-
Flow characteristics and alkalinity of novel bioceramic root canal sealers
-
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Sidiropoulos, Elisabeth Koulaouzidou, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(4):e42. Published online August 18, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e42
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objective
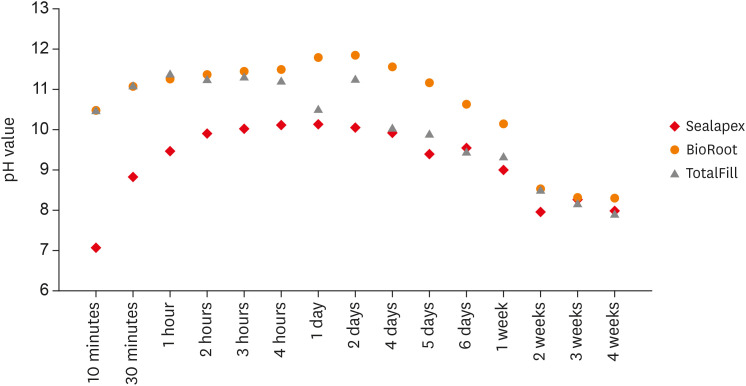
This study aimed to examine the physical properties (pH and flow) of 2 novel bioceramic sealers. Materials and MethodsThe tested sealers were a calcium hydroxide sealer (Sealapex) and 2 bioceramic sealers (BioRoot RCS and TotalFill BC Sealer). Flow measurements were conducted according to ISO 6876/2012, with a press method of 0.05 mL of sealer. The pH of fresh samples was tested immediately after manipulation, while set samples were stored for 3 times the recommended setting time. The predetermined time intervals ranged from 3 minutes to 24 hours for fresh samples and from 10 minutes to 7 days and 4 weeks for the set samples. Analysis of variance was performed, with p = 0.05 considered indicating significance. ResultsThe mean flow values were 26.99 mm for BioRoot, 28.19 for Sealapex, and 30.8 mm for TotalFill BC Sealer, satisfying the ISO standard. In the set samples, BioRoot RCS had higher pH values at 24 hours to 1 week after immersion in distilled water. At 2 weeks, both bioceramic sealers had similar pH values, greater than that of Sealapex. In the fresh samples, the bioceramic sealers had significantly higher initial pH values than Sealapex (p < 0.05). At 24 hours post-immersion, all sealers showed an alkaline pH, with the highest pH observed for TotalFill. ConclusionsThe TotalFill BC Sealer demonstrated the highest flow. The bioceramic sealers initially presented higher alkaline activity than the polymeric calcium hydroxide sealer. However, at 3 and 4 weeks post-immersion, all sealers had similar pH values.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Physicochemical properties of AH plus bioceramic sealer, Bio-C Sealer, and ADseal root canal sealer
Tamer M. Hamdy, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Shehabeldin Saber
Head & Face Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Characterization and Assessment of Physical Properties of 3 Single Syringe Hydraulic Cement–based Sealers
Veksina Raman, Josette Camilleri
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(3): 381. CrossRef - The Impact of Silver Nanoparticles on Dentinal Tubule Penetration of Endodontic Bioceramic Sealer
Sundus Bukhary, Sarah Alkahtany, Amal Almohaimede, Nourah Alkhayatt, Shahad Alsulaiman, Salma Alohali
Applied Sciences.2024; 14(24): 11639. CrossRef - Influence of root canal moisture on the penetration of TotalFill bioceramic sealer into the dentinal tubules: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Archika M Singh, Tarek M Elsewify, Walid S El-Sayed, Husam H Nuawafleh, Ranya F Elemam, Bassem M Eid
Saudi Endodontic Journal.2024; 14(2): 187. CrossRef - Unusual Canal Morphology in Mandibular Premolars With Two Distal and One Mesial Canal: A Case Series
Jinesh A, Sanjana Jayakumar Nair, Saurabh Gupta, Harsh Chansoria, Gaurav Rawat
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A scientometric, bibliometric, and thematic map analysis of hydraulic calcium silicate root canal sealers
Anastasios Katakidis, Konstantinos Kodonas, Anastasia Fardi, Christos Gogos
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal, chemical and physical analysis of VDW.1Seal, Fill Root ST, and ADseal root canal sealers
Shehabeldin Saber, Manar M. Galal, Amira Galal Ismail, Tamer M. Hamdy
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - α-tricalcium phosphate/fluorapatite-based cement - promising dental root canal filling material
Abdul Kazuz, Zeljko Radovanovic, Djordje Veljovic, Vesna Kojic, Dimitar Jakimov, Tamara Vlajic-Tovilovic, Vesna Miletic, Rada Petrovic, Djordje Janackovic
Processing and Application of Ceramics.2022; 16(1): 22. CrossRef
-
2,280
View
-
23
Download
-
8
Crossref
-
Top 50 cited articles on dental stem cell research
-
Konstantinos Kodonas, Anastasia Fardi, Christos Gogos, Nikolaos Economides
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(2):e17. Published online February 11, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e17
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
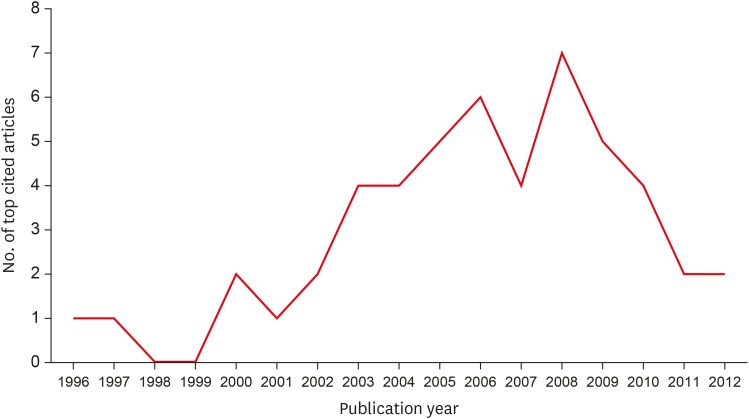
Citation analysis provides a unique insight into how scientific interests and research trends have changed over time. The aim of this study was to report on the 50 top-cited papers in dental stem cell research using the Science Citation Index Expanded provided by the Web of Science database to determine the academic importance of each contribution. Materials and MethodsAfter the screening, article title and type, total citations and citations per year, publication journal, publication year, first and senior authors, country of origin, institution, and university of reprint author were documented for the 50 top-cited articles in dental stem cell research. Keyword analysis was performed to determine which keywords were most/least popular. ResultsTop 50-cited articles were cited between 179 to 2,275 times. The majority of papers were published in 2008 and originated from the United States with the highest contribution from the National Institute of Dental & Craniofacial Research. Journal of Dental Research published the highest number of top-cited articles, followed by Stem Cells and Journal of Endodontics. The greatest number of articles was published by two individual authors, Shi and Gronthos. Among 197 unique keywords, dental pulp stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells were the most frequently used. Thirty-eight of the 50 most cited articles were original articles, and 37 of them were in the field of basic science. ConclusionsBasic science studies in dental stem cell research published in high impact factor journals had the highest citation rates.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Establishment of Dental Pulp Cell Culture System for Analyzing Dentinogenesis in Mouse Incisors
Yuka Kato, Insoon Chang, Satoshi Yokose
Dentistry Journal.2025; 13(6): 270. CrossRef - Revitalizing Dental Diagnostics: A Bibliometric Analysis of the Rising Impact of 3D Imaging in Dentistry
Ravinder S Saini, Mario Alberto Alarcón-Sánchez, Naseer Ahmed, Artak Heboyan
The Journal of Basic and Clinical Dentistry.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Contemporary research trends on nanoparticles in endodontics: a bibliometric and scientometric analysis of the top 100 most-cited articles
Sıla Nur Usta, Zeliha Uğur-Aydın, Kadriye Demirkaya, Cumhur Aydın
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The 100 top-cited articles in uveitis from 1950 to 2022
Li Huang, Wei Yang, Tianyu Yao, Zhiru Zhang, Xiaorong Gao, Yujiao Dan, Yue He
International Ophthalmology.2023; 43(12): 4631. CrossRef - The 50 most-cited articles on temporomandibular disorders: A bibliometric analysis
Martina Ferrillo, Vittorio Gallo, Lorenzo Lippi, Alessandro Bruni, Roberta Montrella, Claudio Curci, Dario Calafiore, Marco Invernizzi, Mario Migliario, Alessandro de Sire
Journal of Back and Musculoskeletal Rehabilitation.2023; 36(2): 279. CrossRef - The 50 most-cited articles on clear aligner treatment: A bibliometric and visualized analysis
Alessandro Bruni, Francesca Giulia Serra, Vittorio Gallo, Andrea Deregibus, Tommaso Castroflorio
American Journal of Orthodontics and Dentofacial Orthopedics.2021; 159(4): e343. CrossRef
-
2,283
View
-
14
Download
-
6
Crossref
|