Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Influence of adjacent restorative material and distance on the accuracy of inlay cavity impressions with intraoral scanner: an in vitro study
- So-Yeon Lee, Sung-Ae Son, Jae-Hoon Kim, Deog-Gyu Seo, Jeong-Kil Park
- Restor Dent Endod 2026;51(1):e6. Published online January 23, 2026
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2026.51.e6
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
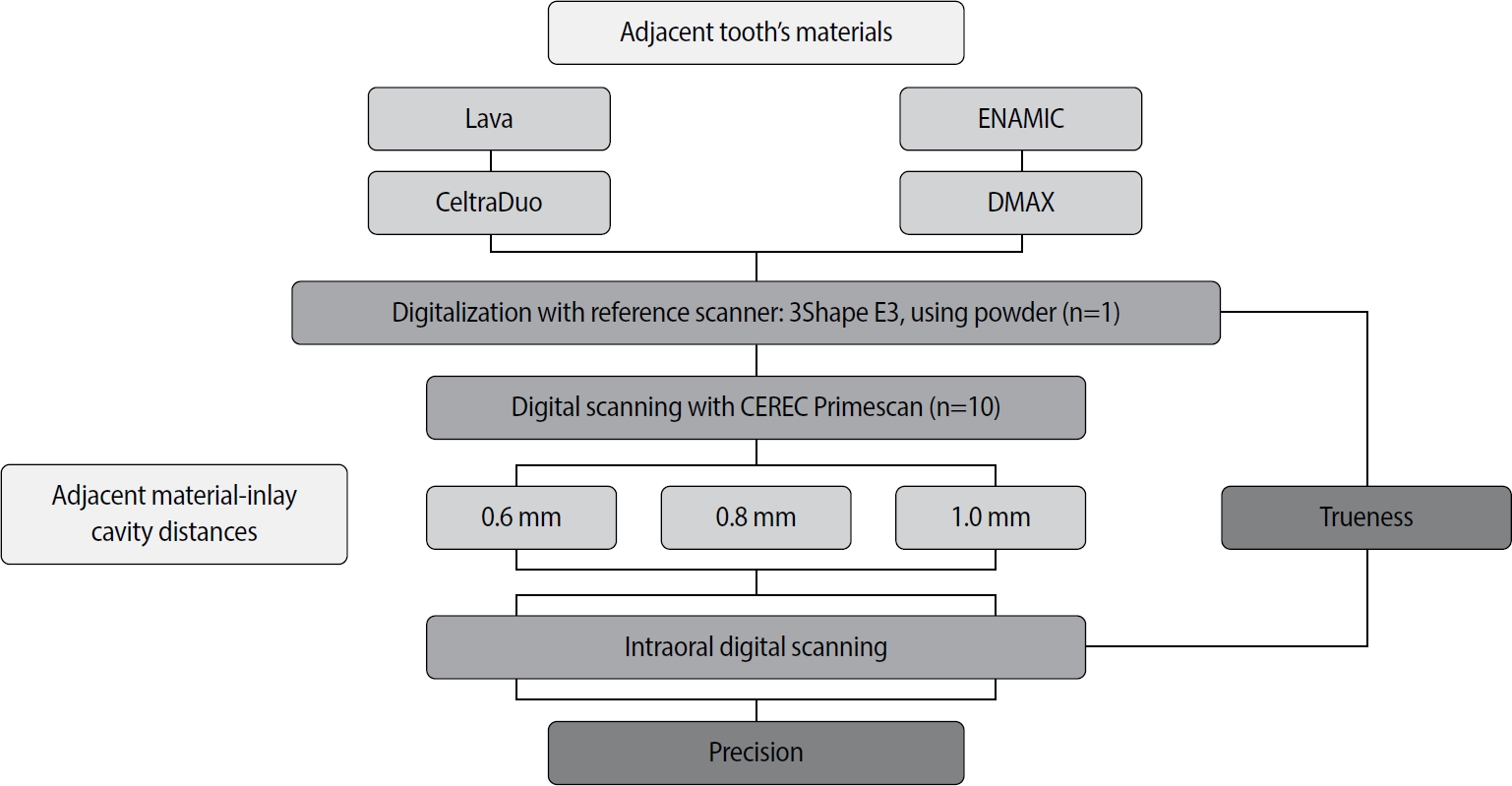
This study aimed to evaluate the influence of adjacent restorative material and interproximal distance on the accuracy of digital impressions of inlay cavities obtained using an intraoral scanner.
Methods
A disto-occlusal inlay cavity was prepared on a mandibular right first molar model, and digital scans were performed using a CEREC Primescan (Dentsply Sirona). The adjacent restorative materials used were Lava (3M ESPE), ENAMIC (VITA Zahnfabrik), Celtra Duo (Dentsply Sirona), and DMAX (DMAX), and the interproximal distances were set to 0.6 mm, 0.8 mm, and 1.0 mm. The obtained scan data were analyzed using GOM Inspect software (GOM GmbH).
Results
Trueness, maximum positive and negative deviations, and precision were significantly influenced by both the adjacent restorative material and the interproximal distance, while their interaction showed a significant effect only on precision. Celtra Duo demonstrated the highest trueness, with mean deviation values decreasing from 7.8 μm at a 0.6 mm interproximal distance to 7.3 μm at 1.0 mm. ENAMIC showed the best precision, presenting mean deviations of 2.6 μm at 0.6 mm, 2.9 μm at 0.8 mm, and 2.4 μm at 1.0 mm. A narrow interproximal distance of 0.6 mm resulted in lower trueness, measured at 8.3 μm, and the highest precision deviation of 3.4 μm. In contrast, an interproximal distance of 1.0 mm yielded improved scan accuracy, with increased trueness and reduced precision variation.
Conclusions
Digital impression accuracy of inlay cavities was influenced by adjacent restorative material and interproximal distance, suggesting clinical consideration is needed in CAD/CAM workflows to optimize restoration fit.
- 555 View
- 31 Download

- Tip and taper compatibility of accessory gutta-percha points with rotary and reciprocating instruments
- Júlia Niero Zanatta Streck, Sabrina Arcaro, Renan Antônio Ceretta, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida, Patrícia Maria Poli Kopper, Anarela Vassen Bernardi
- Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e22. Published online June 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e22
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives This study was conducted to evaluate and compare the tip and taper compatibility of accessory gutta-percha points (AGPs) with various rotary and reciprocating instruments.
Materials and Methods Using a profile analyzer, tip and taper measurements were taken of 10 AGPs of each of the 14 models available from Odous de Deus and the 4 models available from Dentsply-Maillefer. Diameter measurements were taken at 1-mm intervals, from 3 mm from the tip (D3) to 16 mm.
Results Based on the mean values obtained, 3-dimensional (3D) models of the AGPs were drawn in Autodesk Fusion 360 and superimposed on 3D models of each instrument selected (Mtwo, Reciproc, RaCe, K3, and ProDesign Logic) to determine the compatibility between the instrument and the AGP. Data corresponding to the tips and tapers of the various AGPs, as well as the tip and taper differences between the AGPs and the instruments, were analyzed using descriptive statistics. The tapers of the AGPs were subject to the American National Standards Institute/American Dental Association No. 57 standard. The Odous de Deus extra-long medium and extra-long extra-medium AGPs were shown to be compatible with Mtwo, K3, and ProDesign Logic instruments with taper 0.06 and tip sizes 25 and 30, while the Dentsply fine and fine medium cones were compatible with Mtwo, RaCe, and K3 instruments with conicity of 0.04 and tip sizes 35 and 40.
Conclusions Both the Odous de Deus and Dentsply commercial brands included 2 AGP models with tip (D3) and taper compatibility with Mtwo, RaCe, K3, and/or Prodesign Logic instruments.
- 2,214 View
- 42 Download

- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
- Shin-Young Park, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2012;37(2):68-73. Published online May 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2012.37.2.68
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives The purpose of this study was to assess the accuracy of Root ZX (J. Morita Corp.) according to the location of major foramen and open apex.
Materials and Methods 81 mandibular premolars with mature apices were selected. After access preparation, 27 teeth were instrumented to simulate open apices. 54 teeth were classified according to location of major foramen under surgical microscope (×16). The file was fixed at the location of apical constriction by Root ZX using glass ionomer cement. The apical 4 mm of the apex was exposed and photo was taken and the distance from file tip to the major foramen was measured by calibrating metal ruler on graph paper. The results were statistically analyzed using ANOVA and Scheffe test at
p < 0.05 level.Results Mean distance from file tip to major foramen was 0.308 mm in Tip foramen group (I), 0.519 mm in Lateral foramen group (II) and 0.932 mm in open apex group (III). Root ZX located apical constriction accurately within ± 0.5 mm in group I of 85.71%, in group II of 59.09%, and in group III of 33.33%. There was a statistically significant difference between group I and III (
p < 0.05).Conclusion Root ZX located apical constriction accurately regardless of location of major foramen. However, Root ZX couldn't find it in open apex. Clinicians have to use a combination of methods to determine an appropriate working length at open apex. It may be more successful than relying on just electronic apex locator.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of file size in measuring electronic working length of teeth with open apex
Ryeon Jin, Ju-Hee Jeong, A-Ra Cho, Hyoung-Hoon Jo
Oral Biology Research.2022; 46(1): 36. CrossRef
- Effect of file size in measuring electronic working length of teeth with open apex
- 1,318 View
- 4 Download
- 1 Crossref

- In vivo evaluation of accuracy and consistency of two electronic apex locators
- Chien-Yun Pi, Euiseong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2010;35(6):453-460. Published online November 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.453
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub Objectives To evaluate the accuracy and consistency of two different apex locators at both the Apex and 0.5 marks.
Materials and Methods Twenty-six root canals was scheduled for extraction for periodontal or prosthodontic reasons. Thirteen canals were measured using Root ZX and the rest by i-ROOT. The root canal length was measured both the at 0.5 mark and the Apex mark. The file was then fixed to the tooth, and the distance from the file tip to the major foramen of each canal was measured after removing the root dentin under the microscope so that the major foramen and the file tip were seen.
Results When the Apex mark was used, 100% of both the Root ZX and i-ROOT groups were within 0.5 mm of the major foramen.
When 0.5 mark was used, 100% of the Root ZX group and 77% of the i-ROOT group were within 0.5 mm of the major foramen.
In terms of standard deviation and quartile value, the Apex mark was more consistent than 0.5 mark in the Root ZX group, and 0.5 mark was more consistent in the i-ROOT group, but there was no statistically significant difference when compared with
t -test.The root canal length difference between the Apex mark and 0.5 mark was 0.22 mm and 0.46 mm in the Root ZX and i-ROOT groups, respectively.
Conclusions In this study, the Apex mark was the more consistent mark. Therefore, it is recommended to subtract 0.5 mm, which is the average length between the apex and apical constriction, from the root canal length at the Apex mark to obtain the working length clinically.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Influence of Apical Periodontitis on the Accuracy of 3 Electronic Root Canal Length Measurement Devices: An In Vivo Study
Masoud Saatchi, Mohammad Ghasem Aminozarbian, Seyed Mohsen Hasheminia, Amin Mortaheb
Journal of Endodontics.2014; 40(3): 355. CrossRef
- Influence of Apical Periodontitis on the Accuracy of 3 Electronic Root Canal Length Measurement Devices: An In Vivo Study
- 1,276 View
- 3 Download
- 1 Crossref

-
In vitro evaluation of accuracy and consistency of four different electronic apex locators - Jae-Hyun Cho, Kee-Yeon Kum, Seung-Jong Lee
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):390-397. Published online September 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.390
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy and the consistency of four different electronic apex locators in an
in vitro model.Fourty extracted premolars were used for the study. Four electronic apex locators (EAL) were Root ZX, SmarPex, Elements Diagnostic Unit (EDU), and E-Magic Finder Deluxe (EMF). After access preparation, the teeth were embedded in an alginate model and the length measurements were carried out at "0.5"and "Apex"mark using four EALs. The file was cemented at the location of the manufacturers'instruction (Root ZX, EDU, EMF: 0.5 mark, SmarPex: Apex mark). The apical 4mm of the apex was exposed and the distance from the file tip to the major foramen was measured by Image ProPlus (× 100). The distance from the file tip to the major foramen was calculated at 0.5 and Apex mark and the consistency of 0.5 and Apex mark was compared by SD and Quartile of Box plots.
In this study, Root ZX and EMF located the apical constriction accurately within ± 0.5 mm in 100%, whereas SmarPex and EDU located in 90% and in 70% respectively. For Root ZX and EMF, there was no significant difference between the consistency of 0.5 and Apex mark. However, for the EDU and SmarPex, Apex mark was more consistent than 0.5 mark.
From the evaluation of the consistency in this study, for Root ZX and EMF, both 0.5 and Apex mark can be used as a standard mark. And for EDU and SmarPex, the Apex mark can be recommended to be used as a standard mark.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
Shin-Young Park, Dong-Kyun Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2012; 37(2): 68. CrossRef
- An evaluation of the accuracy of Root ZX according to the conditions of major apical foramen
- 1,371 View
- 1 Download
- 1 Crossref

-
In vitro comparison of measurement accuracy in pre-enlarged and enlarged canals with four apex locators - Sang-Yup Sung, Jeong-Kil Park, Bock Hur, Hyeon-Cheol Kim
- J Korean Acad Conserv Dent 2006;31(5):371-377. Published online September 30, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2006.31.5.371
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub The purposes of this study were to assess the accuracy of measurements in pre-enlarged canals with small instruments and to compare the accuracies, in enlarged canal, with small size instruments and instruments that match the actual canal diameter using Root ZX, Bingo1020, SmarPex, and e-Magic Finder. Ten extracted teeth were embedded in an alginate model made for testing apex locators. A size 10 file was placed into the root canal until the tip of the file reached the plane of the major diameter of the foramen under a dental operating microscope at the 25 × magnification. The measurement was done with digital caliper and defined as actual length. Electronic length measurement with a size 10 file in pre-enlarged canal was done by reading the index indicating Apex of each device to gain a definite value. After completion of canal enlargement to a size 45 file, each difference between actual length and electric measurement value with a size 10 and 40 files in enlarged canal was recorded as L10 and L40. The one-way ANOVA and Scheffe's multiple range tests were computed for analyze the differences among the four apex locators in the same group. The Student's t-test between L10 and L40 of each locator was done. The accuracies of electronic measurements were significantly different among the 4 devices. The file size made no difference on the accuracy of electronic measurement in enlarged canal with same device. The e-Magic Finder was the most accurate device among the 4 apex locators used in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Working Length Determination Using Two Fifth-Generation Apex Locators With Radiovisiography: An In vivo Study
H. K. Shwetha, C. N. Vijay Kumar, Arun J. Kumar, Ashwini Bhaskar, M Kavyashree, S Amrita
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2025; 17(2): 69. CrossRef
- Working Length Determination Using Two Fifth-Generation Apex Locators With Radiovisiography: An In vivo Study
- 1,278 View
- 0 Download
- 1 Crossref


 KACD
KACD

 First
First Prev
Prev


