-
Effect of post space preparation drills on the incidence of root dentin defects
-
Thaíse Ayres Bezerra Zuli, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Gislaine Figueiredo Zarza Arguello Gonçalves, Aurélio Rosa da Silva Júnior, Álvaro Henrique Borges, Andreza Maria Fábio Aranha
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e53. Published online October 16, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e53
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
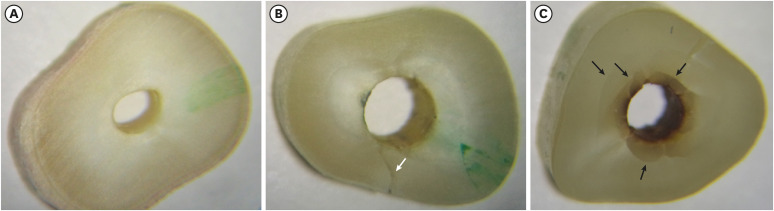
This study investigated the incidence of root dentin defects after the use of different post space preparation (PSP) drills. Materials and MethodsSeventy-two bovine incisors were selected and obtained 14-mm-long root sections. Twelve roots served as controls with no intervention (G1). The 60 root canals remaining were instrumented using the crown-down technique with the ProTaper Next system and obturated using the lateral condensation technique. Specimens were randomly distributed into 5 groups (n = 12) according to the operative steps performed: G2, root canal instrumentation and filling (I+F); G3, I+F and PSP with Gates-Glidden drills; G4, I+F and PSP with Largo-Peeso reamers; G5, I+F and PSP with Exacto drill; and G6, I+F and PSP with WhitePost drill. Roots were sectioned at 3, 6, 9, and 12 mm from the apex, and digital images were captured. The presence of root dentin defects was recorded. Data were analyzed by the χ2 test, with p < 0.05 considered to indicate statistical significance. ResultsRoot dentin defects were observed in 39.6% of the root sections. No defects were observed in G1. G5 had significantly more cracks and craze lines than G1, G2, and G3 (p < 0.05), and more fractures than G1, G2, G3, and G4 (p < 0.05). When all root sections were analyzed together, significantly more defects were observed at the 12-mm level than at the 3-mm level (p < 0.05). ConclusionsPSP drills caused defects in the root dentin. Gates-Glidden drills caused fewer root defects than Largo-Peeso reamers and Exacto drills.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of dentinal crack formation during post space preparation using different fiber post systems with micro-computed tomography
Ayşe Nur Kuşuçar, Damla Kırıcı
BMC Oral Health.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Fracture and Crack Behavior of Weakened Incisors Restored With Fiber Posts, Polyethylene Reinforcement, or 3D-Printed Endocrowns
Diana Codas-Duarte, Laís L Pelozo, Jardel F Mazzi-Chaves, Fabiane C Lopes-Olhê, Manoel D Sousa-Neto, Aline E Souza-Gabriel
Cureus.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Selecting drill size for post space preparation based on final endodontic radiographs: An in vitro study
Farzaneh Farid, Julfikar Haider, Marjan Sadeghpour Shahab, Nika Rezaeikalantari
Technology and Health Care.2024; 32(4): 2575. CrossRef - Cone Beam Computed Tomography Analysis of Post Space in Bifurcated Premolars Using ParaPost and Peeso Reamer Drills
Abdulaziz Saleh Alqahtani, Omar Nasser Almonabhi, Abdulmajeed Moh. Almutairi, Reem R. Alnatsha
The Open Dentistry Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Comparative Evaluation of Real-Time Guided Dynamic Navigation and Conventional Techniques for Post Space Preparation During Post Endodontic Management: An In Vitro Study
Sherifa Shervani, Sihivahanan Dhanasekaran, Vijay Venkatesh
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
Giulliano C. Serpa, Orlando A. Guedes, Neurinelma S. S. Freitas, Julio A. Silva, Carlos Estrela, Daniel A. Decurcio
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 190. CrossRef
-
2,795
View
-
35
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Comparative analysis of physicochemical properties of root perforation sealer materials
-
Maura Cristiane Gonçales Orçati Dorileo, Fábio Luis Miranda Pedro, Matheus Coelho Bandeca, Orlando Aguirre Guedes, Ricardo Dalla Villa, Alvaro Henrique Borges
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(3):201-209. Published online June 30, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.3.201
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the solubility, dimensional alteration, pH, electrical conductivity, and radiopacity of root perforation sealer materials. Materials and MethodsFor the pH test, the samples were immersed in distilled water for different periods of time. Then, the samples were retained in plastic recipients, and the electrical conductivity of the solution was measured. The solubility, dimensional alteration, and radiopacity properties were evaluated according to Specification No. 57 of the American National Standards Institute/American Dental Association (ANSI/ADA). Statistical analyses were carried out using analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Tukey's test at a significance level of 5%. When the sample distribution was not normal, a nonparametric ANOVA was performed with a Kruskal-Wallis test (α = 0.05). ResultsThe results showed that white structural Portland cement (PC) had the highest solubility, while mineral trioxide aggregate (MTA)-based cements, ProRoot MTA (Dentsply-Tulsa Dental) and MTA BIO (Ângelus Ind. Prod.), had the lowest values. MTA BIO showed the lowest dimensional alteration values and white PC presented the highest values. No differences among the tested materials were observed in the the pH and electrical conductivity analyses. Only the MTA-based cements met the ANSI/ADA recommendations regarding radiopacity, overcoming the three steps of the aluminum step wedge. ConclusionsOn the basis of these results, we concluded that the values of solubility and dimensional alteration of the materials were in accordance with the ANSI/ADA specifications. PCs did not fulfill the ANSI/ADA requirements regarding radiopacity. No differences were observed among the materials with respect to the pH and electrical conductivity analyses.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Chemical and in vivo analyses of calcium silicate‐based materials in bone and connective tissues
Ana Cristina Padilha Janini, Lauter Eston Pelepenko, Brenda Fornazaro Moraes, Victor Augusto Benedicto dos Santos, Matheus Barros‐Costa, Isabela Alvarenga Maciel dos Santos, Fábio Roberto de Souza Batista, Juliana de Aguiar Silveira Meira, Mariza Akemi Ma
International Endodontic Journal.2025; 58(3): 484. CrossRef - A comparative study on solubility of root end filling materials - An in vitro study
Supriya Makam, Geeta Hiremath, Balaram Naik
Endodontology.2025; 37(2): 205. CrossRef - Physicochemical and antibacterial properties of ZnO/chitosan-modified mineral trioxide aggregate composites
Mariyam Mariyam, Siti Sunarintyas, Leny Yuliatun, Dyah Irnawati, Adhi Dwi Hatmanto, Nuryono Nuryono
Case Studies in Chemical and Environmental Engineering.2024; 9: 100749. CrossRef - Portland Cement: An Overview as a Root Repair Material
Shahriar Shahi, Elaheh Fakhri, Hamidreza Yavari, Solmaz Maleki Dizaj, Sara Salatin, Khadijeh Khezri, Victor Feitosa
BioMed Research International.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A micro-computed tomographic study using a novel test model to assess the filling ability and volumetric changes of bioceramic root repair materials
Fernanda Ferrari Esteves Torres, Jader Camilo Pinto, Gabriella Oliveira Figueira, Juliane Maria Guerreiro-Tanomaru, Mario Tanomaru-Filho
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - COMPARISON OF MINERAL TRIOXIDE AGGREGATE, ENDOSEQUENCE ROOT REPAIR MATERIAL, AND BIODENTINE USED FOR REPAIRING ROOT PERFORATIONS: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Faisal ALGHAMDİ, Esraa ALJAHDALİ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2019; 22(4): 469. CrossRef - Effects of the addition of nanoparticulate calcium carbonate on setting time, dimensional change, compressive strength, solubility and pH of MTA
A. Bernardi, E. A. Bortoluzzi, W. T. Felippe, M. C. S. Felippe, W. S. Wan, C. S. Teixeira
International Endodontic Journal.2017; 50(1): 97. CrossRef - The use of a biocompatible cement in endodontic surgery. A randomized clinical trial 1
Sérgio Ribeiro da Silva, José Dias da Silva Neto, Taylor Brandão Schnaider, Daniela Francescato Veiga, Neil Ferreira Novo, Marcos Mesquita Filho, Lydia Masako Ferreira
Acta Cirurgica Brasileira.2016; 31(6): 422. CrossRef - Evaluation of Sealing Effect and Working Time of Root Canal Filling MTA Materials
Hyojin Kim, Youngjin Kim, Soonhyeun Nam, Kwon Taeyub, Hyunjung Kim
THE JOURNAL OF THE KOREAN ACADEMY OF PEDTATRIC DENTISTRY.2016; 43(2): 129. CrossRef - Portland cement versus MTA as a root-end filling material. A pilot study
Sérgio Ribeiro da Silva, José Dias da Silva Neto, Daniela Francescato Veiga, Taylor Brandão Schnaider, Lydia Masako Ferreira
Acta Cirurgica Brasileira.2015; 30(2): 160. CrossRef
-
1,813
View
-
7
Download
-
10
Crossref
|