Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cyclic fatigue resistance, torsional resistance, and metallurgical characteristics of M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold NiTi files
- Eugenio Pedullà, Fabio Lo Savio, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Gabriele Miccoli, Elena Bruno, Silvia Rapisarda, Seok Woo Chang, Ernesto Rapisarda, Guido La Rosa, Gianluca Gambarini, Luca Testarelli
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e25. Published online April 23, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e25
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
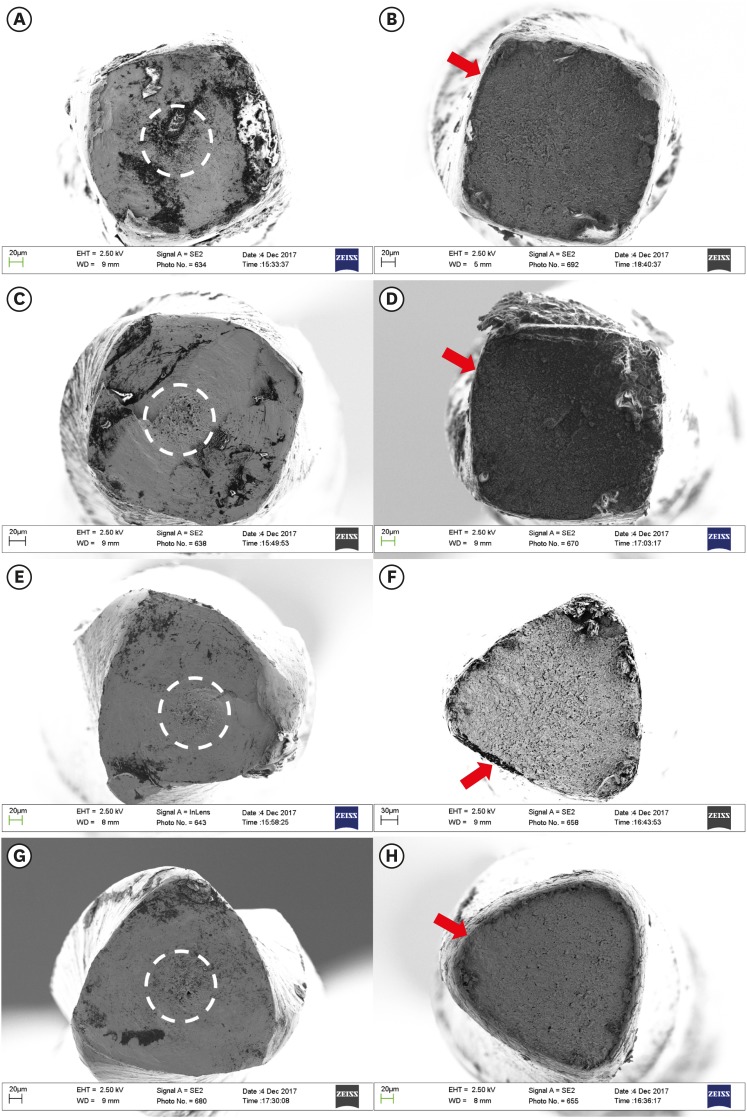
ePub Objectives To evaluate the mechanical properties and metallurgical characteristics of the M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (United Dental).
Materials and Methods One hundred and sixty new M3 Rotary and M3 Pro Gold files (sizes 20/0.04 and 25/0.04) were used. Torque and angle of rotation at failure (
n = 20) were measured according to ISO 3630-1. Cyclic fatigue resistance was tested by measuring the number of cycles to failure in an artificial stainless steel canal (60° angle of curvature and a 5-mm radius). The metallurgical characteristics were investigated by differential scanning calorimetry. Data were analyzed using analysis of variance and the Student-Newman-Keuls test.Results Comparing the same size of the 2 different instruments, cyclic fatigue resistance was significantly higher in the M3 Pro Gold files than in the M3 Rotary files (
p < 0.001). No significant difference was observed between the files in the maximum torque load, while a significantly higher angular rotation to fracture was observed for M3 Pro Gold (p < 0.05). In the DSC analysis, the M3 Pro Gold files showed one prominent peak on the heating curve and 2 prominent peaks on the cooling curve. In contrast, the M3 Rotary files showed 1 small peak on the heating curve and 1 small peak on the cooling curve.Conclusions The M3 Pro Gold files showed greater flexibility and angular rotation than the M3 Rotary files, without decrement of their torque resistance. The superior flexibility of M3 Pro Gold files can be attributed to their martensite phase.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
Reyhaneh Shoorgashti, Marzie Jafari, Mohadeseh Alimohammadi, Niloofar Ebrahimi
Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health Studies.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in Niti and Glide Path Rotary System: Preparation of Canal Centering and Transportation in Double-curved Root Canals
Calvin Reinnaldi, Wiena Widyastuti, Taufiq Ariwibowo, Sri Ratna Laksmiastuti
The Open Dentistry Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - In Vitro Cleaning Efficacy of Neolix and M3 Immatural Rotary Files in Comparison with Hand Files in Primary Molar Root Canals
Shabnam Maleki, Effat Khodadadi, Seyedali Seyedmajidi, Elham Mahmoudi
Journal of Research in Dental and Maxillofacial Sciences.2025; 10(2): 88. CrossRef - Comparison of Debris Extrusion and Instrumentation Time Among ProTaper Next, Neoniti, and M3‐Pro Gold Rotary Systems: An In Vitro Study
Robab Farhang, Bita Alizadeh, Saeedeh Galledar, Sara Noorolouny, Rashin Alyali, Bahareh Pouya, Ahmad Nouroloyouni, Elango Natarajan
Advances in Materials Science and Engineering.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Continuous Rotation and Optimal Torque Reverse Kinematics on the Cyclic Fatigue Strength of Endodontic NiTi Clockwise Cutting Rotary Instruments
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel J. N. L. Silva, Duarte Marques, Marco A. Versiani
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(10): 317. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of WaveOne Gold in Reciprocation, ProGlider in Rotary Motion, and Manual Files in a Reciprocating Handpiece Within Simulated Curved Canals: An In Vitro Study
Shivangi M Pujara, Hardik B Shah, Leena H Jobanputra
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The extended finite element method in endodontics: A scoping review and future directions for cyclic fatigue testing of nickel–titanium instruments
Philip Yuan‐Ho Chien, Laurence James Walsh, Ove Andreas Peters
Clinical and Experimental Dental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluatation of two nickle-titanium systems’ (Neolix and X Pro Gold) resistance to fracture after immersion in sodium hypochlorite.
Solmaz Araghi, Abbas Delvarani, Faeze dehghan, Parisa Kaghazloo
journal of research in dental sciences.2024; 21(1): 17. CrossRef - Characterization of the file‐specific heat‐treated ProTaper Ultimate rotary system
Jorge N. R. Martins, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Duarte Marques, Natasha Ajuz, Mário Rito Pereira, Rui Pereira da Costa, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(4): 530. CrossRef - Influence of different heat treatments and temperatures on the cyclic fatigue resistance of endodontic instruments with the same design
Walid Nehme, Alfred Naaman, Franck Diemer, Maria Laura Leotta, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Eugenio Pedullà
Clinical Oral Investigations.2022; 27(4): 1793. CrossRef - Analysis of cyclic fatigue resistance of ProTaper Universal and ProTaper Next rotary instruments
Nenad Stosic, Jelena Popovic, Marija Andjelkovic-Apostolovic, Aleksandar Mitic, Radomir Barac, Marija Nikolic, Marko Igic
Stomatoloski glasnik Srbije.2022; 69(3): 109. CrossRef - What Meaningful Information Are the Instruments Mechanical Testing Giving Us? A Comprehensive Review
Jorge N.R. Martins, Rui F. Martins, Francisco Manuel Braz Fernandes, Emmanuel J.N.L. Silva
Journal of Endodontics.2022; 48(8): 985. CrossRef - Metallurgical Tests in Endodontics: A Narrative Review
Alessio Zanza, Marco Seracchiani, Rodolfo Reda, Gabriele Miccoli, Luca Testarelli, Dario Di Nardo
Bioengineering.2022; 9(1): 30. CrossRef - A Comparative Study of Four different Contemporary NiTi Rotary Endodontic Files by Metallurgical and Mechanical Analysis with Energy-dispersive X-ray Spectrophotometry with FE-SEM and Cyclic Fatigue Resistance Evaluation
Akash Azad, Shraddha Chokshi
Journal of Research and Advancement in Dentistry.2022; 14(1): 21. CrossRef - Impact of Peracetic Acid on the Dynamic Cyclic Fatigue of Heat-Treated Nickel-Titanium Rotary Endodontic Instrument
Suhad Jabbar Hamed Al-Nasrawi, Zuha Ayad Jaber, Nibrass Talib Al-Quraine, Abtesam Imhemed Aljdaimi, Sattar Jabbar Abdul-Zahra Al-Hmedat, Saleh Zidan, Julfikar Haider, Luca Testarelli
International Journal of Dentistry.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Influence of shaft length on torsional behavior of endodontic nickel–titanium instruments
Gianluca Gambarini, Marco Seracchiani, Alessio Zanza, Gabriele Miccoli, Andrea Del Giudice, Luca Testarelli
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 568. CrossRef - Cyclic Fatigue Resistance of Nickel-titanium Rotary Instruments according to the Angle of File Access and Radius of Root Canal
Eugenio Pedullà, Giusy Rita Maria La Rosa, Chiara Virgillito, Ernesto Rapisarda, Hyeon-Cheol Kim, Luigi Generali
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(3): 431. CrossRef - Torsional Resistance of Two New Heat Treated Nickel Titanium Rotary Instruments: An in Vitro Evaluation
Gianluca Gambarini, Gabriele Miccoli, Dario Di Nardo, Andrea Del Giudice, Alessandro Mazzoni, Marco Seracchiani, Luca Testarelli
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of heat treatment on torsional resistance and surface roughness of nickel‐titanium instruments
E. J. N. L. Silva, J. F. N. Giraldes, C. O. de Lima, V. T. L. Vieira, C. N. Elias, H. S. Antunes
International Endodontic Journal.2019; 52(11): 1645. CrossRef
- Comparative Evaluation of Dentinal Microcrack Using M3 ProGold, Mtwo Rotary File and Hand File in Root Canal Therapy: An In-Vitro Study
- 1,943 View
- 22 Download
- 19 Crossref

- Rheological characterization of thermoplasticized injectable gutta percha and resilon
- Juhea Chang, Seung-Ho Baek, In-Bog Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2011;36(5):377-384. Published online September 30, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2011.36.5.377
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to observe the change in the viscoelastic properties of thermoplasticized injectable root canal filling materials as a function of temperature and to compare the handling characteristics of these materials.
Materials and Methods Three commercial gutta perchas and Resilon (Pentron Clinical Technologies) in a pellet form were heated in the Obtura-II system (Obtura Spartan) at 140℃ and 200℃, and the extrusion temperature of the thermoplasticized materials was measured. The viscoelastic properties of the materials as a function of temperature were evaluated using a rheometer. The elastic modulus
G' , viscous modulusG" , loss tangenttan δ, and complex viscosity η* were determined. The phase transition temperature was determined by both the rheometer and a differential scanning calorimeter (DSC). The consistency of the materials was compared under compacting pressure at 60℃ and 40℃ by a squeeze test.Results The three gutta perchas had dissimilar profiles in viscoelastic properties with varying temperature. The phase transition of softened materials into solidification occurred at 40℃ to 50℃, and the onset temperatures obtained by a rheometer and a DSC were similar to each other. The onset temperature of phase transition and the consistency upon compaction pressure were different among the materials (
p < 0.05). Resilon had a rheologically similar pattern to the gutta perchas, and was featured between high and low-flow gutta perchas.Conclusions The rheological characteristics of the thermoplasticized root canal filling materials changed under a cooling process. The dissimilar viscoelastic properties among the materials require different handling characteristics during an injecting and compacting procedure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The investigation of composition and thermal behavior of two types of backfilling gutta-percha
Pai-Chun Huang, Yi-Ting Wu, Yung-Hao Hsu, Szu-Chin Liao, Ya-Hsuan Wang, James L. Gutmann, Haw-Ming Huang, Sung-Chih Hsieh
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(1): 414. CrossRef - Thermal behavior and viscoelastic properties of gutta-percha used for back-filling the root canal
Yung-Hao Hsu, Hsin-Hui Wang, Yung-Kang Shen, James L. Gutmann, Sung-Chih Hsieh
Journal of Dental Sciences.2020; 15(1): 28. CrossRef - Comparison between Gutta-Percha and Resin-Coated Gutta-Percha using Different Obturation Techniques
Nashwan A. Al-Afifi, Mariam Abdullah, Samah M. Al-Amery, Mohamed Abdulmunem
Journal of Applied Biomaterials & Functional Materials.2016; 14(3): e307. CrossRef - Temperature‐dependent rheological property changes of thermoplastic gutta‐percha root filling materials
H. J. Moon, J. H. Lee, J. H. Ahn, H. J. Song, Y. J. Park
International Endodontic Journal.2015; 48(6): 556. CrossRef
- The investigation of composition and thermal behavior of two types of backfilling gutta-percha
- 1,586 View
- 5 Download
- 4 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


