination and stained with HE stain. The pulpal tissue responses to direct pulp capping materials were assessed.
In MTA, calcium hydroxide, and photo-polymerized calcium hydroxide groups, initial mild inflammatory cell infiltration, newly formed odontoblast-like cell layer and hard tissue bridge formation were observed. Compared with dentin adhesive system, these materials were biocompatible and good for pulp tissue regeneration.
In dentin adhesive system group, severe inflammatory cell infiltration, pulp tissue degeneration and pulp tissue necrosis were observed. It seemed evident that application of dentin adhesive system in direct pulp capping of beagle dog teeth cannot lead to acceptable repair of the pulp tissue with dentine bridge formation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Experimental Study of Pulp Capping Using Xenogenic Demineralized Dentin Paste
Ji-Young Yun, Yong-Hoon Choi, Young-Kyun Kim, In-Woong Um, Joo-Cheol Park, Ji-Yoon Kim
Journal of Hard Tissue Biology.2016; 25(3): 321. CrossRef - Comparison of gene expression profiles of human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate and calcium hydroxide
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, Woocheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2011; 36(5): 397. CrossRef - Gene expression profiling in human dental pulp cells treated with mineral trioxide aggregate
Yong-Beom Kim, Won-Jun Shon, WooCheol Lee, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Ho Baek, Kwang-Shik Bae
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(3): 152. CrossRef - Histology of dental pulp healing after tooth replantation in rats
Eun-Jin Go, Han-Seong Jung, Eui-Seong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Conservative Dentistry.2010; 35(4): 273. CrossRef
- Experimental Study of Pulp Capping Using Xenogenic Demineralized Dentin Paste
- 1,315 View
- 11 Download
- 4 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


