-
The prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption based on cone-beam computed tomographic imaging: a cross-sectional study
-
Matheus Diniz Ferreira, Matheus Barros-Costa, Felipe Ferreira Costa, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
-
Restor Dent Endod 2022;47(4):e39. Published online October 11, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2022.47.e39
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
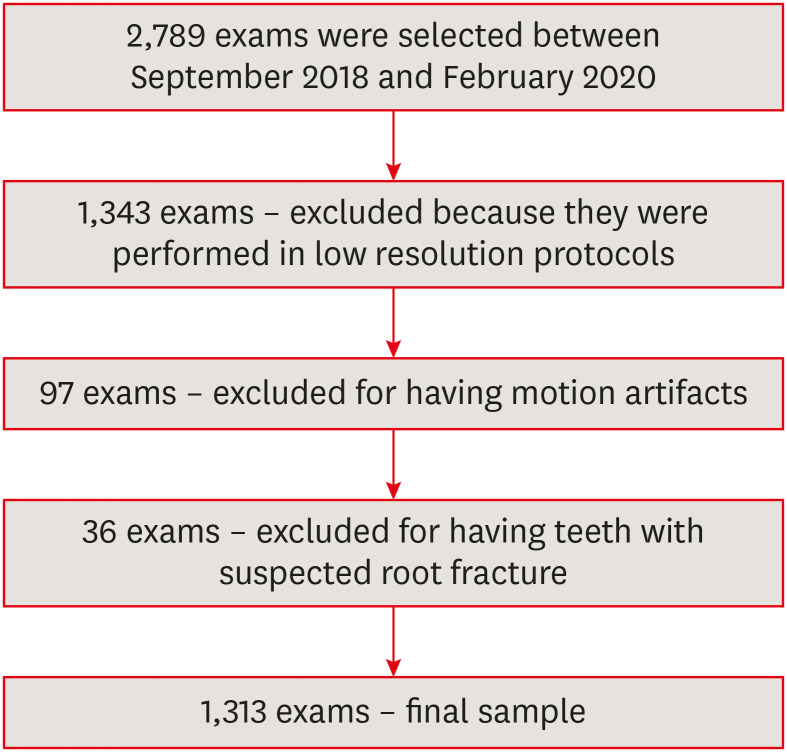
This study investigated the prevalence and characteristics of external cervical resorption (ECR) regarding sex, age, tooth, stages of progression, and portal of entry, using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans. Materials and MethodsCBCT scans of 1,313 patients from a Brazilian subpopulation comprising 883 female and 430 male patients (mean age, 55.2 years), acquired using a PreXion 3D CBCT unit, were evaluated. All permanent teeth included in the scans were evaluated for the presence of ECR according to the 3-dimensional classification and the portal of entry. The association between the presence of ECR and the factors studied was assessed using the χ2 test. Intra-observer agreement was analyzed with the kappa test (α = 0.05). ResultsIn total, 6,240 teeth were analyzed, of which 84 (1.35%) were affected by ECR. A significant association was found between the presence of ECR and sex, with a higher prevalence in male patients (p = 0.002). The most frequently affected teeth were the mandibular and maxillary central incisors. The most common height was the mid-third of the root. For the portal of entry, 44% of cases were on the proximal surfaces, 40.5% on the lingual/palatal surface and 15.5% on the buccal surface. Intra-observer agreement was excellent. ConclusionsThe prevalence of ECR was 1.35%, with a higher prevalence in male patients and a wide age distribution. The mandibular and maxillary central incisors were the most commonly affected teeth, and cases of ECR most frequently showed a height into the mid-third of the root and proximal entry.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Prise en charge des lésions cervicales
C. Mocquot, L. Detzen, I. Fontanille, B. Orlik, F. Decup
EMC - Médecine buccale.2025; 18(3): 1. CrossRef - Features of external root resorption as predictors of disease progression: A CBCT cross-sectional study
Tânia Maria Soares Reis, Daniella Ribeiro Ferrari, Rafael Binato Junqueira, Priscila Dias Peyneau, Eduardo Murad Villoria, Maria Augusta Visconti, Francielle Silvestre Verner
Odontology.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence and Characterization of External Cervical Resorption Using Cone Beam Computed Tomography
Isadora Carneiro Pereira Machado, Marilia Oliveira Morais, Adriana Lustosa Pereira Bicalho, Patricia Helena Pereira Ferrari, Juliano Martins Bueno, José Luiz Cintra Junqueira, Mariana Quirino Silveira Soares
Journal of Endodontics.2024; 50(2): 164. CrossRef - Influence of tube current and metal artifact reduction on the diagnosis of external cervical resorption in teeth adjacent to a dental implant in CBCT: an ex-vivo study
Thamiles Gonzalez-Passos, Matheus Barros-Costa, Matheus L Oliveira, Deborah Queiroz Freitas
Clinical Oral Investigations.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Maxillary anterior teeth with extensive root resorption treated with multidisciplinary approach: A case report
Thais Machado de Carvalho Coutinho, Carollyne Souza Campello, Juliana Pires Abdelnur, Vivian Ronquete, Carlos Henrique Sardenberg Pereira, Marilia F Marceliano-Alves
International Journal of Case Reports and Images.2023; 14(1): 8. CrossRef - Clinical and radiographic features of external cervical resorption – An observational study
Shanon Patel, Francesc Abella, Kreena Patel, Paul Lambrechts, Nassr Al‐Nuaimi
International Endodontic Journal.2023; 56(12): 1475. CrossRef
-
3,070
View
-
43
Download
-
5
Web of Science
-
6
Crossref
|