Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
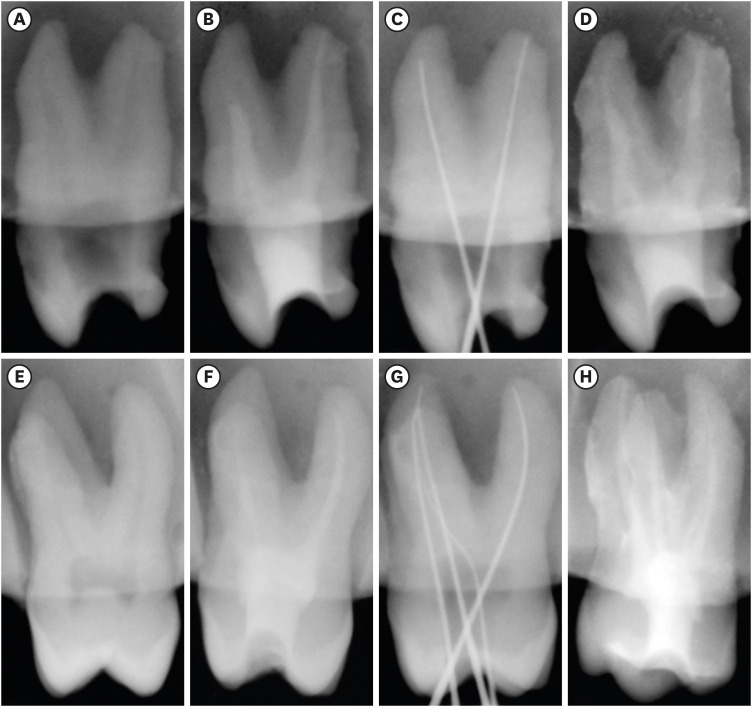
- Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
- Shashirekha Govind, Amit Jena, Satabdi Pattanaik, Mahaprasad Anarasi, Satyajit Mohapatra, Vinay Shivagange
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e33. Published online June 4, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of ionic and non-ionic-based contrast media (
in vitro study) and the combinatorial effect of chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution (CERS) (in vivo study) for visualization of the root canal anatomy.Materials and Methods In vitr o study (120 teeth): The root canal of maxillary premolars and molars (in vitro group 1 and 2 respectively,n = 60 each) were analyzed using 4 different contrast media (subgroups: Omnipaque 350, Iopamidol, Xenetix 350, and Urografin 76;n = 15 each) in combination with 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Based on the results of thein vitro study,in vivo study (80 teeth) was done to compare Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl with CERS (in vivo group 1 and 2 respectively,n = 40 each) on maxillary and mandibular premolars and molars. Two endodontists used radiovisiography to assess the depth of ingress and identify the aberrant root anatomy after access cavity preparation, and after initial cleaning and shaping of canals. Kruskal-Wallis test was used forin vitro comparison (p < 0.05), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Mann-WhitneyU test forin vivo analysis (p < 0.01).Results In vitro study, Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl facilitated a significant higher visualization (p < 0.05). Forin vivo study, CERS had a statistically significant depth of ingress (p < 0.01), and was efficient in identifying the aberrant root canal anatomy of premolars and molars.Conclusions CERS facilitates better visualization of the root canal anatomy of human premolars and molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Improving Endodontic Radiograph Interpretation with TV-CLAHE for Enhanced Root Canal Detection
Barbara Obuchowicz, Joanna Zarzecka, Michał Strzelecki, Marzena Jakubowska, Rafał Obuchowicz, Adam Piórkowski, Elżbieta Zarzecka-Francica, Julia Lasek
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(15): 5554. CrossRef - Efficacy of sonic and ultrasonic activation on irrigant penetration in different tapered preparations: An in vitro study
M. Rama Sowmya, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Pradeep Solete, Sahil Choudhari, S Delphine Priscilla Antony, Mohammed Mustafa
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 370. CrossRef - Analysis of the value of visualized root canal technique in the clinical treatment of endodontics
Nana SUN, Nannan WANG, Xin QIAN
Panminerva Medica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
- 1,790 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref

- The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
- Wook-Jin Seong, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Soocheol Jeong, Youngcheul Heo, Woo-Bin Song, Mansur Ahmad
- Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):146-153. Published online August 23, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.146
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Aluminum step wedge (ASW) equivalent radiodensity (eRD) has been used to quantify restorative material's radiodensity. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of image acquisition control (IAC) of a digital X-ray system on the radiodensity quantification under different exposure time settings.
Materials and Methods Three 1-mm thick restorative material samples with various opacities were prepared. Samples were radiographed alongside an ASW using one of three digital radiographic modes (linear mapping (L), nonlinear mapping (N), and nonlinear mapping and automatic exposure control activated (E)) under 3 exposure time settings (underexposure, normal-exposure, and overexposure). The ASW eRD of restorative materials, attenuation coefficients and contrasts of ASW, and the correlation coefficient of linear relationship between logarithms of gray-scale value and thicknesses of ASW were compared under 9 conditions.
Results The ASW eRD measurements of restorative materials by three digital radiographic modes were statistically different (
p = 0.049) but clinically similar. The relationship between logarithms of background corrected grey scale value and thickness of ASW was highly linear but attenuation coefficients and contrasts varied significantly among 3 radiographic modes. Varying exposure times did not affect ASW eRD significantly.Conclusions Even though different digital radiographic modes induced large variation on attenuation of coefficient and contrast of ASW, E mode improved diagnostic quality of the image significantly under the under-exposure condition by improving contrasts, while maintaining ASW eRDs of restorative materials similar. Under the condition of this study, underexposure time may be acceptable clinically with digital X-ray system using automatic gain control that reduces radiation exposure for patient.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Is the radiopacity of CAD/CAM aesthetic materials sufficient?
Rua S. Babaier, Modi S. Aldeeb, Nick Silikas, David C. Watts
Dental Materials.2022; 38(6): 1072. CrossRef
- Is the radiopacity of CAD/CAM aesthetic materials sufficient?
- 1,662 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref

- The reduction methods of operator's radiation dose for portable dental X-ray machines
- Jeong-Yeon Cho, Won-Jeong Han
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(3):160-164. Published online August 29, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.3.160
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was aimed to investigate the methods to reduce operator's radiation dose when taking intraoral radiographs with portable dental X-ray machines.
Materials and Methods Two kinds of portable dental X-ray machines (DX3000, Dexcowin and Rextar, Posdion) were used. Operator's radiation dose was measured with an 1,800 cc ionization chamber (RadCal Corp.) at the hand level of X-ray tubehead and at the operator's chest and waist levels with and without the backscatter shield. The operator's radiation dose at the hand level was measured with and without lead gloves and with long and short cones.
Results The backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the hand level of X-ray tubehead to 23 - 32%, the lead gloves to 26 - 31%, and long cone to 48 - 52%. And the backscatter shield reduced operator's radiation dose at the operator's chest and waist levels to 0.1 - 37%.
Conclusions When portable dental X-ray systems are used, it is recommended to select X-ray machine attached with a backscatter shield and a long cone and to wear the lead gloves.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessment of the Occupational Radiation Dose from a Handheld Portable X-ray Unit During Full-mouth Intraoral Dental Radiographs in the Dog and the Cat – A Pilot Study
Lenin A. Villamizar-Martinez, Jeannie Losey
Journal of Veterinary Dentistry.2024; 41(2): 106. CrossRef - Seguridad y protección radiológica con el uso de rayos X portátiles. Revisión de literatura
Francisco Javier Marichi-Rodríguez, Janeth Serrano-Bello, Marine Ortiz-Magdaleno, Febe Carolina Vázquez-Vázquez
Revista Odontológica Mexicana Órgano Oficial de la Facultad de Odontología UNAM.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Operator and Patient Doses after Irradiation with Handheld X-ray Devices
Ali Altındağ, Hakan Eren, Kaan Orhan, Sebahat Görgün
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(18): 10414. CrossRef - Hand-held dental X-ray device: Attention to correct use
Guilherme Ceschia Martins, Thaíza Gonçalves Rocha, Thaís de Lima Azeredo, Andréa de Castro Domingos, Maria Augusta Visconti, Eduardo Murad Villoria
Imaging Science in Dentistry.2023; 53(3): 265. CrossRef - Effect of cranium structure on dose distribution during intraoral radiography
Takeru Ishii, Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Atsuharu Nitanda, Akihiro Ochiai, Shinji Kito, Hirofumi Aboshi, Hideki Saka
Journal of Oral Biosciences.2022; 64(1): 131. CrossRef - Application of the Monte Carlo Method for the Evaluation of Scattered Radiation Dose Due to the Use of Handheld X-Ray in Dentistry
A Cc Gonzales, M R Soares, W O G Batista, A R Cardeña, J P Marquez, J R Vega
Radiation Protection Dosimetry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - ASSESSMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL RADIATION DOSE FROM CAMERA MODEL INTRAORAL HANDHELD X-RAY DEVICE WITHOUT STRAY RADIATION PROTECTION SHIELD
Mahkameh Moshfeghi, Yaser Safi, Alireza Afzalan, Mitra Ghazizadeh Ahsaie
Radiation Protection Dosimetry.2022; 198(1-2): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of radiation exposure to operators of portable hand-held dental X-ray units
Justin Leadbeatter, Jennifer Diffey
Physical and Engineering Sciences in Medicine.2021; 44(2): 377. CrossRef - Comparison of air dose and operator exposure from portable X-ray units
Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Ruri Asami, Takeru Ishii, Shinji Kito, Yuichi Tamatsu, Hirofumi Aboshi, Hideki Saka
Legal Medicine.2020; 47: 101787. CrossRef - Dental research using intraoral techniques with portable digital radiography adapted for fieldwork in Qubbet el-Hawa (Egypt)
Sandra López-Lázaro, Violeta C. Yendreka, Alejandro Jiménez-Serrano, José Alba-Gómez, Gabriel M. Fonseca
Archaeological and Anthropological Sciences.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of stray radiation to the operator for five hand-held dental X-ray devices
Richard Smith, Richard Tremblay, Graeme M Wardlaw
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2019; 48(5): 20180301. CrossRef - Assessment of image quality and exposure parameters of an intraoral portable X-rays device
Elton G Zenóbio, Madelon AF Zenóbio, Carolina DB Azevedo, Maria do Socorro Nogueira, Cláudio D Almeida, Flávio R Manzi
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2019; 48(3): 20180329. CrossRef - The study of protection of operators and surrounding workers at the time of using portable intraoral X-ray unit
Atsushi Iwawaki, Yusei Otaka, Ruri Asami, Tomonori Ozawa, Maki Izawa, Hideki Saka
Legal Medicine.2018; 33: 66. CrossRef - The effects of device position on the operator's radiation dose when using a handheld portable X-ray device
Jimmy Makdissi, Ravikiran R Pawar, Ben Johnson, Bun S Chong
Dentomaxillofacial Radiology.2016; 45(3): 20150245. CrossRef - Patient and staff dosimetry during radiographic procedures in an intensive care unit
Rosario Fernández, Miguel Moreno-Torres, Antonia M Contreras, María I Núñez, Damián Guirado, Luis Peñas
Journal of Radiological Protection.2015; 35(3): 727. CrossRef - The effects of image acquisition control of digital X-ray system on radiodensity quantification
Wook-Jin Seong, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Soocheol Jeong, Youngcheul Heo, Woo-Bin Song, Mansur Ahmad
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2013; 38(3): 146. CrossRef
- Assessment of the Occupational Radiation Dose from a Handheld Portable X-ray Unit During Full-mouth Intraoral Dental Radiographs in the Dog and the Cat – A Pilot Study
- 5,676 View
- 33 Download
- 16 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


