-
Concentrated growth factor scaffold-based pulpotomy of permanent molars with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis
-
Arthi K. Harith, Vishnupriya Koteeswaran, Dinesh Kowsky, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan, Suresh Nandini
-
Restor Dent Endod 2025;50(1):e1. Published online January 17, 2025
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2025.50.e1
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
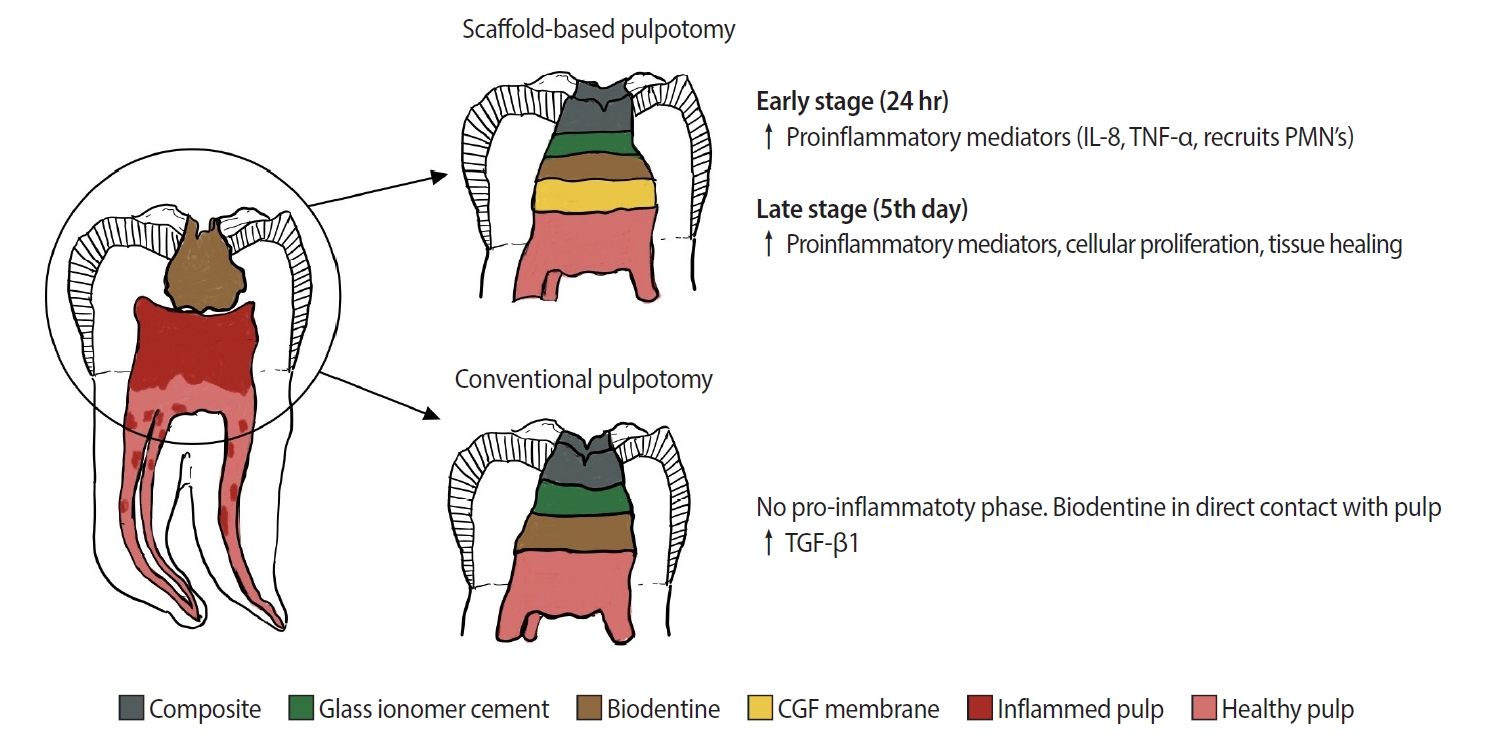
Pulpotomy is a minimally invasive procedure that aims to retain the vitality of the radicular pulp by removing the inflamed coronal pulp tissue. This case series presents the successful management of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis by pulpotomy with concentrated growth factor (CGF) scaffolds.
Methods
Six permanent mandibular molars with a diagnosis of symptomatic irreversible pulpitis were included. Under Local anesthesia and rubber dam isolation, caries were excavated using high-speed bur under coolant. Full coronal pulpotomy was done and hemostasis was achieved. CGF membrane was prepared and placed over the radicular pulp and layered with Biodentine (Septodont). Final restoration of type IX glass ionomer cement and bulk fill composite resin was placed. Patients were assessed for various clinical and radiographic parameters at intervals of 1 week and 3, 6, and 12 months. Five patients fulfilled the success criteria at the end of 1 year.
Results
Pulpotomy is considered an alternative treatment modality for root canal treatment in symptomatic irreversible pulpitis aiming at alleviating symptoms and maintaining vitality. CGF scaffold when used as a capping material acts as a reservoir for growth factors with anti-inflammatory properties and enhances healing.
Conclusions
Scaffold-based pulpotomy can be considered a biological approach to healing inflamed pulp.
-
Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
-
Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(2):149-154. Published online March 4, 2015
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.2.149
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study evaluated the penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate (CHX) into root dentinal tubules and the influence of passive ultrasonic irrigation (PUI) using a confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM). Materials and MethodsTwenty freshly extracted anterior teeth were decoronated and instrumented using Mtwo rotary files up to size 40, 4% taper. The samples were randomly divided into two groups (n = 10), that is, conventional syringe irrigation (CSI) and PUI. CHX was mixed with Rhodamine B dye and was used as the final irrigant. The teeth were sectioned at coronal, middle and apical levels and viewed under CLSM to record the penetration depth of CHX. The data were statistically analyzed using Kruskal-Wallis and Mann-Whitney U tests. ResultsThe mean penetration depths of 2% CHX in coronal, middle and apical thirds were 138 µm, 80 µm and 44 µm in CSI group, respectively, whereas the mean penetration depths were 209 µm, 138 µm and 72 µm respectively in PUI group. Statistically significant difference was present between CSI group and PUI group at all three levels (p < 0.01 for coronal third and p < 0.001 for middle and apical thirds). On intragroup analysis, both groups showed statistically significant difference among three levels (p < 0.001). ConclusionsPenetration depth of 2% CHX into root dentinal tubules is deeper in coronal third when compared to middle and apical third. PUI aided in deeper penetration of 2% CHX into dentinal tubules when compared to conventional syringe irrigation at all three levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The ability of different diffusing enhancers to deliver chlorhexidine into dentinal tubules: An in vitro evaluation
Yi Luo, Mengting Duan, Runze Liu, Pei Liu, Wei Fan, Bing Fan
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(4): 2226. CrossRef - The effect of 2% chlorhexidine iontophoresis on dentin sealing ability of etch-and-rinse adhesive: An in vitro study
Kanittha Kijsamanmith, Panisara Srisatayasatien, Nichapa Thanindratarn, Chanisa Vichainarong, Jirapat Panyasukum
Journal of Dental Sciences.2024; 19(2): 846. CrossRef - Influence of different presentation forms of chlorhexidine on contaminated root canals during agitation
Ana B. S. Lopes, Augusto R. Lima, Juliana D. Bronzato, Daniel R. Herrera, Priscila A. Francisco, Maria C. C. Carvalho, Gabriel Abuna, Mario Sinhoreti, Brenda P. F. A. Gomes
Australian Endodontic Journal.2024; 50(3): 513. CrossRef - Evaluation of the transdentinal capability of the intrinsic antibacterial cetylpyridinium chloride/cholesterol sterosomes in vitro and in vivo
Xiaojun Yang, Chaoning Zhan, Tianjiao Cheng, Minchun Huang, Weiwen Ge, Yiqing Zhang, Ting Chen, Yanli Lu, Zhong‐Kai Cui, Jin Hou
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(2): 245. CrossRef - Dentinal tubule penetration of sodium hypochlorite in root canals with and without mechanical preparation and different irrigant activation methods
Renata Aqel de Oliveira, Theodoro Weissheimer, Gabriel Barcelos Só, Ricardo Abreu da Rosa, Matheus Albino Souza, Rodrigo Gonçalves Ribeiro, Marcus Vinicius Reis Só
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of Lipidic Nanoplatform for Intra-Oral Delivery of Chlorhexidine: Characterization, Biocompatibility, and Assessment of Depth of Penetration in Extracted Human Teeth
Krishnaraj Somyaji Shirur, Bharath Singh Padya, Abhijeet Pandey, Manasa Manjunath Hegde, Aparna I. Narayan, Bola Sadashiva Satish Rao, Varadaraj G. Bhat, Srinivas Mutalik
Nanomaterials.2022; 12(19): 3372. CrossRef - Value addition property of a cationic surfactant on endodontic irrigant: A confocal laser scanning microscope study
Sembagalakshmi Thirunarayanan, MithraN Hegde
Journal of Conservative Dentistry.2022; 25(4): 380. CrossRef - The effect of different irrigants on sealer penetration into dentinal tubules with and without activation, using confocal scanning microscope
HelaylA Alshaibani, ShibuThomas Mathew
Journal of the International Clinical Dental Research Organization.2022; 14(1): 37. CrossRef - Calcium hydroxide/iodoform nanoparticles as an intracanal filling medication: synthesis, characterization, and in vitro study using a bovine primary tooth model
Arturo Garrocho-Rangel, Diana María Escobar-García, Mariana Gutiérrez-Sánchez, Denisse Herrera-Badillo, Fernanda Carranco-Rodríguez, Juan Carlos Flores-Arriaga, Amaury Pozos-Guillén
Odontology.2021; 109(3): 687. CrossRef - The influence of irrigant activation, concentration and contact time on sodium hypochlorite penetration into root dentine: an ex vivo experiment
S. S. Virdee, D. J. J. Farnell, M. A. Silva, J. Camilleri, P. R. Cooper, P. L. Tomson
International Endodontic Journal.2020; 53(7): 986. CrossRef - Efficacy of different irrigation methods on dentinal tubule penetration of Chlorhexidine, QMix and Irritrol: A confocal laser scanning microscopy study
Meltem Küçük, Fatma Kermeoğlu
Australian Endodontic Journal.2019; 45(2): 202. CrossRef - Sodium hypochlorite penetration into dentinal tubules after manual dynamic agitation and ultrasonic activation: a histochemical evaluation
Luigi Generali, Erica Campolongo, Ugo Consolo, Carlo Bertoldi, Luciano Giardino, Francesco Cavani
Odontology.2018; 106(4): 454. CrossRef - Push-out bond strength and dentinal tubule penetration of different root canal sealers used with coated core materials
Derya Deniz Sungur, Nuhan Purali, Erdal Coşgun, Semra Calt
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(2): 114. CrossRef
-
1,683
View
-
16
Download
-
13
Crossref
|