-
Effect of an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent on the dentin shear bond strength of a universal adhesive
-
Sujin Kim, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(2):e14. Published online March 22, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e14
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
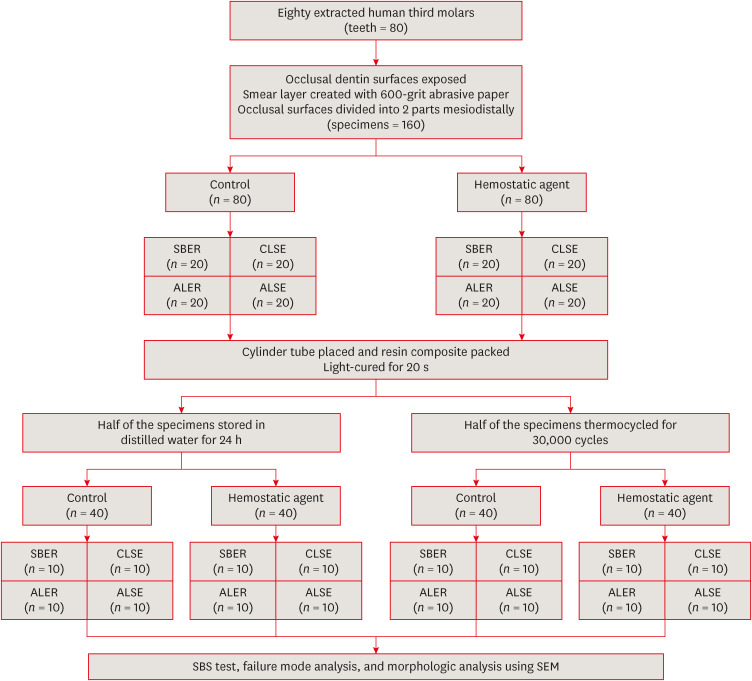
This study investigated the effect of an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a universal adhesive to dentin. Materials and MethodsEighty extracted human molars were trimmed at the occlusal dentin surfaces and divided mesiodistally. According to hemostatic agent application, specimens were randomly allocated into control (C) and hemostatic agent (Traxodent; H) groups. Each group was divided into 4 subgroups according to the adhesive system (n = 20): Scotchbond Multi-Purpose (SBER), Clearfil SE Bond (CLSE), All-Bond Universal etch-and-rinse mode (ALER), and All-Bond Universal self-etch mode (ALSE). SBS was measured for half of the specimens at 24 hours, and the other half were thermocycled in water baths (group T). Fracture surfaces were examined to determine the failure mode. The SBS was measured, and data were analyzed using 1-way analysis of variance, the Student’s t-test, and the Tukey honestly significant difference test (p = 0.05). ResultsNo significant differences in SBS were found between groups C and H for any adhesive system at 24 hours. After thermocycling, a statistically significant difference was observed between CT+ALSE and HT+ALSE (p < 0.05). When All-Bond Universal was applied to hemostatic agent-contaminated dentin, the SBS of H+ALSE was significantly lower than that of H+ALER (p < 0.05). The SBER subgroups showed no significant differences in SBS regardless of treatment and thermocycling. ConclusionsWhen exposed dentin was contaminated by an aluminum chloride hemostatic agent before dentin adhesive treatment, application of All-Bond Universal in etch-and-rinse mode was superior to self-etch mode.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Nature-driven blue-emissive N, S-CDs: Harnessing sequential "switch-off-on" fluorescence signals for detection of chrysin and Al³⁺ along with cellular imaging versatility
Maha Mohammad Abdel-Monem, Mohamed I. Walash, Asmaa Kamal El-Deen
Talanta Open.2025; : 100466. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of the Shear Bond Strength of Self-Adhesive and Glass Ionomer Cement to Dentin After Removal of Hemostatic Agents Using Different Cleansing Protocols: An In Vitro Study
Hemashree Namburajan, Mathew Chalakuzhiyil Abraham, Vidhyasankari N, Rajkumar K, Abhinayaa Suthagar, Vishnupriya Venkatasubramanian, Sindhuja Nagarajan
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Emalje- og dentinadhesiver: Avgjørende faser i klinisk behandling
Torgils Lægreid, Tom Paulseth, Arne Lund
Den norske tannlegeforenings Tidende.2024; 134(8): 604. CrossRef
-
2,603
View
-
65
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
3
Crossref
-
Mandibular bone necrosis after use of paraformaldehyde-containing paste
-
Chi-hwan Lee, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2016;41(4):332-337. Published online November 8, 2016
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2016.41.4.332
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Paraformaldehyde has been used in the past as a pulpotomy agent. However, it has a severe cytotoxic effect and may cause alveolar bone necrosis. Depulpin, a devitalizing agent containing 49% paraformaldehyde, is no longer used frequently due to its severe side effects. In the two cases described in the present study, Depulpin was used as a devitalizing agent during root canal treatment. It caused a gradual loss of sensibility in adjacent teeth, gingival necrosis, and osteomyelitis. This case report demonstrates the serious side effects of using a paraformaldehyde-containing paste as a devitalizing agent for pulp, particularly mandibular bone necrosis. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Numb chin syndrome caused by paraformaldehyde-containing devitalizing agent – Case report
Jyh-Kwei Chen, Yeung-Yi Hsu, Chun-Pin Chiang, Meng-Ling Chiang
Journal of Dental Sciences.2023; 18(2): 955. CrossRef - Non-radiation and non-drug–induced maxillary osteomyelitis: Study of underlying risk factors, presentation, management and treatment outcomes
Kumar Nilesh, Pankaj Patil, Digvijay Patil, Monica Patil
Medical Journal Armed Forces India.2022; 78: S145. CrossRef - Acute toxicity potential and impact on periodontal and periapical tissue of Pulp Out: A paste contained jatropha, sidaguri, and melittin
Maria Tanumihardja, A.M. Windha, N. Musfirah, G.K. Punggawa, Andi Fatima, A.H.M. Nur Fadhila, Esfandiary, Nurhayaty Natsir, Husni Cangara, Lukman Muslimin
Toxicology Reports.2022; 9: 1788. CrossRef - Comparative evaluation of the effect of two pulpal medicaments on pain and bleeding status of mandibular molars with irreversible pulpitis post-failure of inferior alveolar nerve block: a double-blind, randomized, clinical trial
Naomi Ranjan Singh, Lora Mishra, Ajinkya M. Pawar, Nike Kurniawati, Dian Agustin Wahjuningrum
PeerJ.2022; 10: e13397. CrossRef - Dental implant restoration of mandibular bone necrosis defects caused by use of paraformaldehyde-containing paste: A case report
Won-Pyo Lee, Ho-Keel Hwang, Hyoung-Hoon Jo
Oral Biology Research.2019; 43(1): 110. CrossRef - Is Panoramic Radiography an Accurate Imaging Technique for the Detection of Endodontically Treated Asymptomatic Apical Periodontitis?
Cosimo Nardi, Linda Calistri, Giulia Grazzini, Isacco Desideri, Chiara Lorini, Mariaelena Occhipinti, Francesco Mungai, Stefano Colagrande
Journal of Endodontics.2018; 44(10): 1500. CrossRef - A case of high density abnormality in x-ray findings of mandible caused by leakage of root canal filling paste
Haruko Kashiwamura, Kyoko Oka, Yoko Tuchihashi, Hanako Yoshioka, Mayumi Kato, Atsuko Baba, Toyohiro Kagawa, Kazuhiko Okamura, Masao Ozaki
Pediatric Dental Journal.2017; 27(3): 162. CrossRef
-
2,104
View
-
16
Download
-
7
Crossref
-
The effect of saliva decontamination procedures on dentin bond strength after universal adhesive curing
-
Jayang Kim, Sungok Hong, Yoorina Choi, Sujung Park
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(4):299-305. Published online October 2, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.4.299
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effectiveness of multiple decontamination procedures for salivary contamination after curing of a universal adhesive on dentin bond strength according to its etch modes. Materials and MethodsForty-two extracted bovine incisors were trimmed by exposing the labial dentin surfaces and embedded in cylindrical molds. A universal adhesive (All-Bond Universal, Bisco) was used. The teeth were randomly divided into groups according to etch mode and decontamination procedure. The adhesive was applied according to the manufacturer's instructions for a given etch mode. With the exception of the control groups, the cured adhesive was contaminated with saliva for 20 sec. In the self-etch group, the teeth were divided into three groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive. In the etch-and-rinse group, the teeth were divided into four groups: control, decontamination with rinsing and drying, decontamination with rinsing, drying, and adhesive, and decontamination with rinsing, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive. A composite resin (Filtek Z350XT, 3M ESPE) was used for filling and was cured on the treated surfaces. Shear bond strength was measured, and failure modes were evaluated. The data were subjected to one-way analysis of variation and Tukey's HSD test. ResultsThe etch-and-rinse subgroup that was decontaminated by rinse, drying, re-etching, and reapplication of adhesive showed a significantly higher bond strength. ConclusionsWhen salivary contamination occurs after curing of the universal adhesive, additional etching improves the bond strength to dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparative evaluation of different methods of saliva decontamination on microshear bond strength of composite to composite: An in vitro study
Sara Ordooei Javan, Reza Movahedian, Somayeh Hosseini Tabatabaei
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in Resin-Dentin Bonding: Evaluating Pre-Treatment Techniques for Improved Adhesion
Rim Bourgi
Journal of Dental Health and Oral Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef - Effect of contamination and decontamination methods on the bond strength of adhesive systems to dentin: A systematic review
Rim Bourgi, Carlos Enrique Cuevas‐Suarez, Walter Devoto, Ana Josefina Monjarás‐Ávila, Paulo Monteiro, Khalil Kharma, Monika Lukomska‐Szymanska, Louis Hardan
Journal of Esthetic and Restorative Dentistry.2023; 35(8): 1218. CrossRef - Universal adhesive application to contaminated/non-contaminated dentin with three different protocols: An in vitro shear bond strength and SEM analysis
Tuğçe BALOGLU GONCU, Nasibe Aycan YILMAZ
Dental Materials Journal.2022; 41(4): 633. CrossRef - Tükürük kontaminasyon/dekontaminasyonunun üniversal adezivlerin dentine bağlanma dayanımına etkisi
Cansu ATALAY, Aybüke USLU, Ece MERAL, Ayşe YAZICI, A. Atila ERTAN
Selcuk Dental Journal.2021; 8(3): 611. CrossRef - Bioactive glass ceramic can improve the bond strength of sealant/enamel?
R. E. Silveira, R. G. Vivanco, R. C. de Morais, G. Da Col dos Santos Pinto, F. de C. P. Pires-de-Souza
European Archives of Paediatric Dentistry.2019; 20(4): 325. CrossRef - Universal dental adhesives: Current status, laboratory testing, and clinical performance
Sanket Nagarkar, Nicole Theis‐Mahon, Jorge Perdigão
Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials.2019; 107(6): 2121. CrossRef - Effect of Saliva Decontamination on Bond Strength of 1-step Self-etching Adhesives to Dentin of Primary Posterior Teeth
Junhee Lee, Shin Kim, Taesung Jeong, Jonghyun Shin, Eungyung Lee, Jiyeon Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2019; 46(3): 274. CrossRef - Polymeric materials and films in dentistry: An overview
Dinesh Rokaya, Viritpon Srimaneepong, Janak Sapkota, Jiaqian Qin, Krisana Siraleartmukul, Vilailuck Siriwongrungson
Journal of Advanced Research.2018; 14: 25. CrossRef - Cytotoxicity of Light-Cured Dental Materials according to Different Sample Preparation Methods
Myung-Jin Lee, Mi-Joo Kim, Jae-Sung Kwon, Sang-Bae Lee, Kwang-Mahn Kim
Materials.2017; 10(3): 288. CrossRef
-
2,145
View
-
14
Download
-
10
Crossref
|