-
A micro-computed tomography evaluation of voids using calcium silicate-based materials in teeth with simulated internal root resorption
-
Vildan Tek, Sevinç Aktemur Türker
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(1):e5. Published online November 29, 2019
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e5
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
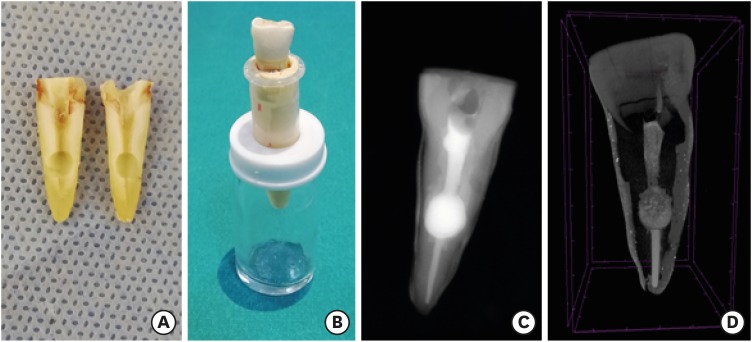
The obturation quality of MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC root canal sealer (RCS), and warm gutta-percha (WGP) in teeth with simulated internal root resorption (IRR) was evaluated by using micro-computed tomography. Materials and MethodsStandardized IRR cavities were created using 40 extracted maxillary central incisor teeth and randomly assigned into 4 groups (n = 10). IRR cavities were filled with MTA, Biodentine, Total Fill BC RCS (bulk-fill form) and WGP + Total Fill BC RCS. Percentage of voids between resorptive cavity walls and obturation material (external void), and inside the filling materials (internal voids) were measured. ResultsTotal Fill BC sealer in the bulk-fill form presented significantly highest values of external and internal void percentages (p < 0.05). Biodentine showed a significantly lowest external void percentage (p < 0.05). WGP + Total Fill BC RCS presented significantly lower values of internal void percentages than all groups (p < 0.05), except Biodentine (p > 0.05). ConclusionNone of the filling materials were created void-free obturation in resorption cavities. Biodentine may favor its application in teeth with IRR over Angelus MTA and bulk-fill form of Total Fill BC.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Removal of AH Plus Bioceramic Sealer from Artificial Internal Resorption Cavities Using Different Irrigation Activation Systems
Mine Büker, Meltem Sümbüllü, Emine Şimşek, Fadime Sena Sezer
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2025; 28(3): 383. CrossRef - Functional and Bioactive Performance of Premixed Bioceramic Sealers with Warm Obturation: A Scoping Review
Patryk Wiśniewski, Stanisław Krokosz, Małgorzata Pietruska, Anna Zalewska
Gels.2025; 11(11): 932. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effectiveness of different supplemental cleaning techniques in the retreatment of roots with small simulated internal resorption cavities: an in vitro comparative study
Sine Güngör Us, Özgür Uzun, Nazlı Merve Güngör
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Different Techniques and Materials for Filling in 3-dimensional Printed Teeth Replicas with Perforating Internal Resorption by Means of Micro–Computed Tomography
Angelo J.S. Torres-Carrillo, Helena C. Assis, Rodrigo E. Salazar-Gamarra, Leonardo Moreira Teodosio, Alice C. Silva-Sousa, Jardel F. Mazzi-Chaves, Priscila B. Ferreira-Soares, Manoel D. Sousa-Neto, Fabiane C. Lopes-Olhê
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 205. CrossRef - Three-Dimensional Measurement of Obturation Quality of Bioceramic Materials in Filling Artificial Internal Root Resorption Cavities Using Different Obturation Techniques: An In Vitro Comparative Study
Ammar M. Sharki, Ahmed H. Ali
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(7): 997. CrossRef - Evaluation of calcium hydroxide root canal filling materials by cone beam computed tomography and three-dimensional modeling
Asel Usdat Ozturk, Ekin Dogan, Venus Seyedoskuyi, Berk Senguler, Asli Topaloglu-Ak
Folia Medica.2024; 66(2): 250. CrossRef - Clinical applications of calcium silicate‐based materials: a narrative review
S Küçükkaya Eren
Australian Dental Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study root canal fillings
Gustavo De‐Deus, Erick Miranda Souza, Emmanuel João Nogueira Leal Silva, Felipe Gonçalves Belladonna, Marco Simões‐Carvalho, Daniele Moreira Cavalcante, Marco Aurélio Versiani
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S2): 384. CrossRef - An Updated Review on Properties and Indications of Calcium Silicate‐Based Cements in Endodontic Therapy
Fateme Eskandari, Alireza Razavian, Rozhina Hamidi, Khadije Yousefi, Susan Borzou, Zohaib Khurshid
International Journal of Dentistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy Of Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers In Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Hattan Mohammed Omar Baismail, Mohammed Ghazi Moiser Albalawi, Alaa Mofareh Thoilek Alanazi, Muhannad Atallah Saleem Alatawi, Badr Soliman Alhussain
Annals of Dental Specialty.2021; 9(1): 87. CrossRef
-
2,327
View
-
26
Download
-
10
Crossref
-
Incidence of apical crack formation and propagation during removal of root canal filling materials with different engine driven nickel-titanium instruments
-
Taha Özyürek, Vildan Tek, Koray Yılmaz, Gülşah Uslu
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(4):332-341. Published online November 4, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.4.332
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To determine the incidence of crack formation and propagation in apical root dentin after retreatment procedures performed using ProTaper Universal Retreatment (PTR), Mtwo-R, ProTaper Next (PTN), and Twisted File Adaptive (TFA) systems. Materials and MethodsThe study consisted of 120 extracted mandibular premolars. One millimeter from the apex of each tooth was ground perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth, and the apical surface was polished. Twenty teeth served as the negative control group. One hundred teeth were prepared, obturated, and then divided into 5 retreatment groups. The retreatment procedures were performed using the following files: PTR, Mtwo-R, PTN, TFA, and hand files. After filling material removal, apical enlargement was done using apical size 0.50 mm ProTaper Universal (PTU), Mtwo, PTN, TFA, and hand files. Digital images of the apical root surfaces were recorded before preparation, after preparation, after obturation, after filling removal, and after apical enlargement using a stereomicroscope. The images were then inspected for the presence of new apical cracks and crack propagation. Data were analyzed with χ2 tests using SPSS 21.0 software. ResultsNew cracks and crack propagation occurred in all the experimental groups during the retreatment process. Nickel-titanium rotary file systems caused significantly more apical crack formation and propagation than the hand files. The PTU system caused significantly more apical cracks than the other groups after the apical enlargement stage. ConclusionsThis study showed that retreatment procedures and apical enlargement after the use of retreatment files can cause crack formation and propagation in apical dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Microcracks induced by XP-endo retreatment system in root canals filled with bioceramic sealer: A micro-computed tomographic analysis
Sarah M. Alkahtany
The Saudi Dental Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of different retreatment methods on apical root microcracks initiation and propagation: An in vitro study
Shweta Lodha, Zinnie Nanda
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 175. CrossRef - Efficacy of Endodontic Files in Root Canal Retreatment: A Systematic Review of In Vitro Studies
Anna Soler-Doria, José Luis Sanz, Marcello Maddalone, Leopoldo Forner
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2025; 16(8): 293. CrossRef - Efficacy of Various Heat-treated Retreatment File Systems on Dentin Removal and Crack Analysis: An in vitro Study
Swathi Suresh, Pradeep Solete, Delphine Priscilla Antony, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Adimulapu Hima Sandeep, Sruthi Sairaman, Marco Cicciù, Giuseppe Minervini
Pesquisa Brasileira em Odontopediatria e Clínica Integrada.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A comparative evaluation of the dentinal microcracks formed and propagated during the removal of gutta-percha using hand and three rotary retreatment file systems: A micro-computed tomography study
Srivastava Sanjeev, Rita Gupta, Dubey Sandeep, Tewari Tanu, Shukla Namita, Singh Arohan
Endodontology.2023; 35(2): 155. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of incidence of dentinal defects after root canal preparation using hand, rotary, and reciprocating files: An ex vivo study
Debanjan Das, Sudipto Barai, Rohit Kumar, Sourav Bhattacharyya, AsimB Maity, Pushpa Shankarappa
Journal of International Oral Health.2022; 14(1): 78. CrossRef - Critical analysis of research methods and experimental models to study removal of root filling materials
Mahdi A. Ajina, Pratik K. Shah, Bun San Chong
International Endodontic Journal.2022; 55(S1): 119. CrossRef - Evaluation of Dentinal Crack Propagation, Amount of Gutta Percha Remaining and Time Required During Removal of Gutta Percha Using Two Different Rotary Instruments and Hand Instruments - An In vitro Study
S Tejaswi, A Singh, S Manglekar, UK Ambikathanaya, S Shetty
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2022; 25(4): 524. CrossRef - The Influence of Root Canal Preparation with ProTaper Next, WaveOne Gold, and Twisted Files on Dentine Crack Formation
Wojciech Eliasz, Beata Czarnecka, Anna Surdacka
Machines.2021; 9(12): 332. CrossRef - The potential effect of instrumentation with different nickel titanium rotary systems on dentinal crack formation—An in vitro study
Márk Fráter, András Jakab, Gábor Braunitzer, Zsolt Tóth, Katalin Nagy, Andrej M. Kielbassa
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0238790. CrossRef - Micro–computed Tomographic Assessment of the Residual Filling Volume, Apical Transportation, and Crack Formation after Retreatment with Reciproc and Reciproc Blue Systems in Curved Root Canals
Damla Kırıcı, Sezer Demirbuga, Ertuğrul Karataş
Journal of Endodontics.2020; 46(2): 238. CrossRef - Force and vibration generated in apical direction by three endodontic files of different kinematics during simulated canal preparation: An in vitro analytical study
Ankit Nayak, PK Kankar, Prashant K Jain, Niharika Jain
Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part H: Journal of Engineering in Medicine.2019; 233(8): 839. CrossRef - Effect of Aging on Dentinal Crack Formation after Treatment and Retreatment Procedures: a Micro-CT Study
Lilian Rachel de Lima Aboud, Bernardo Camargo dos Santos, Ricardo Tadeu Lopes, Leonardo Aboud Costa Viana, Miriam Fátima Zaccaro Scelza
Brazilian Dental Journal.2018; 29(6): 530. CrossRef
-
1,685
View
-
12
Download
-
13
Crossref
|