Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- A global overview of enamel microabrasion for white spot lesions: a bibliometric review
- Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Karina Cardoso, Michely Cristina Goebel, Pablo Silveira Santos, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Juliana Silva Ribeiro, Carla Miranda Santana, Mariane Cardoso
- Restor Dent Endod 2024;49(3):e29. Published online July 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2024.49.e29
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub This study aimed to identify and analyze articles on enamel microabrasion for the treatment of white spot lesions. A search was conducted on the Web of Science. The following parameters were recorded and analyzed: number of citations, year, journal, impact factor, study design, theme, country and continent, institution, authors, and keywords. Data was analyzed using VOSviewer software. The initial search resulted in 1,126 documents, of which 94 articles were included. The highest number of citations an article received was 65. The oldest article was published in 1975, and the most recent in 2023. The most frequent study design was case report (
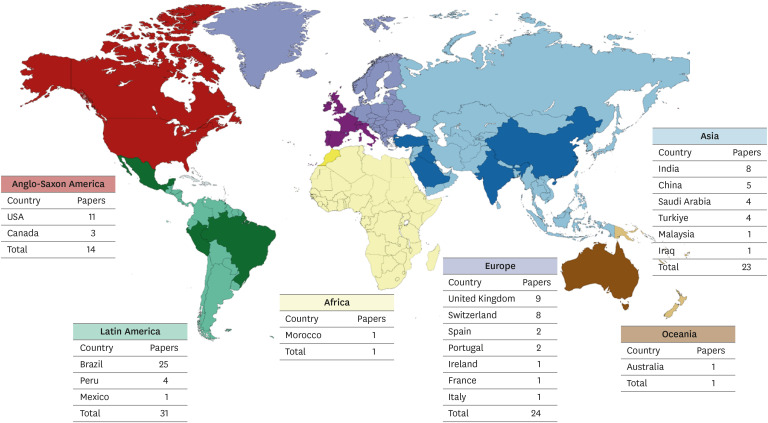
n = 42). Regarding the themes, it was observed that the main objective of the studies was to evaluate the clinical performance of enamel microabrasion (n = 75), primarily using Opalustre (Ultradent Products Inc., South Jordan, UT, USA) (n = 37) for treating white stains caused by dental fluorosis (n = 41). Most articles originated from Latin America (n = 31), mainly from Brazil (n = 26). The most frequent author was Sundfeld RH (n = 10). This study reveals research trends in the field of enamel microabrasion. The publications were mainly case reports/series using Opalustre for the removal of fluorosis stains.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
Michael Willian Favoreto, Leticia Condolo, Camila Mendes Camargo, Rafael Rodrigues Lima, Karol Carrillo, Abraham Lincoln Calixto, Alessandra Reis, Alessandro D. Loguercio
Journal of Dentistry.2025; 156: 105655. CrossRef - Micro- and Macroabrasion in the Esthetic Zone: A Narrative Review and Case Study
Jose Villalobos-Tinoco, Carlos A. Jurado, Silvia Rojas-Rueda, Nechama S. Citrin, Staley Colvert, Jose Luis Gutierrez-Quintero, Salwa Mekled
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(5): 183. CrossRef - Evaluation of demineralization changes in molar tissues in vitro using electrical impedance spectroscopy
V. D. Goncharov, M. A. Gorelikova, K. V. Shadrina, L. Yu. Orekhova, V. D. Berezkin, E. S. Nemovskaya, A. A. Petrov
Parodontologiya.2025; 30(3): 254. CrossRef
- Impact of microabrasion and a remineralizing agent before in-office bleaching on hydrogen peroxide permeability, color alteration, and enamel morphology
- 5,500 View
- 148 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref

- Ten years of minimally invasive access cavities in Endodontics: a bibliometric analysis of the 25 most-cited studies
- Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Karem Paula Pinto, Natasha C. Ajuz, Luciana Moura Sassone
- Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e42. Published online July 21, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e42
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study aimed to analyze the main features of the 25 most-cited articles in minimally invasive access cavities.
Materials and Methods An electronic search was conducted on the Clarivate Analytics' Web of Science ‘All Databases’ to identify the most-cited articles related to this topic. Citation counts were cross-matched with data from Elsevier's Scopus and Google Scholar. Information about authors, contributing institutions and countries, year and journal of publication, study design and topic, access cavity, and keywords were analyzed.
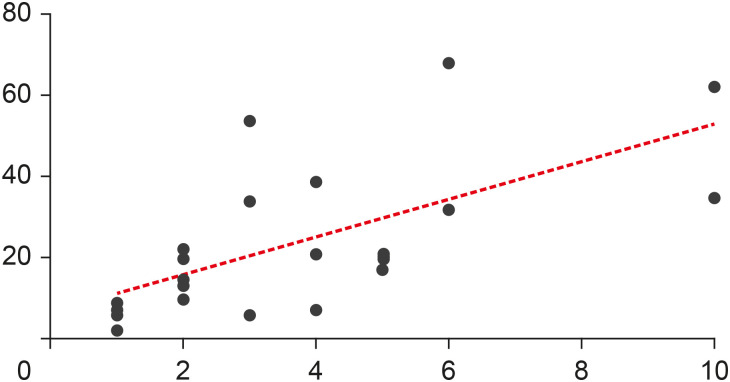
Results The top 25 most-cited articles received a total of 572 (Web of Science), 1,160 (Google Scholar) and 631 (Scopus) citations. It was observed a positive significant association between the number of citations and age of publication (
r = 0.6907,p < 0.0001); however, there was no significant association regarding citation density and age of publication (r = −0.2631,p = 0.2038). TheJournal of Endodontics made the highest contribution (n = 15, 60%). The United States had the largest number of publications (n = 7) followed by Brazil (n = 4), with the most contributions from the University of Tennessee and Grande Rio University (n = 3), respectively. The highest number of most-cited articles wereex vivo studies (n = 16), and ‘fracture resistance’ was the major topic studied (n = 10).Conclusions This study revealed a growing interest for researchers in the field of minimally invasive access cavities. Future trends are focused on the expansion of collaborative networks and the conduction of laboratory studies on under-investigated parameters.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Trends in Internal Root Resorption from 1947 to 2022: A Bibliometric Analysis of the 50 Most-cited Articles
Laise Pena Braga Monteiro, Larissa Pillar Gomes Martel, Roberta Fonseca de Castro, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal da Silva, Juliana Melo da Silva Brandão
Journal of Advanced Oral Research.2025; 16(2): 196. CrossRef - Bibliometric analysis of the publications that list the most-cited articles in endodontics
Oscar Alejandro Gutiérrez-Alvarez, Luis Alberto Pantoja-Villa, Benigno Miguel Calderón-Rojas
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 128. CrossRef - Sixty Years of Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Use in Endodontics: A Comprehensive Bibliometric Study
Camila Segatto Hartmann, Luiz Fernando Monteiro Czornobay, Julia Menezes Savaris, Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Bruno Alexandre Pacheco de Castro Henriques, Mariane Cardoso, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Cleonice da Silveira Teixe
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of the forces applied by rubber dam clamps on mandibular first molar teeth with different endodontic access cavities: a 3D FEA study
Mehmet Eskibağlar, Serkan Erdem, Büşra Karaağaç Eskibağlar, Mete Onur Kaman
PeerJ.2024; 12: e17921. CrossRef - A Global Overview of Guided Endodontics: A Bibliometric Analysis
Thaine Oliveira Lima, Aurélio de Oliveira Rocha, Lucas Menezes dos Anjos, Nailson Silva Meneses Júnior, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Mariane Cardoso, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(1): 10. CrossRef - Novel method for augmented reality guided endodontics: An in vitro study
Marco Farronato, Andres Torres, Mariano S. Pedano, Reinhilde Jacobs
Journal of Dentistry.2023; 132: 104476. CrossRef - Contribution of Türkiye to the Field of Endodontology: A Visualized Bibliometric Analysis Based on Web of Science
Olcay ÖZDEMİR, Yağız ÖZBAY, Neslihan YILMAZ ÇIRAKOĞLU
Medical Records.2023; 5(1): 91. CrossRef - Effect of access cavities on the biomechanics of mandibular molars: a finite element analysis
Xiao Wang, Dan Wang, Yi-rong Wang, Xiao-gang Cheng, Long-xing Ni, Wei Wang, Yu Tian
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Contemporary research trends on nanoparticles in endodontics: a bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the top 100 most-cited articles
Sıla Nur Usta, Zeliha Uğur-Aydın, Kadriye Demirkaya, Cumhur Aydın
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evolving trend of systematic reviews and meta-analyses in endodontics: A bibliometric study
GalvinSim Siang Lin, JiaZheng Leong, WenXin Chong, MikoChong Kha Chee, ChinSheng Lee, Manahil Maqbool, TahirYusuf Noorani
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2022; 12(3): 236. CrossRef - Global research trends on photodynamic therapy in endodontics: A bibliometric analysis
Lucas Peixoto de Araújo, Wellington Luiz de Oliveira da Rosa, Leandro Bueno Gobbo, Tamares Andrade da Silva, José Flávio Affonso de Almeida, Caio Cezar Randi Ferraz
Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy.2022; 40: 103039. CrossRef - Minimal Invasive Endodontics: A Comprehensive Narrative Review
Jaydip Marvaniya, Kishan Agarwal, Dhaval N Mehta, Nirav Parmar, Ritwik Shyamal , Jenee Patel
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Trends in Internal Root Resorption from 1947 to 2022: A Bibliometric Analysis of the 50 Most-cited Articles
- 3,213 View
- 28 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


