-
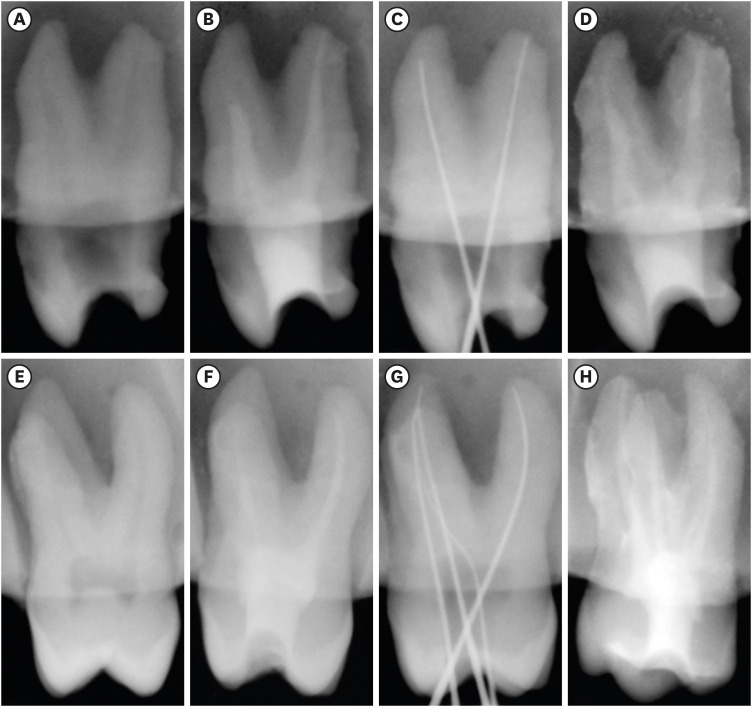
Enhanced visualization of the root canal morphology using a chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution
-
Shashirekha Govind, Amit Jena, Satabdi Pattanaik, Mahaprasad Anarasi, Satyajit Mohapatra, Vinay Shivagange
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(3):e33. Published online June 4, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e33
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to investigate the efficacy of ionic and non-ionic-based contrast media (in vitro study) and the combinatorial effect of chitosan-based endo-radiopaque solution (CERS) (in vivo study) for visualization of the root canal anatomy. Materials and MethodsIn vitro study (120 teeth): The root canal of maxillary premolars and molars (in vitro group 1 and 2 respectively, n = 60 each) were analyzed using 4 different contrast media (subgroups: Omnipaque 350, Iopamidol, Xenetix 350, and Urografin 76; n = 15 each) in combination with 5.25% sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl). Based on the results of the in vitro study, in vivo study (80 teeth) was done to compare Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl with CERS (in vivo group 1 and 2 respectively, n = 40 each) on maxillary and mandibular premolars and molars. Two endodontists used radiovisiography to assess the depth of ingress and identify the aberrant root anatomy after access cavity preparation, and after initial cleaning and shaping of canals. Kruskal-Wallis test was used for in vitro comparison (p < 0.05), and Wilcoxon signed-rank test and Mann-Whitney U test for in vivo analysis (p < 0.01). ResultsIn vitro study, Xenetix 350 + 5.25% NaOCl facilitated a significant higher visualization (p < 0.05). For in vivo study, CERS had a statistically significant depth of ingress (p < 0.01), and was efficient in identifying the aberrant root canal anatomy of premolars and molars. ConclusionsCERS facilitates better visualization of the root canal anatomy of human premolars and molars.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Influence of irrigating solutions on the hydration of calcium silicate-based dental biomaterials: An in vitro study
Pradeep M. Divya, Amit Jena, Saumyakanta Mohanty, Govind Shashirekha, Rashmi Rekha Mallick, Priyanka Sarangi
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(8): 758. CrossRef - Improving Endodontic Radiograph Interpretation with TV-CLAHE for Enhanced Root Canal Detection
Barbara Obuchowicz, Joanna Zarzecka, Michał Strzelecki, Marzena Jakubowska, Rafał Obuchowicz, Adam Piórkowski, Elżbieta Zarzecka-Francica, Julia Lasek
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2025; 14(15): 5554. CrossRef - Efficacy of sonic and ultrasonic activation on irrigant penetration in different tapered preparations: An in vitro study
M. Rama Sowmya, Kavalipurapu Venkata Teja, Pradeep Solete, Sahil Choudhari, S Delphine Priscilla Antony, Mohammed Mustafa
Endodontology.2024; 36(4): 370. CrossRef - Analysis of the value of visualized root canal technique in the clinical treatment of endodontics
Nana SUN, Nannan WANG, Xin QIAN
Panminerva Medica.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
-
1,566
View
-
18
Download
-
2
Web of Science
-
4
Crossref
|