-
Effects of zinc oxide and calcium–doped zinc oxide nanocrystals on cytotoxicity and reactive oxygen species production in different cell culture models
-
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Juliane Zacour Marinho, Thaynara Rodrigues Silva, Noelio Oliveira Dantas, Jéssica Fernanda Sena Bonvicini, Ana Paula Turrioni
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e54. Published online October 19, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e54
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
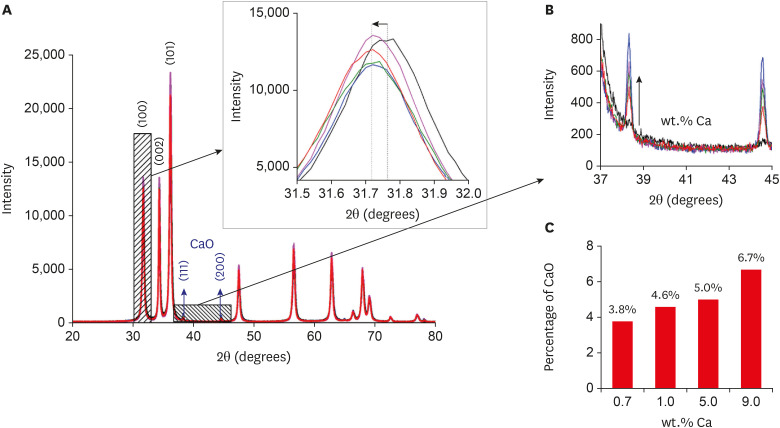
This study aimed to synthesize nanocrystals (NCs) of zinc oxide (ZnO) and calcium ion (Ca2+)-doped ZnO with different percentages of calcium oxide (CaO), to evaluate cytotoxicity and to assess the effects of the most promising NCs on cytotoxicity depending on lipopolysaccharide (LPS) stimulation. Materials and MethodsNanomaterials were synthesized (ZnO and ZnO:xCa, x = 0.7; 1.0; 5.0; 9.0) and characterized using X-ray diffractometry, scanning electron microscopy, and methylene blue degradation. SAOS-2 and RAW 264.7 were treated with NCs, and evaluated for viability using the MTT assay. NCs with lower cytotoxicity were maintained in contact with LPS-stimulated (+LPS) and nonstimulated (−LPS) human dental pulp cells (hDPCs). Cell viability, nitric oxide (NO), and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production were evaluated. Cells kept in culture medium or LPS served as negative and positive controls, respectively. One-way analysis of variance and the Dunnett test (α = 0.05) were used for statistical testing. ResultsZnO:0.7Ca and ZnO:1.0Ca at 10 µg/mL were not cytotoxic to SAOS-2 and RAW 264.7. +LPS and −LPS hDPCs treated with ZnO, ZnO:0.7Ca, and ZnO:1.0Ca presented similar NO production to negative control (p > 0.05) and lower production compared to positive control (p < 0.05). All NCs showed reduced ROS production compared with the positive control group both in +LPS and −LPS cells (p < 0.05). ConclusionsNCs were successfully synthesized. ZnO, ZnO:0.7Ca and ZnO:1.0Ca presented the highest percentages of cell viability, decreased ROS and NO production in +LPS cells, and maintenance of NO production at basal levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Waste-derived Ca and Zn-based bimetallic (Ca/Zn) nanorods encapsulated chitosan-based haemostatic dressing bandage: A step towards waste to bandages
Pooja Thakur, Rishabh Anand Omar, Neetu Talreja, Divya Chauhan, Mohammad Ashfaq
Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry.2025; 143: 327. CrossRef - Europium and calcium-co-doped TiO2 nanocrystals: tuning the biocompatibility and luminescence traceability of Drosophila melanogaster
Jerusa Maria de Oliveira, Larissa Iolanda M. de Almeida, Francisco Rubens Alves dos Santos, João Paulo S. de Carvalho, Amanda I. dos S. Barbosa, Marcus Andrei R. F. da Costa, Vanessa Tomaz Maciel, Gabriela L. de Souza, Alysson N. Magalhães, Marcos V. Verm
Environmental Science: Nano.2025; 12(1): 835. CrossRef - Development and evaluation of capsules loaded with red propolis extract and metallic nanoparticles using the ionic gelation method
Ilza Fernanda Barboza Duarte Rodrigues, Jéssica Maria Pereira, Lívia Maria Santos de Lima, Kathleen Gomes Lins Silva, Melissa Rosa Silva, Valdemir da Costa Silva, Salvana Priscylla Manso Costa, Ticiano Gomes do Nascimento, Adeildo Junior de Oliveira, John
Journal of Apicultural Research.2025; 64(4): 1151. CrossRef - Structural, optical, and magnetic behavior and the nucleation of a Griffiths-like phase in (Ca,V)-doped ZnO nanoparticles
S. Mrabet, N. Ihzaz, M. N. Bessadok, C. Vázquez-Vázquez, M. Alshammari, O. M. Lemine, D. Ananias, L. El Mir
Dalton Transactions.2025; 54(18): 7400. CrossRef - The effect of iron oxide synergism on the structural and magnetic properties of iron-doped ZnO
Adenilson F. dos Santos, Angela Marta da Silva, Thaís Karine de Lima, Noelio O. Dantas, Marcio A. Correa, Anielle Christine A. Silva
Next Materials.2025; 9: 101047. CrossRef - IN VITRO EVALUATION OF THE ANTI-LEISHMANIAL ROLE OF MILTEFOSINE-LOADED MESOPORUSZNO NANOPARTICLES IN RAW 264.7 MACROPHAGES
PARAG GHOSH, DILEEP KUMAR BHARATI, DIBYA DAS, SUBAS CHANDRA DINDA, ANIRBANDEEP BOSE
Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research.2025; : 231. CrossRef - Development of antibacterial dual-cure dental resin composites via tetrapod-shaped zinc oxide incorporation
Hwalim Lee, Yu-Jin Kim, Ye-Jin Yang, Jung-Hwan Lee, Hae-Hyoung Lee
Dental Materials.2024; 40(11): 1762. CrossRef - Investigation on the non-linear behaviour of silicon nanowires and assessment of the biosensing potential
M M A Hakim
Engineering Research Express.2023; 5(2): 025017. CrossRef - Evaluation of Cytotoxicity, Cell Attachment, and Elemental Characterization of Three Calcium Silicate-Based Sealers
Anahi de Paula Melo, Camila Maria Peres de Rosatto, Danilo Cassiano Ferraz, Gabriela Leite de Souza, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Materials.2023; 16(20): 6705. CrossRef - Metallic Nanoparticles: A New Frontier in the Fight Against Leishmaniasis
Rhanoica Oliveira Guerra, José Rodrigues do Carmo Neto, Tarcísio de Albuquerque Martins, Thaís Soares Farnesi de-Assunção, Virmondes Rodrigues Junior, Carlo José Freire de Oliveira, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Marcos Vinicius da Silva
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 29(26): 4547. CrossRef - In situ synthesis of zinc oxide/selenium composite for UV blocker application
Chaoqun Xia, Shi Liu, Baining Cui, Mingjun Li, Hongshui Wang, Chunyong Liang, Phong A. Tran, Yan Wang, Huan Zhou, Lei Yang
International Journal of Applied Ceramic Technology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Biocompatibility and Connectivity of Semiconductor Nanostructures for Cardiac Tissue Engineering Applications
Roberto Gaetani, Yuriy Derevyanchuk, Andrea Notargiacomo, Marialilia Pea, Massimiliano Renzi, Elisa Messina, Fabrizio Palma
Bioengineering.2022; 9(11): 621. CrossRef - Calcium-doped zinc oxide nanocrystals as an innovative intracanal medicament: a pilot study
Gabriela Leite de Souza, Thamara Eduarda Alves Magalhães, Gabrielle Alves Nunes Freitas, Nelly Xiomara Alvarado Lemus, Gabriella Lopes de Rezende Barbosa, Anielle Christine Almeida Silva, Camilla Christian Gomes Moura
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,924
View
-
13
Download
-
13
Crossref
|