Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Resolvin E1 incorporated carboxymethyl chitosan scaffold accelerates repair of dental pulp stem cells under inflammatory conditions: a laboratory investigation
- Hemalatha P Balasubramanian, Nandini Suresh, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e40. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e40
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
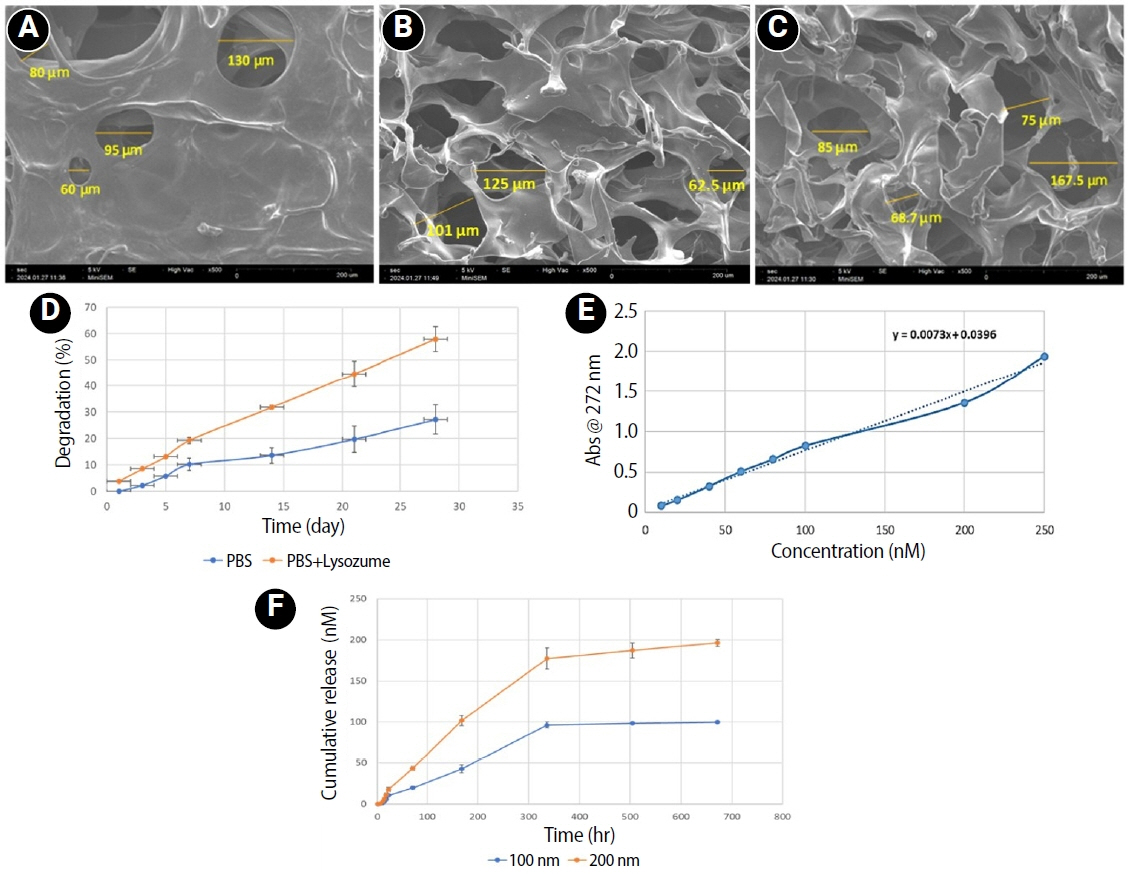
This study fabricated and characterized a resolvin E1 (RvE1)-loaded carboxymethyl chitosan (CMC) scaffold and determined its cytotoxicity and mineralization potential on inflamed human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
Methods
CMC scaffold incorporated with two concentrations of RvE1 (100 and 200 nM) was fabricated and characterized. The scaffolds’ porosity, drug release kinetics, and degradation were assessed. The impact of RvE1 on inflamed hDPSCs proliferation, proinflammatory gene expression (tumor necrosis factor alpha [TNF-α]), alkaline phosphatase activity, and alizarin red S staining was evaluated.
Results
Scanning electron microscopy analysis demonstrated a highly porous interconnected microstructure. Release kinetics showed gradual RvE1 release peaking at day 14. Cumulative degradation of the CMC scaffold at 28 days was 57.35%. Inflamed hDPSCs exposed to 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold exhibited significantly improved viability compared to 100 nM. Both RvE1-CMC scaffolds significantly suppressed the expression of TNF-α at 7 days. Alkaline phosphatase activity was enhanced by both RvE1 concentrations on days 7 and 14. Alizarin red staining revealed superior mineralization potential of 200 nM RvE1 on days 14 and 21.
Conclusions
This study concludes 200 nM RvE1-CMC scaffold is a promising therapy for inflamed pulp conditions, enhancing cell proliferation and biomineralization potential in inflamed hDPSCs.
- 530 View
- 25 Download

- Effects of CTHRC1 on odontogenic differentiation and angiogenesis in human dental pulp stem cells
- Jong-soon Kim, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, In-Nam Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, Yun-Chan Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e18. Published online April 28, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
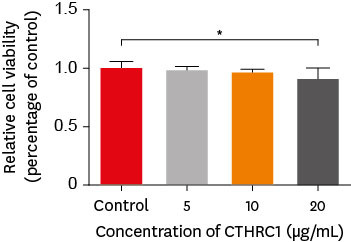
ePub Objectives This study aimed to determine whether collagen triple helix repeat containing-1 (CTHRC1), which is involved in vascular remodeling and bone formation, can stimulate odontogenic differentiation and angiogenesis when administered to human dental pulp stem cells (hDPSCs).
Materials and Methods The viability of hDPSCs upon exposure to CTHRC1 was assessed with the WST-1 assay. CTHRC1 doses of 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL were administered to hDPSCs. Reverse-transcription polymerase reaction was used to detect dentin sialophosphoprotein, dentin matrix protein 1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and fibroblast growth factor 2. The formation of mineralization nodules was evaluated using Alizarin red. A scratch wound assay was conducted to evaluate the effect of CTHRC1 on cell migration. Data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance followed by the Tukey
post hoc test. The threshold for statistical significance was set atp < 0.05.Results CTHRC1 doses of 5, 10, and 20 µg/mL had no significant effect on the viability of hDPSCs. Mineralized nodules were formed and odontogenic markers were upregulated, indicating that CTHRC1 promoted odontogenic differentiation. Scratch wound assays demonstrated that CTHRC1 significantly enhanced the migration of hDPSCs.
Conclusions CTHRC1 promoted odontogenic differentiation and mineralization in hDPSCs.
- 1,592 View
- 34 Download

-
In vitro characterization of human dental pulp stem cells isolated by three different methods - Ji-Hyun Jang, Hyeon-Woo Lee, Kyu Min Cho, Hee-Woong Shin, Mo Kwan Kang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):283-295. Published online October 12, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.283
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives In this study, we characterized human dental pulp cells (HDPCs) obtained by different culture methods to establish the most suitable methodology for dental tissue engineering and regenerative endodontic applications.
Materials and Methods HDPCs were isolated by the outgrowth method (HDPCs-OG), the enzymatic digestion method (collagenase/dispase/trypsin, HDPCs-ED), or the combination of both methods (HDPCs-Combined). The expression of mesenchymal stem cell markers (CD105, CD90, and CD73) was investigated.
In vitro differentiation capacities of HDPCs into adipogenic, osteogenic, and chondrogenic lineages were compared. Differentiation markers were analyzed by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and western blotting.Results Our data indicated that whole HDPCs-ED, HPDCs-OG, and HDPCs-Combined could be differentiated into adipogenic, chrondrogenic, and osteogenic cell types. However, we found that the methods for isolating and culturing HDPCs influence the differentiation capacities of cells. HDPCs-OG and HDPCs-ED were preferably differentiated into adipogenic and osteogenic cells, respectively. Differentiation markers shown by RT-PCR and western blotting analysis were mostly upregulated in the treated groups compared with the control groups.
Conclusions Our findings confirmed that cell populations formed by two different culture methods and the combined culture method exhibited different properties. The results of this study could provide an insight into regenerative endodontic treatment using HDPCs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of simulated microgravity on dental pulp stem cell stemness
Huailong Hou, Zhengjun Qiu, Jingyi Che, Yanping Li, Jingxuan Sun, Weiwei Zhang, Jinjie Ma, Shuang Zhang, Mengdi Li, Yumei Niu, Lina He
Journal of Molecular Histology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Validated methods for isolation and qualification of mesenchymal stromal/stem cells from different sources
Vincenzo Mattei, Francesca Santilli, Fanny Pulcini, Jessica Fabrizi, Loreto Lancia, Costantino Santacroce, Francesca Megiorni, Simona Ceccarelli, Emanuela Paldino, Roberto Gramignoli, Maria G. Roubelakis, Sadri Bahareh, Massoud Vosough, Sveva Bollini, Umb
Journal of Translational Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - ISOLATION OF HUMAN ADULT DENTAL PULP STEM CELLS USING ENZYMATIC DIGESTION
Sehrish Khan, Saima Butt, Shumaila Usman, Sana Mirza
JOURNAL OF KHYBER COLLEGE OF DENTISTRY.2024; 14(4): 9. CrossRef - Diş Hekimliğinde Oromaksillofasiyal Bölgeden Alınabilen Mezenkimal Kök Hücreler
Sefer MAHMUTOĞLU, Ayşegül MENDİ, Derviş YILMAZ
ADO Klinik Bilimler Dergisi.2022; 11(2): 184. CrossRef - Sinking Our Teeth in Getting Dental Stem Cells to Clinics for Bone Regeneration
Sarah Hani Shoushrah, Janis Lisa Transfeld, Christian Horst Tonk, Dominik Büchner, Steffen Witzleben, Martin A. Sieber, Margit Schulze, Edda Tobiasch
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(12): 6387. CrossRef - Isolation, Characterization, and Differentiation of Stem Cells From Various Dental Sources: An In Vitro Study
Sandeep S. Katti, Kishore Bhat, Chetana Bogar
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2021; 12(2): 254. CrossRef - Intra-Individual Variability of Human Dental Pulp Stem Cell Features Isolated from the Same Donor
Nela Pilbauerova, Jan Schmidt, Tomas Soukup, Jan Duska, Jakub Suchanek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(24): 13515. CrossRef - Comparison of Osteogenic Potentials of Dental Pulp and Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Using the New Cell Transplantation Platform, CellSaic, in a Rat Congenital Cleft-Jaw Model
Jinzhao Lyu, Yoshiya Hashimoto, Yoshitomo Honda, Naoyuki Matsumoto
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(17): 9478. CrossRef - In Vitro Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cells Cultured in Two Microsphere-Forming Culture Plates
Nam-Ung Bu, Hyo-Seol Lee, Bin-Na Lee, Yun-Chan Hwang, Sun-Young Kim, Seok Woo Chang, Kyoung-Kyu Choi, Duck-Su Kim, Ji-Hyun Jang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 242. CrossRef - Micro-computed tomographic evaluation of the flow and filling ability of endodontic materials using different test models
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Gisselle Moraima Chavez-Andrade, Jader Camilo Pinto, Fábio Luiz Camargo Villela Berbert, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Enzymatic Isolation, Amplification and Characterization of Dental Pulp Stem Cells
Nela Pilbauerova, T. Soukup, T. Suchánková Kleplová, J. Suchánek
Folia Biologica.2019; 65(3): 124. CrossRef - Metabolism as an early predictor of DPSCs aging
Dannie Macrin, Ammar Alghadeer, Yan Ting Zhao, Jason W. Miklas, Abdiasis M. Hussein, Damien Detraux, Aaron M. Robitaille, Anup Madan, Randall T. Moon, Yuliang Wang, Arikketh Devi, Julie Mathieu, Hannele Ruohola-Baker
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of platelet lysate in culture of PDLSCs: anin vitrocomparative study
Duaa A. Abuarqoub, Nazneen Aslam, Raghda B. Barham, Nidaa A. Ababneh, Diana A. Shahin, Abdallah A. Al-oweidi, Hanan D. Jafar, Mazin A. Al-Salihi, Abdalla S. Awidi
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7465. CrossRef - Progress in the use of dental pulp stem cells in regenerative medicine
Eduardo Anitua, María Troya, Mar Zalduendo
Cytotherapy.2018; 20(4): 479. CrossRef - Identification of a novel heterozygous mutation of ACAN in a Korean family with proportionate short stature
Yoo-Mi Kim, Chong Kun Cheon, Han Hyuk Lim, Han-Wook Yoo
Journal of Genetic Medicine.2018; 15(2): 102. CrossRef - Conditioned medium from relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis patients reduces the expression and release of inflammatory cytokines induced by LPS-gingivalis in THP-1 and MO3.13 cell lines
Patrizia Ballerini, Francesca Diomede, Nicola Petragnani, Simona Cicchitti, Ilaria Merciaro, Marcos F.X.B. Cavalcanti, Oriana Trubiani
Cytokine.2017; 96: 261. CrossRef
- Effects of simulated microgravity on dental pulp stem cell stemness
- 2,238 View
- 19 Download
- 16 Crossref

- Effect of dentin treatment on proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells
- Minjeong Park, Nan-Sim Pang, Il-Young Jung
- Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):290-298. Published online September 23, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.290
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives Sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) is an excellent bactericidal agent, but it is detrimental to stem cell survival, whereas intracanal medicaments such as calcium hydroxide (Ca[OH]2) promote the survival and proliferation of stem cells. This study evaluated the effect of sequential NaOCl and Ca[OH]2 application on the attachment and differentiation of dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs).
Materials and Methods DPSCs were obtained from human third molars. All dentin specimens were treated with 5.25% NaOCl for 30 min. DPSCs were seeded on the dentin specimens and processed with additional 1 mg/mL Ca[OH]2, 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) treatment, file instrumentation, or a combination of these methods. After 7 day of culture, we examined DPSC morphology using scanning electron microscopy and determined the cell survival rate with 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay. We measured cell adhesion gene expression levels after 4 day of culture and odontogenic differentiation gene expression levels after 4 wk using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction.
Results DPSCs did not attach to the dentin in the NaOCl-treated group. The gene expression levels of fibronectin-1 and secreted phosphoprotein-1 gene in both the Ca[OH]2- and the EDTA-treated groups were significantly higher than those in the other groups. All Ca[OH]2-treated groups showed higher expression levels of dentin matrix protein-1 than that of the control. The dentin sialophosphoprotein level was significantly higher in the groups treated with both Ca[OH]2 and EDTA.
Conclusions The application of Ca[OH]2 and additional treatment such as EDTA or instrumentation promoted the attachment and differentiation of DPSCs after NaOCl treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of Intracanal Medications on the Viability of Human Periodontal Ligament‐Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Arian Braido, Walbert de Andrade Vieira, Bruno Cazotti Pereira, Karina Gonzales Silvério, Paulo Henrique Gabriel, Aline Cristine Gomes Matta, Emerson Alves Martins, Adriana de Jesus Soares
Australian Endodontic Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of erbium yttrium aluminium garnet laser dentin conditioning on dental pulp stem cells viability
Aryan Jafari, Mehdi Vatanpour, Nooshin Barikrow, Pouyan Razavi, Sohrab Tour Savadkouhi
Heliyon.2024; 10(5): e26954. CrossRef - Comparison of the effect of NaOCL, curcumin, and EDTA on differentiation, proliferation, and adhesion of dental pulp stem cells
Vahid Zand, Amin Salem Milani, Carolyn Primus, Marzie Aghazade, Hadi Mokhtari, Sabete Bagheri Sabzevar, Pardis Tehranchi
Journal of Oral Biology and Craniofacial Research.2023; 13(2): 347. CrossRef - Differential Effects of Extracellular Matrix Glycoproteins Fibronectin and Laminin-5 on Dental Pulp Stem Cell Phenotypes and Responsiveness
Hyungbin Lee, Allen Bae, John Kim, Karl Kingsley
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2023; 14(2): 91. CrossRef - Assessment of the Influence of Various Concentrations of Sodium Hypochlorite on Stem Cell Derived From Human Exfoliated Deciduous Teeth (SHED) Proliferation and Differentiation
Viral Maru, Ashwini KB, Manisha Madkaikar, R K Sarada Devi, Ashita Gada, Salil Bapat
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of sodium hypochlorite and ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on proliferation, osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation, and mechanosensitive gene expression of human dental pulp stem cells
Yuejun Li, Changlong Jin, Shouliang Zhao, Han Xie
Tissue and Cell.2022; 79: 101955. CrossRef - Influence of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid on regenerative endodontics: A systematic review
Alexandre H. dos Reis‐Prado, Lucas G. Abreu, Rogéria R. Fagundes, Sabrina de C. Oliveira, Marco C. Bottino, Antônio P. Ribeiro‐Sobrinho, Francine Benetti
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(6): 579. CrossRef - An in-vitro Comparative Evaluation of Quantitative Release of Transforming Growth Factor β-1 from Dentin upon the Action of Endodontic Irrigants, Medicaments, Ultrasonic Activation, and Low-Level Laser Irradiation
Anilkumar Akhila, V. P. Prabath Singh, Kerala R. Varma, Senthil V. Vasudevan, V. Sukhithasri, Salu Sasikumar
Amrita Journal of Medicine.2021; 17(2): 34. CrossRef - Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma-Conditioned Root Dentin Promotes Attraction and Attachment of Primary Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells in Real-Time Ex Vivo
Yeon-Jee Yoo, Min-Ji Kang, Hiran Perinpanayagam, Joo-Cheol Park, Seung-Ho Baek, Kee-Yeon Kum
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(15): 6836. CrossRef - The Effects of Intracanal Irrigants and Medicaments on Dental-Derived Stem Cells Fate in Regenerative Endodontics: An update
Sara Ayoub, Ali Cheayto, Sanaa Bassam, Mehdi Najar, Antoine Berbéri, Mohammad Fayyad-Kazan
Stem Cell Reviews and Reports.2020; 16(4): 650. CrossRef - An Immunofluorescence Study to Analyze Wound Healing Outcomes of Regenerative Endodontics in an Immature Premolar with Chronic Apical Abscess
Jeen Nee Lui, Wen Yi Lim, Domenico Ricucci
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(5): 627. CrossRef - Dynamic Irrigation Promotes Apical Papilla Cell Attachment in an Ex Vivo Immature Root Canal Model
Sanupong Prompreecha, Thanapat Sastraruji, Phumisak Louwakul, Tanida Srisuwan
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(5): 744. CrossRef - Odontoblast-like differentiation and mineral formation of pulpsphere derived cells on human root canal dentin in vitro
Jörg Neunzehn, Sandra Pötschke, Christian Hannig, Hans-Peter Wiesmann, Marie-Theres Weber
Head & Face Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Epigallocatechin Gallate, an Antibacterial Cross-linking Agent, on Proliferation and Differentiation of Human Dental Pulp Cells Cultured in Collagen Scaffolds
Young-Sun Kwon, Hee-Jin Kim, Yun-Chan Hwang, Vinicius Rosa, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(2): 289. CrossRef
- Effect of Intracanal Medications on the Viability of Human Periodontal Ligament‐Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- 1,583 View
- 6 Download
- 14 Crossref

-
Morphological evaluation during
in vitro chondrogenesis of dental pulp stromal cells - Choo-Ryung Chung, Ha-Na Kim, Yeul Park, Min-Jeong Kim, Young-Ju Oh, Su-Jung Shin, Yoon-Jeong Choi, Kyung-Ho Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(1):34-40. Published online March 2, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.1.34
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The aim was to confirm the stem cell-like properties of the dental pulp stromal cells and to evaluate the morphologic changes during
in vitro chondrogenesis.Materials and Methods Stromal cells were outgrown from the dental pulp tissue of the premolars. Surface markers were investigated and cell proliferation rate was compared to other mesenchymal stem cells. Multipotency of the pulp cells was confirmed by inducing osteogenesis, adipogenesis and chondrogenesis. The morphologic changes in the chondrogenic pellet during the 21 day of induction were evaluated under light microscope and transmission electron microscope. TUNEL assay was used to evaluate apoptosis within the chondrogenic pellets.
Results Pulp cells were CD90, 105 positive and CD31, 34 negative. They showed similar proliferation rate to other stem cells. Pulp cells differentiated to osteogenic, adipogenic and chondrogenic tissues. During chondrogenesis, 3-dimensional pellet was created with multi-layers, hypertrophic chondrocyte-like cells and cartilage-like extracellular matrix. However, cell morphology became irregular and apoptotic cells were increased after 7 day of chondrogenic induction.
Conclusions Pulp cells indicated mesenchymal stem cell-like characteristics. During the
in vitro chondrogenesis, cellular activity was superior during the earlier phase (within 7 day) of differentiation.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Local myogenic pulp‐derived cell injection enhances craniofacial muscle regeneration in vivo
J. E. Jung, M. J. Song, S. Shin, Y. J. Choi, K. H. Kim, C. J. Chung
Orthodontics & Craniofacial Research.2017; 20(1): 35. CrossRef - Immune Tolerance of Human Dental Pulp-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mediated by CD4+CD25+ FoxP3+ Regulatory T-Cells and Induced by TGF-β1 and IL-10
Jong Won Hong, Jung Hyun Lim, Chooryung J. Chung, Tae Jo Kang, Tae Yeon Kim, Young Seok Kim, Tae Suk Roh, Dae Hyun Lew
Yonsei Medical Journal.2017; 58(5): 1031. CrossRef - In vitrocharacterization of human dental pulp stem cells isolated by three different methods
Ji-Hyun Jang, Hyeon-Woo Lee, Kyu Min Cho, Hee-Woong Shin, Mo Kwan Kang, Sang Hyuk Park, Euiseong Kim
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(4): 283. CrossRef - Effects of two fast-setting calcium-silicate cements on cell viability and angiogenic factor release in human pulp-derived cells
Chooryung J. Chung, Euiseong Kim, Minju Song, Jeong-Won Park, Su-Jung Shin
Odontology.2016; 104(2): 143. CrossRef - A Simplified Method for the Aspiration of Bone Marrow from Patients Undergoing Hip and Knee Joint Replacement for Isolating Mesenchymal Stem Cells andIn VitroChondrogenesis
Subhash C. Juneja, Sowmya Viswanathan, Milan Ganguly, Christian Veillette
Bone Marrow Research.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Local Injection of Pulp Cells Enhances Wound Healing during the Initial Proliferative Phase through the Stimulation of Host Angiogenesis
Hyungjoo Yang, Sujung Shin, Jhiweon Ahn, YoonJeong Choi, Kyung-Ho Kim, Chooryung J. Chung
Journal of Endodontics.2013; 39(6): 788. CrossRef
- Local myogenic pulp‐derived cell injection enhances craniofacial muscle regeneration in vivo
- 1,039 View
- 1 Download
- 6 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


