-
A 3-year retrospective study of clinical durability of bulk-filled resin composite restorations
-
Muhittin Ugurlu, Fatmanur Sari
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(1):e5. Published online December 30, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e5
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
This study aimed to assess the clinical longevity of a bulk-fill resin composite in Class II restorations for 3-year. Materials and MethodsPatient record files acquired from the 40 patients who were treated due to needed 2 similar sizes Class II composite restorations were used for this retrospective study. In the experimental cavity, the flowable resin composite SDR was inserted in the dentinal part as a 4 mm intermediate layer. A 2 mm coverage layer with a nano-hybrid resin composite (CeramX) was placed on SDR. The control restoration was performed by an incremental technique of 2 mm using the nano-hybrid resin composite. The restorations were blindly assessed by 2 calibrated examiners using modified United States Public Health Service criteria at baseline and 1, 2, and 3 years. The data were analyzed using non-parametric tests (p = 0.05). ResultsEighty Class II restorations were evaluated. After 3-years, 4 restorations (5%) failed, 1 SDR + CeramX, and 3 CeramX restorations. The annual failure rate (AFR) of the restorations was 1.7%. The SDR + CeramX group revealed an AFR of 0.8%, and the CeramX group an AFR of 2.5% (p > 0.05). Regarding anatomical form and marginal adaptation, significant alterations were observed in the CeramX group after 3-years (p < 0.05). The changes in the color match were observed in each group over time (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe use of SDR demonstrated good clinical durability in deep Class II resin composite restorations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Evaluation of Surface Roughness and Microhardness of New Generation Bulk-Fill Composites
Zehra SÜSGÜN YILDIRIM, Ezgi SONKAYA, Zeliha Gonca BEK KÜRKLÜ
Cumhuriyet Dental Journal.2023; 26(2): 180. CrossRef - Damping Behaviour and Mechanical Properties of Restorative Materials for Primary Teeth
Thomas Niem, Roland Frankenberger, Stefanie Amend, Bernd Wöstmann, Norbert Krämer
Materials.2022; 15(21): 7698. CrossRef
-
3,256
View
-
27
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
2
Crossref
-
Bonding of a resin-modified glass ionomer cement to dentin using universal adhesives
-
Muhittin Ugurlu
-
Restor Dent Endod 2020;45(3):e36. Published online June 15, 2020
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e36
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
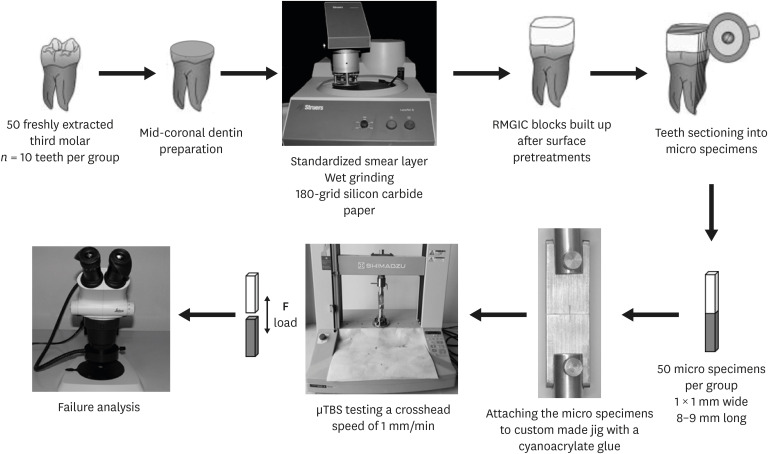
This study aims to assess the effect of universal adhesives pretreatment on the bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement to dentin. Materials and MethodsFifty caries-free human third molars were employed. The teeth were randomly assigned into five groups (n = 10) based on dentin surface pretreatments: Single Bond Universal (3M Oral Care), Gluma Bond Universal (Heraeus Kulzer), Prime&Bond Elect (Dentsply), Cavity Conditioner (GC) and control (no surface treatment). After Fuji II LC (GC) was bonded to the dentin surfaces, the specimens were stored for 7 days at 37°C. The specimens were segmented into microspecimens, and the microspecimens were subjugated to microtensile bond strength testing (1.0 mm/min). The modes of failure analyzed using a stereomicroscope and scanning electron microscopy. Data were statistically analyzed with one-way analysis of variance and Duncan tests (p = 0.05). ResultsThe surface pretreatments with the universal adhesives and conditioner increased the bond strength of Fuji II LC to dentin (p < 0.05). Single Bond Universal and Gluma Bond Universal provided higher bond strength to Fuji II LC than Cavity Conditioner (p < 0.05). The bond strengths obtained from Prime&Bond Elect and Cavity Conditioner were not statistically different (p > 0.05). ConclusionsThe universal adhesives and polyacrylic acid conditioner could increase the bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) to dentin. The use of universal adhesives before the application of RMGIC may be more beneficial in improving bond strength.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Clinical evaluation of giomer-based injectable resin composite versus resin-modified glass ionomer in class V carious lesions over 18 months: A randomized clinical trial
Reham Hendam, Rania Mosallam, Dina Kamal
Journal of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics.2025; 28(1): 50. CrossRef - Push-Out Bond Strength of Different Luting Cements Following Post Space Irrigation with 2% Chitosan: An In Vitro Study
Shimaa Rifaat, Ahmed Rahoma, Hind Muneer Alharbi, Sawsan Jamal Kazim, Shrouq Ali Aljuaid, Basmah Omar Alakloby, Faraz A. Farooqi, Noha Taymour
Prosthesis.2025; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Bioactive restorative materials in dentistry: a comprehensive review of mechanisms, clinical applications, and future directions
Dina Abozaid, Amr Azab, Mohammad A. Bahnsawy, Mohamed Eldebawy, Abdullah Ayad, Romesa soomro, Enas Elwakeel, Maged Ahmed Mohamed
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Nanosilver Fluoride Application on the Microtensile Bond Strength of Glass Ionomer Cement and Resin-modified Glass Ionomer Cement on Primary Carious Dentin: An In Vitro Study
Ila Srinivasan, Yuthi Milit, Anushka Das, Neeraja Ramamurthy
International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry.2024; 17(5): 565. CrossRef - Effect of Surface Treatments on Shear-bond Strength of Glass Ionomer Cements to Silver Diamine Fluoride-treated Simulated Carious Dentin
WT Koh, OT Yeoh, NA Yahya, AU Yap
Operative Dentistry.2024; 49(6): 714. CrossRef - Desensitizing agents’ post-bleaching effect on orthodontic bracket bond strength
Gufa Bagus Pamungkas, Dyah Karunia, Sri Suparwitri
Dental Journal.2024; 57(1): 45. CrossRef - Successful Rehabilitation of Traumatized Immature Teeth by Different Vital Pulp Therapies in Pediatric Patients
Mohammad Kamran Khan
Journal of the Scientific Society.2023; 50(1): 111. CrossRef - Do bioactive materials show greater retention rates in restoring permanent teeth than non-bioactive materials? A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Juliana Benace Fernandes, Sheila Mondragón Contreras, Manuela da Silva Spinola, Graziela Ribeiro Batista, Eduardo Bresciani, Taciana Marco Ferraz Caneppele
Clinical Oral Investigations.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of tooth preparation on the microleakage of fissure sealant
Gesti Kartiko Sari, Sri Kuswandari, Putri Kusuma Wardani Mahendra
Dental Journal (Majalah Kedokteran Gigi).2022; 55(2): 67. CrossRef - Rheological Properties, Surface Microhardness, and Dentin Shear Bond Strength of Resin-Modified Glass Ionomer Cements Containing Methacrylate-Functionalized Polyacids and Spherical Pre-Reacted Glass Fillers
Whithipa Thepveera, Wisitsin Potiprapanpong, Arnit Toneluck, Somruethai Channasanon, Chutikarn Khamsuk, Naruporn Monmaturapoj, Siriporn Tanodekaew, Piyaphong Panpisut
Journal of Functional Biomaterials.2021; 12(3): 42. CrossRef
-
3,601
View
-
36
Download
-
10
Crossref
|