Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of moisture and pH on setting time and microhardness of three premixed calcium silicate-based root canal sealers: an in vitro experimental study
- Sooyoun Kim
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e41. Published online November 28, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e41
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The study aimed to investigate how environmental conditions impact the setting time and microhardness of premixed calcium silicate-based sealers.
Methods
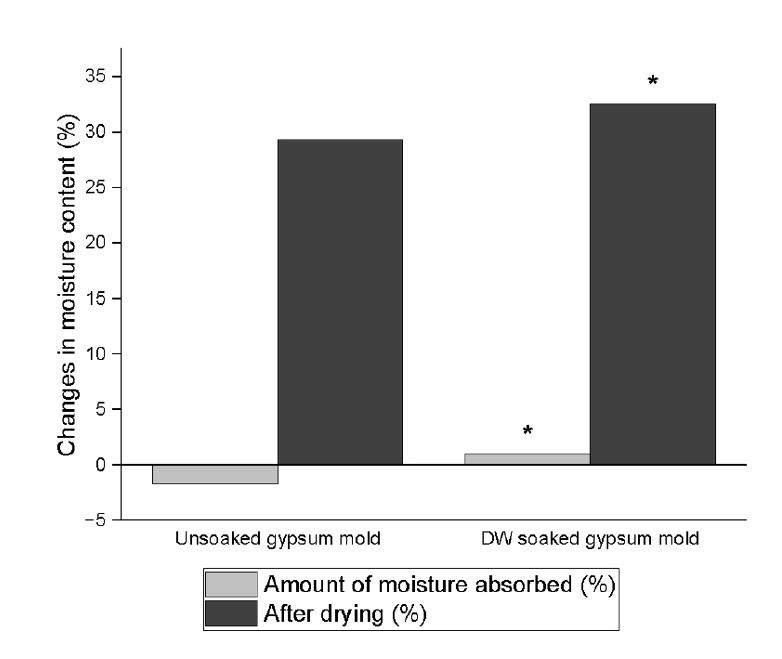
The setting time and microhardness of three sealers (Endoseal MTA [MARUCHI], One-Fil [MEDICLUS], and Well-Root ST [VERICOM]) were evaluated under four environmental conditions: unsoaked, distilled water-soaked, phosphate-buffered saline-soaked, and pH 5-soaked gypsum molds (n = 12/group/condition). The setting time was measured with Gilmore needles, and microhardness was assessed using a Vickers tester after 3 days. Welch’s analysis of variance and Games-Howell post hoc tests were used for statistical analysis.
Results
The sealer type and environmental conditions significantly influenced setting time and microhardness (p < 0.001). The initial and final setting times were the shortest in the unsoaked samples. For Endoseal MTA and One-Fil, the unsoaked condition exhibited significantly shorter setting times than the soaked conditions. Well-Root ST exhibited significantly longer setting times in acidic conditions. Surface microhardness was highest in the unsoaked group (p < 0.001). Among the soaked groups, the phosphate-buffered saline-soaked group had the lowest hardness for Endoseal MTA, whereas the pH 5-soaked group exhibited the lowest hardness for One-Fil and Well-Root ST. Endoseal MTA consistently demonstrated a lower microhardness than the other sealers (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
Moisture, pH, and solution chemistry influenced the setting time and microhardness of premixed calcium silicate sealers. Although acidic conditions generally prolong the setting time and reduce hardness, the effects vary based on the sealers used and the setting environment.
- 722 View
- 51 Download

- Physicochemical properties of a calcium aluminate cement containing nanoparticles of zinc oxide
- Amanda Freitas da Rosa, Thuany Schmitz Amaral, Maria Eduarda Paz Dotto, Taynara Santos Goulart, Hebert Luís Rossetto, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e3. Published online December 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e3
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study evaluated the effect of different nanoparticulated zinc oxide (nano-ZnO) and conventional-ZnO ratios on the physicochemical properties of calcium aluminate cement (CAC).
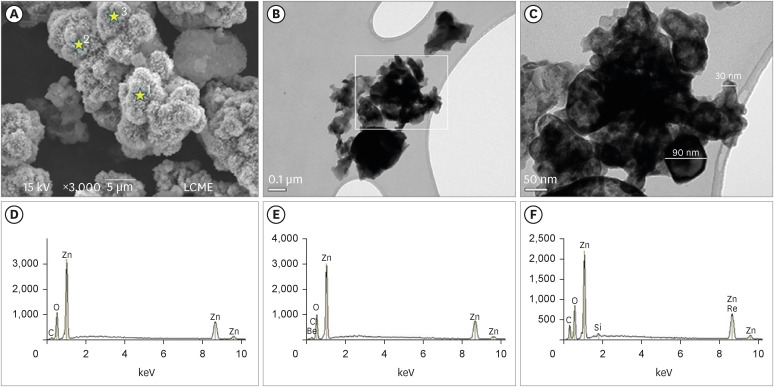
Materials and Methods The conventional-ZnO and nano-ZnO were added to the cement powder in the following proportions: G1 (20% conventional-ZnO), G2 (15% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO), G3 (12% conventional-ZnO + 3% nano-ZnO) and G4 (10% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO). The radiopacity (Rad), setting time (Set), dimensional change (Dc), solubility (Sol), compressive strength (Cst), and pH were evaluated. The nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO were also assessed using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Radiopacity data were analyzed by the 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni tests (
p < 0.05). The data of the other properties were analyzed by the ANOVA, Tukey, and Fisher tests (p < 0.05).Results The nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO powders presented particles with few impurities and nanometric and micrometric sizes, respectively. G1 had the highest Rad mean value (
p < 0.05). When compared to G1, groups containing nano-ZnO had a significant reduction in the Set (p < 0.05) and lower values of Dc at 24 hours (p < 0.05). The Cst was higher for G4, with a significant difference for the other groups (p < 0.05). The Sol did not present significant differences among groups (p > 0.05).Conclusions The addition of nano-ZnO to CAC improved its dimensional change, setting time, and compressive strength, which may be promising for the clinical performance of this cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Calcium aluminate cement: a study on the effect of additives for dental applications
Sara Ghorbani, Rahim Naghizadeh, Ebrahim Ghasemi, Hamidreza Rezaie
Advances in Cement Research.2025; 37(4): 269. CrossRef - Experimental Study on Cement-Based Materials Modified by Nano-Zinc Oxide and Nano-Zirconia Based on Response Surface Optimization Design
Hongyin Hu, Fufei Wu, Jiao Chen, Shuangshuang Guan, Peng Qu, Hongqin Zhang, Yuyi Chen, Zirun Xu, Chuanteng Huang, Shuang Pu
Materials.2025; 18(7): 1515. CrossRef - Radiographic, mechanical, and chemical properties of mineral trioxide aggregate from nanosilica and clam shell calcium carbonate
Leny Yuliatun, Muhammad Adly Rahandi Lubis, Muhammad Khaliim Jati Kusala, Lia Destiarti, Ratna Betriani, Jolang Budiarta, Mariyam Mariyam
Polyhedron.2025; 278: 117590. CrossRef - Application of Calcium Aluminate-Based Materials for Direct Pulp Capping – In Vivo Study
Ognjenka Janković, Smiljana Paraš, Tijana Adamović, Ljiljana Tadić Latinović, Radmila Arbutina, Igor Đukić, Saša Marin, Marko Bulajić, Karolina Vukoje, Vukoman Jokanović, Verica Pavlić
Acta Veterinaria.2025; 75(2): 212. CrossRef - Nanotechnology for calcium aluminate cement: thematic analysis
Lapyote Prasittisopin
REVIEWS ON ADVANCED MATERIALS SCIENCE.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Calcium aluminate cement: a study on the effect of additives for dental applications
- 1,892 View
- 45 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


