Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Effect of the restorative technique on load-bearing capacity, cusp deflection, and stress distribution of endodontically-treated premolars with MOD restoration
- Daniel Maranha da Rocha, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Pietro Ausiello, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Milena Cerqueira da Rocha, Rebeca Di Nicoló, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
- Restor Dent Endod 2019;44(3):e33. Published online August 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2019.44.e33
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
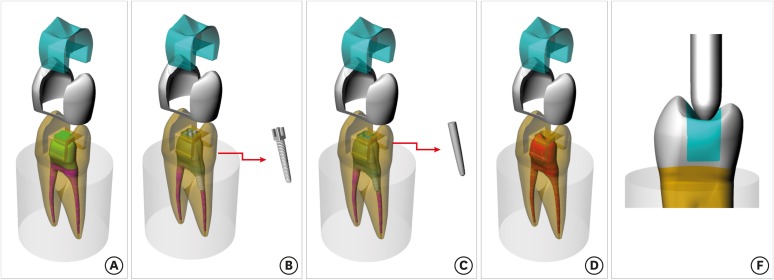
ePub Objectives To evaluate the influence of the restorative technique on the mechanical response of endodontically-treated upper premolars with mesio-occluso-distal (MOD) cavity.
Materials and Methods Forty-eight premolars received MOD preparation (4 groups,
n = 12) with different restorative techniques: glass ionomer cement + composite resin (the GIC group), a metallic post + composite resin (the MP group), a fiberglass post + composite resin (the FGP group), or no endodontic treatment + restoration with composite resin (the CR group). Cusp strain and load-bearing capacity were evaluated. One-way analysis of variance and the Tukey test were used with α = 5%. Finite element analysis (FEA) was used to calculate displacement and tensile stress for the teeth and restorations.Results MP showed the highest cusp (
p = 0.027) deflection (24.28 ± 5.09 µm/µm), followed by FGP (20.61 ± 5.05 µm/µm), CR (17.72 ± 6.32 µm/µm), and GIC (17.62 ± 7.00 µm/µm). For load-bearing, CR (38.89 ± 3.24 N) showed the highest, followed by GIC (37.51 ± 6.69 N), FGP (29.80 ± 10.03 N), and MP (18.41 ± 4.15 N) (p = 0.001) value. FEA showed similar behavior in the restorations in all groups, while MP showed the highest stress concentration in the tooth and post.Conclusions There is no mechanical advantage in using intraradicular posts for endodontically-treated premolars requiring MOD restoration. Filling the pulp chamber with GIC and restoring the tooth with only CR showed the most promising results for cusp deflection, failure load, and stress distribution.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- How to adaptively balance ‘classic’ or ‘conservative’ approaches in tooth defect management: a 3D-finite element analysis study
Jiani Xu, Xu Liang, Lili Hu, Chen Sun, Zhipeng Zhang, Jiawei Yang, Jie Wang
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Inkjet-printed strain gauge sensors: Materials, manufacturing, and emerging applications
Lara Abdel Salam, Samir Mustapha, Alexandra Mikhael, Nisrine Bakri, Sahera Saleh, Massoud L. Khraiche
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical.2025; 394: 116934. CrossRef - Influence of endodontic access cavity design on mechanical properties of a first mandibular premolar tooth: a finite element analysis study
Taha Özyürek, Gülşah Uslu, Burçin Arıcan, Mustafa Gündoğar, Mohammad Hossein Nekoofar, Paul Michael Howell Dummer
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the Effect of Different Cavity Designs and Temporary Restoration Materials on the Fracture Resistance of Upper Premolars, Undergone Re-treatment: An In-Vitro Study
Parnian Alavinejad, Mohammad Yazdizadeh, Ali Mombeinipour, Ebrahim Karimzadeh
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences.2024; 94(3): 677. CrossRef - Fracture resistance and failure mode of endodontically treated premolars reconstructed by different preparation approaches: Cervical margin relocation and crown lengthening with complete and partial ferrule with three different post and core systems
Mehran Falahchai, Naghmeh Musapoor, Soroosh Mokhtari, Yasamin Babaee Hemmati, Hamid Neshandar Asli
Journal of Prosthodontics.2024; 33(8): 774. CrossRef - Comparison of the stress distribution in base materials and thicknesses in composite resin restorations
Min-Kwan Jung, Mi-Jeong Jeon, Jae-Hoon Kim, Sung-Ae Son, Jeong-Kil Park, Deog-Gyu Seo
Heliyon.2024; 10(3): e25040. CrossRef -
Fracture resistance and failure pattern of endodontically treated maxillary premolars restored with transfixed glass fiber post: an
in vitro
and finite element analysis
Saleem Abdulrab, Greta Geerts, Ganesh Thiagarajan
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 27(4): 419. CrossRef - Influence of size-anatomy of the maxillary central incisor on the biomechanical performance of post-and-core restoration with different ferrule heights
Domingo Santos Pantaleón, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Franklin García-Godoy
The Journal of Advanced Prosthodontics.2024; 16(2): 77. CrossRef - Influence of internal angle and shape of the lining on residual stress of Class II molar restorations
Qianqian Zuo, Annan Li, Haidong Teng, Zhan Liu
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 27(5): 680. CrossRef - Evaluation of stress distribution in coronal base and restorative materials: A narrative review of finite element analysis studies
Yelda Polat, İzzet Yavuz
Conservative Dentistry Journal.2024; 14(2): 47. CrossRef - The influence of horizontal glass fiber posts on fracture strength and fracture pattern of endodontically treated teeth: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of in vitro studies
Saleem Abdulrab, Greta Geerts, Sadeq Ali Al‐Maweri, Mohammed Nasser Alhajj, Hatem Alhadainy, Raidan Ba‐Hattab
Journal of Prosthodontics.2023; 32(6): 469. CrossRef - Stress distribution of a novel bundle fiber post with curved roots and oval canals
Deniz Yanık, Nurullah Turker
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2022; 34(3): 550. CrossRef - The Effect of Endodontic Treatment and Thermocycling on Cuspal Deflection of Teeth Restored with Different Direct Resin Composites
Cansu Atalay, Ayse Ruya Yazici, Aynur Sidika Horuztepe, Emre Nagas
Conservative Dentistry and Endodontic Journal.2022; 6(2): 38. CrossRef - The use of different adhesive filling material and mass combinations to restore class II cavities under loading and shrinkage effects: a 3D-FEA
P. Ausiello, S. Ciaramella, A. De Benedictis, A. Lanzotti, J. P. M. Tribst, D. C. Watts
Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical Engineering.2021; 24(5): 485. CrossRef - Biomechanical Analysis of a Custom-Made Mouthguard Reinforced With Different Elastic Modulus Laminates During a Simulated Maxillofacial Trauma
João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Pietro Ausiello, Arianna De Benedictis, Marco Antonio Bottino, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges
Craniomaxillofacial Trauma & Reconstruction.2021; 14(3): 254. CrossRef - Mechanical Assessment of Glass Ionomer Cements Incorporated with Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Dental Applications
Manuela Spinola, Amanda Maria Oliveira Dal Piva, Patrícia Uchôas Barbosa, Carlos Rocha Gomes Torres, Eduardo Bresciani
Oral.2021; 1(3): 190. CrossRef - Stress Concentration of Endodontically Treated Molars Restored with Transfixed Glass Fiber Post: 3D-Finite Element Analysis
Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Manassés Tercio Vieira Grangeiro, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Renata Marques de Melo, Kusai Baroudi, Laís Regiane Silva-Concilio, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Materials.2021; 14(15): 4249. CrossRef - Computer Aided Design Modelling and Finite Element Analysis of Premolar Proximal Cavities Restored with Resin Composites
Amanda Guedes Nogueira Matuda, Marcos Paulo Motta Silveira, Guilherme Schmitt de Andrade, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, João Paulo Mendes Tribst, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Luca Testarelli, Gabriella Mosca, Pietro Ausiello
Materials.2021; 14(9): 2366. CrossRef - Effect of Shrinking and No Shrinking Dentine and Enamel Replacing Materials in Posterior Restoration: A 3D-FEA Study
Pietro Ausiello, Amanda Maria de Oliveira Dal Piva, Alexandre Luiz Souto Borges, Antonio Lanzotti, Fausto Zamparini, Ettore Epifania, João Paulo Mendes Tribst
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(5): 2215. CrossRef - Effect of Fiber-Reinforced Composite and Elastic Post on the Fracture Resistance of Premolars with Root Canal Treatment—An In Vitro Pilot Study
Jesús Mena-Álvarez, Rubén Agustín-Panadero, Alvaro Zubizarreta-Macho
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(21): 7616. CrossRef
- How to adaptively balance ‘classic’ or ‘conservative’ approaches in tooth defect management: a 3D-finite element analysis study
- 2,232 View
- 23 Download
- 20 Crossref

- Influence of cavity size and restoration methods on the cusp deflection in composite restoration
- Mi-Ra Lee, In-Bog Lee, Chang-In Seok, Sang-Tag Lee, Chung-Moon Um
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2004;29(6):532-540. Published online November 30, 2004
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2004.29.6.532
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The aim of this study was to measure the cusp deflection during composite restoration for MOD cavity in premolar and to examine the influence of cavity dimension, C-factor and restoration method on the cusp deflection.
Thirty extracted maxillary premolar were prepared to four different sizes of MOD cavity and divided into six groups. The width and depth of the cavity were as follows. Group 1; 1.5 × 1 mm, Group 2; 1.5 × 2 mm, Group 3; 3 × 1 mm, and Group 4-6; 3 × 2 mm respectively. Group 1-4 were restored using bulk filling method with Z-250 composite. However, Group 5 was restored incrementally, and Group 6 was restored with an indirect resin inlay.
The cusp deflection was recorded at the buccal and lingual cusp tips using LVDT probe for 10,000 seconds. The measured cusp deflections were compared between groups, and the relationship between the cube of the length of cavity wall/the cube of the thickness of cavity wall (L3 / T3), C-factor and cusp deflection or %flexure (100 × cuspal deflection / cavity width) was analyzed.
The cusp deflection of Group 1-4 were 12.1 µm, 17.2 µm, 16.2 µm and 26.4 µm respectively. The C-factor was related to the %flexure rather than the cusp deflection. There was a strong positive correlationship between the L3 / T3 and the cusp deflection. The cusp deflection of Group 5 and 6 were 17.4 µm and 17.9 µm respectively, which are much lower value than that of Group 4.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of Premolar Cuspal Deflection in Bulk or in Incremental Composite Restoration Methods
ME Kim, SH Park
Operative Dentistry.2011; 36(3): 326. CrossRef
- Comparison of Premolar Cuspal Deflection in Bulk or in Incremental Composite Restoration Methods
- 1,306 View
- 5 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


