-
Tip and taper compatibility of accessory gutta-percha points with rotary and reciprocating instruments
-
Júlia Niero Zanatta Streck, Sabrina Arcaro, Renan Antônio Ceretta, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Josiane de Almeida, Patrícia Maria Poli Kopper, Anarela Vassen Bernardi
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(3):e22. Published online June 8, 2023
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e22
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
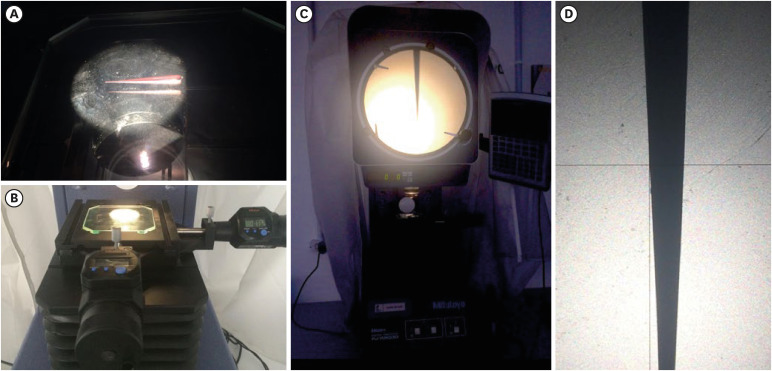
This study was conducted to evaluate and compare the tip and taper compatibility of accessory gutta-percha points (AGPs) with various rotary and reciprocating instruments. Materials and MethodsUsing a profile analyzer, tip and taper measurements were taken of 10 AGPs of each of the 14 models available from Odous de Deus and the 4 models available from Dentsply-Maillefer. Diameter measurements were taken at 1-mm intervals, from 3 mm from the tip (D3) to 16 mm. ResultsBased on the mean values obtained, 3-dimensional (3D) models of the AGPs were drawn in Autodesk Fusion 360 and superimposed on 3D models of each instrument selected (Mtwo, Reciproc, RaCe, K3, and ProDesign Logic) to determine the compatibility between the instrument and the AGP. Data corresponding to the tips and tapers of the various AGPs, as well as the tip and taper differences between the AGPs and the instruments, were analyzed using descriptive statistics. The tapers of the AGPs were subject to the American National Standards Institute/American Dental Association No. 57 standard. The Odous de Deus extra-long medium and extra-long extra-medium AGPs were shown to be compatible with Mtwo, K3, and ProDesign Logic instruments with taper 0.06 and tip sizes 25 and 30, while the Dentsply fine and fine medium cones were compatible with Mtwo, RaCe, and K3 instruments with conicity of 0.04 and tip sizes 35 and 40. ConclusionsBoth the Odous de Deus and Dentsply commercial brands included 2 AGP models with tip (D3) and taper compatibility with Mtwo, RaCe, K3, and/or Prodesign Logic instruments.
-
Physicochemical properties of a calcium aluminate cement containing nanoparticles of zinc oxide
-
Amanda Freitas da Rosa, Thuany Schmitz Amaral, Maria Eduarda Paz Dotto, Taynara Santos Goulart, Hebert Luís Rossetto, Eduardo Antunes Bortoluzzi, Cleonice da Silveira Teixeira, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
-
Restor Dent Endod 2023;48(1):e3. Published online December 8, 2022
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2023.48.e3
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
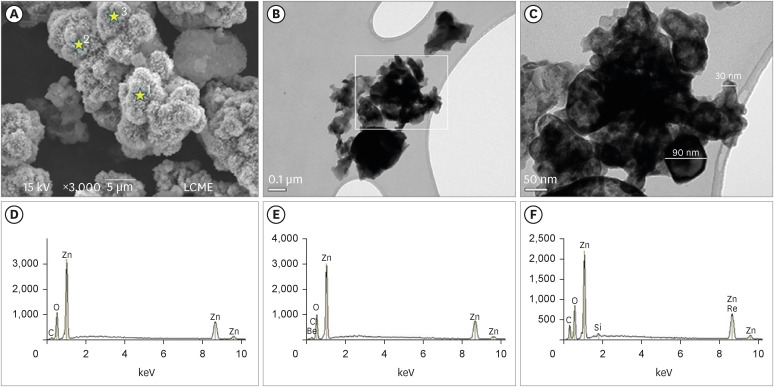
This study evaluated the effect of different nanoparticulated zinc oxide (nano-ZnO) and conventional-ZnO ratios on the physicochemical properties of calcium aluminate cement (CAC). Materials and MethodsThe conventional-ZnO and nano-ZnO were added to the cement powder in the following proportions: G1 (20% conventional-ZnO), G2 (15% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO), G3 (12% conventional-ZnO + 3% nano-ZnO) and G4 (10% conventional-ZnO + 5% nano-ZnO). The radiopacity (Rad), setting time (Set), dimensional change (Dc), solubility (Sol), compressive strength (Cst), and pH were evaluated. The nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO were also assessed using scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy. Radiopacity data were analyzed by the 1-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni tests (p < 0.05). The data of the other properties were analyzed by the ANOVA, Tukey, and Fisher tests (p < 0.05). ResultsThe nano-ZnO and CAC containing conventional-ZnO powders presented particles with few impurities and nanometric and micrometric sizes, respectively. G1 had the highest Rad mean value (p < 0.05). When compared to G1, groups containing nano-ZnO had a significant reduction in the Set (p < 0.05) and lower values of Dc at 24 hours (p < 0.05). The Cst was higher for G4, with a significant difference for the other groups (p < 0.05). The Sol did not present significant differences among groups (p > 0.05). ConclusionsThe addition of nano-ZnO to CAC improved its dimensional change, setting time, and compressive strength, which may be promising for the clinical performance of this cement.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Calcium aluminate cement: a study on the effect of additives for dental applications
Sara Ghorbani, Rahim Naghizadeh, Ebrahim Ghasemi, Hamidreza Rezaie
Advances in Cement Research.2025; : 1. CrossRef
-
248
View
-
11
Download
-
1
Web of Science
-
1
Crossref
-
Microtensile bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system using different bonding strategies
-
Laura Alves Bastos, Ana Beatriz Silva Sousa, Brahim Drubi-Filho, Fernanda de Carvalho Panzeri Pires-de-Souza, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
-
Restor Dent Endod 2015;40(1):23-29. Published online August 25, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2015.40.1.23
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of pre-etching on the bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system to dentin. Materials and MethodsThirty human molars were randomly divided into 5 groups according to the different bonding strategies. For teeth restored with silorane-based composite (Filtek Silorane, 3M ESPE), the specific self-etching adhesive system (Adhesive System P90, 3M ESPE) was used with and without pre-etching (Pre-etching/Silorane and Silorane groups). Teeth restored with methacrylate based-composite (Filtek Z250, 3M ESPE) were hybridized with the two-step self-etching system (Clearfil SE Bond, Kuraray), with and without pre-etching (Pre-etching/Methacrylate and Methacrylate groups), or three-step adhesive system (Adper Scotchbond Multi-Purpose, 3M ESPE) (Three-step/Methacrylate group) (n = 6). The restored teeth were sectioned into stick-shaped test specimens (1.0 × 1.0 mm), and coupled to a universal test machine (0.5 mm/min) to perform microtensile testing. ResultsPre-etching/Methacrylate group presented the highest bond strength values, with significant difference from Silorane and Three-step/Methacrylate groups (p < 0.05). However, it was not significantly different from Preetching/Silorane and Methacrylate groups. ConclusionsPre-etching increased bond strength of silorane-based composite specific adhesive system to dentin.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Is the presence of 10-MDP associated to higher bonding performance for self-etching adhesive systems? A meta-analysis of in vitro studies
Julia Fehrenbach, Cristina Pereira Isolan, Eliseu Aldrighi Münchow
Dental Materials.2021; 37(10): 1463. CrossRef
-
178
View
-
1
Download
-
1
Crossref
-
Effect of ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal
-
Anny Carine Barros Aguiar, Daniely Amorim de Meireles, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Angela Delfina Bitencourt Garrido, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(4):265-269. Published online July 17, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.4.265
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To evaluate the effect of different ultrasonic tip designs on intraradicular post removal. Materials and MethodsThe crowns of forty human canine teeth were removed, and after biomechanical preparation and filling, the roots were embedded in acrylic resin blocks. The post spaces were made, and root canal molding was performed with self-cured acrylic resin. After casting (Cu-Al), the posts were cemented with zinc phosphate cement. The specimens were randomly separated into 4 groups (n = 10), as follows: G1 - no ultrasonic vibration (control); G2 - ultrasonic vibration using an elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip; G3 - ultrasonic vibration with a flattened convex and linear active tip; G4 - ultrasonic vibration with active semicircular tapered tip. Ultrasonic vibration was applied for 15 seconds on each post surface and tensile test was performed in a Universal Testing Machine (Instron 4444 - 1 mm/min). ResultsG4 presented the highest mean values, however, with no statistically significant difference in comparison to G3 (P > 0.05). G2 presented the lowest mean values with statistically significant difference to G3 and G4 (P < 0.05). ConclusionsUltrasonic vibration with elongated cylindrical-shaped and active rounded tip was most effective in reducing force required for intraradicular post removal.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - The effect of ultrasonic vibration protocols for cast post removal on the incidence of root dentin defects
Giulliano C. Serpa, Orlando A. Guedes, Neurinelma S. S. Freitas, Julio A. Silva, Carlos Estrela, Daniel A. Decurcio
Journal of Oral Science.2023; 65(3): 190. CrossRef - Activación ultrasónica durante la preparación bio químico mecánica del tratamiento endodóntico no quirúrgico. Revisión de la literatura
Gisselle Cantanzaro, Nelsin Villaroel, Diana Dorta
ODOUS Científica .2022; 22(2): 135. CrossRef - Endodontic Retreatment Using Dynamic Navigation: A Case Report
Jonathan Bardales-Alcocer, Marco Ramírez-Salomón, Elma Vega-Lizama, María López-Villanueva, Gabriel Alvarado-Cárdenas, Kenneth S. Serota, Jorgeraul Ramírez-Wong
Journal of Endodontics.2021; 47(6): 1007. CrossRef - Assessment of a Cavity to Optimize Ultrasonic Efficiency to Remove Intraradicular Posts
Izabela Araujo Aguiar Graça, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, André Augusto Franco Marques, Leandro de Moura Martins, Ângela Delfina Bittencourt Garrido
Journal of Endodontics.2017; 43(8): 1350. CrossRef - REMOVAL ALLOY CAST ROOT INLAY BY LOWPOWER ULTRASONIC AND STANDARD TIP
L. D. Vejsgejm, T. N. Gomenjuk
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2017; 14(4): 37. CrossRef - Questioning the spot light on Hi-tech endodontics
Jojo Kottoor, Denzil Albuquerque
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2016; 41(1): 80. CrossRef
-
202
View
-
3
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Effect of passive ultrasonic agitation during final irrigation on cleaning capacity of hybrid instrumentation
-
Marcilene Coelho Vinhorte, Eduardo Hideki Suzuki, Maíra Sousa de Carvalho, André Augusto Franco Marques, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia
-
Restor Dent Endod 2014;39(2):104-108. Published online March 21, 2014
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2014.39.2.104
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To evaluate the effect of passive ultrasonic agitation on the cleaning capacity of a hybrid instrumentation technique. Materials and MethodsTwenty mandibular incisors with mesiodistal-flattened root shape had their crowns sectioned at 1 mm from the cementoenamel junction. Instrumentation was initiated by catheterization with K-type files (Denstply Maillefer) #10, #15, and #20 at 3 mm from the working length. Cervical preparation was performed with Largo bur #1 (Dentsply Maillefer) followed by apical instrumentation with K-type files #15, #20 and #25, and finishing with ProTaper F2 file (Denstply Maillefer). All files were used up to the working length under irrigation with 1 mL of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite (Biodynâmica) at each instrument change. At the end of instrumentation, the roots were randomly separated into 2 groups (n = 10). All specimens received final irrigation with 1 mL of 2.5% sodium hypochlorite. The solution remained in the root canals in Group 1 for one minute; and ultrasonic agitation was performed in Group 2 for one minute using a straight tip inserted at 1 mm from working length. The specimens were processed histologically and the sections were analyzed under optic microscope (×64) to quantify debris present in the root canal. ResultsThe samples submitted to ultrasonic agitation (Group 2) presented significant decrease in the amount of debris in comparison with those of Group 1 (p < 0.05). ConclusionsThe hybrid instrumentation technique associated with passive ultrasonic agitation promoted greater debris removal in the apical third of the root canals.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Micro-CT Evaluation of Different Root Canal Irrigation Protocols on the Removal of Accumulated Hard Tissue Debris: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ailin Liang, Luo Huang, Baoyu Li, Yihua Huang, Xiaoyan Zhou, Xufang Zhang, Qimei Gong
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(20): 6053. CrossRef - Ultrasonic Irrigant Activation during Root Canal Treatment: A Systematic Review
Petruţa E. Căpută, Anastasios Retsas, Lydwien Kuijk, Luis E. Chávez de Paz, Christos Boutsioukis
Journal of Endodontics.2019; 45(1): 31. CrossRef - Effect of Endodontic Irrigation Protocols on Crown Fracture Resistance
Marina Baechtold, Leonardo da Cunha, Erick Souza, Marilisa Gabardo, Kauhanna de Oliveira, Flares Baratto-Filho, Denise Leonardi
The Journal of Contemporary Dental Practice.2018; 19(7): 768. CrossRef - Influence of Prior Cervical Enlargement on Apical Cleaning Using Single File
Denise Piotto Leonardi, Celso Alfredo Schramm, Allan Fernando Giovanini, Cibelli Mariane Silveira, Flávia Sens Fagundes Tomazinho, Flares Baratto-Filho
The Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College.2015; 56(2): 85. CrossRef - Effect of three different irrigation solutions applied by passive ultrasonic irrigation
Carmen Llena, Leopoldo Forner, Raquel Cambralla, Adrian Lozano
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 143. CrossRef - Evaluation of penetration depth of 2% chlorhexidine digluconate into root dentinal tubules using confocal laser scanning microscope
Sekar Vadhana, Jothi Latha, Natanasabapathy Velmurugan
Restorative Dentistry & Endodontics.2015; 40(2): 149. CrossRef
-
197
View
-
1
Download
-
6
Crossref
-
Endodontic treatment of mandibular molar with root dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system
-
Daniely Amorin Meireles, Mariana Mena Barreto Bastos, André Augusto Franco Marques, Lucas da Fonseca Roberti Garcia, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado
-
Restor Dent Endod 2013;38(3):167-171. Published online August 23, 2013
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2013.38.3.167
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
Biomechanical preparation of root canals with accentuated curvature is challenging. New rotatory systems, such as Reciproc, require a shorter period of time to prepare curved canals, and became a viable alternative for endodontic treatment of teeth with root dilaceration. Thus, this study aimed to report a clinical case of endodontic therapy of root with accentuated dilaceration using Reciproc single-file system. Mandibular right second molar was diagnosed as asymptomatic irreversible pulpitis. Pulp chamber access was performed, and glide path was created with #10 K-file (Dentsply Maillefer) and PathFile #13, #16 and #19 (Dentsply Maillefer) up to the temporary working length. The working length measured corresponded to 20 mm in the mesio-buccal and mesio-lingual canals, and 22 mm in the distal canal. The R25 file (VDW GmbH) was used in all the canals for instrumentation and final preparation, followed by filling with Reciproc gutta-percha cones (VDW GmbH) and AH Plus sealer (Dentsply Maillefer), using thermal compaction technique. The case has been receiving follow-up for 6 mon and no painful symptomatology or periapical lesions have been found. Despite the difficulties, the treatment could be performed in a shorter period of time than the conventional methods. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Surface Characteristics of Reciprocating Instruments Before and After Use - A SEM Analysis
Aida Rene Assayag Hanan, Daniely Amorin de Meireles, Emílio Carlos Sponchiado Júnior, Simone Hanan, Milton Carlos Kuga, Idomeo Bonetti Filho
Brazilian Dental Journal.2015; 26(2): 121. CrossRef - Endodontic Treatment of an Anomalous Anterior Tooth with the Aid of a 3-dimensional Printed Physical Tooth Model
Chanhee Byun, Changhwan Kim, Seungryong Cho, Seung Hoon Baek, Gyutae Kim, Sahng G. Kim, Sun-Young Kim
Journal of Endodontics.2015; 41(6): 961. CrossRef
-
208
View
-
1
Download
-
2
Crossref
|