-
Effect of hydrogel-based antibiotic intracanal medicaments on crown discoloration
-
Rayan B. Yaghmoor, Jeffrey A. Platt, Kenneth J. Spolnik, Tien Min Gabriel Chu, Ghaeth H. Yassen
-
Restor Dent Endod 2021;46(4):e52. Published online October 5, 2021
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2021.46.e52
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
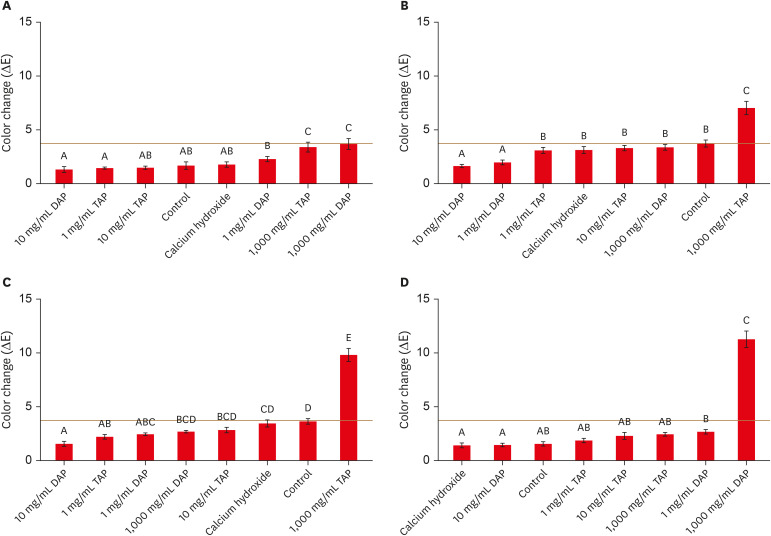
This study evaluated the effects of low and moderate concentrations of triple antibiotic paste (TAP) and double antibiotic paste (DAP) loaded into a hydrogel system on crown discoloration and explored whether application of an adhesive bonding agent prevented crown discoloration. Materials and MethodsIntact human molars (n = 160) were horizontally sectioned 1 mm apical to the cementoenamel junction. The crowns were randomized into 8 experimental groups (calcium hydroxide, Ca[OH]2; 1, 10, and 1,000 mg/mL TAP and DAP; and no medicament. The pulp chambers in half of the samples were coated with an adhesive bonding agent before receiving the intracanal medicament. Color changes (ΔE) were detected by spectrophotometry after 1 day, 1 week, and 4 weeks, and after 5,000 thermal cycles, with ΔE = 3.7 as a perceptible threshold. The 1-sample t-test was used to determine the significance of color changes relative to 3.7. Analysis of variance was used to evaluate the effects of treatment, adhesive, and time on color change, and the level of significance was p < 0.05. ResultsCa(OH)2 and 1 and 10 mg/mL DAP did not cause clinically perceivable tooth discoloration. Adhesive agent use significantly decreased tooth discoloration in the 1,000 mg/mL TAP group up to 4 weeks. However, adhesive use did not significantly improve coronal discoloration after thermocycling when 1,000 mg/mL TAP was used. ConclusionsCa(OH)2 and 1 and 10 mg/mL DAP showed no clinical discoloration. Using an adhesive significantly improved coronal discoloration up to 4 weeks with 1,000 mg/mL TAP.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Comparative analysis of tooth discoloration induced by different intracanal medicaments in regenerative endodontics: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
Ashlesha Nageshwar Madankar, Sulabha Radke, Shanmuga Priya, Darshan Dakshindas
Endodontology.2026; 38(1): 8. CrossRef - Tooth discoloration caused by nanographene oxide as an irrigant and intracanal medicament in the endodontic treatment of extracted single-rooted teeth: An ex-vivo study
Abbas Abbaszadegan, Zeinab Rafiee, Bahar Asheghi, Ahmad Gholami, Mohmed Isaqali Karobari
PLOS One.2025; 20(6): e0325430. CrossRef - Root development of immature necrotic permanent teeth following regenerative endodontic process: Case series
Abbasali Khademi, Pedram Iranmanesh, Ali Akhavan, Movahed Ghassem Yeganeh, Samira Khalifezade Esfahani
Dental Research Journal.2025;[Epub] CrossRef - Root Canal Dentin Microhardness after Contact with Antibiotic Medications: An In Vitro Study
Amanda Palmeira Arruda Nogueira, Renata Grazziotin-Soares, Adriana Marques Mesquita Leal, Sérgio Alves Guida Freitas Júnior, Bruna Laís Lins Gonçalves, José Bauer, Meire Coelho Ferreira, Ceci Nunes Carvalho
Dentistry Journal.2024; 12(7): 201. CrossRef - Potential Crown Discoloration Induced by the Combination of Various Intracanal Medicaments and Scaffolds Applied in Regenerative Endodontic Therapy
NB Altun, A Turkyilmaz
Nigerian Journal of Clinical Practice.2024; 27(7): 897. CrossRef
-
2,251
View
-
33
Download
-
4
Web of Science
-
5
Crossref
-
Effects of air-abrasion pressure on the resin bond strength to zirconia: a combined cyclic loading and thermocycling aging study
-
Eman Z. Al-Shehri, Afnan O. Al-Zain, Alaa H. Sabrah, Sarah S. Al-Angari, Laila Al Dehailan, George J. Eckert, Mutlu Özcan, Jeffrey A. Platt, Marco C. Bottino
-
Restor Dent Endod 2017;42(3):206-215. Published online June 5, 2017
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2017.42.3.206
-
-
 Abstract Abstract
 PDF PDF PubReader PubReader ePub ePub
- Objectives
To determine the combined effect of fatigue cyclic loading and thermocycling (CLTC) on the shear bond strength (SBS) of a resin cement to zirconia surfaces that were previously air-abraded with aluminum oxide (Al2O3) particles at different pressures. Materials and MethodsSeventy-two cuboid zirconia specimens were prepared and randomly assigned to 3 groups according to the air-abrasion pressures (1, 2, and 2.8 bar), and each group was further divided into 2 groups depending on aging parameters (n = 12). Panavia F 2.0 was placed on pre-conditioned zirconia surfaces, and SBS testing was performed either after 24 hours or 10,000 fatigue cycles (cyclic loading) and 5,000 thermocycles. Non-contact profilometry was used to measure surface roughness. Failure modes were evaluated under optical and scanning electron microscopy. The data were analyzed using 2-way analysis of variance and χ2 tests (α = 0.05). ResultsThe 2.8 bar group showed significantly higher surface roughness compared to the 1 bar group (p < 0.05). The interaction between pressure and time/cycling was not significant on SBS, and pressure did not have a significant effect either. SBS was significantly higher (p = 0.006) for 24 hours storage compared to CLTC. The 2 bar-CLTC group presented significantly higher percentage of pre-test failure during fatigue compared to the other groups. Mixed-failure mode was more frequent than adhesive failure. ConclusionsCLTC significantly decreased the SBS values regardless of the air-abrasion pressure used.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by  - Shear bond strength of resin to additively manufactured zirconia with different surface treatments
Yanru Shen, Xiang Wang, Chen Yang, Ying Jiang, Feng Wang, Li Peng, Yongsheng Zhou, Yuchun Sun
Surfaces and Interfaces.2024; 54: 105153. CrossRef - Multiscale analysis of the compressive behaviour of polymer-based composites reinforced by hybrid Al2O3/Al fibres
Hao Tang, Jiaqi Xu, Constantinos Soutis, Aleksey Yerokhin
Composites Science and Technology.2024; 255: 110718. CrossRef - An Advanced Surface Treatment Technique for Coating Three-Dimensional-Printed Polyamide 12 by Hydroxyapatite
Abdulaziz Alhotan, Saleh Alhijji, Sahar Ahmed Abdalbary, Rania E. Bayoumi, Jukka P. Matinlinna, Tamer M. Hamdy, Rasha M. Abdelraouf
Coatings.2024; 14(9): 1181. CrossRef -
Does incorporation of TiO
2
nanotubes in air-abraded high translucent zirconia influence shear bond strength?*
Bahadır Ezmek, Osman Cumhur Sipahi
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2023; 37(22): 3206. CrossRef - Effects of aging and light-curing unit type on the volume and internal porosity of bulk-fill resin composite restoration
Afnan O. Al-Zain, Elaf A. Alboloshi, Walaa A. Amir, Maryam A. Alghilan, Eliseu A. Münchow
The Saudi Dental Journal.2022; 34(3): 243. CrossRef - Influence of surface treatments and cyclic fatigue on subsurface defects and mechanical properties of zirconia frameworks
Alaaeldin Elraggal, Nikolaos Silikas, Moustafa Aboushelib
Dental Materials.2021; 37(5): 905. CrossRef - Effects of low-temperature degradation on the surface roughness of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia polycrystal ceramics: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hui Yang, Yi-Li Xu, Guang Hong, Hao Yu
The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry.2021; 125(2): 222. CrossRef - Effect of surface treatments on repair strength, roughness and morphology in aged metal-free crowns
Yançanã Luizy Gruber, Thaís Emanuelle Bakaus, Bruna Fortes Bittencourt, João Carlos Gomes, Alessandra Reis, Giovana Mongruel Gomes
Brazilian Journal of Oral Sciences.2020; 19: e206155. CrossRef - Retentive Force of Glass-Ceramic Soldered Customized Zirconia Abutment Copings with Prefabricated Titanium Bases
Jeremias Hey, Monika Kasaliyska, Andreas Kiesow, Ramona Schweyen, Christin Arnold
Materials.2020; 13(14): 3193. CrossRef - Solvent-aided direct adhesion of a metal/polymer joint using micro/nano hierarchical structures
Gyosik Jun, Jeong-Won Lee, Younghun Shin, Kihwan Kim, Woonbong Hwang
Journal of Materials Processing Technology.2020; 285: 116744. CrossRef - Study of physicochemical properties and effects on bonding to zirconia ceramics of five resin cements
Xiuju Liu, Zhaoying Liu, Xuan Li, Han Wang, Gaigai Yu, Song Zhu
Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology.2020; 34(18): 2031. CrossRef - The effect of air-particle abrasion and a zirconia primer application on resin cement bonding strength to zirconia
Alana M. Dantas, Fernanda Campos, Sarina M. Pereira, Elis J. dos Santos, Laudenice L. Pereira, Dayanne M. Moura, Rodrigo O. Souza
Minerva Stomatologica.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Non-Thermal Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Treatment on Shear Bond Strength between Y-TZP and Self-Adhesive Resin Cement
Dae-Sung Kim, Jong-Ju Ahn, Eun-Bin Bae, Gyoo-Cheon Kim, Chang-Mo Jeong, Jung-Bo Huh, So-Hyoun Lee
Materials.2019; 12(20): 3321. CrossRef - Effect of airborne particle abrasion and sintering order on the surface roughness and shear bond strength between Y-TZP ceramic and resin cement
Yener OKUTAN, Munir Tolga YUCEL, Tugce GEZER, Mustafa Borga DONMEZ
Dental Materials Journal.2019; 38(2): 241. CrossRef
-
2,288
View
-
13
Download
-
14
Crossref
|