Previous issues
- Page Path
- HOME > Browse articles > Previous issues
Research Articles
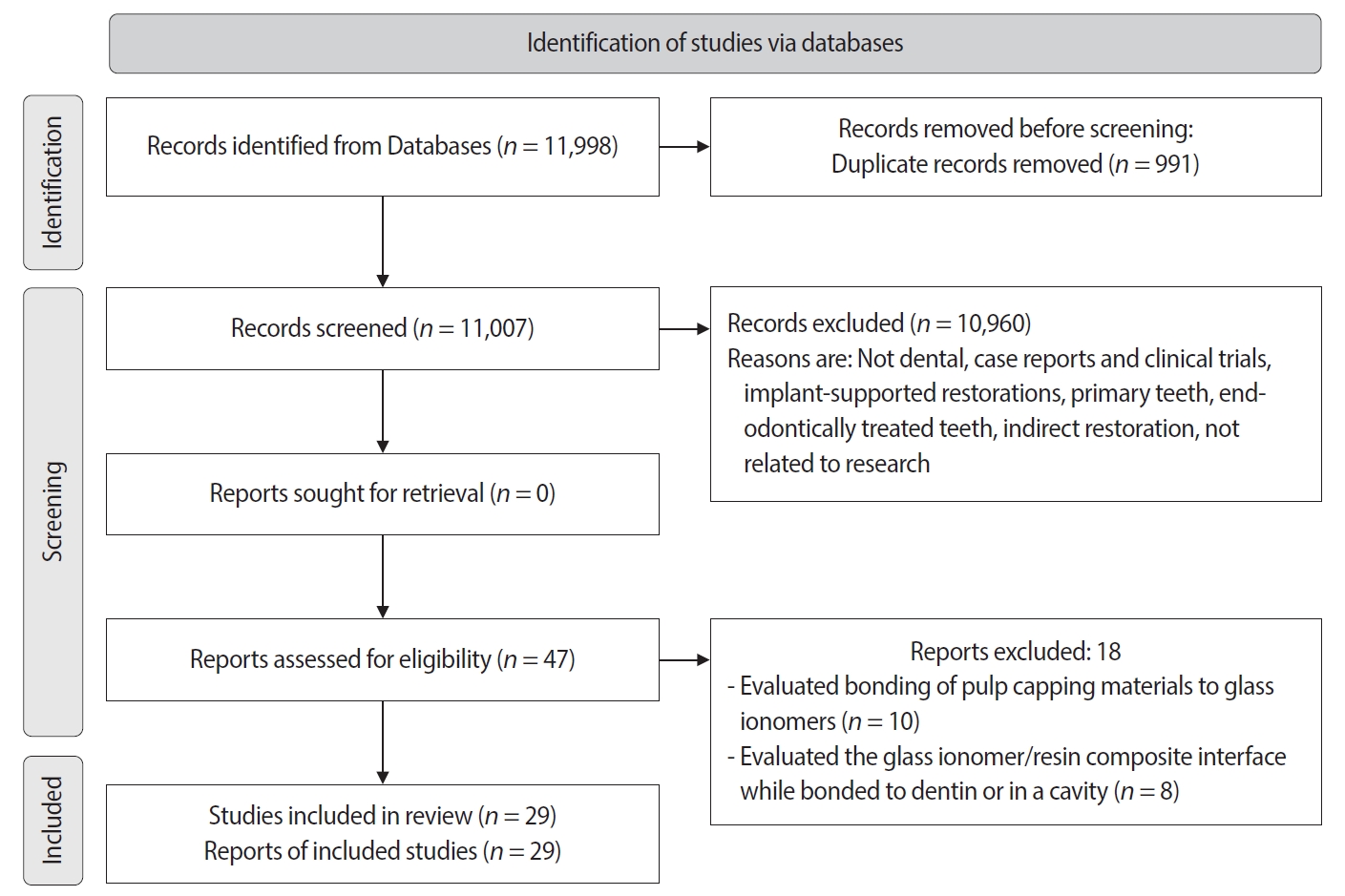
- Effect of surface treatment on glass ionomers in sandwich restorations: a systematic review and meta-analysis of laboratory studies
- Hoda S. Ismail, Ashraf Ibrahim Ali, Franklin Garcia-Godoy
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e13. Published online April 16, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e13
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of different surface treatments on the bond strength between new or aged glass ionomers (GI) and resin composites in sandwich restorations.
Methods
A comprehensive search was conducted in three databases to identify studies focusing on the bond strength of new or aged GIs and resin composites in laboratory settings. The selected studies were assessed for potential biases based on predetermined criteria. Additionally, a meta-analysis was performed using three studies.
Results
A total of 29 studies were included, with 24 investigating the bond strength of new GIs and five focusing on GI repair. Three studies were included in the meta-analysis (with a 95% confidence interval) which revealed no significant difference in the mean MPa values of resin-modified glass ionomer (RMGI) treated with phosphoric acid or Er,Cr:YSGG laser before the application of an etch-and-rinse adhesive. Surface treatment was found to be crucial for achieving optimal bonding between GI and resin composite, regardless of the GI’s condition.
Conclusions
The combination of mechanical and chemical surface treatments does not significantly affect the bond strength between new RMGI and composite. However, for GI repair, it is recommended to use both treatments to enhance the bond strength. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The impact of alloy treatment on the dynamic cyclic fatigue resistance of triangular base cross-section NiTi endodontic instruments
Rashid El Abed, Amre R. Atmeh, Mohamed Jamal, Anas Al Jadaa, Hamza El-Faraj, Abdel Rahman Bani Amer, Taher Al Omari
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- The impact of alloy treatment on the dynamic cyclic fatigue resistance of triangular base cross-section NiTi endodontic instruments
- 8,716 View
- 218 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Evaluation of the effects of different file systems and apical functions of integrated endodontic motors on debris extrusion: an ex vivo experimental study
- Sıla Nur Usta, Antonio Magan-Fernandez, Cumhur Aydın
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e14. Published online April 14, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e14
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate the effects of two different file systems operated with three apical functions of an endodontic motor integrated with an electronic apex locator on debris extrusion.
Methods
Sixty single-rooted teeth were prepared and divided into two main groups and three subgroups based on the file system (OneShape [Micro-Mega SA] and WaveOne [Dentsply Maillefer]) and apical function of the endodontic motor used (auto apical stop [AAS], auto apical reverse [AAR], and auto apical slowdown [ASD]). The teeth were mounted in pre-weighed glass tubes filled with 0.9% sodium chloride to complete the circuit with the apex locator. Files were advanced until the respective apical function (stop, reverse, or slowdown) was activated. The extruded debris was collected, dried, and weighed by subtracting pre-weighed values from post-weighed values. Preparation time was also recorded. Statistical analyses were performed to compare the groups.
Results
OneShape was associated with significantly less debris extrusion compared to WaveOne, regardless of the apical function (p < 0.05). The ASD function resulted in the least debris extrusion compared to AAS and AAR (p < 0.05). Preparation time was significantly longer in the ASD function (p < 0.05), while no differences were observed between the file systems (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
The OneShape file system and the ASD function produced the least amount of apical debris. While the ASD function requires more preparation time, its potential to minimize debris extrusion suggests it may reduce postoperative symptoms. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammatory Mediator Levels and Postoperative Pain Following Root Canal Shaping with Different Apical Actions: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Mustafa Mert Tulgar, Yağmur Kılıç, Oğuz Karalar, Huriye Erbak Yılmaz, Emrah Karataşlıoğlu
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammatory Mediator Levels and Postoperative Pain Following Root Canal Shaping with Different Apical Actions: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- 4,444 View
- 228 Download
- 1 Crossref

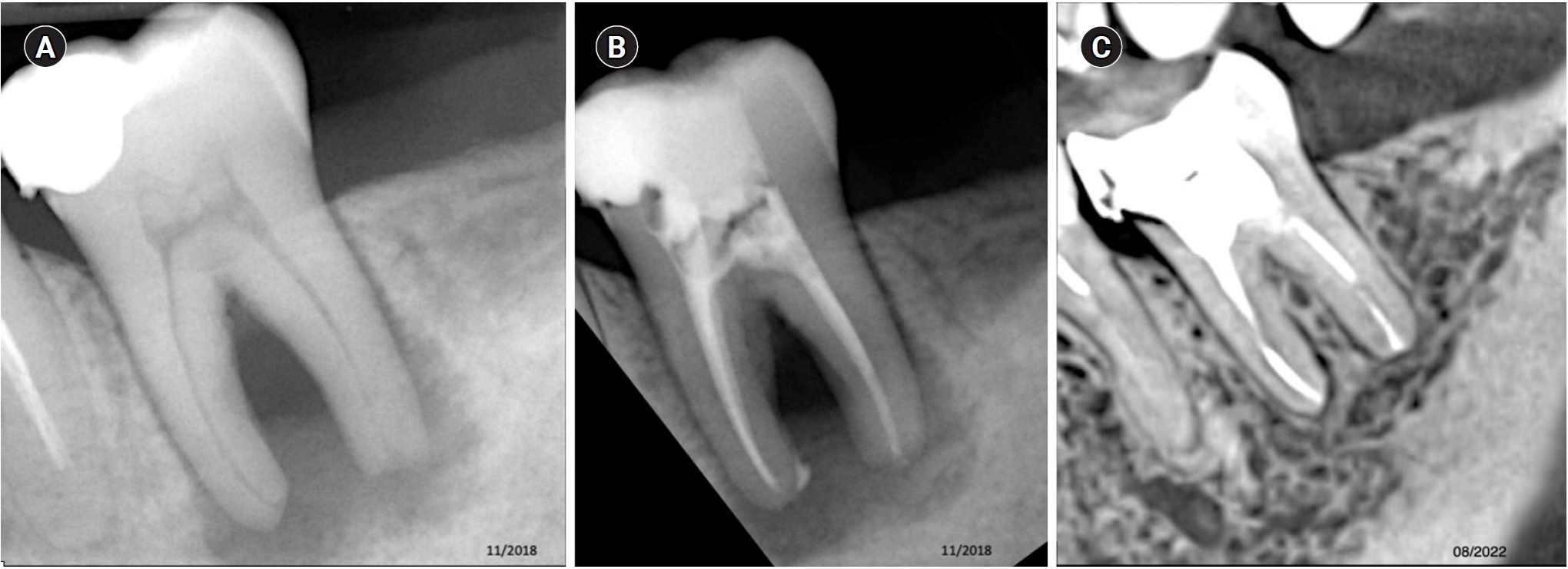
- Impact of the use of high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of the treatment of teeth with periapical lesions: an observational clinical study
- Fabricio Hinojosa Pedraza, Abel Victor Isidro Teves-Cordova, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e15. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e15
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The aim of this study was to demonstrate the impact of a high-power 810-nm diode laser as monotherapy on the clinical and tomographic success of treating teeth with periapical lesions, through a series of 31 cases.
Methods
Teeth with apical lesions underwent endodontic treatment in which a high-power 810-nm diode laser with saline solution was used as monotherapy for disinfection. This type of therapy aimed to replace the traditional irrigation protocol with sodium hypochlorite. This research is the first to assess the clinical success of this alternative treatment, along with tomographic evaluations conducted over periods ranging from 2 to 7 years, analyzed using the periapical index based on cone-beam computed tomography (CBCTPAI). All cases were performed by a single clinician following the same laser protocol, which involved using 1 W of continuous power and four cycles of 20 seconds of laser activation.
Results
All teeth showed no clinical symptoms upon follow-up examination. However, the tomographic evaluation revealed that the success rates for teeth receiving primary treatment were 60% and 80% according to strict and loose criteria, respectively. For teeth requiring retreatment, the success rates were 12.5% and 37.5% using strict and loose criteria, respectively.
Conclusions
The teeth with apical lesions that underwent primary treatment did not present clinical symptoms, but they showed a moderate success rate on tomographic evaluation. However, despite lacking clinical symptoms, teeth with apical lesions that required retreatment had a very low success rate on tomographic evaluation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
Ioana-Roxana Munteanu, George-Dumitru Constantin, Ruxandra-Elena Luca, Ioana Veja, Mariana-Ioana Miron
Medicina.2025; 61(12): 2157. CrossRef
- Diode Laser-Guided Protocol for Endo-Perio Lesions: Toward a Multi-Stage Therapeutic Strategy—A Case Series and Brief Literature Review
- 4,037 View
- 193 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

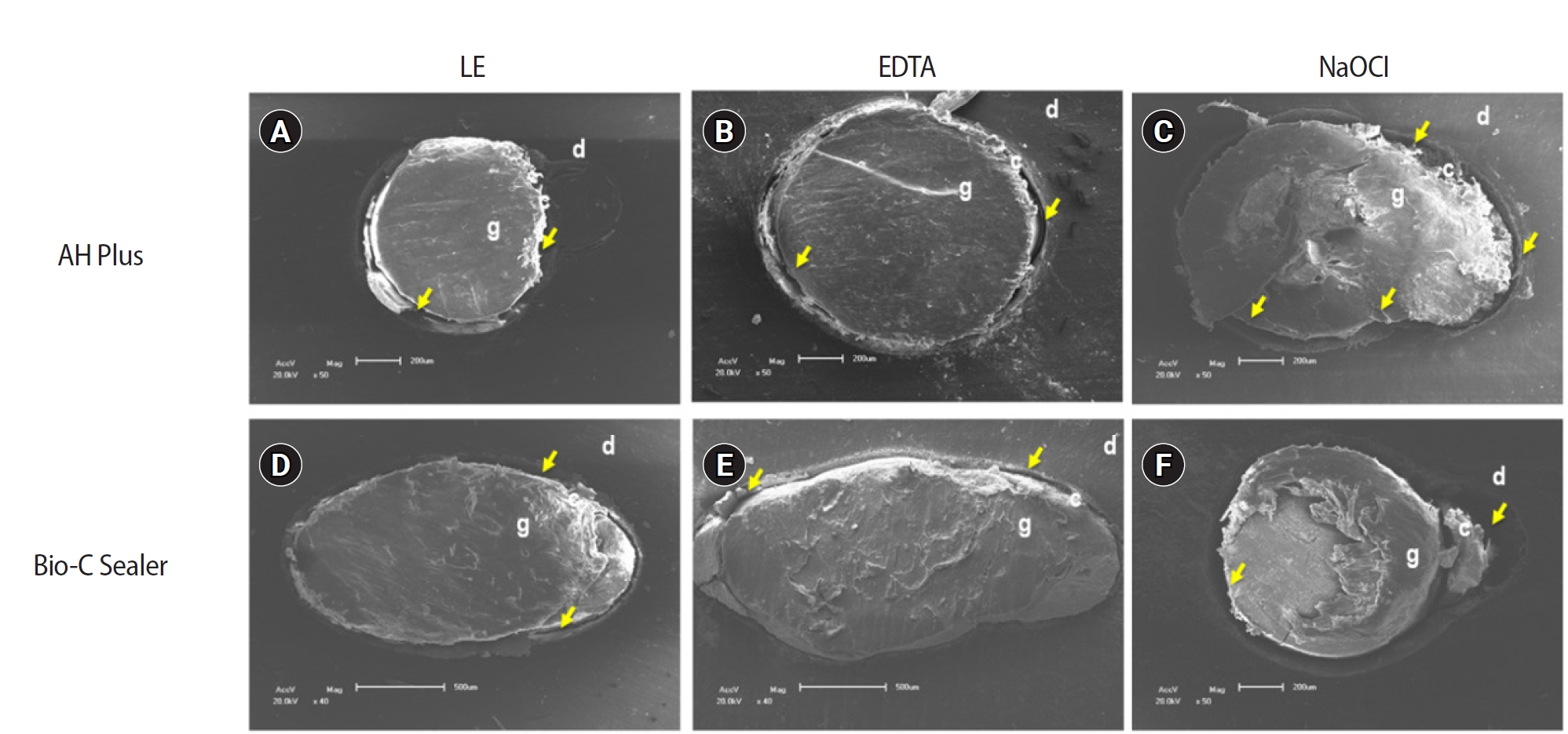
- The effect of limonene extract on the adhesion of different endodontic cements to root dentin: an in vitro experimental study
- Nayara Lima Ferraz Aguiar, Eduardo José Soares, Guilherme Nilson Alves dos Santos, Anna Luísa Araújo Pimenta, Laryssa Karla Romano, Ricardo Gariba Silva, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e16. Published online May 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e16
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The study aimed to evaluate the effect of limonene extract (LE) on push-out bond strength (BS) to root dentin in endodontically treated teeth.
Methods
Single-rooted teeth were selected and instrumented using the reciprocating technique, then divided into three groups based on the final irrigating solution: 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl), 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), and 5% LE. The roots were further divided (n = 12) and obturated using the single-cone technique with epoxy resin-based (ERB) or bioceramic sealer (Bio-C). After 3 days, the roots were sectioned into 2-mm slices, obtaining two slices from each root third. Push-out BS testing was conducted at 0.5 mm/min, followed by failure pattern and adhesive interface analysis using scanning electron microscopy. Push-out BS data were analyzed by three-way analysis of variance and Tukey post-hoc test (p < 0.05).
Results
ERB showed higher BS when irrigated with EDTA (5.0 ± 2.3 MPa) compared to NaOCl (1.8 ± 1.1 MPa) (p = 0.0005), particularly in the cervical third. LE yielded intermediate values without significant differences from the other irrigants (3.5 ± 1.9 MPa) (p > 0.05). For Bio-C, the highest BS was observed in the apical third, especially with LE (9.4 ± 5.0 MPa), differing from other thirds and final irrigating solutions (p < 0.05). Mixed failure patterns were most prevalent, regardless of the irrigant solutions.
Conclusions
The combination of LE with Bio-C demonstrated superior BS in the apical third, suggesting its potential as a final irrigating solution in endodontic treatments.
- 2,528 View
- 223 Download

- Bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system: trends, collaborations, and research gaps
- Raimundo Sales de Oliveira Neto, Thais de Moraes Souza, João Vitor Oliveira de Amorim, Thaine Oliveira Lima, Guilherme Ferreira da Silva, Rodrigo Ricci Vivan, Murilo Priori Alcalde, Marco Antonio Hungaro Duarte
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e17. Published online May 12, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e17
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
The study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of the GentleWave system (Sonendo, Inc.).
Methods
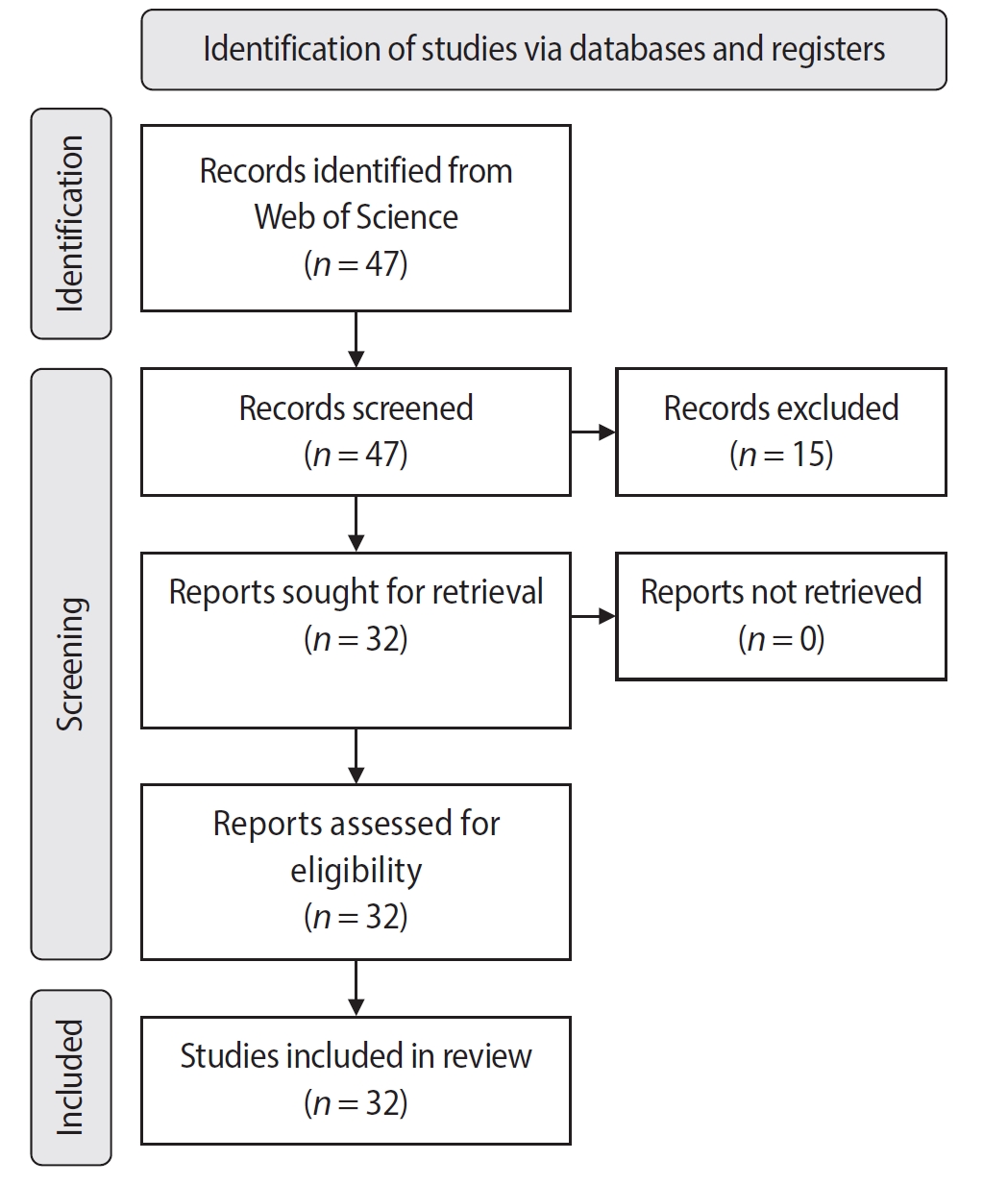
An electronic search was conducted in June 2024 using the Web of Science Collection database. Two reviewers independently screened publications, extracting data on authorship, publication details, study design, and citation metrics. Statistical analyses were performed in R to assess variable correlations, while the VOSviewer (Visualization of Similarities Viewer) software was used to map author and keyword networks.
Results
The search yielded 47 records, with 32 studies included. Publications spanned 2014 to 2024. The Journal of Endodontics published the highest number of studies (n = 15), and the International Endodontic Journal had the highest impact factor (5.4). The University of British Columbia and Sonendo, Inc. were the most frequent affiliations. Among the 32 articles, 28 were in vitro studies, primarily focusing on microbiology (n = 9). A total of 95 authors were identified, with Haapasalo and Shen being the most cited (n = 229). The articles accumulated 495 citations, demonstrating a strong positive correlation between the number of studies and citation counts (r = 0.98).
Conclusions
The analysis highlights a predominance of in vitro studies. Geographic concentration in the United States and Canada limits diversity, while the strong correlation between study numbers and citations suggests that increased publication volume enhances visibility. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Three-year Outcomes of Conventional Versus Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment Protocols: A Retrospective Study
Kiavash Hossini, He Liu, Ya Shen, Jolanta Aleksejuniene, Fahda Algahtani, Ahmed Hieawy
Journal of Endodontics.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Three-year Outcomes of Conventional Versus Minimally Invasive Endodontic Treatment Protocols: A Retrospective Study
- 3,545 View
- 88 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Dentin thickness of C-shaped root canal walls in mandibular premolars based on cone-beam computed tomography: a retrospective cross-sectional study
- Elif Aslan, Ali Canberk Ulusoy, Bilge Hakan Sen, B. Guniz Baksi, Erinc Onem, Ali Mert
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e18. Published online May 15, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e18
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
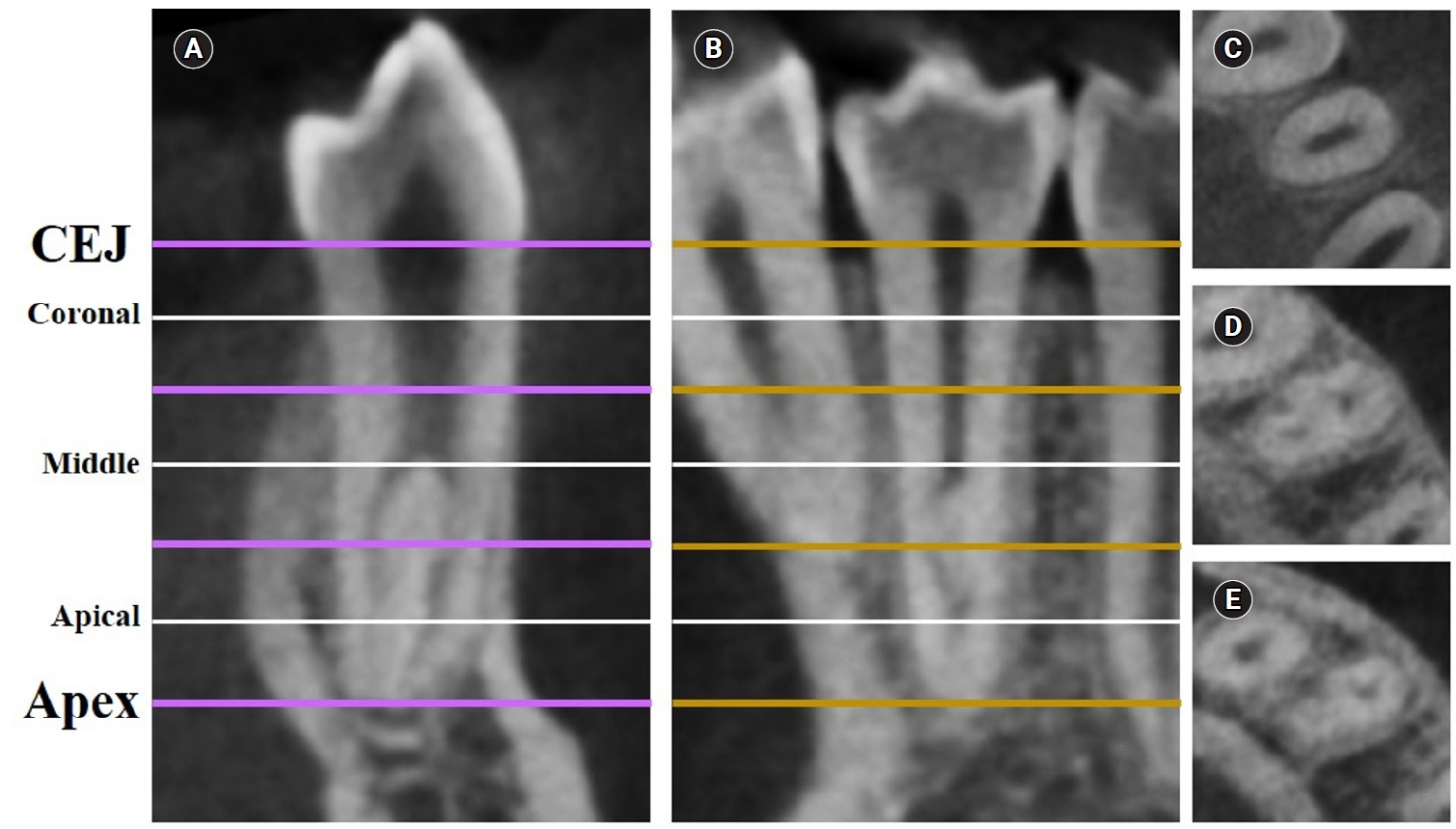
This study aimed to measure the dentin thickness of C-shaped canals in mandibular first and second premolars at coronal, middle, and apical root levels using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Methods
Dentin thicknesses of buccal, lingual, mesial, and distal root walls of 41 C-shaped premolars were measured at three different root levels on axial CBCT slices. The measurements were made at the midpoint of each third, along with 1 mm below and above the midpoint. C-shape configurations of the premolar root canals were also recorded. Analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis, and the independent samples t-tests were used for the comparisons (p = 0.05).
Results
The thickest walls for both premolars were buccal and lingual walls at all three root levels (p < 0.05). The thinnest walls for the first premolar teeth were mesial and distal walls of the lingual canal, while it was the mesial end of the buccal and lingual canals for the second premolars (p < 0.05). Dentin wall thicknesses at the mesial end of buccal and lingual canals of C1-shaped first premolars were thinner than C2-shaped first premolars at the apical level (p < 0.05).
Conclusions
Danger zones for C-shaped mandibular first and second premolars are predominantly mesial walls facing the radicular groove and distal wall of the lingual canal. CBCT imaging during endodontic treatment is recommended to avoid complications. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
Ahmed A. Madfa, Abdullah F. Alshammari, Eyad Almagadawyi, Ebtsam A. Aledaili, Afaf Al-Haddad
Scientific Reports.2025;[Epub] CrossRef
- Anatomical complexity in mandibular second molars: prevalence of C-shaped canals, radicular grooves, taurodontism, and radices molarum in Saudi population
- 3,609 View
- 135 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref

- Impact of post adhesion on stress distribution: an in silico study
- Kkot-Byeol Bae, Jae-Yoon Choi, Young-Tae Cho, Bin-Na Lee, Hoon-Sang Chang, Yun-Chan Hwang, Won-Mann Oh, In-Nam Hwang
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e19. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e19
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
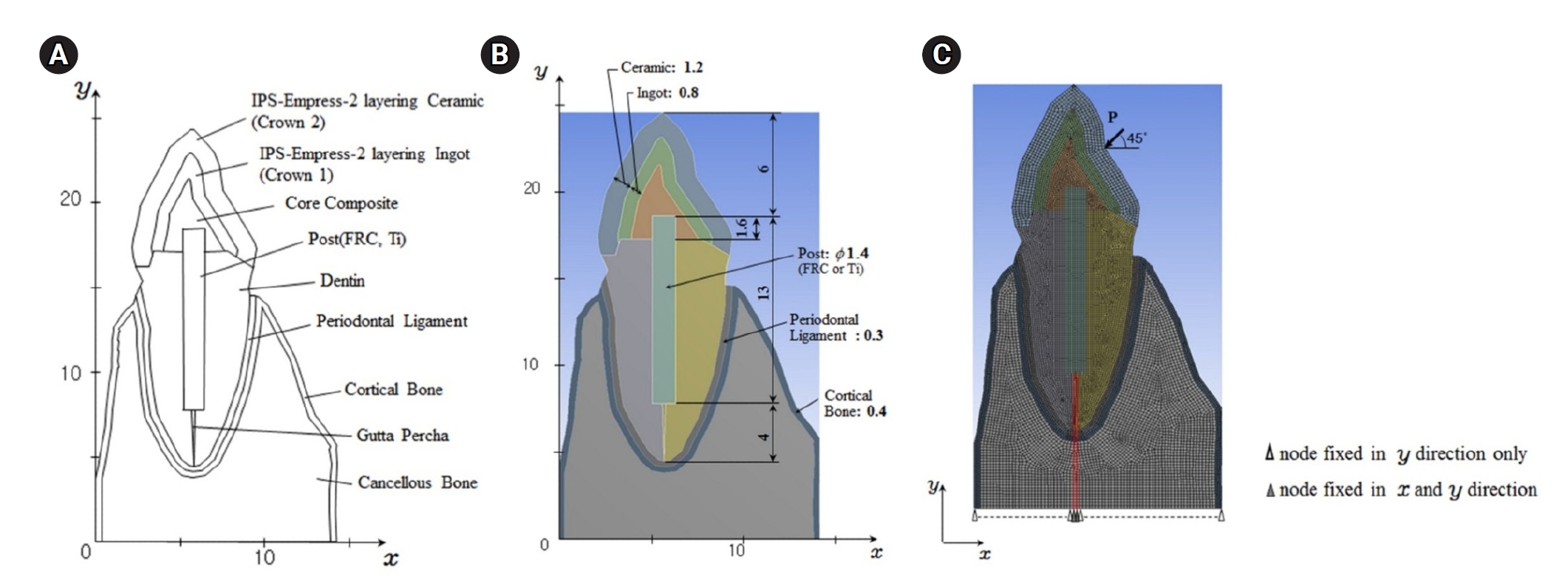
This study aimed to evaluate the stress distribution in teeth restored with different post materials and bonding conditions using finite element analysis (FEA).
Methods
A two-dimensional FEA model of a maxillary central incisor restored with IPS-Empress-2 crown (Ivoclar Vivadent), composite resin core, and posts were created. The model simulated bonded and non-bonded conditions for both fiber-reinforced composite (FRC) and titanium (Ti) posts. Stress distribution was analyzed using ANSYS 14.0 software under a 100-N load applied at a 45° angle to the long axis of the tooth.
Results
The results revealed that stress concentration was significantly higher in non-bonded posts compared to bonded ones. FRC posts exhibited stress values closer to those of dentin, whereas Ti posts demonstrated higher stress concentration, particularly in non-bonded states, increasing the potential risk of damage to surrounding tissues.
Conclusions
FRC posts, with elastic properties similar to dentin and proper adhesion, minimize stress concentration and potential damage to surrounding tissues. Conversely, materials with higher elastic modulus like Ti, can cause unfavorable stress concentrations if not properly bonded, emphasizing the importance of post adhesion in tooth restoration. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Ecofriendly and High-Strength Dental Composites: Structural and Functional Perspectives
Sayem A. Mulla, Amit Patil, Himmat Jaiswal, Bhavani Sangala Nagendra, Ashima Jakhar, Waseem Z. Khan
European Journal of General Dentistry.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in Ecofriendly and High-Strength Dental Composites: Structural and Functional Perspectives
- 2,427 View
- 95 Download
- 1 Crossref

- Cleaning protocols to enhance bond strength of fiberglass posts on root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: an in vitro comparative study
- Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana Delatorre Bronzato, Joice Graciani, Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Rocharles Cavalcante Fontenele, Francisco Haiter Neto, Brenda Paula Figueiredo de Almeida Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano da Silva
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e20. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e20
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study aimed to evaluate whether the agitation protocols using ultrasonic inserts or the XP-endo Finisher R file improved the removal of two different endodontic sealer remnants and the bond strength of fiberglass posts to dentin.
Methods
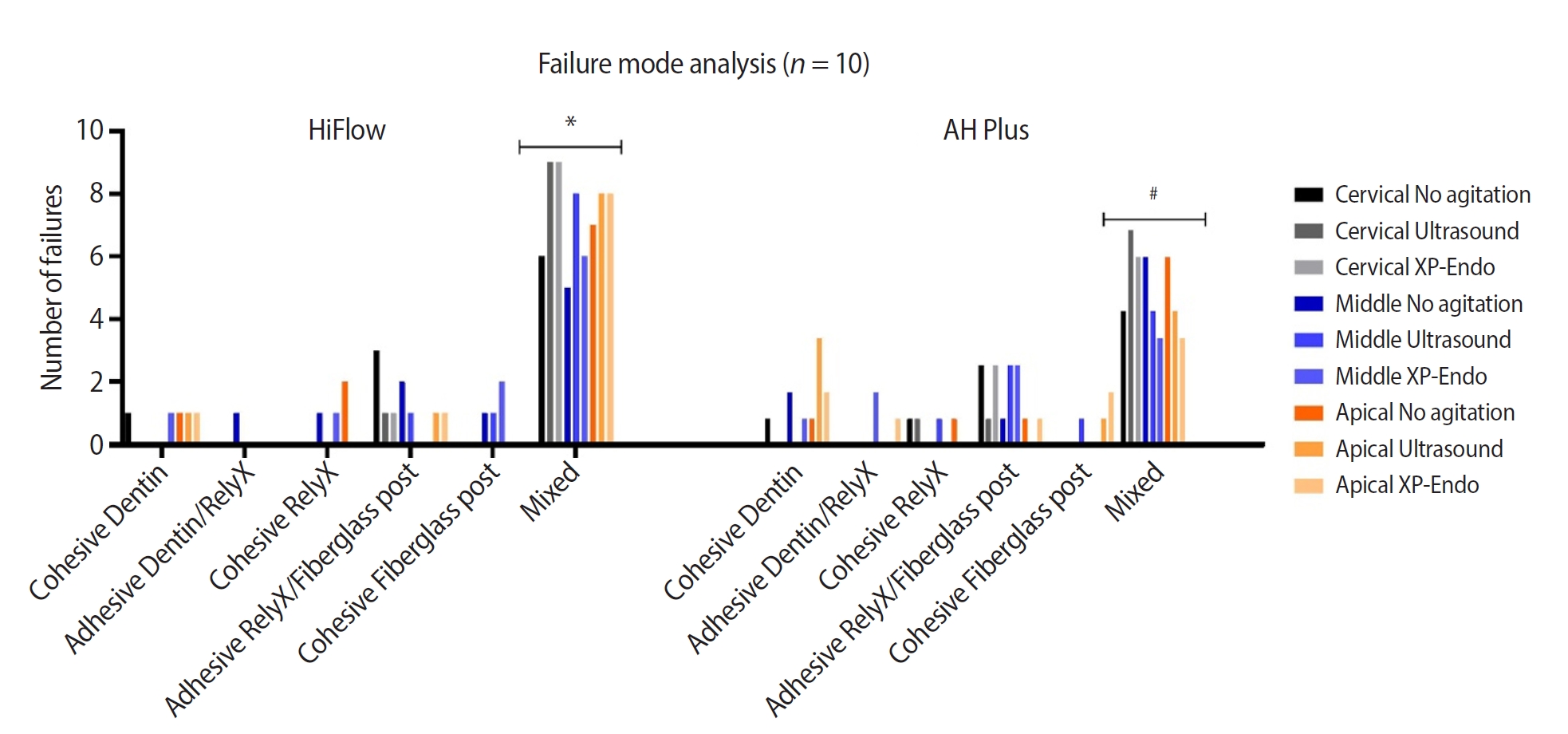
Seventy-two human teeth were selected. The canals were prepared with Reciproc 50 and Easy ProDesign 30/.10 and root filled according to the endodontic sealer groups: AH Plus or EndoSequence BC Sealer HiFlow. The samples were kept at 37ºC and 95% humidity for 28 days. During the post space preparation, the obturation was removed with Largo burs, and the groups were divided according to the irrigant agitation protocols (n = 12): no agitation, agitation with R1-Clearsonic associated with E1-Irrisonic ultrasonic inserts, or agitation with XP-endo Finisher R file. The fiberglass posts were cemented with RelyX ARC. The roots were sectioned into slices and submitted to the push-out test. Micro-computed tomography analysis was used to check the effectiveness of irrigating solution agitation in the elimination of remnants.
Results
The cleaning protocols with agitation were more effective in increasing the bond strength of posts to dentin for both sealer groups compared to non-agitation (p < 0.05). There was no difference between the same cleaning protocols for the different sealers. Among the different thirds, there was no statistical difference for the same sealer in the different cleaning protocols (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Both agitation protocols effectively clean root-filled canals sealed with resin-based and calcium silicate-based sealers during fiberglass post space preparation. These protocols result in improved bond strength compared to non-agitation methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cleaning efficacy and bond interaction of glycine-based air polishing and glass microparticles abrasion on dentin impregnated with premixed bioceramic sealer
Ândresson Aurélio Fernandes Martins, Maria Carolina Sidonio Alves, Bruno Martins Maciel, José Rodolfo Estruc Verbicário, João Felipe Besegato, Wilfredo Gustavo Escalante-Otárola, Milton Carlos Kuga
International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives.2026; 147: 104277. CrossRef - Effect of Endodontic Sealers on the Bond Strength of Glass Fibre Posts: A Systematic Review
Thiago Bessa Marconato Antunes, Juliana D. Bronzato, Vanessa Gallego Arias Pecorari, Jennifer Santos Pereira, Talita Tartari, Adriana de Jesus Soares, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes, Marina Angélica Marciano
Australian Endodontic Journal.2026;[Epub] CrossRef
- Cleaning efficacy and bond interaction of glycine-based air polishing and glass microparticles abrasion on dentin impregnated with premixed bioceramic sealer
- 4,009 View
- 215 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref

- Stress distribution of restorations in external cervical root resorption under occlusal and traumatic loads: a finite element analysis
- Padmapriya Ramanujam, Paul Kevin Abishek Karthikeyan, Vignesh Srinivasan, Selvakarthikeyan Ulaganathan, Velmurugan Natanasabapathy, Nandini Suresh
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e21. Published online May 21, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e21
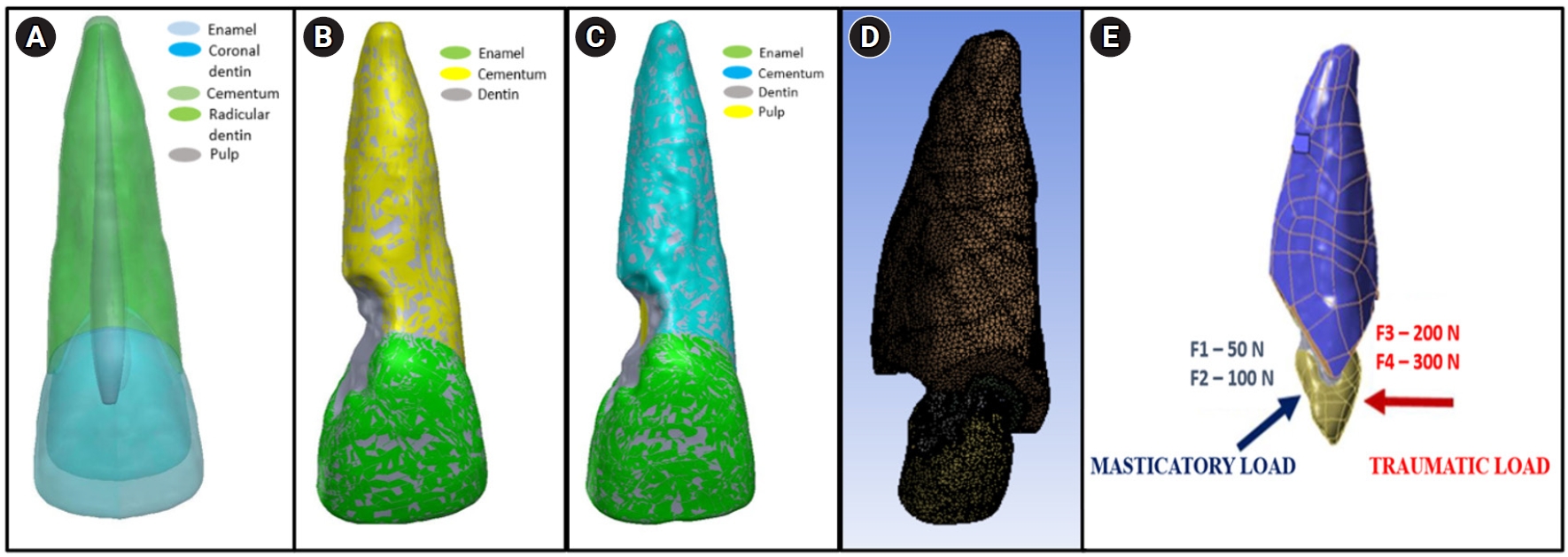
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - Objectives
This study analyzed the stress distribution in a maxillary central incisor with external cervical resorptive defect restored with different restorative materials under normal masticatory and traumatic loading conditions using finite element analysis.
Methods
Cone-beam computed tomography of an extracted intact incisor and created resorptive models (Patel’s 3D classification-2Bd and 2Bp) in the maxillary central incisor was performed for finite element models. The 2Bd models were restored either with glass ionomer cement (GIC)/Biodentine (Septodont) or a combination of both with composite resin. 2Bp models were restored externally with a combination technique and internally with root canal treatment. The other model was external restoration with GIC and internal with fiber post. Two masticatory loads were applied at 45˚ to the palatal aspect, and two traumatic loads were applied at 90˚ to the buccal aspect. Maximum von Mises stresses were calculated, and stress distribution patterns were studied.
Results
In 2Bd models, all restorative strategies decreased stress considerably, similar to the control model under all loads. In 2Bp models, the dentin component showed maximum stress at the deepest portion of the resorptive defect, which transfers into the adjacent pulp space. In 2Bp defects, a multilayered restoration externally and root canal treatment internally provides better stress distribution compared to the placement of a fiber post.
Conclusions
Increase in load, proportionally increased von Mises stress, despite the direction or angulation of the load. Multilayered restoration is preferred for 2Bd defects, and using an internal approach of root canal treatment is suggested to restore 2Bp defects.
- 2,105 View
- 138 Download

Case Report
- Surgical management of maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin after reestablishing maxillary sinus floor healing through a nonsurgical approach: a case report
- Eun-Sook Kang, Min-Kyeong Kim, Mi-Kyung Yu, Kyung-San Min
- Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(2):e12. Published online April 8, 2025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e12
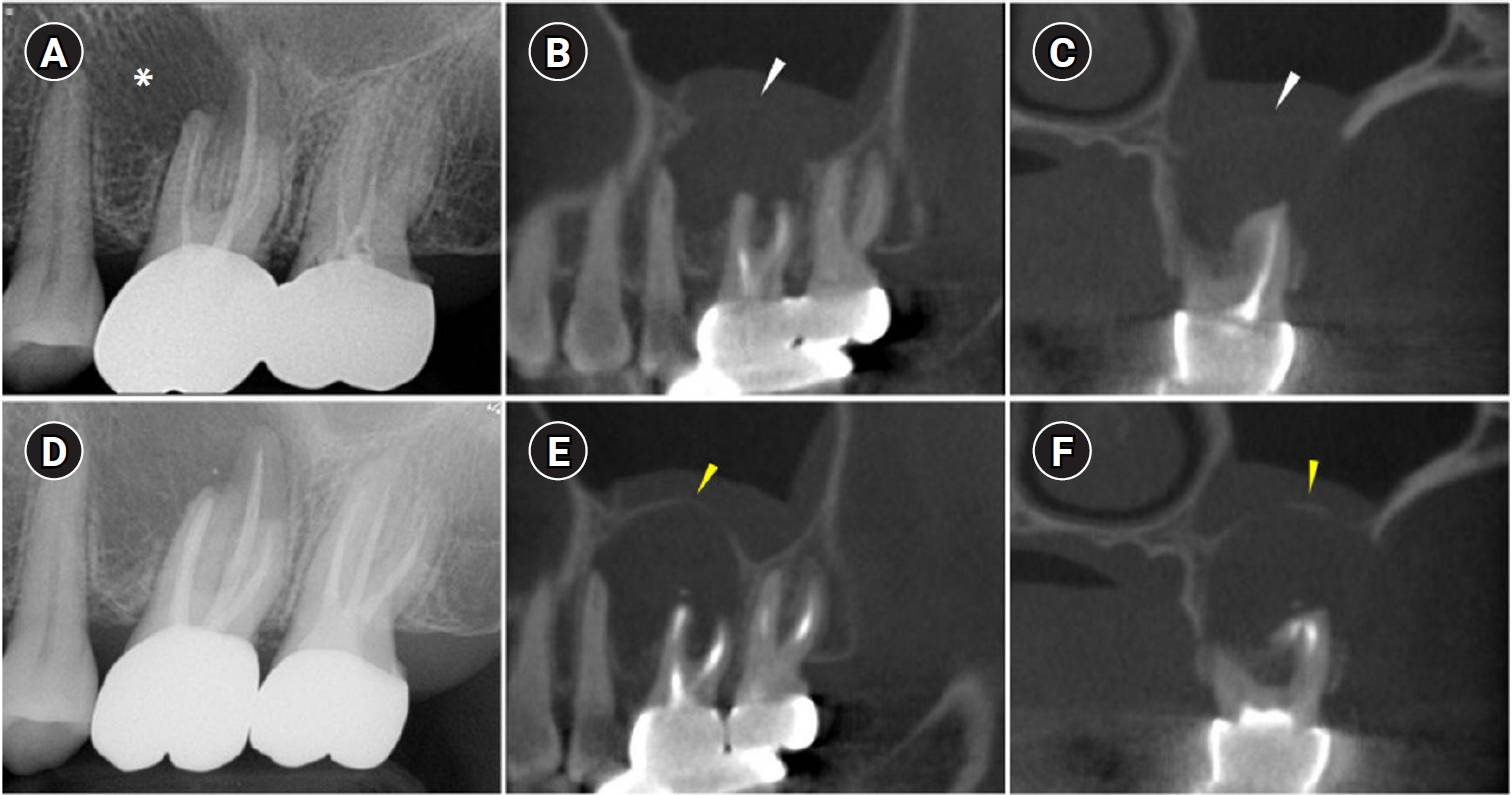
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader ePub
ePub - When root canal infections breach the maxillary sinus floor (MSF), maxillary sinusitis of endodontic origin (MSEO) can result. This case illustrates the surgical management of MSEO following the nonsurgical reestablishment of the MSF. A 55-year-old woman presented with left facial pain and was diagnosed with MSEO originating from the left upper first molar. Despite undergoing nonsurgical root canal treatment, there was no evidence of bony healing after 6 months. However, cone-beam computed tomographic (CBCT) scans revealed the reestablishment of MSF. Subsequently, surgical intervention was carried out using a dental operating microscope. Two years after surgery, CBCT images indicated that the mucosal edema had resolved, and the MSF was well reestablished. Preserving the MSF is crucial for the success of endodontic surgery. When MSEO is present, the integrity of the MSF must be assessed to determine appropriate treatment options.
- 4,151 View
- 211 Download


 KACD
KACD



 First
First Prev
Prev


