Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
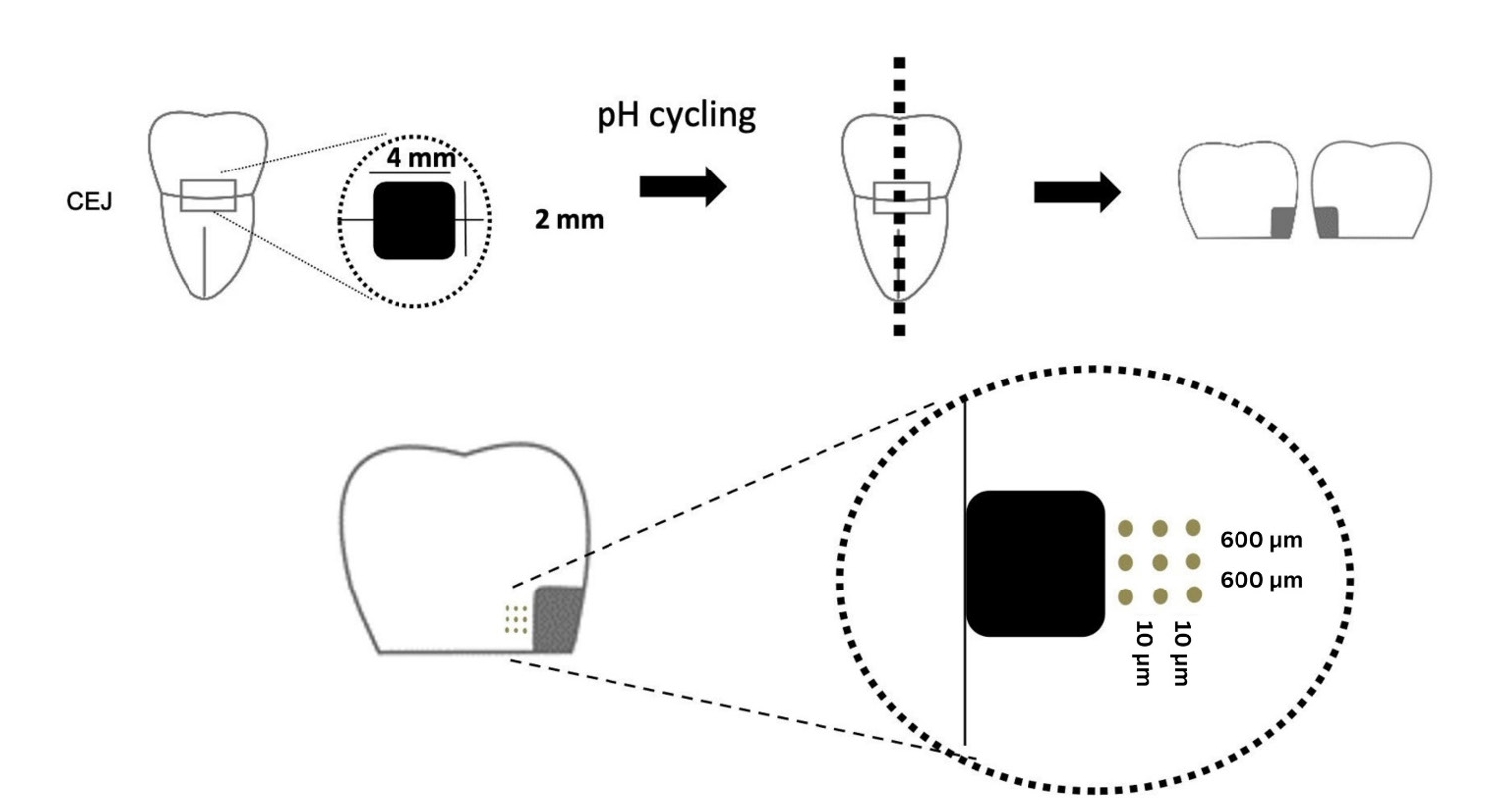
- Comparison of remineralization in caries-affected dentin using calcium silicate, glass ionomer cement, and resin-modified glass ionomer cement: an in vitro study
- Kwanchanok Youcharoen, Onwara Akkaratham, Papichaya Intajak, Pipop Saikaew, Sirichan Chiaraputt
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(4):e37. Published online November 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e37
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study evaluated the ability of calcium silicate cement (CSC) as a remineralizing agent compared with conventional glass ionomer cement (GIC) and resin-modified GIC (RMGIC) to remineralize artificial caries-affected dentin.
Methods
Twenty-five class V cavities were prepared on extracted human third molars. Twenty teeth underwent artificial caries induction. The remaining five teeth with sound dentin serve as the positive control. The twenty demineralized teeth were subdivided into four groups (n = 5): carious dentin without restoration (negative control [NC]), carious dentin restored with CSC (Biodentine, Septodont), carious dentin restored with GI (Fuji IX, GC Corporation), and carious dentin restored with RMGIC (Fuji II LC, GC Corporation). Following restoration, the specimens were stored in artificial saliva for 7 days. The elastic modulus was evaluated by a nanoindentation test. The mineral composition was analyzed by scanning electron microscopy-energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDX), and the mineral composition at the dentin-material interface.
Results
CSC had a higher modulus of elasticity compared to GI, RMGI, and NC groups (p < 0.05). Higher calcium and phosphorus content was observed under CSC restorations, as indicated by SEM-EDX examination, which may lead to better remineralization.
Conclusions
Compared to GI and RMGI, CSC showed the best remineralization and mechanical reinforcement in caries-affected dentin, indicating CSC for use in minimally invasive restorative dentistry.
- 1,805 View
- 213 Download

- Elemental analysis of caries-affected root dentin and artificially demineralized dentin
- Young-Hye Sung, Ho-Hyun Son, Keewook Yi, Juhea Chang
- Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):255-261. Published online August 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.255
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to analyze the mineral composition of naturally- and artificially-produced caries-affected root dentin and to determine the elemental incorporation of resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) into the demineralized dentin.
Materials and Methods Box-formed cavities were prepared on buccal and lingual root surfaces of sound human premolars (
n = 15). One cavity was exposed to a microbial caries model using a strain of Streptococcus mutans. The other cavity was subjected to a chemical model under pH cycling. Premolars and molars with root surface caries were used as a natural caries model (n = 15). Outer caries lesion was removed using a carbide bur and a hand excavator under a dyeing technique and restored with RMGI (FujiII LC, GC Corp.). The weight percentages of calcium (Ca), phosphate (P), and strontium (Sr) and the widths of demineralized dentin were determined by electron probe microanalysis and compared among the groups using ANOVA and Tukey test (p < 0.05).Results There was a pattern of demineralization in all models, as visualized with scanning electron microscopy. Artificial models induced greater losses of Ca and P and larger widths of demineralized dentin than did a natural caries model (
p < 0.05). Sr was diffused into the demineralized dentin layer from RMGI.Conclusions Both microbial and chemical caries models produced similar patterns of mineral composition on the caries-affected dentin. However, the artificial lesions had a relatively larger extent of demineralization than did the natural lesions. RMGI was incorporated into the superficial layer of the caries-affected dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of Fluoride Varnish Versus Conventional Glass Ionomer in Preventing Occlusal Caries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abdullah Dh Alharbi, Masoud Almasoud, Fahad Alfadhli, Abdullah N Alharbi, Talal Aldhufairi, Rahaf Kh Alrashidi, Aisha Alameer, Abdulsalam Alenezi, Yousef Alqattan , Ahmed Abdelaziz
Cureus.2026;[Epub] CrossRef - 3D Multi-modal Imaging of demineralised dentine using combined synchrotron µ-XRD-CT and STXM-CT
Nathanael Leung, Robert A. Harper, Bin Zhu, Stuart A. Bartlett, Konstantin Ignatyev, Richard M. Shelton, Gabriel Landini, Tan Sui
Journal of Structural Biology.2025; 217(2): 108208. CrossRef - A dynamic microcosm biofilm model for root carious-like lesion development: analysis of demineralization and microbiological characterization
Tamires Timm Maske, Glenda Ávila Marques, Bruna Dalongaro Fritsch, Bruna Moraes Kremer, Maximiliano Sérgio Cenci, Pabulo Henrique Rampelotto, Rodrigo Alex Arthur
Biofouling.2025; 41(5): 536. CrossRef - Bond strength durability of three bioactive restorative materials to silver diamine fluoride treated artificially demineralized dentine
Mostafa A. Abdelshafi, Hanan A.N. Soliman, Dina Abdelaziz
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Frontiers of Global Research Trend on Root Caries: A Bibliometric Analysis
Grace Yuchan Xu, Irene Shuping Zhao, Christie Ying Kei Lung, Iris Xiaoxue Yin, Edward Chin Man Lo, Chun Hung Chu
International Dental Journal.2024; 74(6): 1197. CrossRef - Effects of NaF versus SDF treatment on microhardness of artificial radiation caries at cervical and root areas
Pipop SAIKAEW, Karis KATEKOVIT, Anocha BURANARACHADA, Nattapat SAIMALA, Anussara PRAYONGRAT, Pornpoj FUANGTHARNTHIP
Dental Materials Journal.2024; 43(4): 591. CrossRef - Degradable polycaprolactone/buffer composites as pH regulating carrier materials for drug delivery and 3D printed biomaterials
Therese Schüler, Celine Guder, Franziska Alt, Katrin Lorenz, Torsten Sterzenbach, Christian Hannig, Hans-Peter Wiesmann, Benjamin Kruppke
Materialia.2024; 34: 102087. CrossRef - The Effect of Oral Care Foams and a Spray on Salivary pH Changes after Exposure to Acidic Beverages in Young Adults
Maria Polyakova, Anna Egiazaryan, Vladlena Doroshina, Alexandr Zaytsev, Alexey Malashin, Ksenia Babina, Nina Novozhilova
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(4): 93. CrossRef - In Vitro Models Used in the Formation of Root Caries Lesions—A Review of the Literature
Zaid Dohan, Lara T. Friedlander, Paul R. Cooper, Kai-Chun Li, Jithendra T. Ratnayake, May L. Mei
Dentistry Journal.2023; 11(12): 269. CrossRef - Yttrium Trifluoride as a Marker of Infiltration Rate of Decalcified Root Cementum: An In Vitro Study
Anna Nowak-Wachol, Anna Korytkowska-Wałach, Bartosz Chmiela, Kacper Wachol, Maciej Łopaciński, Magdalena Wyszyńska, Yousuf Al-Dulaimi, Małgorzata Skucha-Nowak
Polymers.2022; 14(4): 780. CrossRef - Effect of fluoride, chlorhexidine or Nd:YAG on the progression of root dentin demineralization after removal of the demineralized organic matrix
Andrea Maselli, Tânia Mara da Silva, Lucélia Lemes Gonçalves, Aline Silva Braga, Eduardo Bresciani, Ana Carolina Magalhães, Sérgio Eduardo de Paiva Gonçalves
Journal of Applied Oral Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of ionizing radiation and cariogenic biofilm challenge on root-dentin caries
Camila de Carvalho Almança Lopes, Renata Borges Rodrigues, Maximiliano Sérgio Cenci, Juliana Lays Stolfo Uehara, Tamires Timm Maske, Pedro Henrique Justino Oliveira Limirio, Priscilla Barbosa Ferreira Soares, Veridiana Resende Novais
Clinical Oral Investigations.2021; 25(6): 4059. CrossRef - Silver diamine fluoride treatment of active root caries lesions in older adults: A case series
Chelsea Mitchell, Andrew J Gross, Peter Milgrom, Lloyd Mancl, David B Prince
Journal of Dentistry.2021; 105: 103561. CrossRef - A Hydrogel Drink With High Fructose Content Generates Higher Exogenous Carbohydrate Oxidation and a Reduced Drop in Dental Biofilm pH Compared to Two Other, Commercially Available, Carbohydrate Sports Drinks
Stefan Pettersson, Martin Ahnoff, Fredrik Edin, Peter Lingström, Charlotte Simark Mattsson, Ulrika Andersson-Hall
Frontiers in Nutrition.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effectiveness of Fluoride Varnish Versus Conventional Glass Ionomer in Preventing Occlusal Caries: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- 1,801 View
- 10 Download
- 14 Crossref

- Microtensile bond strength of all-in-one adhesive to caries-affected dentin
- Ji-Deok Moon, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2005;30(1):49-57. Published online January 31, 2005
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2005.30.1.049
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effect of multiple application of all-in-one dentin adhesive system on microtensile bond strength to caries-affected dentin.
Twenty one extracted human molars with occlusal caries extending into mid-dentin were prepared by grinding the occlusal surface flat. The carious lesions were excavated with the aid of caries detector dye. The following adhesives were applied to caries-affected dentin according to manufacturer's directions; Scotchbond™ Multi-Purpose in SM group, Adper Prompt L-Pop™ 1 coat in LP1 group, 2 coats in LP2 group, 3 coats in LP3 group, Xeno® III 1 coat in XN1 group, 2 coats in XN2 group, and 3 coats in XN3 group. After application of the adhesives, a cylinder of resin-based composite was built up on the occlusal surface. Each tooth was sectioned vertically to obtain the 1 × 1 mm2 sticks. The microtensile bond strength was determined. Each specimen was observed under SEM to examine the failure mode. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA.
The results of this study were as follows;
1. The microtensile bond strength values were; SM (14.38 ± 2.01 MPa), LP1 (9.15 ± 1.81 MPa), LP2 (14.08 ± 1.75 MPa), LP3 (14.06 ± 1.45 MPa), XN1 (13.65 ± 1.95 MPa), XN2 (13.98 ± 1.60 MPa), XN3 (13.88 ± 1.66 MPa). LP1 was significantly lower than the other groups in bond strength (p < 0.05). All groups except LP1 were not significantly different in bond strength (p > 0.05).
2. In LP1, there were a higher number of specimens showing adhesive failure. Most specimens of all groups except LP1 showed mixed failure.
- 994 View
- 6 Download


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


