Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
- Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
- Restor Dent Endod 2018;43(2):e17. Published online April 13, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2018.43.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
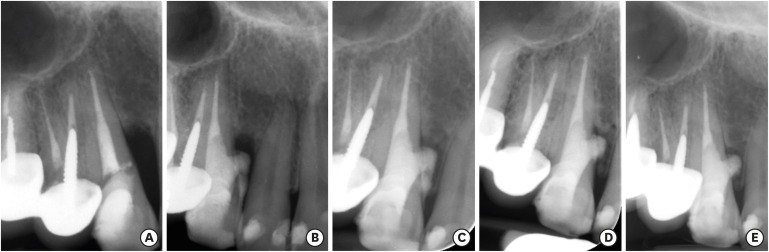
ePub Iatrogenic perforations negatively impact the outcome of endodontic treatments. Studies on prognostic factors showed that perforations in the coronal third of the root with periodontal pocket formation have an unfavorable prognosis. A 36-year-old female was referred for endodontic evaluation of tooth #13 with a history of an iatrogenic perforation, happened 3 years ago. There was a sinus tract associated with perforation, 10 mm probing on the mesial and mesio-palatal, bleeding on probing, radiolucent lesion adjacent to the perforation and complete resorption of the interdental bone between teeth #13 and #12. After the treatment options were discussed, she chose to save the tooth. The tooth was accessed under rubber dam isolation, the perforation site was cleaned and disinfected using 0.5% sodium hypochlorite and sealed with calcium-enriched mixture cement. Eighteen months after treatment the tooth was functional and asymptomatic. The probing depths were normal without bleeding on probing. Radiographically, the interdental crestal bone formed between teeth #13 and #12. Despite all negative prognostic factors in this case (
i.e. , perforations in the coronal third, pocket formation, and radiolucent lesion), healing was unexpectedly achieved via non-surgical repair of the perforation. Further research on biological aspects of healing in the periodontium following iatrogenic perforations are recommended.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
Mana Mowji, Motahareh Khosrojerdi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management of Furcation Defects Using Cervical Sealing With Calcium–Silicate Cements: A Clinical Case Series
Saeed Asgary, Shamimul Hasan
Case Reports in Medicine.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonsurgical Management of Simultaneous Double Lateral Root Perforations in Adjacent Teeth Using CBCT and MTA: A Case Report
Beyhan Başkan, Hatice Kübra Başkan, Beyza Güler, Ricardo Faria Ribeiro
Case Reports in Dentistry.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - External Cervical Resorption: A Volumetric Analysis on Evolution of Defects over Time
Ali Nosrat, Omid Dianat, Prashant Verma, Martin D. Levin, Jeffery B. Price, Anita Aminoshariae, Fabio Antonio Piola Rizzante
Journal of Endodontics.2023; 49(1): 36. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of mineral trioxide aggregate, endoseal, and biodentine in furcation perforation repair
Udita Khare Baralay, Srinidhi Surya Raghavendra
Endodontology.2022; 34(1): 22. CrossRef - Calcium Silicate Cements Application in Lateral Root Perforation Repair: A Case Report with 16-Month Follow-Up
Juan G. Robledo, Pablo A. Rodríguez
Open Journal of Stomatology.2021; 11(08): 317. CrossRef - Vital Pulp Therapy as a Conservative Approach for Management of Invasive Cervical Root Resorption: A Case Series
Saeed Asgary, Mahdieh Nourzadeh, Prashant Verma, M. Lamar Hicks, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(9): 1161. CrossRef
- Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
- 2,915 View
- 14 Download
- 8 Crossref

- Surgical management of a failed internal root resorption treatment: a histological and clinical report
- Saeed Asgary, Mohammad Jafar Eghbal, Leili Mehrdad, Sanam Kheirieh, Ali Nosrat
- Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):137-142. Published online March 21, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.137
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This article presents the successful surgical management of a failed mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA) orthograde obturation of a tooth with a history of impact trauma and perforated internal root resorption. A symptomatic maxillary lateral incisor with a history of perforation due to internal root resorption and nonsurgical repair using MTA was referred. Unintentional overfill of the defect with MTA had occurred 4 yr before the initial visit. The excess MTA had since disappeared, and a radiolucent lesion adjacent to the perforation site was evident radiographically. Surgical endodontic retreatment was performed using calcium enriched mixture (CEM) cement as a repair material. Histological examination of the lesion revealed granulation tissue with chronic inflammation, and small fragments of MTA encapsulated within fibroconnective tissue. At the one and two year follow up exams, all signs and symptoms of disease had resolved and the tooth was functional. Complete radiographic healing of the lesion was observed two years after the initial visit. This case report illustrates how the selection of an appropriate approach to treatment of a perforation can affect the long term prognosis of a tooth. In addition, extrusion of MTA into a periradicular lesion should be avoided.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
Mana Mowji, Motahareh Khosrojerdi
Clinical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Endodontic management of internal replacement resorption of two maxillary central incisors with the aid of cone-beam computed tomography as the diagnostic tool: a case report and review of literature
Fatemeh Eskandari, Safoora Sahebi, Negar Ghorbani Jahandizi, Hossein Mofidi
Journal of Medical Case Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Comprehensive review of composition, properties, clinical applications, and future perspectives of calcium-enriched mixture (CEM) cement: a systematic analysis
Saeed Asgary, Mahtab Aram, Mahta Fazlyab
BioMedical Engineering OnLine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The various forms of tooth resorption
Jordan Samuel Blum
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(2): 191. CrossRef - Bioceramics in Endodontics: Updates and Future Perspectives
Xu Dong, Xin Xu
Bioengineering.2023; 10(3): 354. CrossRef - Imaging techniques and various treatment modalities used in the management of internal root resorption: A systematic review
R. S Digholkar, S D Aggarwal, P S Kurtarkar, P. B Dhatavkar, V L Neil, D N Agarwal
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 85. CrossRef - Treatment of Teeth with Root Resorptions: A Case Report and Systematic Review
Damla Erkal, Abdullah Başoğlu, Damla Kırıcı, Nezahat Arzu Kayar, Simay Koç, Kürşat Er
Galician Medical Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of calcium silicate cements on neuronal conductivity
Derya Deniz-Sungur, Mehmet Ali Onur, Esin Akbay, Gamze Tan, Fügen Daglı-Comert, Taner Cem Sayın
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mineral trioxide aggregate and other bioactive endodontic cements: an updated overview – part II: other clinical applications and complications
M. Torabinejad, M. Parirokh, P. M. H. Dummer
International Endodontic Journal.2018; 51(3): 284. CrossRef - Periodontal healing following non-surgical repair of an old perforation with pocket formation and oral communication
Saeed Asgary, Prashant Verma, Ali Nosrat
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Conservative Management of Class 4 Invasive Cervical Root Resorption Using Calcium-enriched Mixture Cement
Saeed Asgary, Ali Nosrat
Journal of Endodontics.2016; 42(8): 1291. CrossRef - Importance of CBCT in the management plan of upper canine with internal resorption
Roberto Fornara, Dario Re Cecconi
Giornale Italiano di Endodonzia.2015; 29(2): 70. CrossRef
- Managing Internal Inflammatory Root Resorption and Perforation of a Mandibular Primary Molar: A Case Report With 15 Months Follow‐Up
- 2,245 View
- 14 Download
- 14 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


